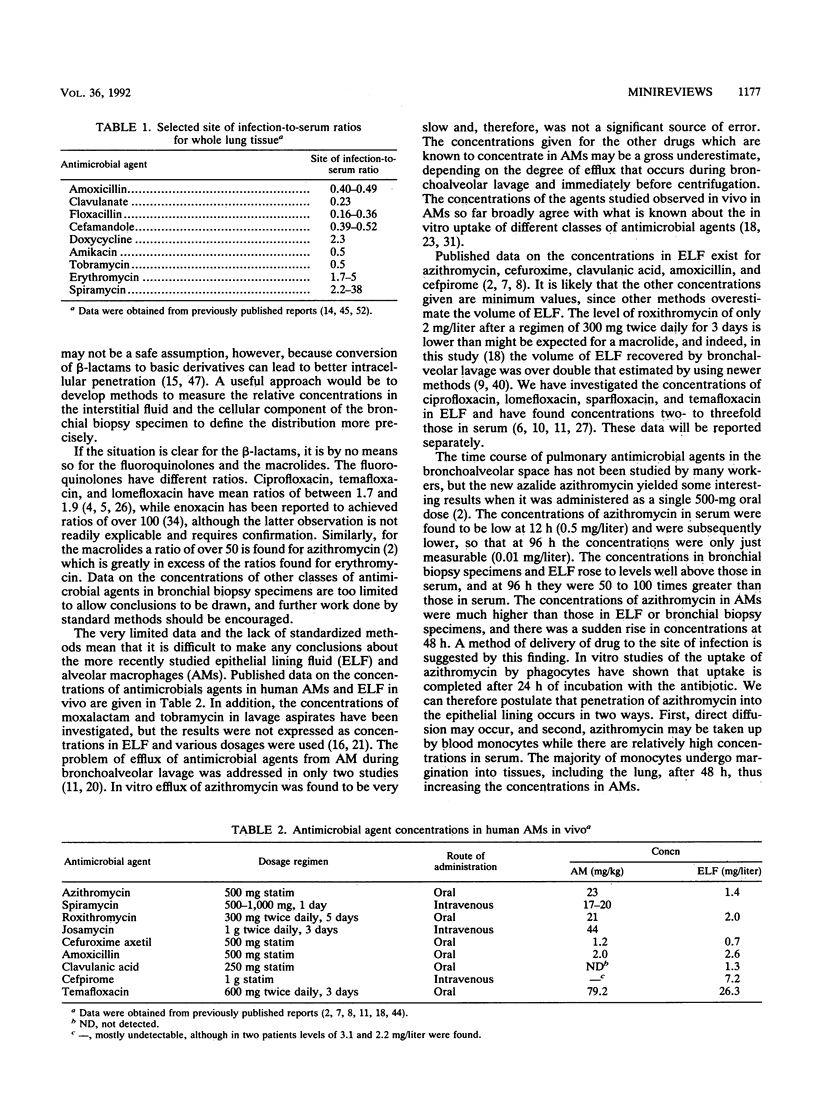
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baldwin D. R., Andrews J. M., Ashby J. P., Wise R., Honeybourne D. Concentrations of cefixime in bronchial mucosa and sputum after three oral multiple dose regimens. Thorax. 1990 May;45(5):401–402. doi: 10.1136/thx.45.5.401. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baldwin D. R., Honeybourne D., Andrews J. M., Ashby J. P., Wise R. Concentrations of oral lomefloxacin in serum and bronchial mucosa. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1990 Jun;34(6):1017–1019. doi: 10.1128/aac.34.6.1017. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baldwin D. R., Honeybourne D., Wise R. Pulmonary disposition of antimicrobial agents: methodological considerations. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1992 Jun;36(6):1171–1175. doi: 10.1128/aac.36.6.1171. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baldwin D. R., Maxwell S. R., Honeybourne D., Andrews J. M., Ashby J. P., Wise R. The penetration of cefpirome into the potential sites of pulmonary infection. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1991 Jul;28(1):79–86. doi: 10.1093/jac/28.1.79. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baldwin D. R., Wilkinson L., Andrews J. M., Ashby J. P., Wise R., Honeybourne D. Concentrations of temafloxacin in serum and bronchial mucosa. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis. 1990 Jun;9(6):432–434. doi: 10.1007/BF01979477. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baldwin D. R., Wise R., Andrews J. M., Ashby J. P., Honeybourne D. Azithromycin concentrations at the sites of pulmonary infection. Eur Respir J. 1990 Sep;3(8):886–890. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baldwin D. R., Wise R., Andrews J. M., Ashby J. P., Honeybourne D. The distribution of temafloxacin in bronchial epithelial lining fluid, alveolar macrophages and bronchial mucosa. Eur Respir J. 1992 Apr;5(4):471–476. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baldwin D. R., Wise R., Andrews J. M., Honeybourne D. Microlavage: a technique for determining the volume of epithelial lining fluid. Thorax. 1991 Sep;46(9):658–662. doi: 10.1136/thx.46.9.658. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barza M., Cuchural G. General principles of antibiotic tissue penetration. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1985 Jan;15 (Suppl A):59–75. doi: 10.1093/jac/15.suppl_a.59. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bennett J. B., Crook S. J., Shaw E. J., Davies R. J. A randomized double blind controlled trial comparing two amoxycillin regimens in the treatment of acute exacerbations of chronic bronchitis. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1988 Feb;21(2):225–232. doi: 10.1093/jac/21.2.225. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bergogne-Berezin E. Penetration of antibiotics into the respiratory tree. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1981 Sep;8(3):171–174. doi: 10.1093/jac/8.3.171. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Braude A. C., Cohen R. D., Penner J. L., Preston M. A., Rebuck A. S. Pulmonary disposition of moxalactam. Chest. 1984 Dec;86(6):881–883. doi: 10.1378/chest.86.6.881. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Braude A. C., Hornstein A., Klein M., Vas S., Rebuck A. S. Pulmonary disposition of tobramycin. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1983 May;127(5):563–565. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1983.127.5.563. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cantin A. M., North S. L., Hubbard R. C., Crystal R. G. Normal alveolar epithelial lining fluid contains high levels of glutathione. J Appl Physiol (1985) 1987 Jul;63(1):152–157. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1987.63.1.152. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chastre J., Brun P., Fourtillan J. B., Soler P., Basset G., Manuel C., Trouillet J. L., Gibert C. Pulmonary disposition of roxithromycin (RU 28965), a new macrolide antibiotic. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1987 Sep;31(9):1312–1316. doi: 10.1128/aac.31.9.1312. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davies B. I., Maesen F. P., Gubbelmans R. Azithromycin (CP-62,993) in acute exacerbations of chronic bronchitis: an open clinical, microbiological and pharmacokinetic study. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1989 May;23(5):743–751. doi: 10.1093/jac/23.5.743. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Easmon C. S., Crane J. P. Uptake of ciprofloxacin by human neutrophils. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1985 Jul;16(1):67–73. doi: 10.1093/jac/16.1.67. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hand W. L., King-Thompson N. L. Contrasts between phagocyte antibiotic uptake and subsequent intracellular bactericidal activity. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1986 Jan;29(1):135–140. doi: 10.1128/aac.29.1.135. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hand W. L., King-Thompson N. L. Membrane transport of clindamycin in alveolar macrophages. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1982 Feb;21(2):241–247. doi: 10.1128/aac.21.2.241. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hand W. L., King-Thompson N. L., Steinberg T. H. Interactions of antibiotics and phagocytes. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1983 Oct;12 (Suppl 100):1–11. doi: 10.1093/jac/12.suppl_c.1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harf R., Panteix G., Desnottes J. F., Diallo N., Leclercq M. Spiramycin uptake by alveolar macrophages. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1988 Jul;22 (Suppl B):135–140. doi: 10.1093/jac/22.supplement_b.135. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartnett B. J., Marlin G. E. Doxycycline in serum and bronchial secretions. Thorax. 1976 Apr;31(2):144–148. doi: 10.1136/thx.31.2.144. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Honeybourne D., Andrews J. M., Ashby J. P., Lodwick R., Wise R. Evaluation of the penetration of ciprofloxacin and amoxycillin into the bronchial mucosa. Thorax. 1988 Sep;43(9):715–719. doi: 10.1136/thx.43.9.715. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ingold A. Sputum and serum levels of amoxycillin in chronic bronchial infections. Br J Dis Chest. 1975 Jul;69:211–216. doi: 10.1016/0007-0971(75)90082-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jackson G. G. Methods for the clinical evaluation of antibiotics in urinary tract infections. Scand J Infect Dis Suppl. 1978;(14):289–294. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johanson W. G., Jr, Woods D. E., Chaudhuri T. Association of respiratory tract colonization with adherence of gram-negative bacilli to epithelial cells. J Infect Dis. 1979 Jun;139(6):667–673. doi: 10.1093/infdis/139.6.667. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson J. D., Hand W. L., Francis J. B., King-Thompson N., Corwin R. W. Antibiotic uptake by alveolar macrophages. J Lab Clin Med. 1980 Mar;95(3):429–439. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MAY J. R., DELVES D. M. TREATMENT OF CHRONIC BRONCHITIS WITH AMPICILLIN: SOME PHARMACOLOGICAL OBSERVATION. Lancet. 1965 May 1;1(7392):929–933. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(65)91253-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MAY J. R. THE BACTERIOLOGY AND CHEMOTHERAPY OF CHRONIC BRONCHITIS. Br J Dis Chest. 1965 Apr;59:57–65. doi: 10.1016/s0007-0971(65)80014-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MAY J. R. The laboratory background to the use of penicillin in chronic bronchitis and bronchiectasis. Br J Tuberc Dis Chest. 1955 Jul;49(3):166–173. doi: 10.1016/s0366-0869(55)80044-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maesen F. P., Beeuwkes H., Davies B. I., Buytendijk H. J., Brombacher P. J., Wessman J. Bacampicillin in acute exacerbations of chronic bronchitis--a dose-range study. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1976 Sep;2(3):279–285. doi: 10.1093/jac/2.3.279. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marlin G. E., Braude P. D., Whelan A. J., Somogyi A. A. Penetration of enoxacin into human bronchial mucosa. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1986 Dec;134(6):1209–1212. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1986.134.5.1209. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marlin G. E., Burgess K. R., Burgoyne J., Funnell G. R., Guinness M. D. Penetration of piperacillin into bronchial mucosa and sputum. Thorax. 1981 Oct;36(10):774–780. doi: 10.1136/thx.36.10.774. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marlin G. E., Davis P. R., Rutland J., Berend N. Plasma and sputum erythromycin concentrations in chronic bronchitis. Thorax. 1980 Jun;35(6):441–445. doi: 10.1136/thx.35.6.441. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marlin G. E., Nicholls A. J., Funnell G. R., Bradbury R. Penetration of cefaclor into bronchial mucosa. Thorax. 1984 Nov;39(11):813–817. doi: 10.1136/thx.39.11.813. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nielson D. W. Electrolyte composition of pulmonary alveolar subphase in anesthetized rabbits. J Appl Physiol (1985) 1986 Mar;60(3):972–979. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1986.60.3.972. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nielson D. W., Goerke J., Clements J. A. Alveolar subphase pH in the lungs of anesthetized rabbits. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Nov;78(11):7119–7123. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.11.7119. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Panteix G., Harf R., de Montclos H., Verdier M. F., Gaspar A., Leclercq M. Josamycin pulmonary penetration determined by broncho-alveolar lavage in man. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1988 Dec;22(6):917–921. doi: 10.1093/jac/22.6.917. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pennington J. E. Penetration of antibiotics into respiratory secretions. Rev Infect Dis. 1981 Jan-Feb;3(1):67–73. doi: 10.1093/clinids/3.1.67. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reifenrath R. Chemical analysis of the lung alveolar surfactant obtained by alveolar micropuncture. Respir Physiol. 1973 Oct;19(1):35–46. doi: 10.1016/0034-5687(73)90088-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Renard C., Vanderhaeghe H. J., Claes P. J., Zenebergh A., Tulkens P. M. Influence of conversion of penicillin G into a basic derivative on its accumulation and subcellular localization in cultured macrophages. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1987 Mar;31(3):410–416. doi: 10.1128/aac.31.3.410. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roselle G. A., Bode R., Hamilton B., Bibler M., Sullivan R., Douce R., Staneck J. L., Bullock W. E. Clinical trial of the efficacy and safety of ticarcillin and clavulanic acid. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1985 Mar;27(3):291–296. doi: 10.1128/aac.27.3.291. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stamey T. A., Fair W. R., Timothy M. M., Millar M. A., Mihara G., Lowery Y. C. Serum versus urinary antimicrobial concentrations in cure of urinary-tract infections. N Engl J Med. 1974 Nov 28;291(22):1159–1163. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197411282912204. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stewart S. M., Anderson I. M., Jones G. R., Calder M. A. Amoxycillin levels in sputum, serum, and saliva. Thorax. 1974 Jan;29(1):110–114. doi: 10.1136/thx.29.1.110. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stewart S. M., Fisher M., Young J. E., Lutz W. Ampicillin levels in sputum, serum, and saliva. Thorax. 1970 May;25(3):304–311. doi: 10.1136/thx.25.3.304. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Valcke Y., Pauwels R., Van der Straeten M. Pharmacokinetics of antibiotics in the lungs. Eur Respir J. 1990 Jun;3(6):715–722. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wong G. A., Pierce T. H., Goldstein E., Hoeprich P. D. Penetration of antimicrobial agents into bronchial secretions. Am J Med. 1975 Aug;59(2):219–223. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(75)90356-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


