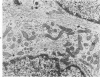Abstract
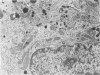
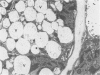
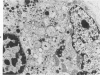
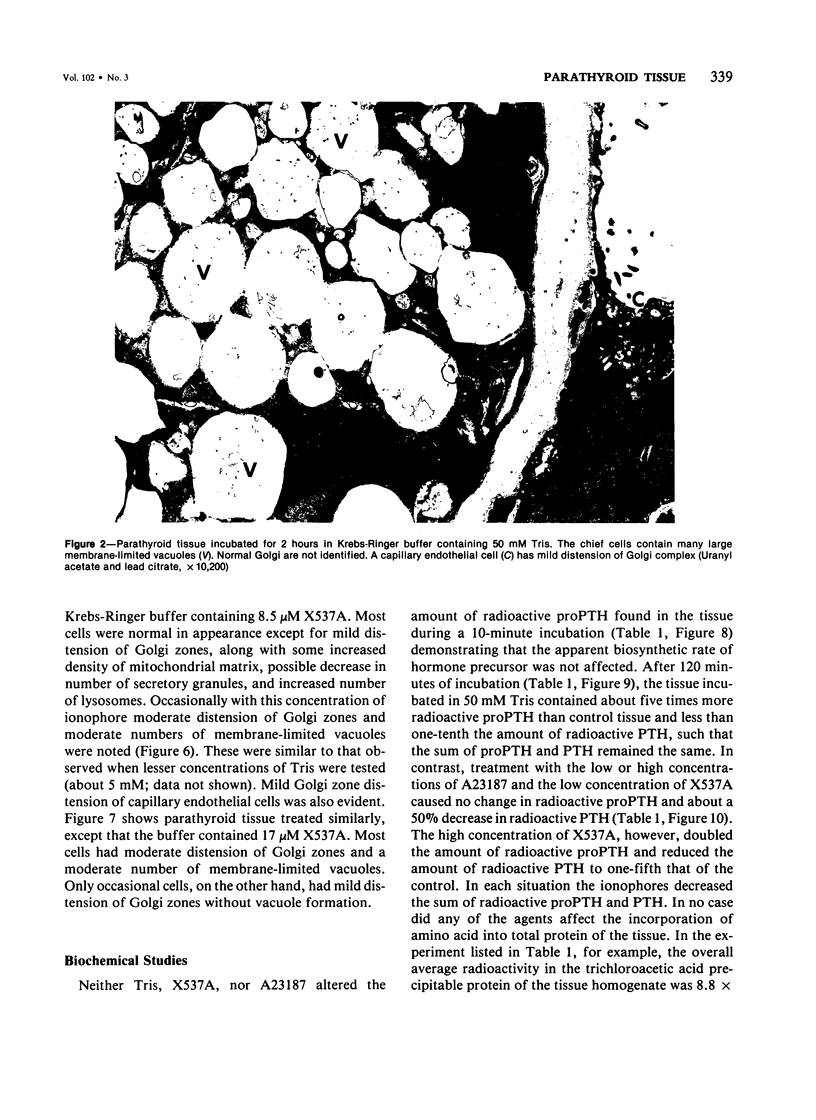
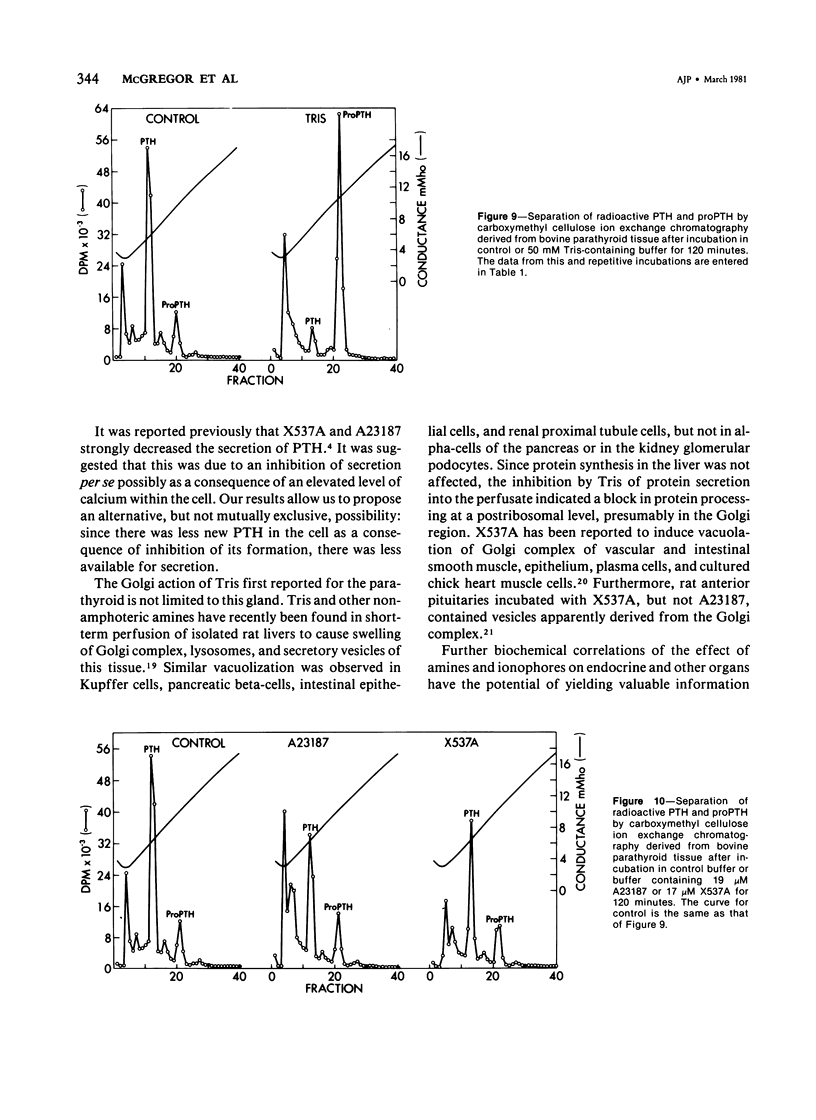
A comparative study of ultrastructural and biochemical effects of Tris and ionophores X537A and A23187 on bovine parathyroid tissue is presented. When parathyroid slices were incubated with 3H-leucine and 3H-lysine for 10 minutes alone or with Tris (50 mM), A23187 (9.5-19 microM) or X537A (8.5-17 microM), the incorporation of the amino acids into radioactive proparathormone (proPTH) was similar, indicating that biosynthesis of the hormone was not affected. After 120 minutes of incubation, however, Tris inhibited the conversion of proPTH to parathormone (PTH), judged by a decrease in cellular and secreted radioactive PTH and a corresponding increase in radioactive cellular proPTH. These changes were accompanied by marked dilatation of Golgi membranes. With both concentrations of A23187 and the low concentration of X537A there were no changes in amounts of radioactive proPTH, moderate decreases in cellular and secreted radioactive PTH, and little discernible distension of the Golgi membranes. At 17 microM X537A there was moderate increase in amount of radioactive proPTH, a marked decrease in amount of radioactive PTH and swelling of the Golgi membranes. Taken together, these findings suggest that Tris inhibited conversion of proPTH to PTH by disrupting the Golgi zone-the site of conversion of proPTH to PTH; that A23187 and the low concentration of X537A decreased production of PTH by enhancing its degradation; and that X537A at the higher concentration acted both by inhibiting conversion of proPTH to PTH and by enhancing the degradation of PTH.
