Abstract
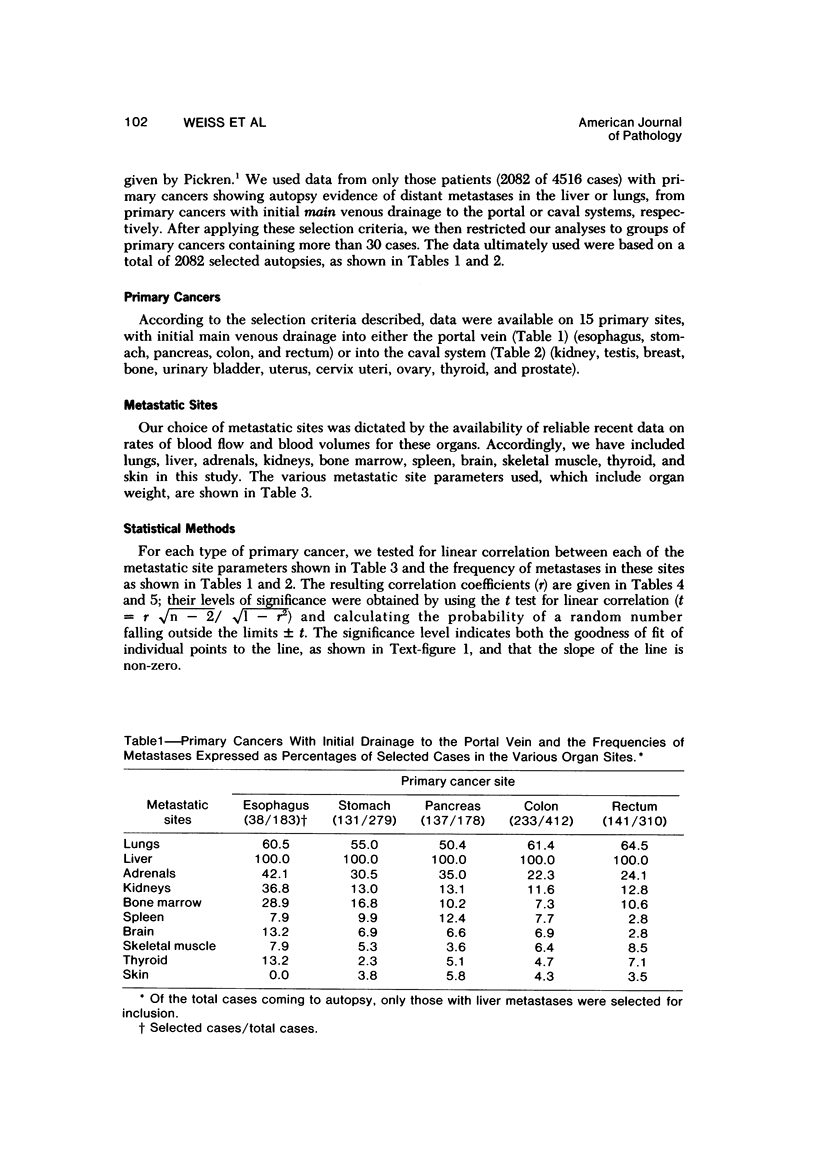
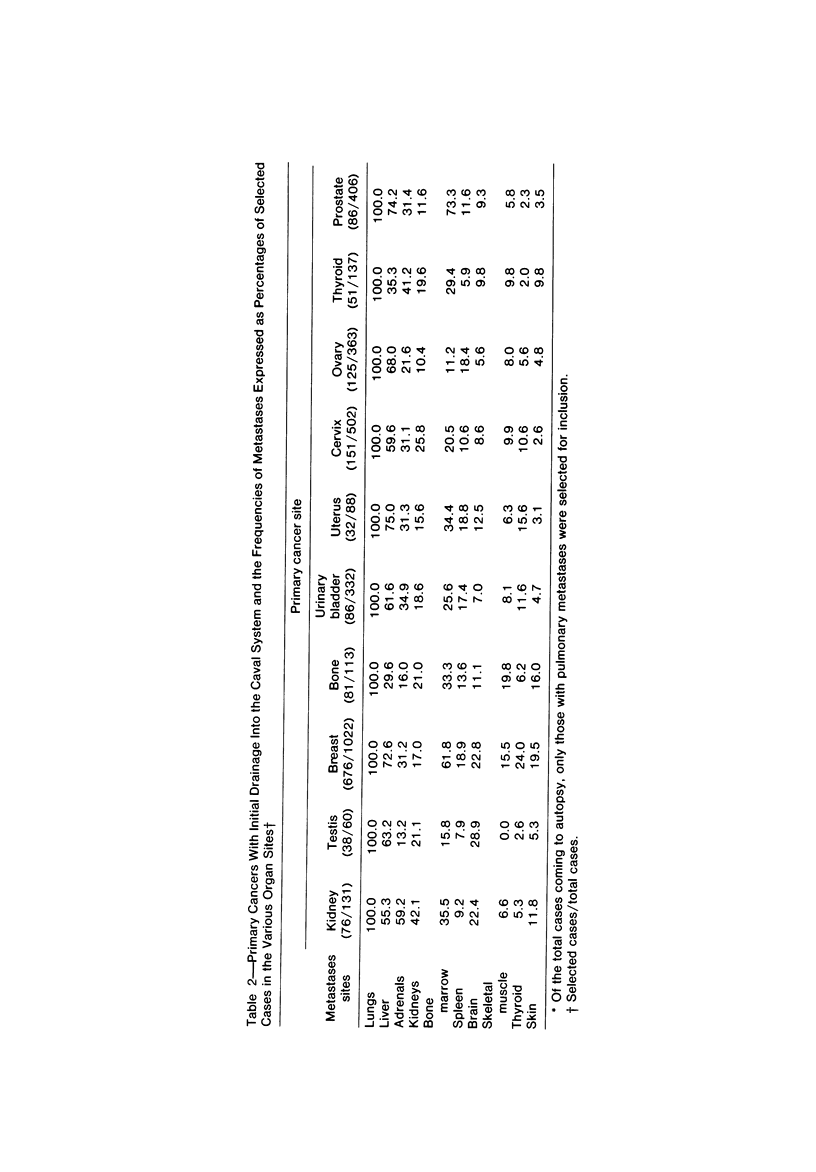
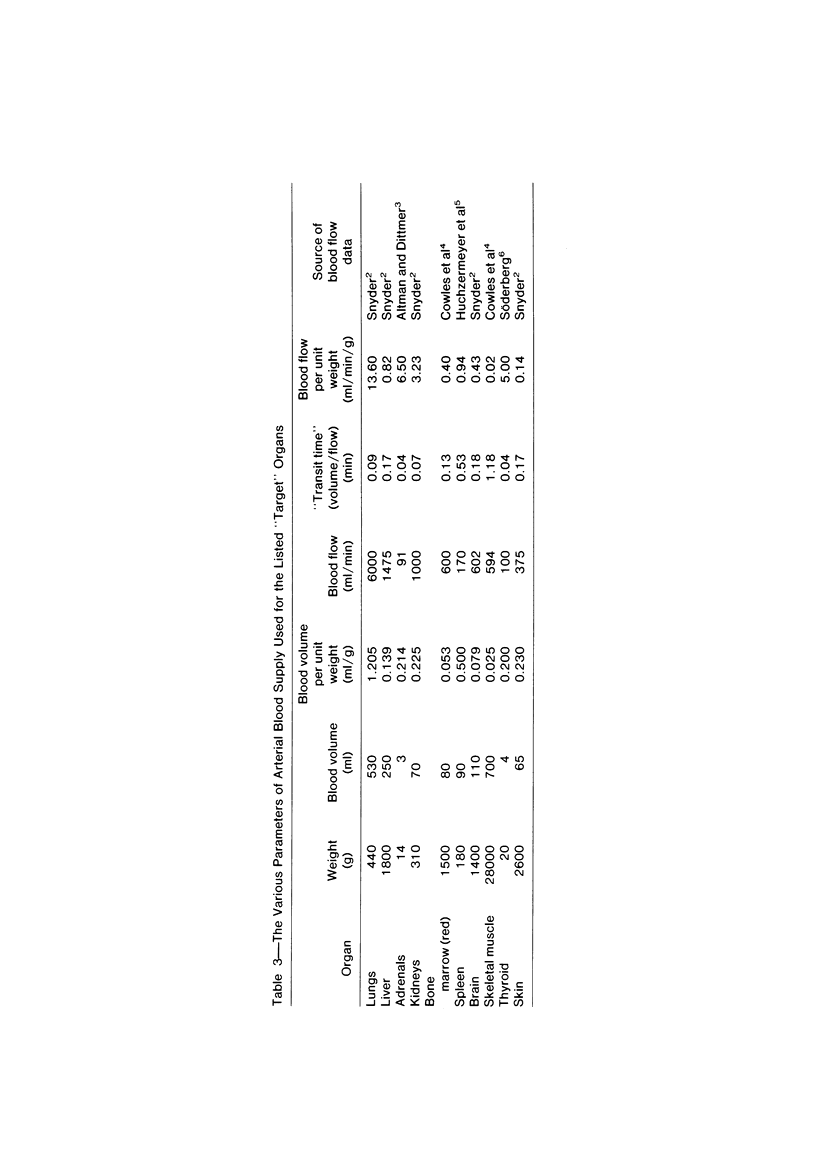
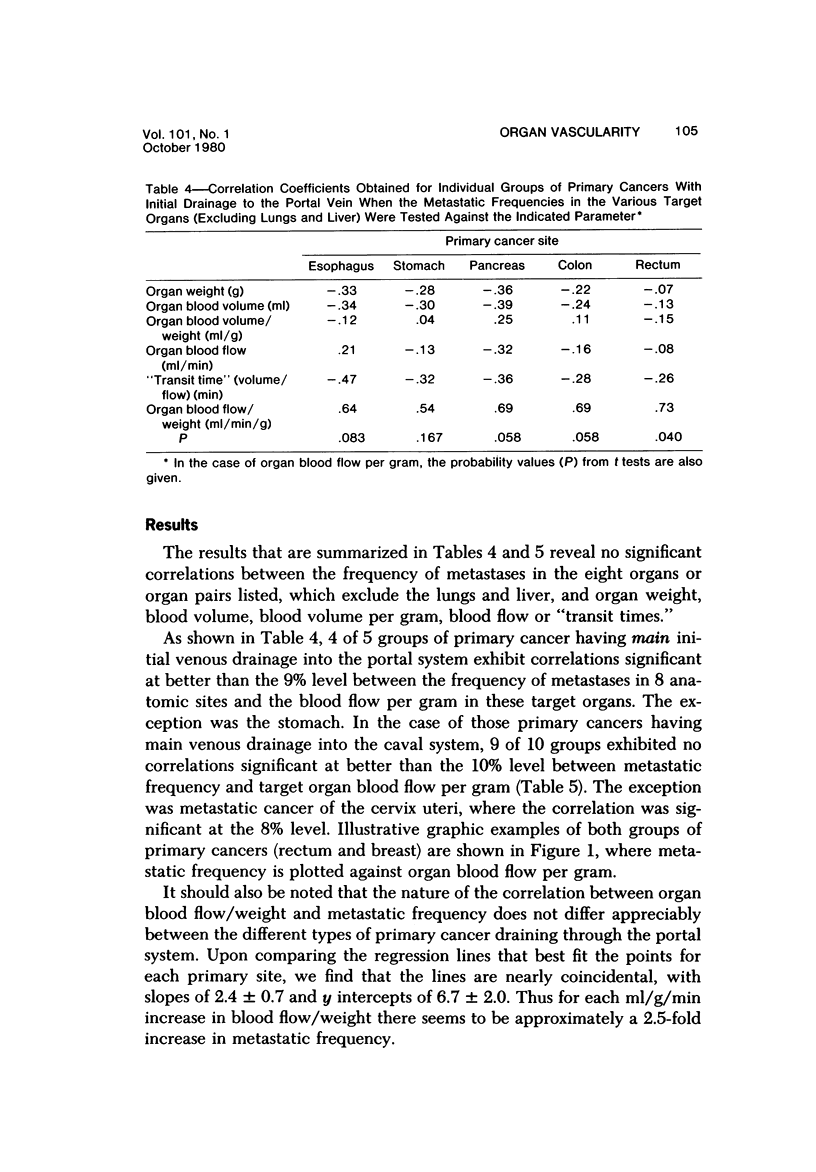
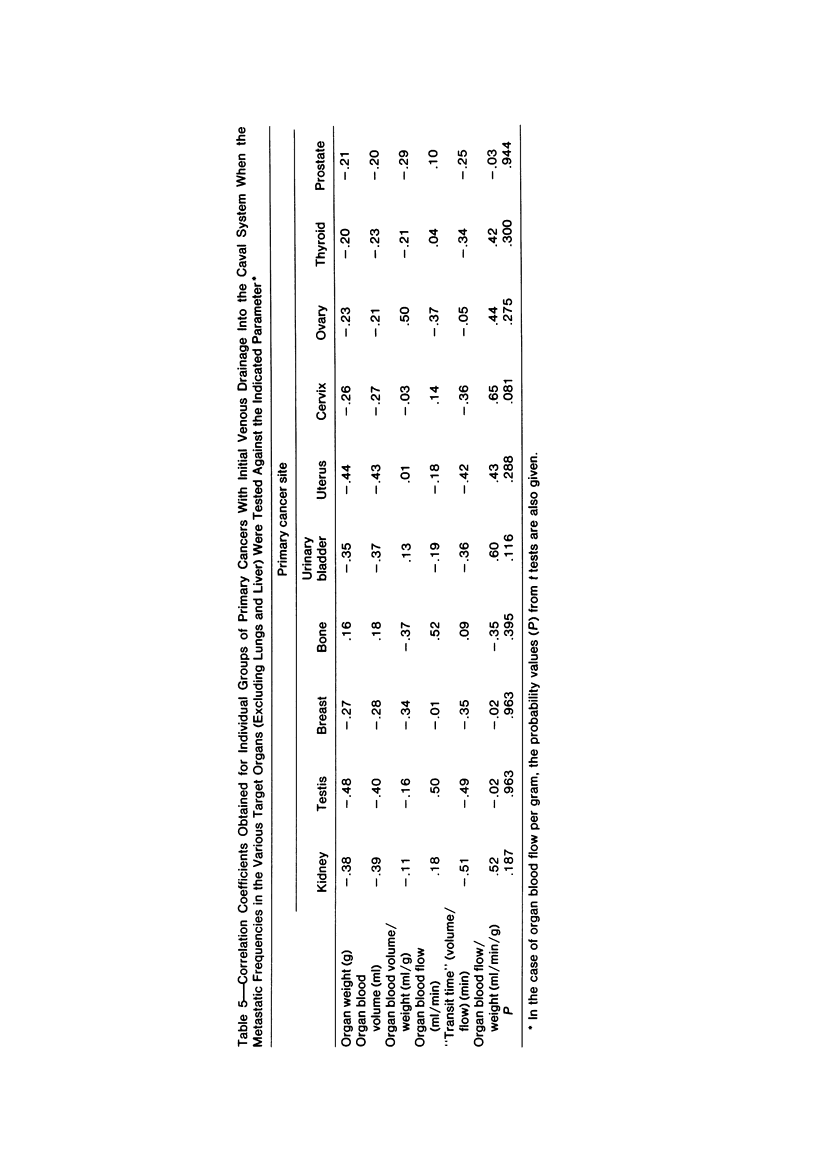
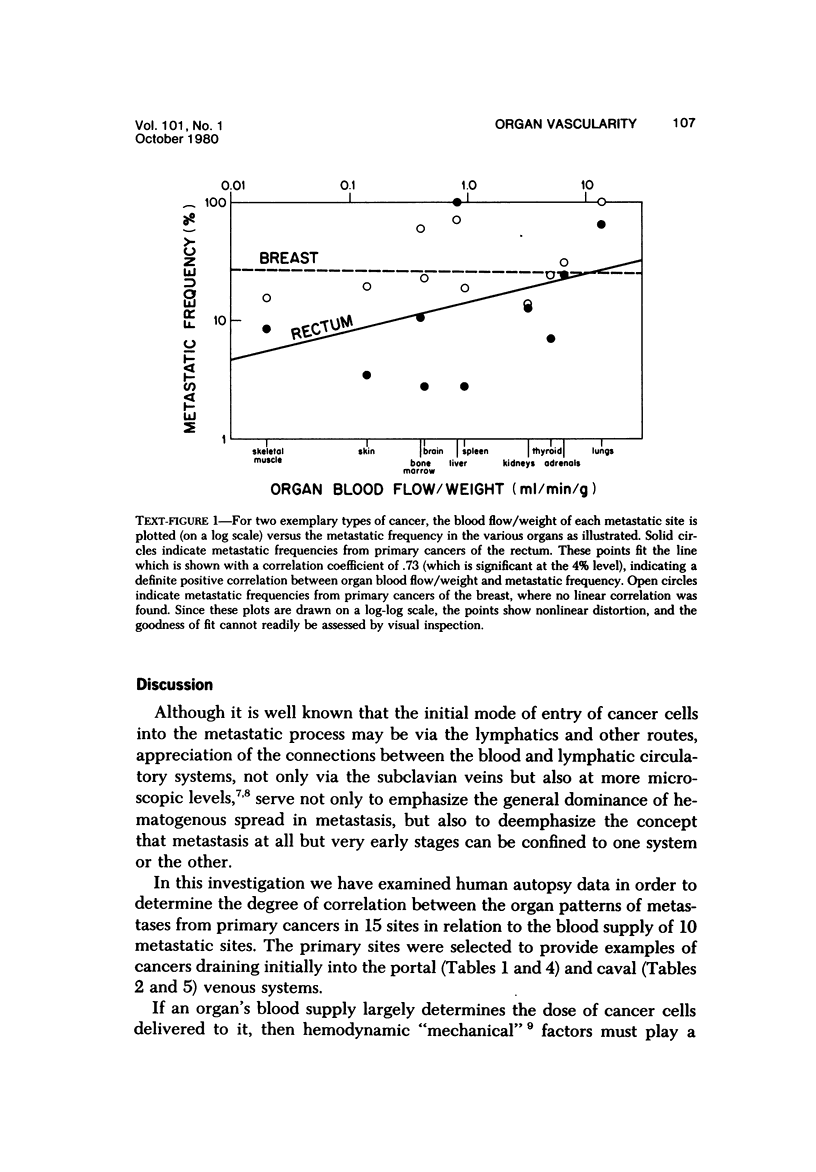
The "hemodynamic" or "mechanical" theory proposes that the frequency of metastases in different organs is primarily determined by the numbers of cancer cells delivered to them in their arterial blood. This theory has not yet been adequately tested in man because reproducible, noninvasive measurements of organ blood flow have only recently become available. Correlation between these data and the metastatic frequency in 10 organs, in groups of patients with primary cancers in 15 anatomic sites, has therefore been sought. No correlation was obtained between metastatic frequency and organ weights, blood volumes, blood volumes per gram, "transit times," or blood flow. However, correlations significant at the 4-8% level were obtained between organ blood flow per gram and metastatic frequency in 4 of 5 groups of primary cancers with initial venous drainage into the portal system, compared with 1 of 10 draining into the caval system. At present, no definitive explanation can be offered for the apparent compliance of one set of primary cancers with the "hemodynamic" theory of metastasis, but not the others.
