Abstract
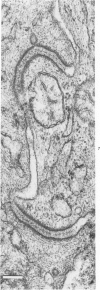
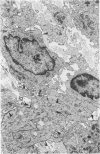
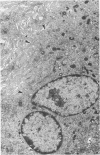
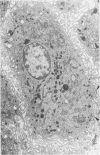
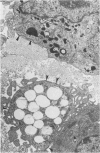
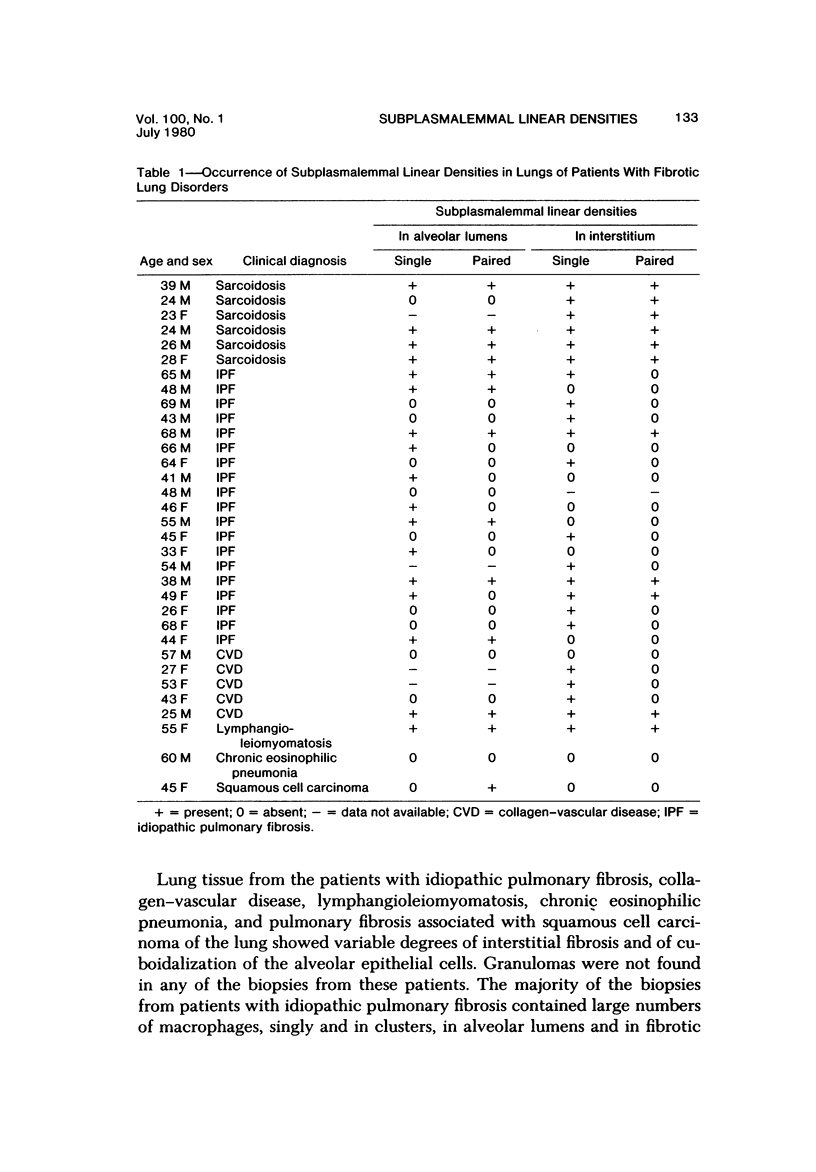
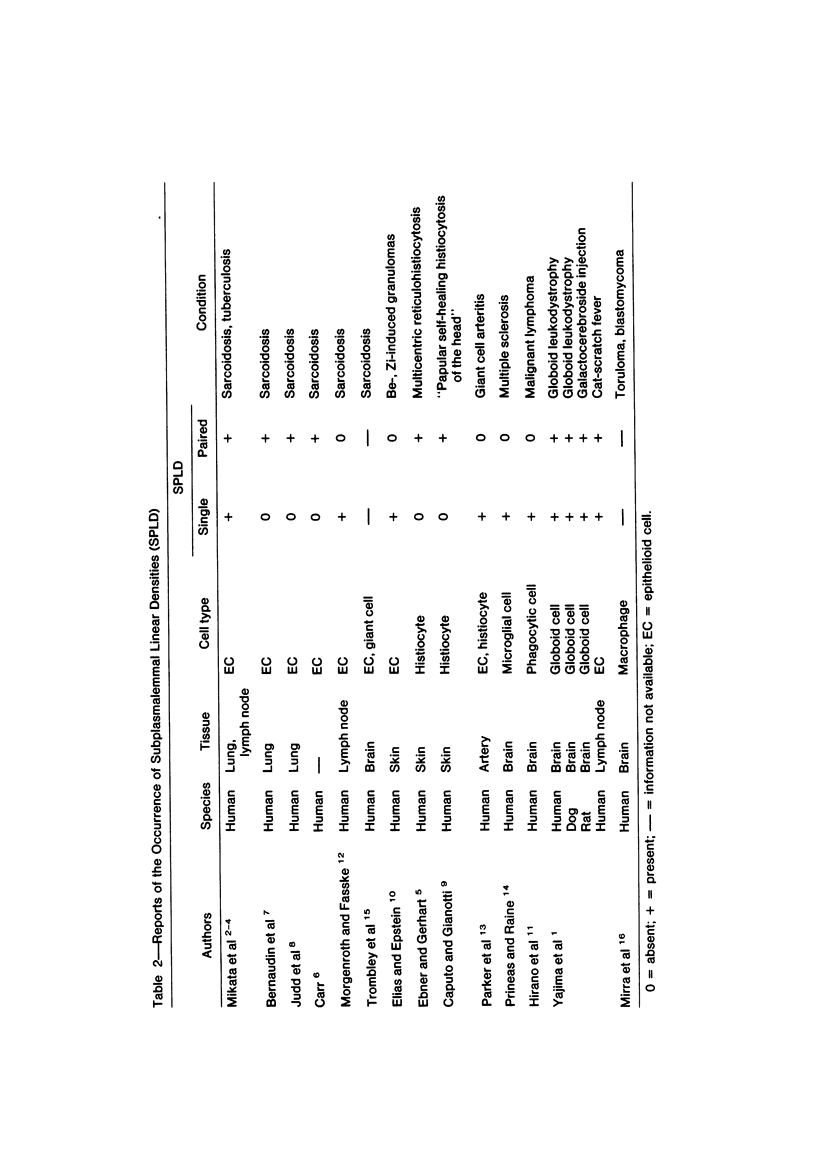
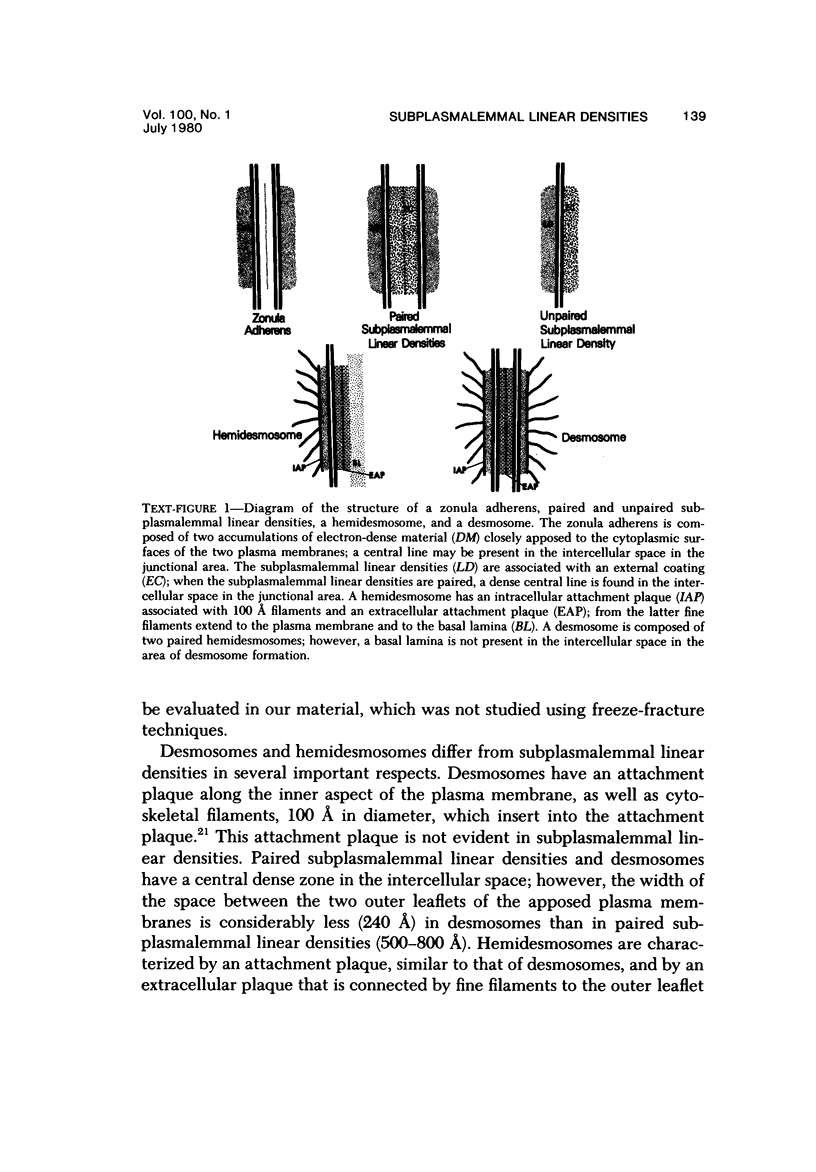
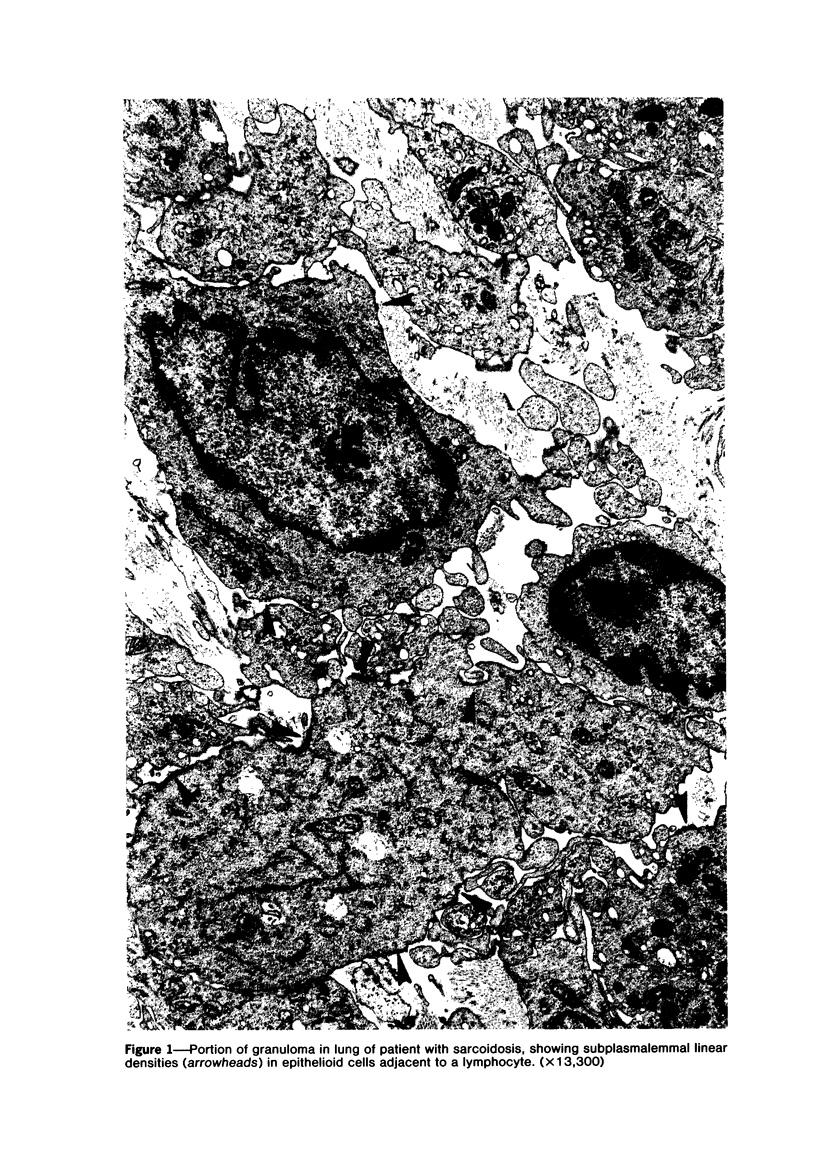