Full text
PDF


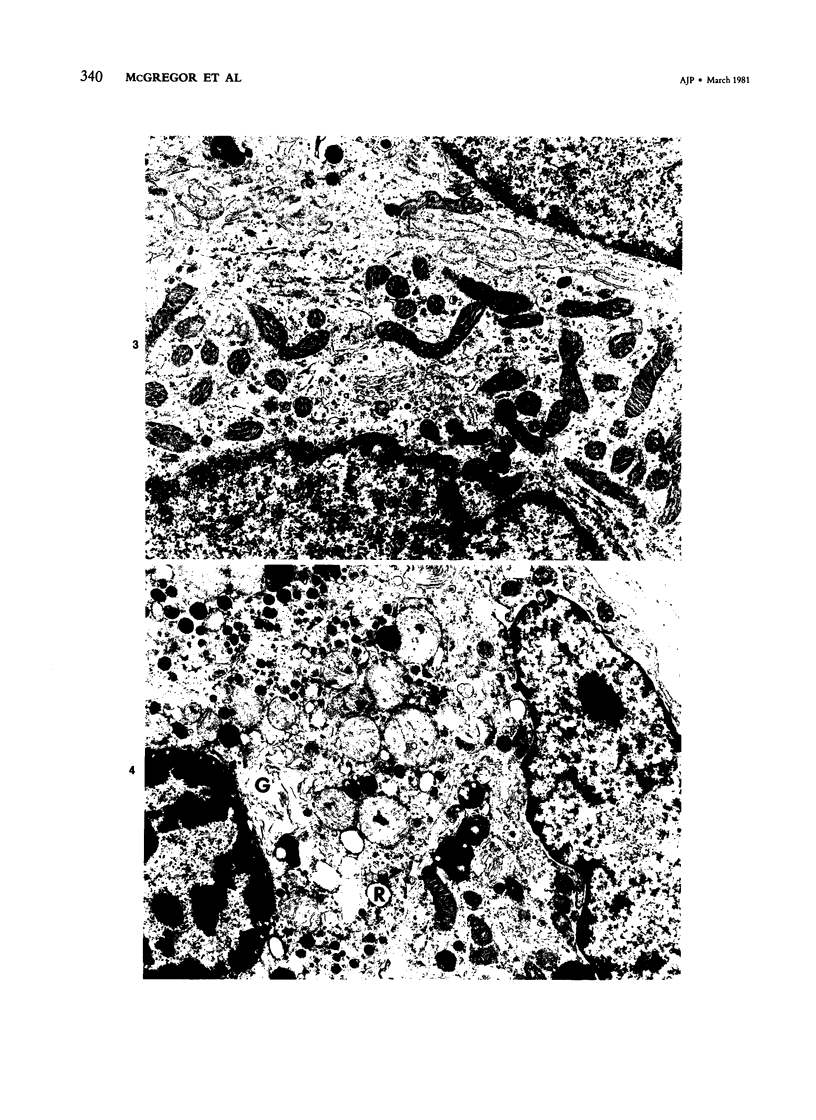
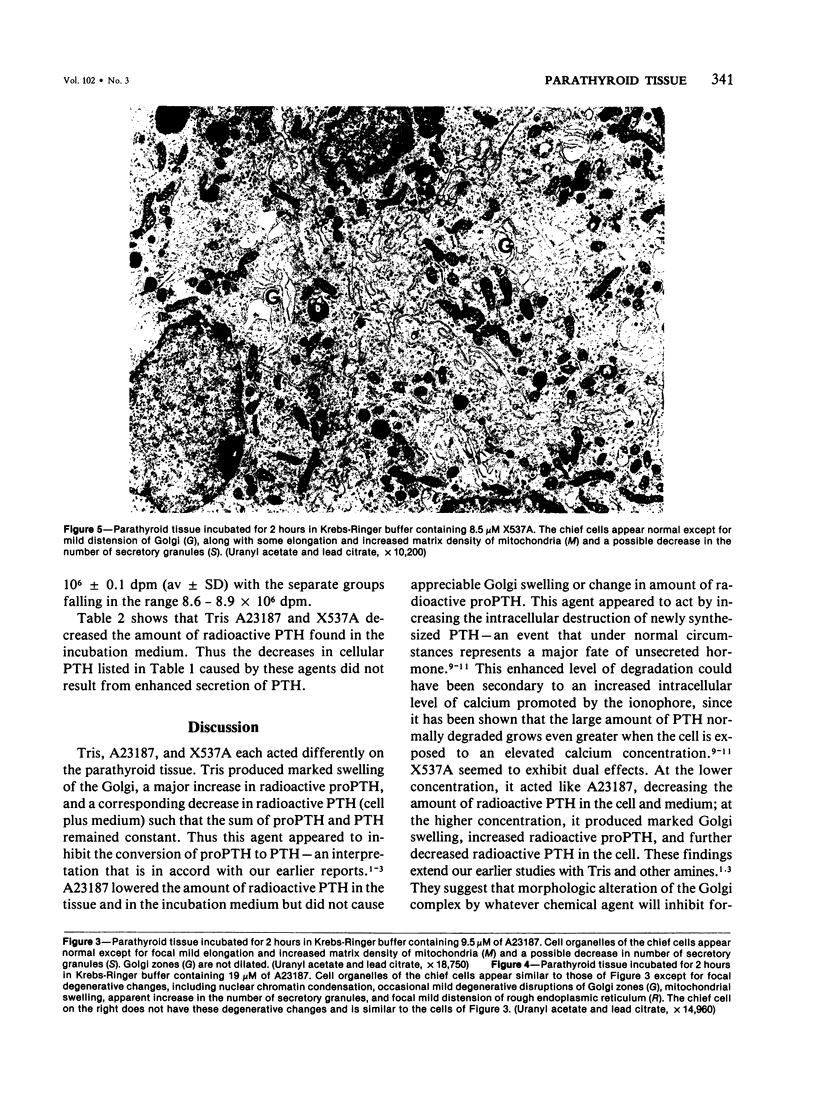
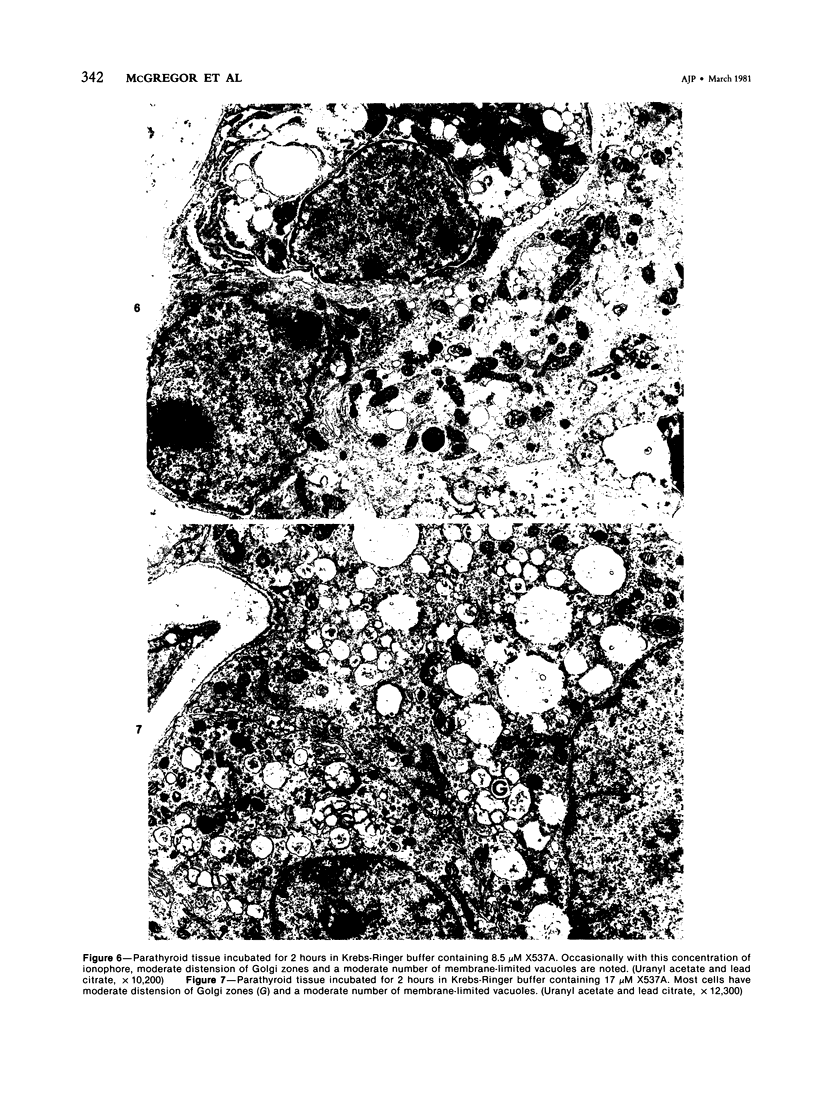
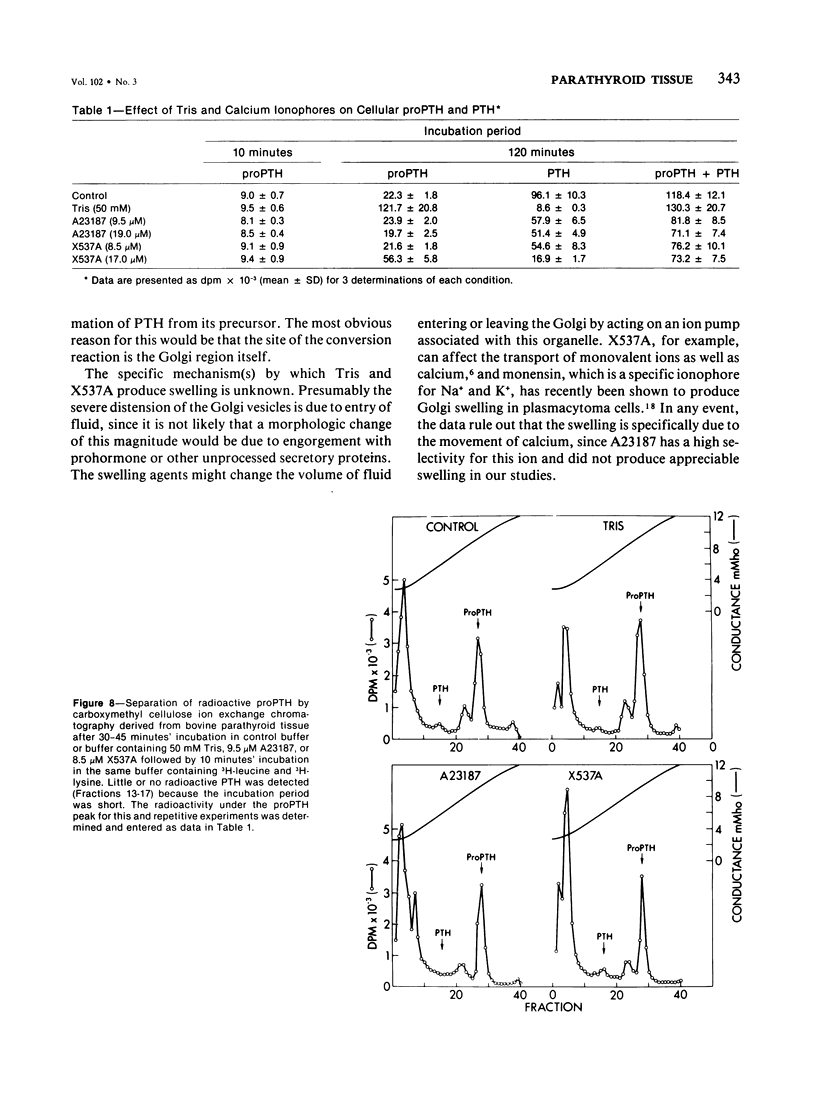

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Chu L. L., MacGregor R. R., Anast C. S., Hamilton J. W., Cohn D. V. Studies on the biosynthesis of rat parathyroid hormone and proparathyroid hormone: adaptation of the parathyroid gland to dietary restriction of calcium. Endocrinology. 1973 Oct;93(4):915–924. doi: 10.1210/endo-93-4-915. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chu L. L., MacGregor R. R., Liu P. I., Hamilton J. W., Cohn D. V. Biosynthesis of proparathyroid hormone and parathyroid hormone by human parathyroid glands. J Clin Invest. 1973 Dec;52(12):3089–3094. doi: 10.1172/JCI107508. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chu L. L., Macgregor R. R., Hamilton J. W., Cohn D. V. Conversion of proparathyroid hormone to parathyroid hormone: the use of amines as specific inhibitors. Endocrinology. 1974 Nov;95(5):1431–1438. doi: 10.1210/endo-95-5-1431. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohn D. V., Hamilton J. W. Newer aspects of parathyroid chemistry and physiology. Cornell Vet. 1976 Jul;66(3):271–300. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Habener J. F., Kemper B., Potts J. T., Jr Calcium-dependent intracellular degradation of parathyroid hormone: a possible mechanism for the regulation of hormone stores. Endocrinology. 1975 Aug;97(2):431–441. doi: 10.1210/endo-97-2-431. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Habener J. F., Stevens T. D., Ravazzola M., Orci L., Potts J. T., Jr Effects of calcium ionophores on the synthesis and release of parathyroid hormone. Endocrinology. 1977 Nov;101(5):1524–1537. doi: 10.1210/endo-101-5-1524. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamilton J. W., Spierto F. W., MacGregor R. R., Cohn D. V. Studies on the biosynthesis in vitro of parathyroid hormone. II. The effect of calcium and magnesium on synthesis of parathyroid hormone isolated from bovine parathyroid tissue and incubation medium. J Biol Chem. 1971 May 25;246(10):3224–3233. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MOLLENHAUER H. H. PLASTIC EMBEDDING MIXTURES FOR USE IN ELECTRON MICROSCOPY. Stain Technol. 1964 Mar;39:111–114. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGregor D. H., Chu L. L., MacGregor R. R., Cohn D. V. Disruption of the Golgi zone and inhibition of the conversion of proparathyroid hormone to parathyroid hormone in human parathyroid tissue by tris(hydroxymethyl)aminomethane. Am J Pathol. 