Abstract
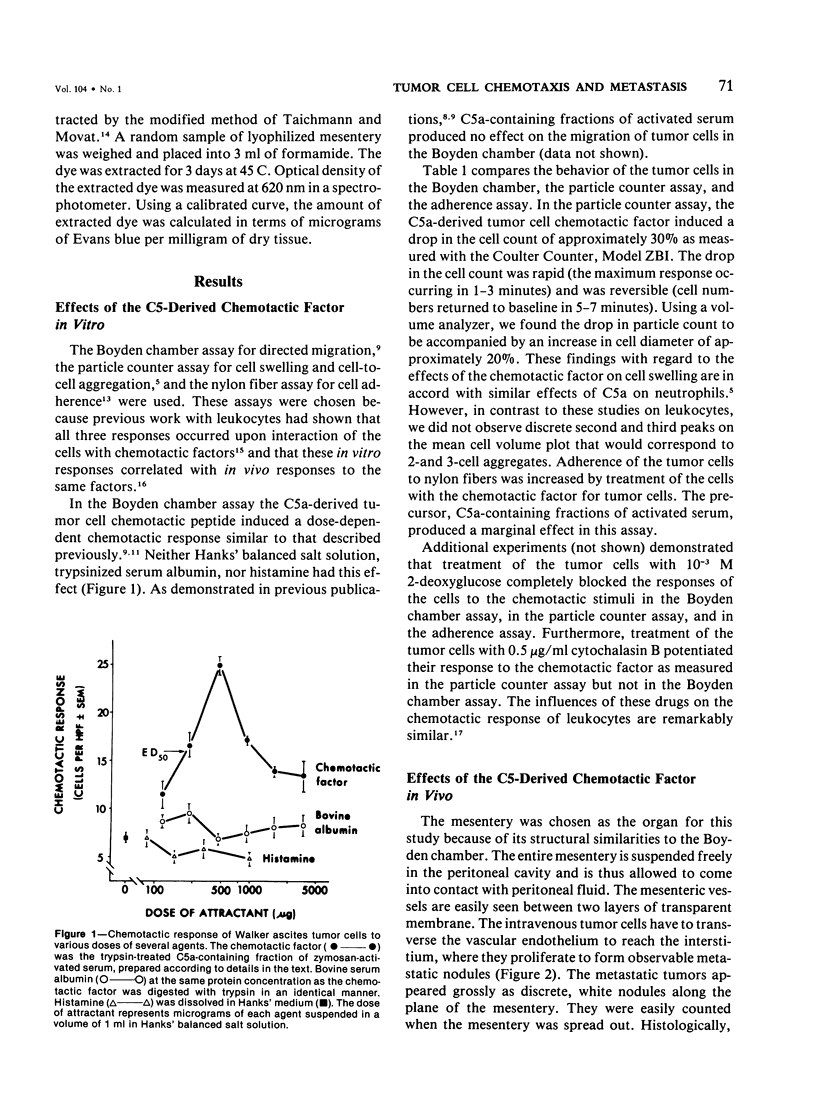
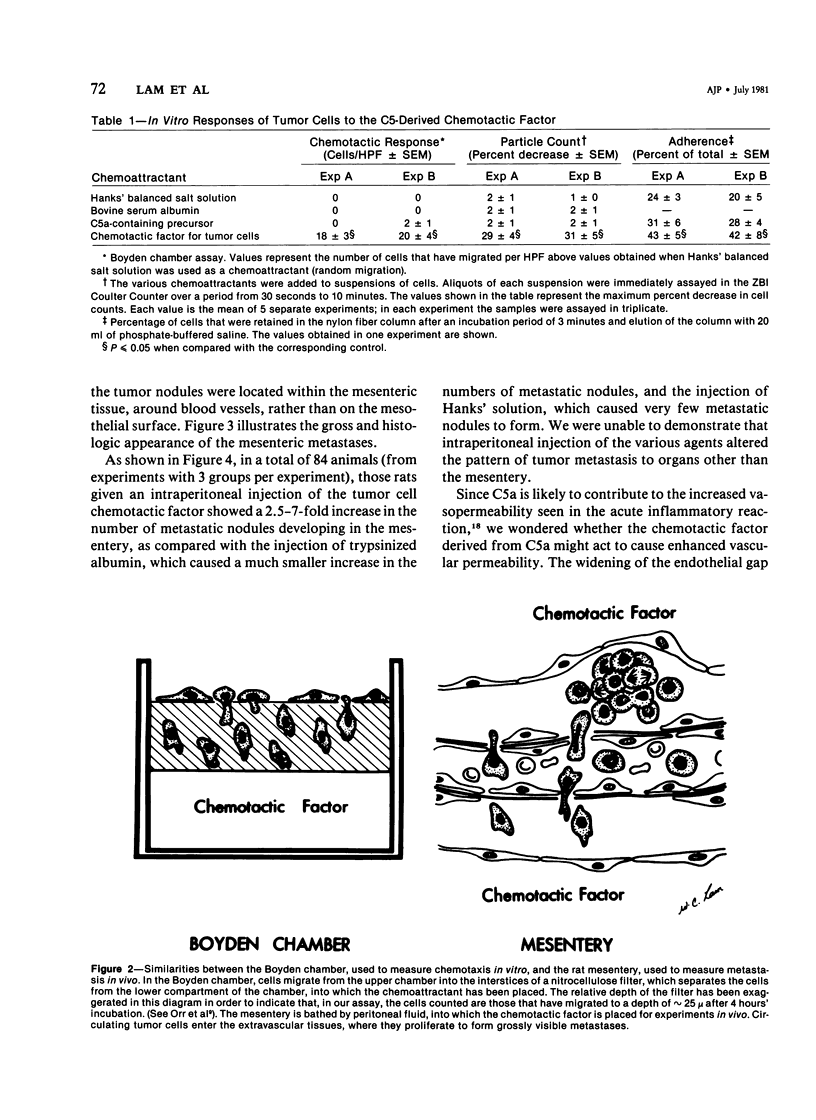
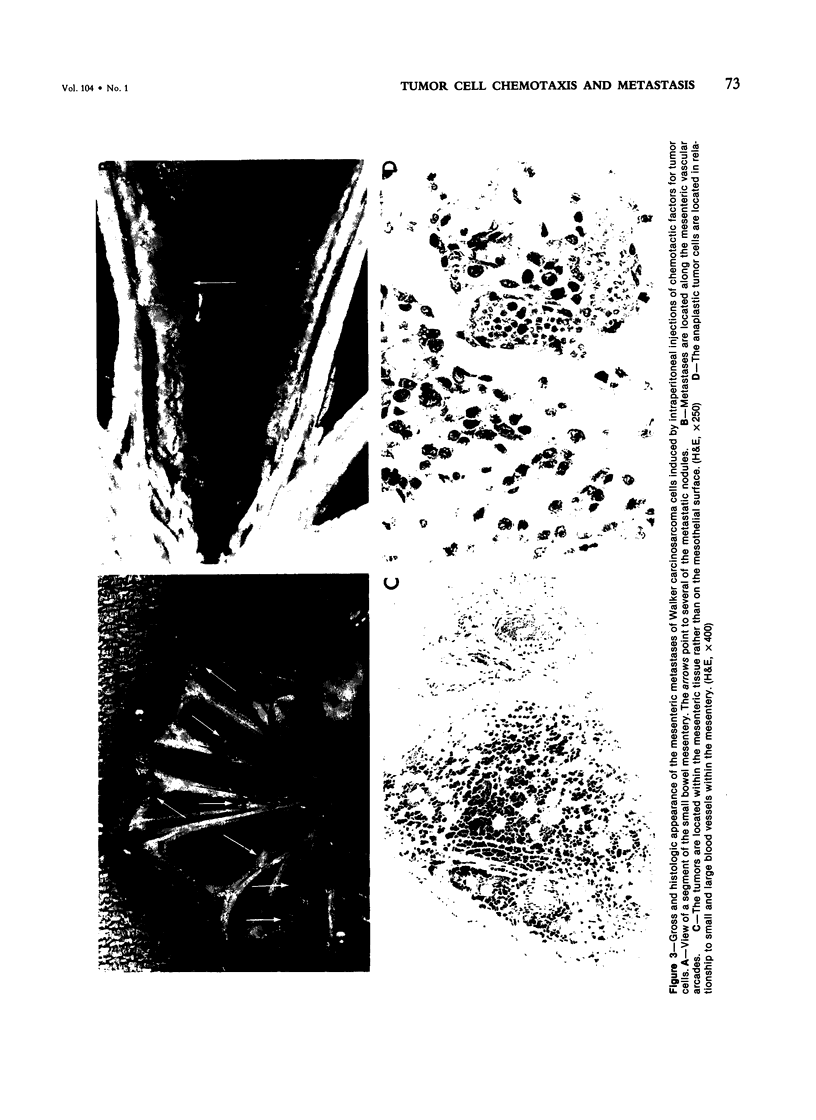
Injection of a C5-derived chemotactic factor for tumor cells into the peritoneal cavities of Sprague-Dawley rats induced diffuse mesenteric metastasis following the intravenous injection of Walker carcinosarcoma cells. Intraperitoneal injections of culture medium, histamine, or of trypsin-treated albumin resulted in many fewer metastases. Intraperitoneal injections of the chemotactic factor, unlike histamine, did not alter mesenteric vasopermeability as measured by the exudation of Evans blue into the mesentery. In vitro, tumor cells responded to the chemotactic factor by demonstrating directed migration in the Boyden chamber, by volume changes, measurable in the Coulter counter, and by demonstrating an increased adherence to nylon fibers. These phenomena are similar to the behavior of neutrophils in the presence of their chemotactic factors. All the responses in vitro were markedly depressed by the addition of 2-deoxyglucose, while the cell swelling response was slightly enhanced by cytochalasin B (again similar to the responses of leukocytes). The data suggest that movement of tumor cells from the circulation may be under chemotactic influence in the manner similar to the responsiveness of neutrophils to leukotactic stimuli in vivo.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- DerHagopian R. P., Sugarbaker E. V., Ketcham A. Inflammatory oncotaxis. JAMA. 1978 Jul 28;240(4):374–375. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fisher B., Fisher E. R., Feduska N. Trauma and the localization of tumor cells. Cancer. 1967 Jan;20(1):23–30. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(1967)20:1<23::aid-cncr2820200103>3.0.co;2-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hugli T. E., Müller-Eberhard H. J. Anaphylatoxins: C3a and C5a. Adv Immunol. 1978;26:1–53. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2776(08)60228-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson K. J., Ward P. A. Acute immunologic pulmonary alveolitis. J Clin Invest. 1974 Aug;54(2):349–357. doi: 10.1172/JCI107770. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kreutzer D. L., O'Flaherty J. T., Orr W., Showell H. J., Ward P. A., Becker E. L. Quantitative comparisons of various biological responses of neutrophils to different active and inactive chemotactic factors. Immunopharmacology. 1978 Dec;1(1):39–47. doi: 10.1016/0162-3109(78)90007-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacGregor R. R., Spagnuolo P. J., Lentnek A. L. Inhibition of granulocyte adherence by ethanol, prednisone, and aspirin, measured with an assay system. N Engl J Med. 1974 Sep 26;291(13):642–646. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197409262911302. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Flaherty J. T., Kreutzer D. L., Showell H. J., Ward P. A. Influence of inhibitors of cellular function on chemotactic factor-induced neutrophil aggregation. J Immunol. 1977 Nov;119(5):1751–1756. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Flaherty J. T., Kreutzer D. L., Ward P. A. Chemotactic factor influences on the aggregation, swelling, and foreign surface adhesiveness of human leukocytes. Am J Pathol. 1978 Mar;90(3):537–550. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Flaherty J. T., Kreutzer D. L., Ward P. A. Neutrophil aggregation and swelling induced by chemotactic agents. J Immunol. 1977 Jul;119(1):232–239. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Flaherty J. T., Ward P. A. Chemotactic factors and the neutrophil. Semin Hematol. 1979 Apr;16(2):163–174. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orr F. W., Varani J., Kreutzer D. L., Senior R. M., Ward P. A. Digestion of the fifth component of complement by leukocyte enzymes. Sequential generation of chemotactic activities for leukocytes and for tumor cells. Am J Pathol. 1979 Jan;94(1):75–83. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orr W., Phan S. H., Varani J., Ward P. A., Kreutzer D. L., Webster R. O., Henson P. M. Chemotactic factor for tumor cells derived from the C5a fragment of complement component C5. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Apr;76(4):1986–1989. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.4.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orr W., Varani J., Gondex M. K., Ward P. A., Mundy G. R. Chemotactic responses of tumor cells to products of resorbing bone. Science. 1979 Jan 12;203(4376):176–179. doi: 10.1126/science.569363. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orr W., Varani J., Ward P. A. Characteristics of the chemotactic response of neoplastic cells to a factor derived from the fifth component of complement. Am J Pathol. 1978 Nov;93(2):405–422. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ozaki T., Yoshida K., Ushijima K., Hayashi H. Studies on the mechanisms of invasion in cancer. II. In vivo effects of a factor chemotactic for cancer cells. Int J Cancer. 1971 Jan 15;7(1):93–100. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910070111. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Romualdez A. G., Jr, Ward P. A. A unique complement derived chemotactic factor for tumor cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Oct;72(10):4128–4132. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.10.4128. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Romualdez A. G., Ward P. A., Torikata T. Relationship between the C5 peptides chemotactic for leukocytes and tumor cells. J Immunol. 1976 Nov;117(5 PT2):1762–1766. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roos E., Dingemans K. P. Mechanisms of metastasis. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1979 Feb 4;560(1):135–166. doi: 10.1016/0304-419x(79)90005-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snyderman R., Phillips J. K., Mergenhagen S. E. Biological activity of complement in vivo. Role of C5 in the accumulation of polymorphonuclear leukocytes in inflammatory exudates. J Exp Med. 1971 Nov 1;134(5):1131–1143. doi: 10.1084/jem.134.5.1131. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taichman N. S., Movat H. Z. Do polymorphonuclear leukocytes play a role in passive cutaneous anaphylaxis of the guinea pig? Int Arch Allergy Appl Immunol. 1966;30(1):97–102. doi: 10.1159/000229797. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ushijima K., Nishi H., Ishikura A., Hayashi H. Characterization of two different factors chemotactic for cancer cells from tumor tissue. Virchows Arch B Cell Pathol. 1976 Aug 11;21(2):119–131. doi: 10.1007/BF02899149. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zigmond S. H. Chemotaxis by polymorphonuclear leukocytes. J Cell Biol. 1978 May;77(2):269–287. doi: 10.1083/jcb.77.2.269. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]