Full text
PDF






Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bengmark S., Hafström L. The natural history of primary and secondary malignant tumors of the liver. I. The prognosis for patients with hepatic metastases from colonic and rectal carcinoma by laparotomy. Cancer. 1969 Jan;23(1):198–202. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(196901)23:1<198::aid-cncr2820230126>3.0.co;2-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brunson K. W., Beattie G., Nicolsin G. L. Selection and altered properties of brain-colonising metastatic melanoma. Nature. 1978 Apr 6;272(5653):543–545. doi: 10.1038/272543a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CLOVIS W. L., GAMBLE W. J., ZEIDMAN I. Immediate passage of tumor cell emboli through the liver and kidney. Cancer Res. 1956 Sep;16(8):814–815. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COMAN D. R., EISENBERG R. B., McCUTCHEON M. Factors affecting the distribution of tumor metastases; experiments with V2 carcinoma of rabbits. Cancer Res. 1949 Nov;9(11):649-51, illust. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COMAN D. R., deLONG R. P., MccUTCHEON M. Studies on the mechanisms of metastasis; the distribution of tumors in various organs in relation to the distribution of arterial emboli. Cancer Res. 1951 Aug;11(8):648–651. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cowles A. L., Borgstedt H. H., Gillies A. J. Tissue weights and rates of blood flow in man for the prediction of anesthetic uptake and distribution. Anesthesiology. 1971 Nov;35(5):523–526. doi: 10.1097/00000542-197111000-00013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DUNN T. B. Normal and pathologic anatomy of the reticular tissue in laboratory mice, with a classification and discussion of neoplasms. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1954 Jun;14(6):1281–1433. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeLONG R. P., COMAN D. R. Relative susceptibility of various organs to tumor transplantation. Cancer Res. 1950 Aug;10(8):513–515. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fidler I. J. Metastasis: quantitative analysis of distribution and fate of tumor emboli labeled with 125 I-5-iodo-2'-deoxyuridine. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1970 Oct;45(4):773–782. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hewitt H. B. The choice of animal tumors for experimental studies of cancer therapy. Adv Cancer Res. 1978;27:149–200. doi: 10.1016/s0065-230x(08)60932-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huchzermeyer H., Schmitz-Feuerhake I., Reblin T. Determination of splenic blood flow by inhalation of radioactive rare gases. Eur J Clin Invest. 1977 Oct;7(5):345–349. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2362.1977.tb01618.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parks R. C. Organ-specific metastasis of a transplantable reticulum cell sarcoma. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1974 Mar;52(3):971–973. doi: 10.1093/jnci/52.3.971. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pilgrim H. I. The kinetics of the organ-specific metastasis of a transplantable reticuloendothelial tumor. Cancer Res. 1969 Jun;29(6):1200–1205. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Proctor J. W. Rat sarcoma model supports both "soil seed" and "mechanical" theories of metastatic spread. Br J Cancer. 1976 Dec;34(6):651–654. doi: 10.1038/bjc.1976.227. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SODERBERG U. Temporal characteristics of thyroid activity. Physiol Rev. 1959 Oct;39:777–810. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1959.39.4.777. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SUGARBAKER E. D. The organ selectivity of experimentally induced metastases in rats. Cancer. 1952 May;5(3):606–612. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(195205)5:3<606::aid-cncr2820050324>3.0.co;2-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sadler T. E., Alexander P. Trapping and destruction of blood-borne syngeneic leukaemia cells in lung, liver and spleen of normal and leukaemic rats. Br J Cancer. 1976 May;33(5):512–520. doi: 10.1038/bjc.1976.82. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saegesser F., Besson A., Kafaï F. Pulmonary coin lesions and metastases. Aktuelle Probl Chir. 1970;14:539–610. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas J. M., Redding W. H., Sloane J. P. The spread of breast cancer: importance of the intrathoracic lymphatic route and its relevance to treatment. Br J Cancer. 1979 Oct;40(4):540–547. doi: 10.1038/bjc.1979.219. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss L. A pathobiologic overview of metastasis. Semin Oncol. 1977 Mar;4(1):5–17. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss L. Cancer cell traffic from the lungs to the liver: an example of metastatic inefficiency. Int J Cancer. 1980 Mar 15;25(3):385–392. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910250313. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss L., Glaves D., Waite D. A. The influence of host immunity on the arrest of circulating cancer cells, and its modification by neuraminidase. Int J Cancer. 1974 Jun 15;13(6):850–862. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910130612. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss L. The retention of circulating Walker-256 cells by Walker-256 tumours. Med Biol. 1978 Dec;56(6):398–402. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ZEIDMAN I., BUSS J. M. Transpulmonary passage of tumor cell emboli. Cancer Res. 1952 Oct;12(10):731–733. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