1977 Jun;87(3):553–568. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mira-Moser F., Schofield J. C., Orci L. Modifications in the release of rat growth hormone in vitro and the morphology of rat anterior pituitaries incubated in various ionophores. Eur J Clin Invest. 1976 Jan 30;6(1):103–111. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2362.1976.tb00499.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morrissey J. J., Cohn D. V. Secretion and degradation of parathormone as a function of intracellular maturation of hormone pools. Modulation by calcium and dibutyryl cyclic AMP. J Cell Biol. 1979 Dec;83(3):521–528. doi: 10.1083/jcb.83.3.521. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peterlik M., Kerjaschki D. Interference of tris(hydroxymethyl)aminomethane with structure and function of Golgi membranes. Lab Invest. 1979 Mar;40(3):313–316. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pressman B. C. Biological applications of ionophores. Annu Rev Biochem. 1976;45:501–530. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.45.070176.002441. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pressman B. C. Properties of ionophores with broad range cation selectivity. Fed Proc. 1973 Jun;32(6):1698–1703. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- REYNOLDS E. S. The use of lead citrate at high pH as an electron-opaque stain in electron microscopy. J Cell Biol. 1963 Apr;17:208–212. doi: 10.1083/jcb.17.1.208. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ravazzola M. Golgi complex alterations induced by X537A in chief cells of rat parathyroid gland. Lab Invest. 1976 Nov;35(5):425–429. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reed P. W., Lardy H. A. A23187: a divalent cation ionophore. J Biol Chem. 1972 Nov 10;247(21):6970–6977. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Somlyo A. P., Garfield R. E., Chacko S., Somlyo A. V. Golgi organelle response to the antibiotic X537A. J Cell Biol. 1975 Aug;66(2):425–443. doi: 10.1083/jcb.66.2.425. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tartakoff A. M., Vassalli P. Plasma cell immunoglobulin secretion: arrest is accompanied by alterations of the golgi complex. J Exp Med. 1977 Nov 1;146(5):1332–1345. doi: 10.1084/jem.146.5.1332. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WATSON M. L. Staining of tissue sections for electron microscopy with heavy metals. J Biophys Biochem Cytol. 1958 Jul 25;4(4):475–478. doi: 10.1083/jcb.4.4.475. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]