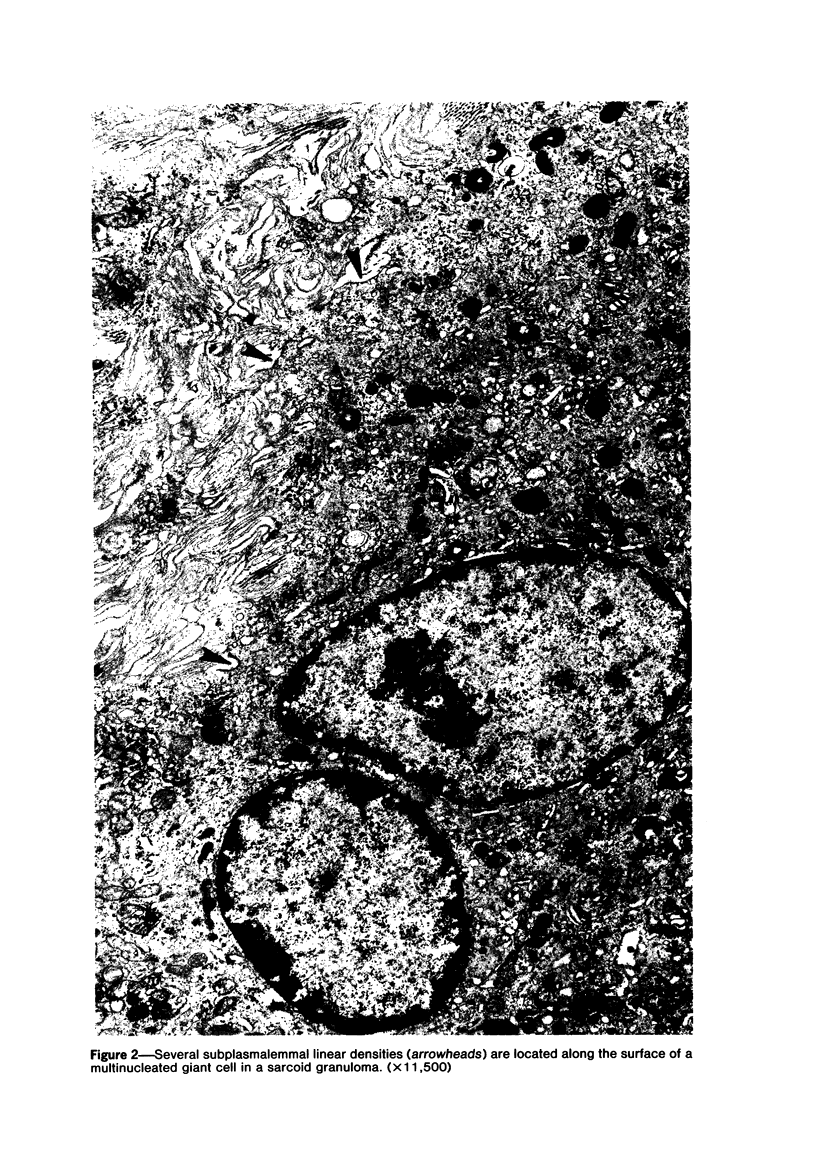
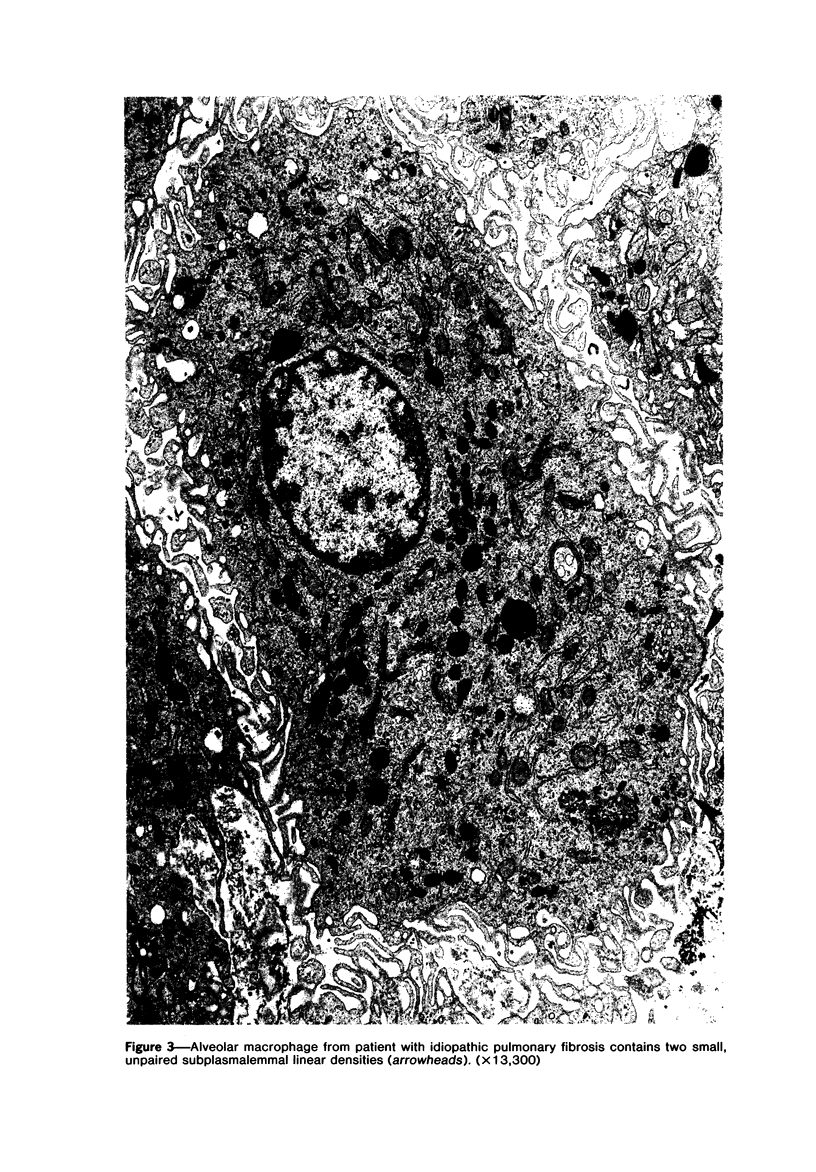
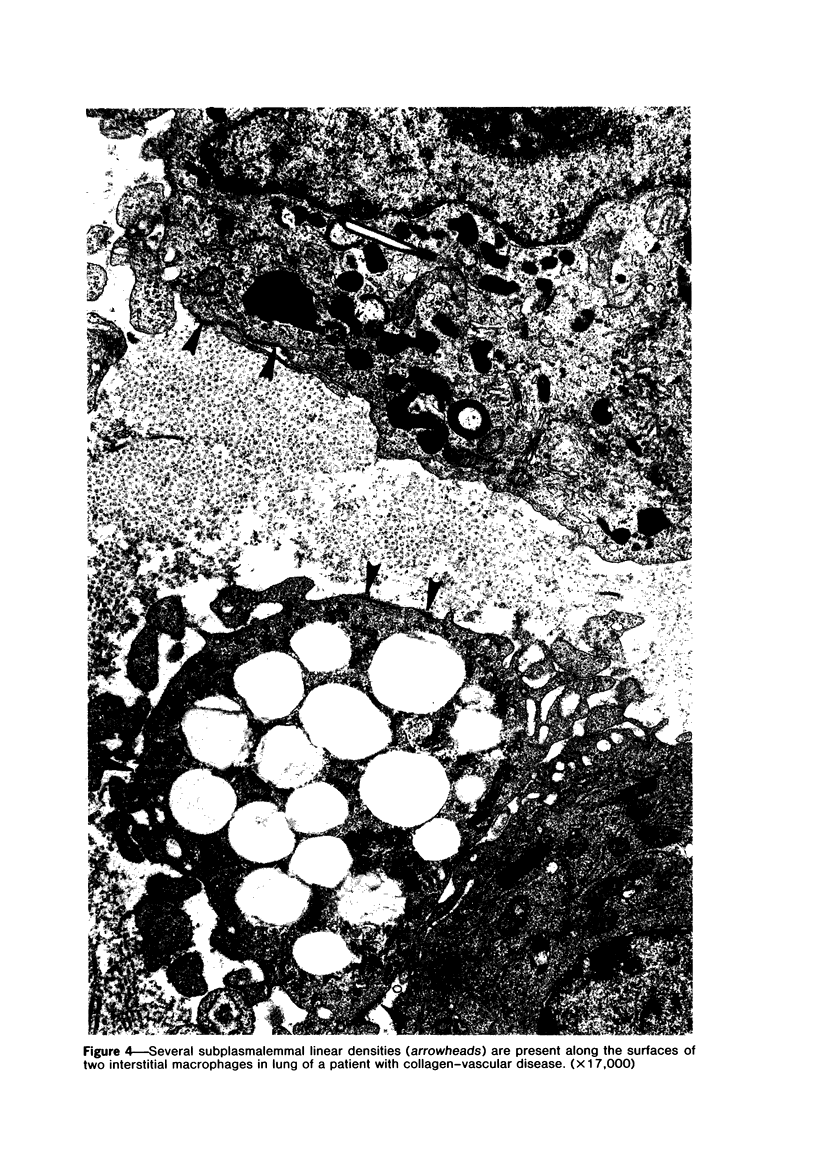
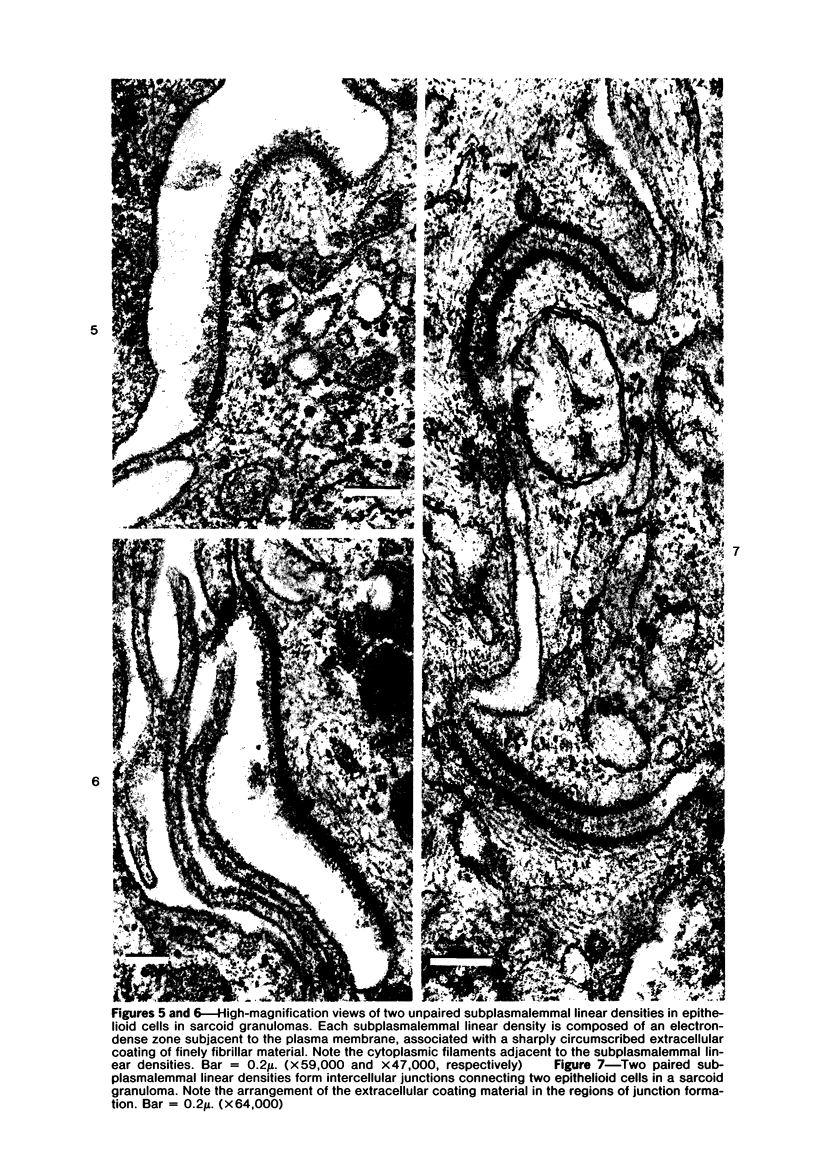
The presence of subplasmalemmal linear densities in cells of the mononuclear phagocyte system was investigated in pulmonary biopsies from 33 patients with fibrotic lung disorders. Subplasmalemmal linear