Abstract
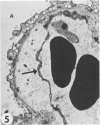
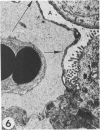
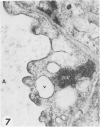
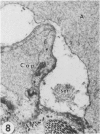
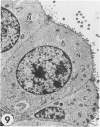
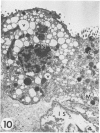
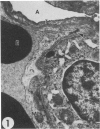
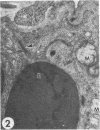
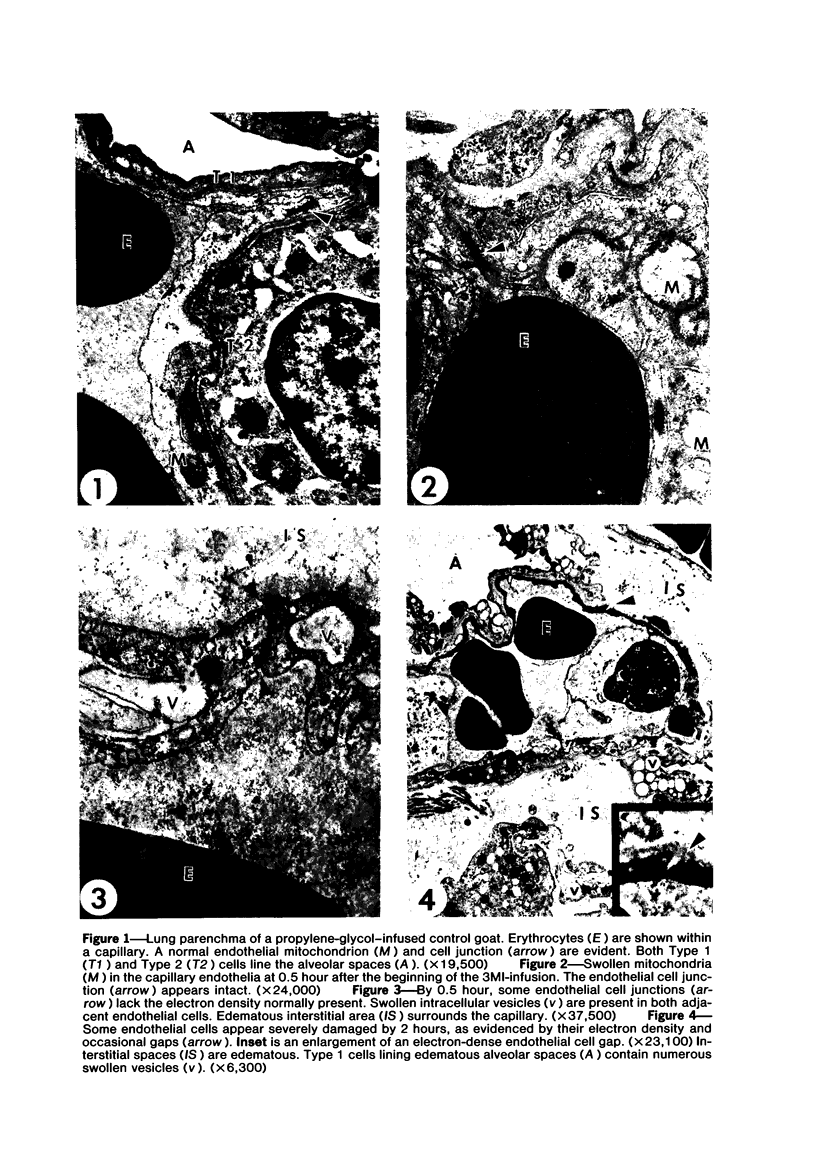
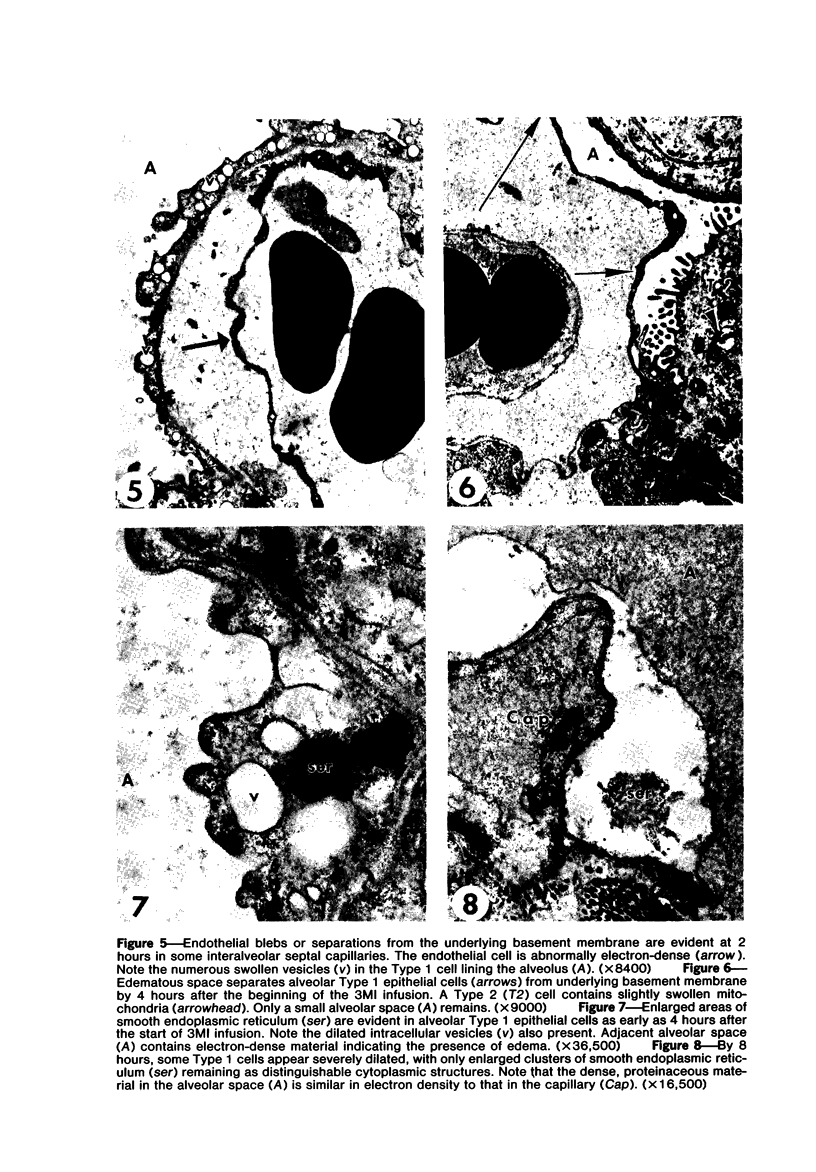
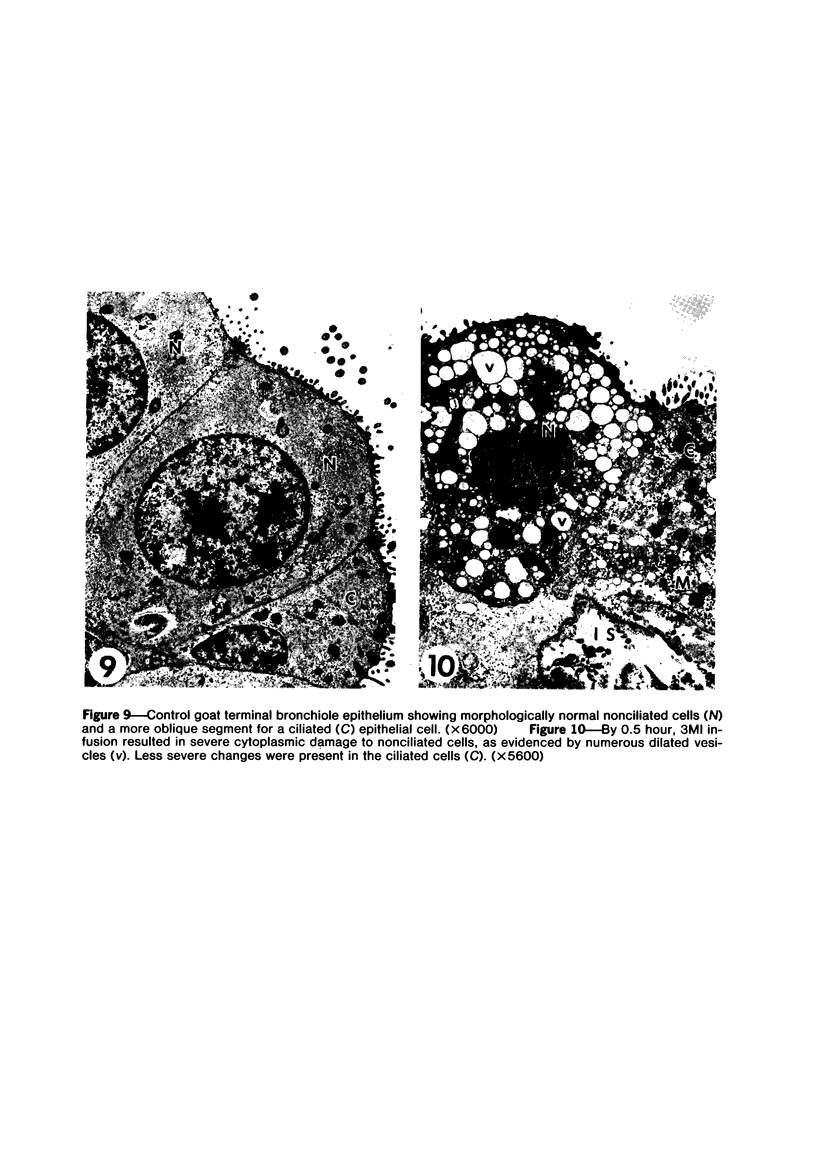
Transmission electron microscopy was used to characterize early pulmonary lesions in goats after a 2-hour intravenous infusion of 0.04 g 3-methylindole (3MI) per kilogram body weight. Groups of 2 or 3 goats were euthanized at 0.5, 2, 4, 8, and 24 hours after the beginning of the infusion. Changes in lung ultrastructure were compared to noninfused and carrier-infused (propylene glycol) controls. By 0.5 hour, mitochondria and intracellular vesicles were swollen in capillary endothelial, alveolar, and nonciliated bronchiolar epithelial cells. Morphologic changes were most severe in the alveolar Type 1 and nonciliated bronchiolar epithelial cells. Interalveolar septums were swollen at 0.5 hour, and interstitial edema was severe at 2 hours. Denuded alveolar epithelial basement membranes were also observed at 2 hours, and some endothelial cells appeared dark and necrotic. Endothelial cells appeared normal after 2 hours. By 4 hours, the remaining intact alveolar Type 1 cells contained larger and more prominent clusters of smooth endoplasmic reticulum, compared with controls. Morphologic changes in alveolar Type 1 and nonciliated bronchiolar epithelial cells became progressively more severe during the 24-hour experiment. These findings