Abstract
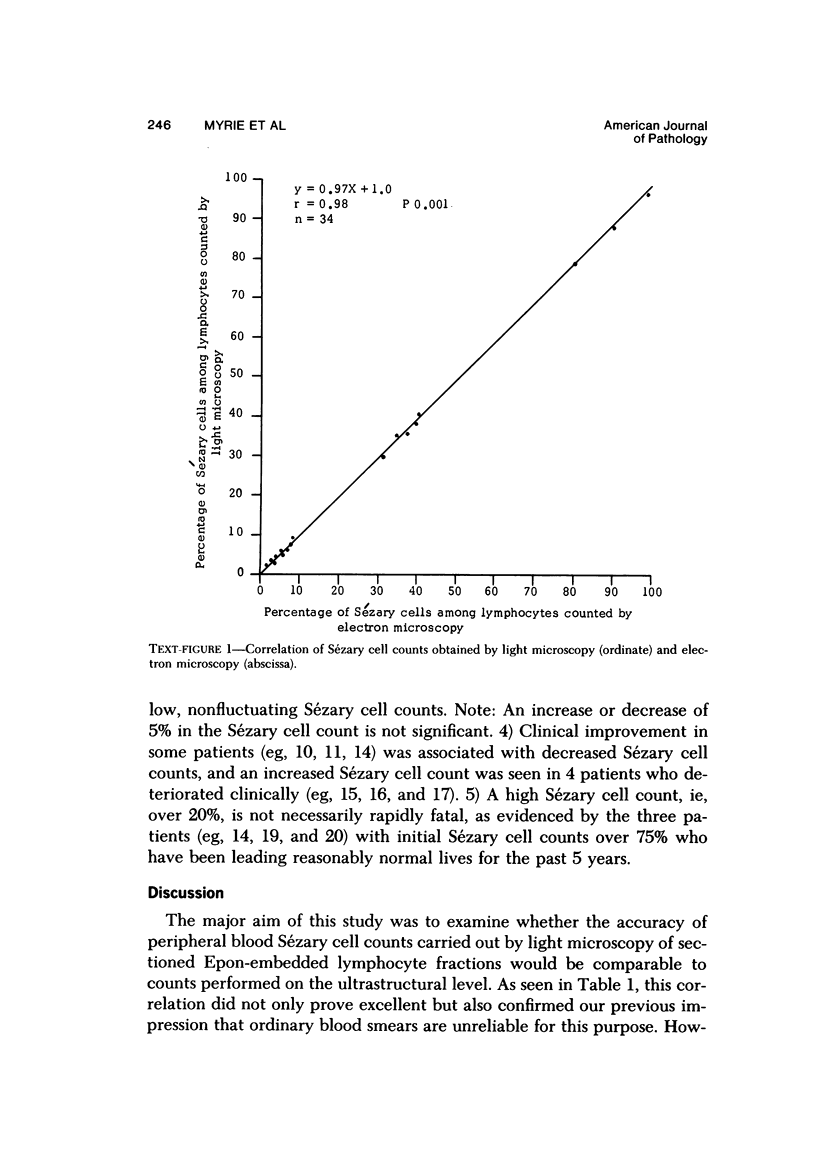
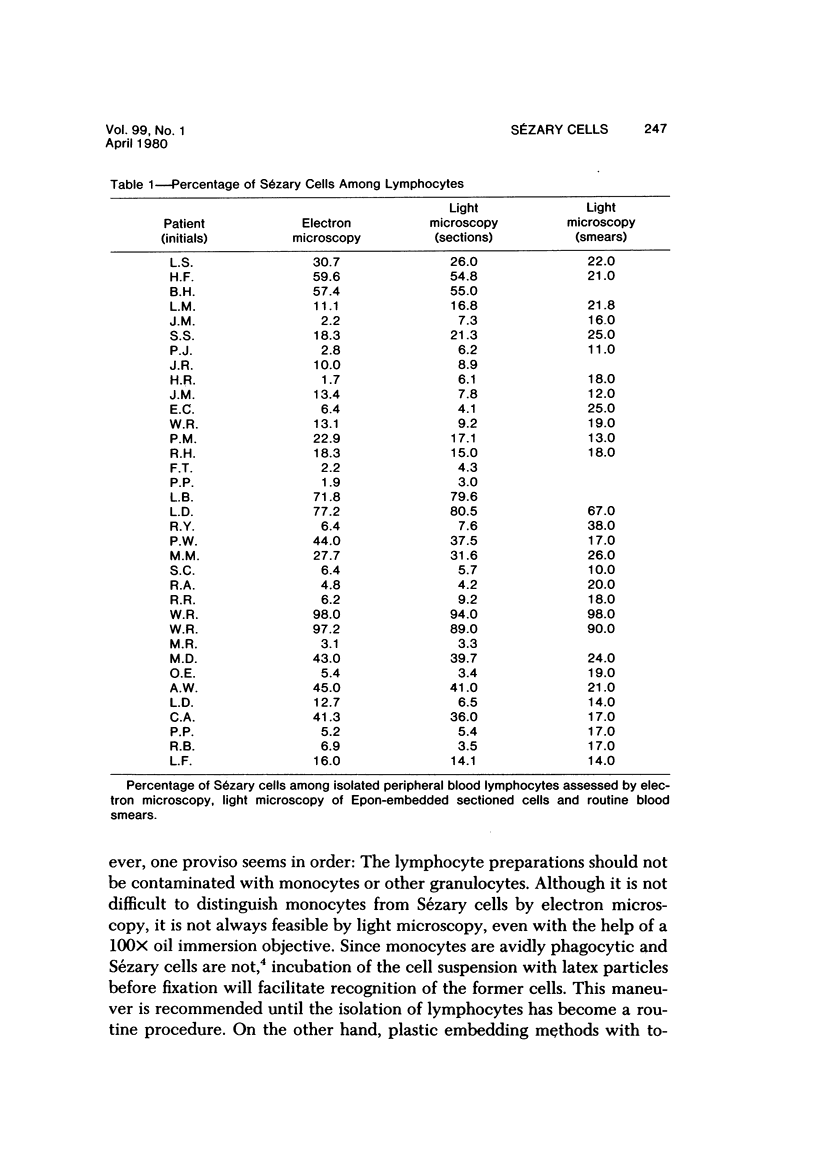
The prognostic implications of circulating Sézary cells in mycosis fungoides (MF) are not known, and the significance of fluctuating Sézary cell counts in either MF or the Sézary syndrome has not been assessed. Such studies have been hampered by the inaccuracy of counts performed on routine blood smears and the unavailability of electron microscopy for routine purposes. The present studies conducted on the peripheral blood of 35 patients with either MF or the Sézary syndrome show that Sézary cell counts performed by light microscopy of sectioned Epon-embedded lymphocyte fractions are as accurate as those carried out at the ultrastructural level. In addition, the studies include preliminary observations concerning 20 patients whose Sézary cell counts were repeated over time intervals ranging from 3 months to over 5 years. The described method should facilitate the performance of blood and lymph node Sézary cell counts on a wider scale, which is a necessity if the significance of circulating Sézary cells is to be evaluated.
Full text
PDF


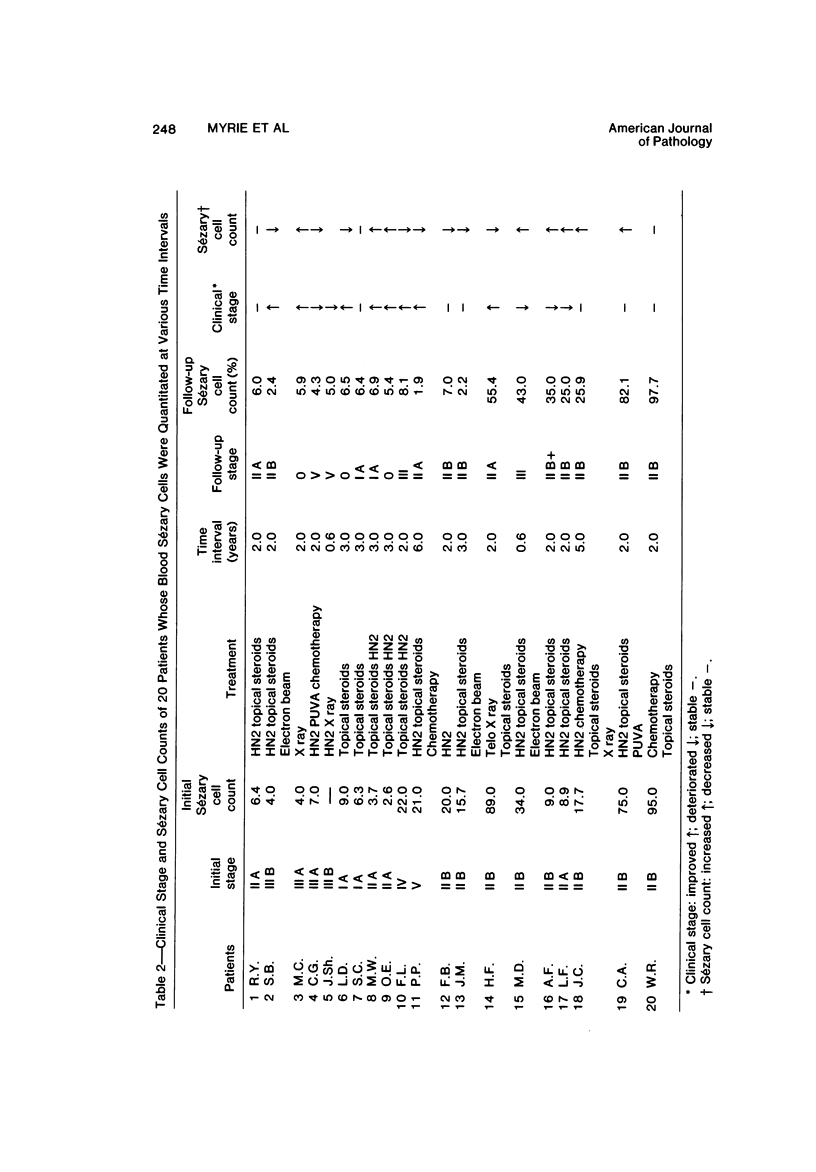


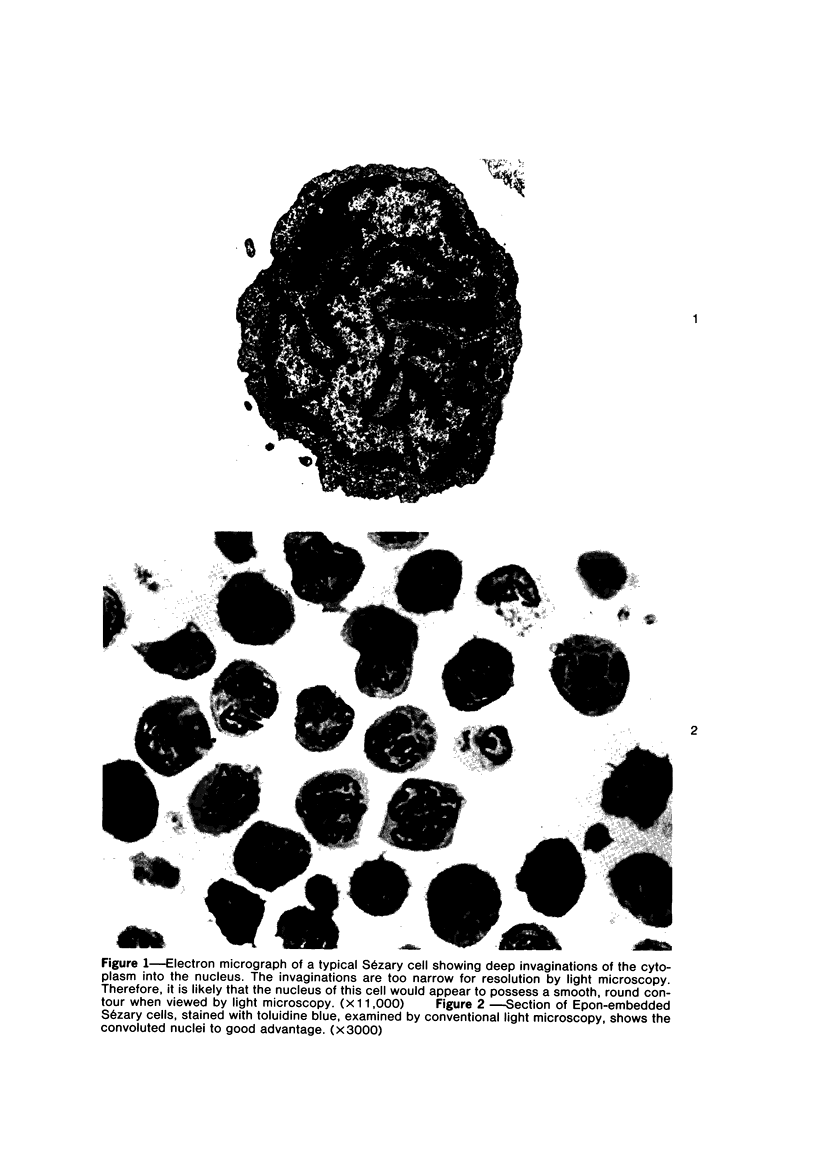