densities, consisting of a thin layer of electron-dense material immediately subjacent to the inner leaflet of the plasma membrane, were found in 30 of the 33 patients, including each of 6 patients with pulmonary sarcoidosis, 18 of 19 patients with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis, 4 of 5 patients with collagen-vascular diseases, 1 patient with pulmonary lymphangioleiomyomatosis, and 1 patient with marked interstitial pulmonary fibrosis associated with squamous cell carcinoma of the lung. Subplasmalemmal linear densities were found in epithelioid cells, macrophages, and giant cells in granulomas in the 6 patients with sarcoidosis and in alveolar macrophages in 4 of these patients. In patients with other fibrotic lung disorders, subplasmalemmal linear densities were limited in distribution to interstitial and alveolar macrophages. In all patients with sarcoidosis some of the subplasmalemmal linear densities of adjacent mononuclear phagocytes, particularly of those in granulomas, were paired and formed specialized intercellular junctions. Such junctions also were observed in macrophages in 10 of the patients with other fibrotic lung disorders. The junctions formed by subplasmalemmal linear densities differed from other types of junctional structures. Subplasmalemmal linear densities appear to function in 1) the binding of action filalar junctions, which may contribute to the immobilization of mononuclear phagocytes in granulomas and alveolar lumens.
