Abstract
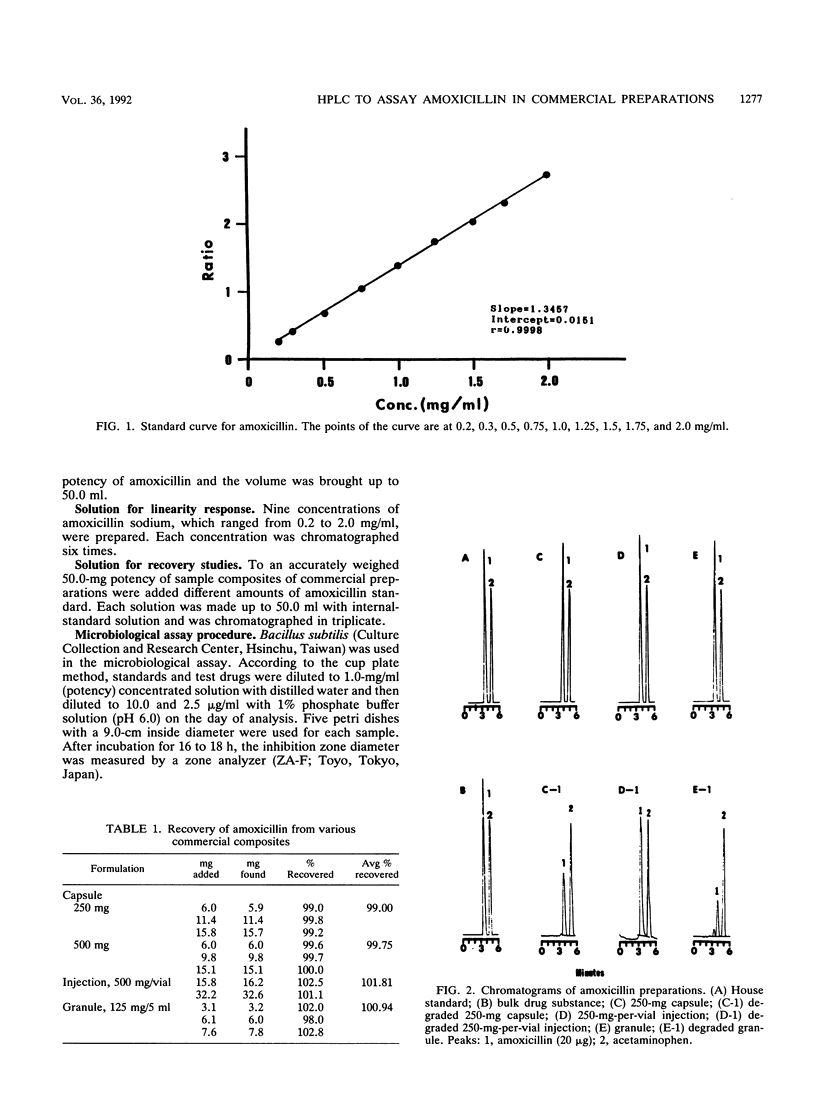
A reversed-phase column liquid chromatographic method was developed for the assay of amoxicillin and its preparations. The linear calibration range was 0.2 to 2.0 mg/ml (r = 0.9998), and recoveries were generally greater than 99%. The high-performance liquid chromatographic assay results were compared with those obtained from a microbiological assay of bulk drug substance and capsule, injection, and granule formulations containing amoxicillin and degraded amoxicillin. At the 99% confidence level, no significant intermethod differences were noted for the paired results. Commercial formulations were also analyzed, and the results obtained by the proposed method closely agreed with those found by the microbiological method. The results indicated that the proposed method is a suitable substitute for the microbiological method for assays and stability studies of amoxicillin preparations.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Carlqvist J., Westerlund D. Automated determination of amoxycillin in biological fluids by column switching in ion-pair reversed-phase liquid chromatographic systems with post-column derivatization. J Chromatogr. 1985 Nov 8;344:285–296. doi: 10.1016/s0378-4347(00)82029-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carlqvist J., Westerlund D. Determination of amoxicillin in body fluids by reversed-phase liquid chromatography coupled with a post-column derivatization procedure. J Chromatogr. 1979 Nov 11;164(3):373–381. doi: 10.1016/s0378-4347(00)81238-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Pourcq P., Hoebus J., Roets E., Hoogmartens J., Vanderhaeghe H. Quantitative determination of amoxicillin and its decomposition products by high-performance liquid chromatography. J Chromatogr. 1985 Mar 15;321(2):441–449. doi: 10.1016/s0021-9673(01)90462-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fong G. W., Martin D. T., Johnson R. N., Kho B. T. Determination of degradation products and impurities of amoxicillin capsules using ternary gradient elution high-performance liquid chromatography. J Chromatogr. 1984 Aug 31;298(3):459–472. doi: 10.1016/s0021-9673(01)92743-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Foulstone M., Reading C. Assay of amoxicillin and clavulanic acid, the components of Augmentin, in biological fluids with high-performance liquid chromatography. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1982 Nov;22(5):753–762. doi: 10.1128/aac.22.5.753. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haginaka J., Wakai J. High-performance liquid chromatographic assay of ampicillin, amoxicillin and ciclacillin in serum and urine using a pre-column reaction with 1,2,4-triazole and mercury(II) chloride. Analyst. 1985 Nov;110(11):1277–1281. doi: 10.1039/an9851001277. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haginaka J., Wakai J. Liquid chromatographic determination of amoxicillin and its metabolites in human urine by postcolumn degradation with sodium hypochlorite. J Chromatogr. 1987 Jan 23;413:219–226. doi: 10.1016/0378-4347(87)80229-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lebelle M. J., Wilson W. L., Lauriault G. High-performance liquid chromatographic determination of amoxycillin in pharmaceutical dosage forms. J Chromatogr. 1980 Dec 5;202(1):144–147. doi: 10.1016/s0021-9673(00)80090-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee T. L., Brooks M. A. High-performance liquid chromatographic determination of amoxicillin in human plasma using a bonded-phase extraction. J Chromatogr. 1984 Mar 9;306:429–435. doi: 10.1016/s0378-4347(00)80911-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maes V., Vuylsteke de Laps L., Vercruysse A. Amoxycillin metabolism studied by combination of HPLC and spectrophotometry on urinary samples. Arch Int Pharmacodyn Ther. 1982 Dec;260(2):290–290. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vree T. B., Hekster Y. A., Baars A. M., Van der Kleijn E. Rapid determination of amoxycillin (clamoxyl) and ampicillin (penbritin) in body fluids of many by means of high-performance liquid chromatography. J Chromatogr. 1978 May 1;145(3):496–501. doi: 10.1016/s0378-4347(00)81384-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


