Full text
PDF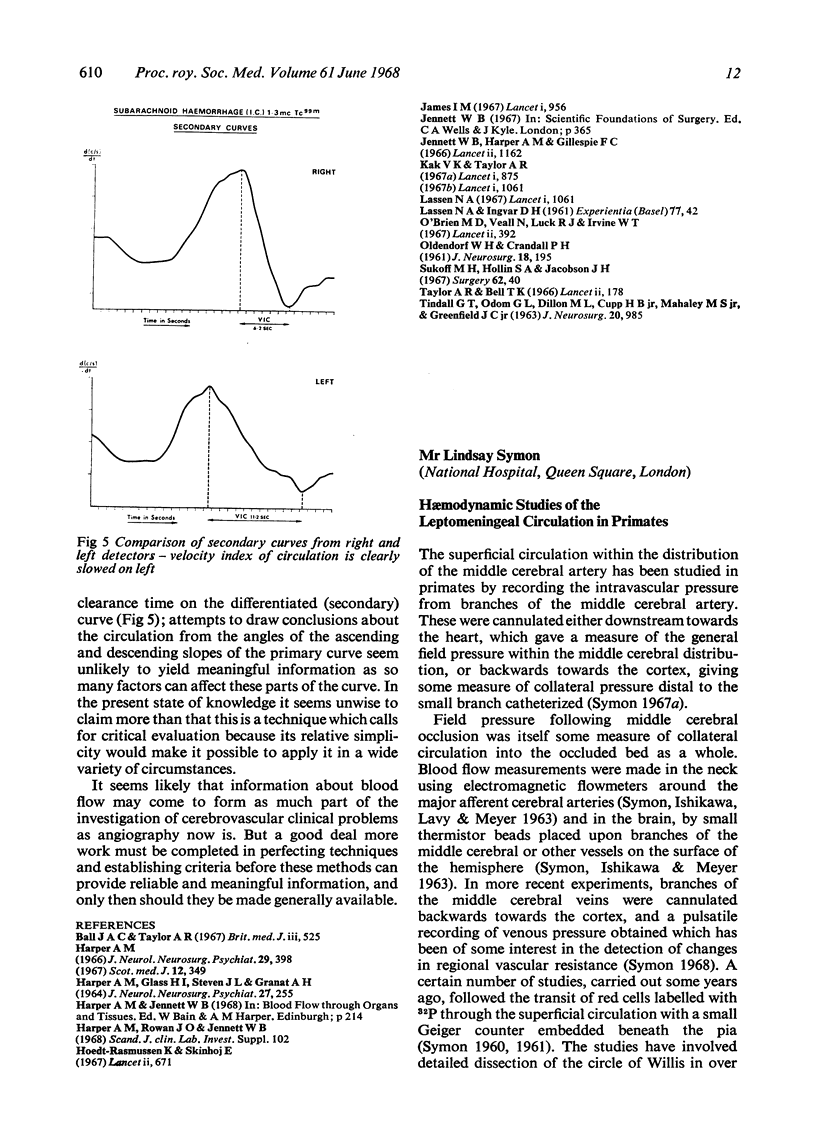


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bayliss W. M. On the local reactions of the arterial wall to changes of internal pressure. J Physiol. 1902 May 28;28(3):220–231. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1902.sp000911. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brawley B. W., Strandness D. E., Jr, Kelly W. A. The physiologic response to therapy in experimental cerebral ischemia. Arch Neurol. 1967 Aug;17(2):180–187. doi: 10.1001/archneur.1967.00470260070008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FEINDEL W., PEROT P. RED CEREBRAL VEINS: A REPORT ON ARTERIOVENOUS SHUNTS IN TUMORS AND CEREBRAL SCARS. J Neurosurg. 1965 Apr;22:315–325. doi: 10.3171/jns.1965.22.4.0315. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harper A. M. Autoregulation of cerebral blood flow: influence of the arterial blood pressure on the blood flow through the cerebral cortex. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1966 Oct;29(5):398–403. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.29.5.398. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ISHIKAWA S., HANDA J., MEYER J. S., HUBER P. HAEMODYNAMICS OF THE CIRCLE OF WILLIS AND THE LEPTOMENINGEAL ANASTOMOSES: AN ELECTROMAGNETIC FLOWMETER STUDY OF INTRACRANIAL ARTERIAL OCCLUSION IN THE MONKEY. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1965 Apr;28:124–136. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.28.2.124. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWE R. D. Adaptation of the circle of Willis to occlusion of the carotid or vertebral artery: its implication in caroticovertebral stenosis. Lancet. 1962 Feb 24;1(7226):395–398. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(62)91357-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MEYER J. S., FANG H. C., DENNY-BROWN D. Polarographic study of cerebral collateral circulation. AMA Arch Neurol Psychiatry. 1954 Sep;72(3):296–312. doi: 10.1001/archneurpsyc.1954.02330030030003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PENRY J. K., NETSKY M. G. Experimental embolic occlusion of a single leptomeningeal artery. Arch Neurol. 1960 Oct;3:391–398. doi: 10.1001/archneur.1960.00450040041005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- POTTER J. M. Redistribution of blood to the brain due to localized cerebral arterial spasm. The possible importance of the small peripheral anastomotic cerebral arteries. Brain. 1959 Sep;82:367–376. doi: 10.1093/brain/82.3.367. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHMIDT H. W. Uber Arterienkreise in der Pia mater des Menschen. Dtsch Z Nervenheilkd. 1955;172(6):526–530. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SYMON L., ISHIKAWA S., LAVY S., MEYER J. S. QUANTITATIVE MEASUREMENT OF CEPHALIC BLOOD FLOW IN THE MONKEY. J Neurosurg. 1963 Mar;20:199–218. doi: 10.3171/jns.1963.20.3.0199. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SYMON L., ISHIKAWA S., MEYER J. S. Cerebral arterial pressure changes and development of leptomeningeal collateral circulation. Neurology. 1963 Mar;13:237–250. doi: 10.1212/wnl.13.3.237. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Symon L. Observations on the leptomeningeal collateral circulation in dogs. J Physiol. 1960 Nov;154(1):1–14.2. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1960.sp006560. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