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Broome J. D., Zucker-Franklin D., Weiner M. S., Bianco C., Nussenzweig V. Leukemic cells with membrane properties of thymus-derived (T) lymphocytes in a case of Sézary's syndrome: morphologic and immunologic studies. Clin Immunol Immunopathol. 1973 Apr;1(3):319–329. doi: 10.1016/0090-1229(73)90049-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brouet J. C., Flandrin G., Seligmann M. Indications of the thymus-derived nature of the proliferating cells in six patients with Sézary's syndrome. N Engl J Med. 1973 Aug 16;289(7):341–344. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197308162890703. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Constantine V. S. Current concepts in mycosis fungoides: its nosology, diagnosis and treatment. Int J Dermatol. 1976 Dec;15:723–731. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-4362.1976.tb00168.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duncan S. C., Winkelmann R. K. Circulating Sézary cells in hospitalized dermatology patients. Br J Dermatol. 1978 Aug;99(2):171–178. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2133.1978.tb01978.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flaxman B. A., Zelazny G., Van Scott E. J. Nonspecificity of characteristic cells in mycosis fungoides. Arch Dermatol. 1971 Aug;104(2):141–147. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fuks Z. Y., Bagshaw M. A., Farber E. M. Prognostic signs and the management of the mycosis fungoides. Cancer. 1973 Dec;32(6):1385–1395. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(197312)32:6<1385::aid-cncr2820320617>3.0.co;2-#. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guccion J. G., Fischmann A. B., Bunn P. A., Jr, Schechter G. P., Patterson R. H., Matthews M. J. Ultrastructural appearance of cutaneous T cell lymphomas in skin, lymph nodes, and peripheral blood. Cancer Treat Rep. 1979 Apr;63(4):565–570. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamminga L., Hartgrink-Groeneveld C. A., van Vloten W. A. Sézary's syndrome: a clinical evaluation of eight patients. Br J Dermatol. 1979 Mar;100(3):291–296. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2133.1979.tb06201.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lamberg S. I., Bunn P. A., Jr Cutaneous T-cell lymphomas. Summary of the Mycosis Fungoides Cooperative Group-National Cancer Institute Workshop. Arch Dermatol. 1979 Sep;115(9):1103–1105. doi: 10.1001/archderm.115.9.1103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levi J. A., Wiernik P. H. Management of mycosis fungoides--current status and future prospects. Medicine (Baltimore) 1975 Jan;54(1):73–88. doi: 10.1097/00005792-197501000-00004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lutzner M., Edelson R., Schein P., Green I., Kirkpatrick C., Ahmed A. Cutaneous T-cell lymphomas: the Sézary syndrome, mycosis fungoides, and related disorders. Ann Intern Med. 1975 Oct;83(4):534–552. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-83-4-534. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zucker-Franklin D., Melton J. W., 3rd, Quagliata F. Ultrastructural, immunologic, and functional studies on Sézary cells: a neoplastic variant of thymus-derived (T) lymphocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 May;71(5):1877–1881. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.5.1877. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zucker-Franklin D. The percentage of monocytes among "mononuclear" cell fractions obtained from normal human blood. J Immunol. 1974 Jan;112(1):234–240. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zucker-Franklin D. Thymus-dependent lymphocytes in lymphoproliferative disorders of the skin (Sézary syndrome and mycosis fungoides). J Invest Dermatol. 1976 Sep;67(3):412–418. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12514715. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]