Full text
PDF











Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anderson R. G., Brown M. S., Goldstein J. L. Role of the coated endocytic vesicle in the uptake of receptor-bound low density lipoprotein in human fibroblasts. Cell. 1977 Mar;10(3):351–364. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90022-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bernaudin J. F., Soler P., Basset F., Chrétien J. La cellule épithélioîde Données ultrastructurales au cours de diverses entités pathologiques humaines. Pathol Biol (Paris) 1975 Jun;23(6):494–498. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caputo R., Gianotti F. Junctions between histiocytes: role of coated vesicles. J Ultrastruct Res. 1979 Sep;68(3):256–264. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5320(79)90158-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooke P. H., Fay F. S. Correlation between fiber length, ultrastructure, and the length-tension relationship of mammalian smooth muscle. J Cell Biol. 1972 Jan;52(1):105–116. doi: 10.1083/jcb.52.1.105. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ebner H., Gebhart W. Zur Ultrastruktur der multizentrischen Reticulohistiocytose. Arch Dermatol Forsch. 1971;240(3):259–270. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elias P. M., Epstein W. L. Ultrastructural observations on experimentally induced foreign-body and organized epithelioid-cell granulomas in man. Am J Pathol. 1968 Jun;52(6):1207–1223. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FARQUHAR M. G., PALADE G. E. Junctional complexes in various epithelia. J Cell Biol. 1963 May;17:375–412. doi: 10.1083/jcb.17.2.375. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friend D. S., Farquhar M. G. Functions of coated vesicles during protein absorption in the rat vas deferens. J Cell Biol. 1967 Nov;35(2):357–376. doi: 10.1083/jcb.35.2.357. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gimbrone M. A., Jr, Cotran R. S. Human vascular smooth muscle in culture. Growth and ultrastructure. Lab Invest. 1975 Jul;33(1):16–27. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldstein J. L., Anderson R. G., Brown M. S. Coated pits, coated vesicles, and receptor-mediated endocytosis. Nature. 1979 Jun 21;279(5715):679–685. doi: 10.1038/279679a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartwig J. H., Stossel T. P. Isolation and properties of actin, myosin, and a new actinbinding protein in rabbit alveolar macrophages. J Biol Chem. 1975 Jul 25;250(14):5696–5705. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirano A., Ghatak N. R., Becker N. H., Zimmerman H. M. A comparison of the fine structure of small blood vessels in intracranial and retroperitoneal malignant lymphomas. Acta Neuropathol. 1974 Feb 28;27(2):93–104. doi: 10.1007/BF00687160. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jockusch B. M., Burger M. M., DaPrada M., Richards J. G., Chaponnier C., Gabbiani G. alpha-Actinin attached to membranes of secretory vesicles. Nature. 1977 Dec 15;270(5638):628–629. doi: 10.1038/270628a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Judd P. A., Finnegan P., Curran R. C. Pulmonary sarcoidosis: A clinico-pathological study. J Pathol. 1975 Apr;115(4):191–198. doi: 10.1002/path.1711150402. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kapanci Y., Assimacopoulos A., Irle C., Zwahlen A., Gabbiani G. "Contractile interstitial cells" in pulmonary alveolar septa: a possible regulator of ventilation-perfusion ratio? Ultrastructural, immunofluorescence, and in vitro studies. J Cell Biol. 1974 Feb;60(2):375–392. doi: 10.1083/jcb.60.2.375. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kawanami O., Ferrans V. J., Roberts W. C., Crystal R. G., Fulmer J. D. Anchoring fibrils. A new connective tissue structure in fibrotic lung disease. Am J Pathol. 1978 Aug;92(2):389–410. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Korn E. D. Biochemistry of actomyosin-dependent cell motility (a review). Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Feb;75(2):588–599. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.2.588. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lazarides E. Actin, alpha-actinin, and tropomyosin interaction in the structural organization of actin filaments in nonmuscle cells. J Cell Biol. 1976 Feb;68(2):202–219. doi: 10.1083/jcb.68.2.202. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levy J. A., Weiss R. M., Dirksen E. R., Rosen M. R. Possible communication between murine macrophages oriented in linear chains in tissue culture. Exp Cell Res. 1976 Dec;103(2):375–385. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(76)90273-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mikata A., Kano Y., Okui S., Hamano S., Okamoto R. [Pathology of sarcoidosis, with special reference to electron microscopic findings of granulomatosus nodes]. Iryo. 1968 May;22(5):637–643. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mikata A. [Electron microscopic examination of the lymph node biopsy]. Rinsho Byori. 1972 Oct;20(10):719–724. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mikata A. [Electron microscopic observations of sarcoid granuloma of the lymph nodes]. Nihon Rinsho. 1968 Jun;26(6):1320–1323. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morgenroth K., Fasske E. Examination of mediastinal lymph node sarcoidosis by electron microscope. Beitr Pathol. 1974 Oct;153(1):51–64. doi: 10.1016/s0005-8165(74)80068-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parker F., Healey L. A., Wilske K. R., Odland G. F. Light and electron microscopic studies on human temporal arteries with special reference to alterations related to senescence, atherosclerosis and giant cell arteritis. Am J Pathol. 1975 Apr;79(1):57–80. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pearse B. M. Clathrin: a unique protein associated with intracellular transfer of membrane by coated vesicles. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Apr;73(4):1255–1259. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.4.1255. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Porvaznik M., MacVittie T. J. Detection of gap junctions between the progeny of a canine macrophage colony-forming cell in vitro. J Cell Biol. 1979 Aug;82(2):555–564. doi: 10.1083/jcb.82.2.555. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prineas J. W., Raine C. S. Electron microscopy and immunoperoxidase studies of early multiple sclerosis lesions. Neurology. 1976 Jun;26(6 Pt 2):29–32. doi: 10.1212/wnl.26.6_part_2.29. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reaven E. P., Axline S. G. Subplasmalemmal microfilaments and microtubules in resting and phagocytizing cultivated macrophages. J Cell Biol. 1973 Oct;59(1):12–27. doi: 10.1083/jcb.59.1.12. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schloss J. A., Goldman R. D. Isolation of a high molecular weight actin-binding protein from baby hamster kidney (BHK-21) cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4484–4488. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4484. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stossel T. P., Hartwig J. H. Interactions between actin, myosin, and an actin-binding protein from rabbit alveolar macrophages. Alveolar macrophage myosin Mg-2+-adenosine triphosphatase requires a cofactor for activation by actin. J Biol Chem. 1975 Jul 25;250(14):5706–5712. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sutton J. S., Weiss L. Transformation of monocytes in tissue culture into macrophages, epithelioid cells, and multinucleated giant cells. An electron microscope study. J Cell Biol. 1966 Feb;28(2):303–332. doi: 10.1083/jcb.28.2.303. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uehara Y., Campbell G. R., Burnstock G. Cytoplasmic filaments in developing and adult vertebrate smooth muscle. J Cell Biol. 1971 Aug;50(2):484–497. doi: 10.1083/jcb.50.2.484. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Willingham M. C., Maxfield F. R., Pastan I. H. alpha 2 Macroglobulin binding to the plasma membrane of cultured fibroblasts. Diffuse binding followed by clustering in coated regions. J Cell Biol. 1979 Sep;82(3):614–625. doi: 10.1083/jcb.82.3.614. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yajima K., Fletcher T. F., Suzuki K. Sub-plasmalemmal linear density: a common structure in globoid cells and mesenchymal cells. Acta Neuropathol. 1977 Aug 31;39(3):195–200. doi: 10.1007/BF00691697. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]