demonstrate that 3MI induces a rapid cytotoxic effect primarily on alveolar Type 1 and nonciliated bronchiolar epithelial cells. Proliferation of smooth endoplasmic reticulum in these cells suggests involvement of the mixed function oxidase system in 3MI-induced pneumotoxicity.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Boyd M. R. Role of metabolic activation in the pathogenesis of chemically induced pulmonary disease: mechanism of action of the lung-toxic furan, 4-ipomeanol. Environ Health Perspect. 1976 Aug;16:127–138. doi: 10.1289/ehp.7616127. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boyd M. R., Statham C. N., Franklin R. B., Mitchell J. R. Pulmonary bronchiolar alkylation and necrosis by 3-methylfuran, a naturally occurring potential atmospheric contaminant. Nature. 1978 Mar 16;272(5650):270–271. doi: 10.1038/272270a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bray T. M., Carlson J. R. Role of mixed-function oxidase in 3-methylindole-induced acute pulmonary edema in goats. Am J Vet Res. 1979 Sep;40(9):1268–1272. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bray T. M., Carlson J. R. The effects of 3-methylindole on hemolysis, transport of Na+, and ATPase activities of bovine erythrocytes. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1975 Mar;148(3):875–879. doi: 10.3181/00379727-148-38651. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bray T. M., Magnuson J. A., Carlson J. R. Nuclear magnetic resonance studies of lecithin-skatole interaction. J Biol Chem. 1974 Feb 10;249(3):914–918. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bray T. M., Sandberg H. E., Carlson J. R. An EPR study of structural perturbations induced by methylindole in the protein and lipid regions of erythrocyte membranes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1975 Apr 8;382(4):534–541. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(75)90220-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Breeze R. G., Pirie H. M., Dawson C. O., Selman I. E., Wiseman A. The pathology of respiratory diseases of adult cattle in Britain. Folia Vet Lat. 1975 Jan-Mar;5(1):95–128. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Breeze R. G., Pirie H. M., Selman I. E., Wiseman A. Fog fever in cattle: cytology of the hyperplastic alveolar epithelium. J Comp Pathol. 1975 Jan;85(1):147–156. doi: 10.1016/0021-9975(75)90093-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carlson J. R., Dickinson E. O., Yokoyama M. T., Bradley B. Pulmonary edema and emphysema in cattle after intraruminal and intravenous administration of 3-methylindole. Am J Vet Res. 1975 Sep;36(9):1341–1347. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dickinson E. O., Yokoyama M. T., Carlson J. R., Bradley B. J. Induction of pulmonary edema and emphysema in goats by intraruminal administration of 3-methylindole. Am J Vet Res. 1976 Jun;37(6):667–672. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guengerich F. P. Studies on the activation of a model furan compound--toxicity and covalent binding of 2-(N-ethylcarbamoylhydroxymethyl)furan. Biochem Pharmacol. 1977 Oct 15;26(20):1909–1915. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(77)90165-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang T. W., Carlson J. R., Bray T. M., Bradley B. J. 3-methylindole-induced pulmonary injury in goats. Am J Pathol. 1977 Jun;87(3):647–666. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hurley J. V. Current views on the mechanisms of pulmonary oedema. J Pathol. 1978 Jun;125(2):59–79. doi: 10.1002/path.1711250202. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pirie H. M., Breeze R. G., Selman I. E., Wiseman A. Indole-acetic acid, 3-methyl indole and type 2 pneumonocyte hyperplasia in a proliferative alveolitis of cattle. Vet Rec. 1976 Mar 27;98(13):259–260. doi: 10.1136/vr.98.13.259. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reid W. D., Ilett K. F., Glick J. M., Krishna G. Metabolism and binding of aromatic hydrocarbons in the lung. Relationship to experimental bronchiolar necrosis. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1973 Apr;107(4):539–551. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1973.107.4.539. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sasame H. A., Gillette J. R., Boyd M. R. Effects of anti-NADPH-cytochrome c reductase and anti-cytochrome b5 antibodies on the hepatic and pulmonary microsomal metabolism and covalent binding of the pulmonary toxin 4-ipomeanol. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1978 Sep 29;84(2):389–395. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(78)90182-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stäubli W., Hess R., Weibel E. R. Correlated morphometric and biochemical studies on the liver cell. II. Effects of phenobarbital on rat hepatocytes. J Cell Biol. 1969 Jul;42(1):92–112. doi: 10.1083/jcb.42.1.92. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Witschi H., Côté M. G. Biochemical pathology of lung damage produced by chemicals. Fed Proc. 1976 Jan;35(1):89–94. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]