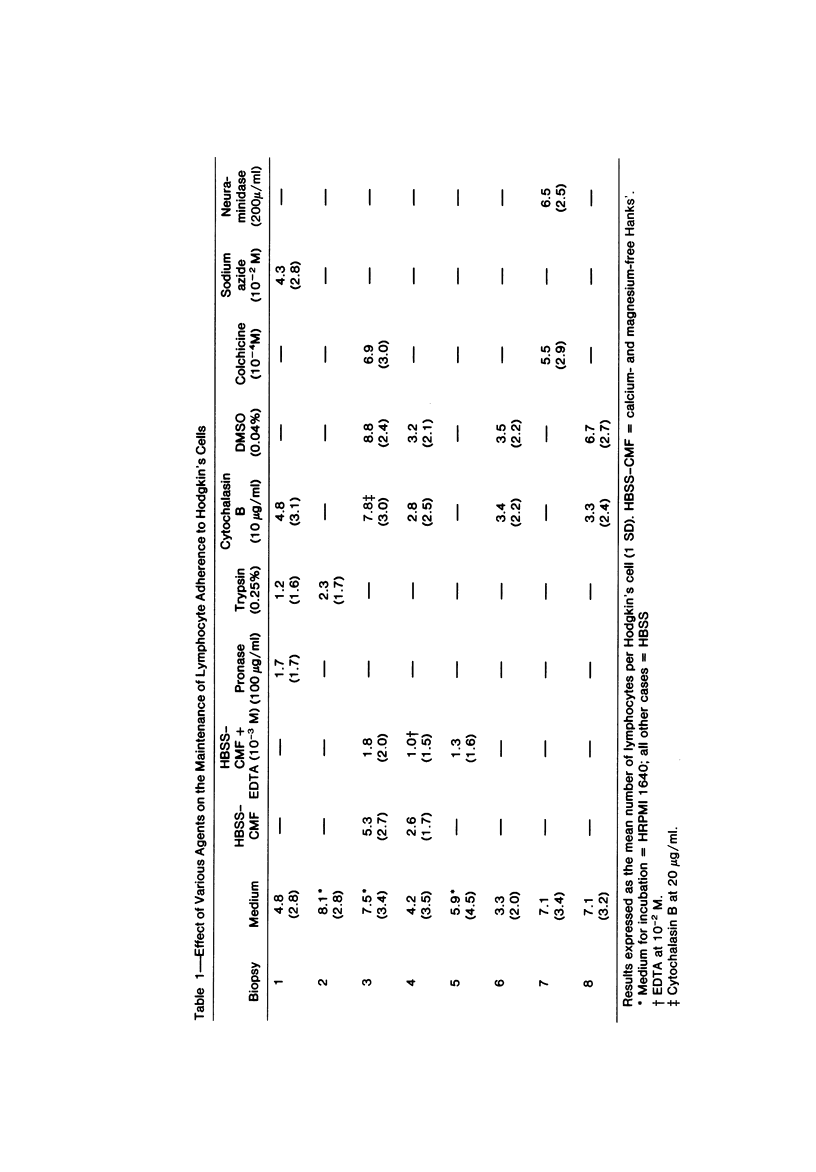
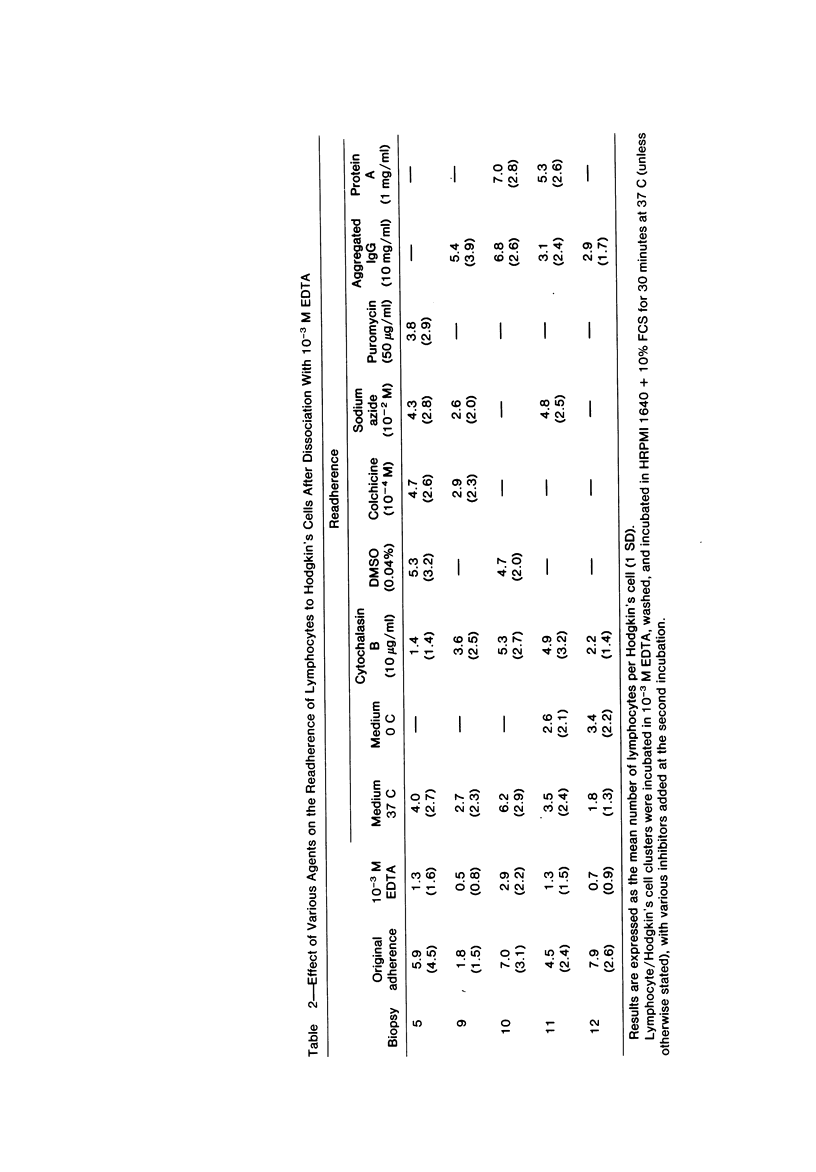
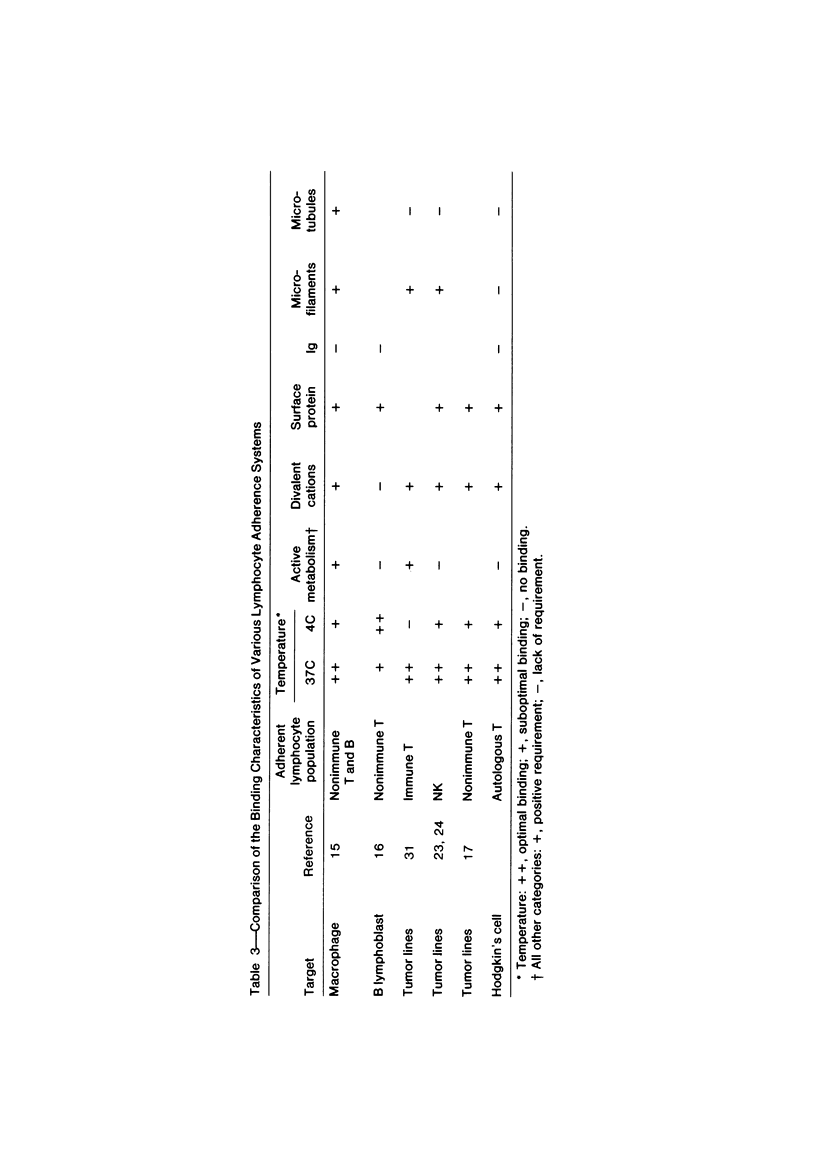
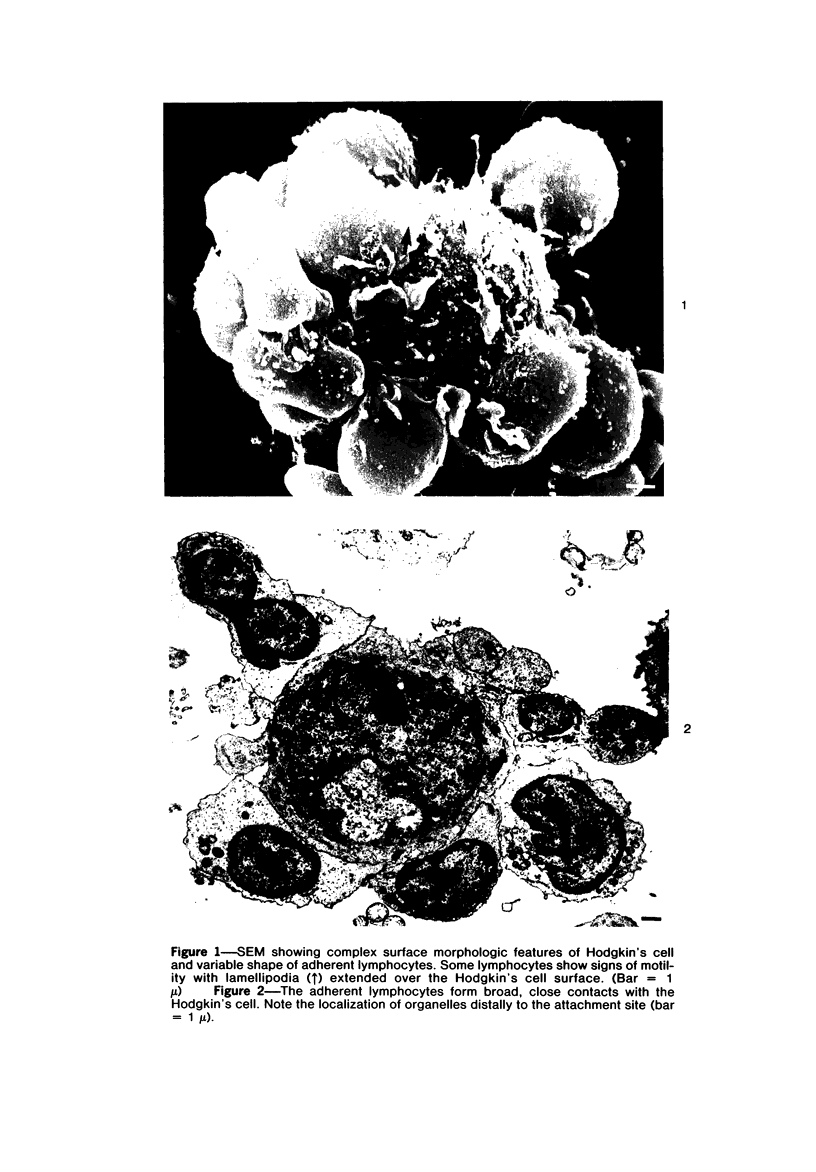
Abstract
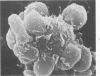
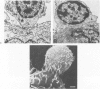
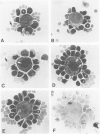
Autologous T lymphocytes form broad, unspecialized, noninvaginating contacts with Reed-Sternberg cells in vitro. These differ from contacts between cytotoxic lymphocytes and their targets and from the uropodal type of lymphocyte adherence described in many antigen- (or mitogen-) dependent systems but show some resemblance to antigen-independent lymphocyte/macrophage contacts. Adherence is not confined to a specific T-cell subset; most adherent cells are negative for ANAE, Fc gamma, and Fc mu receptors. A minority have Fc mu or Fc gamma receptors or show ANAE staining. Adherence is dependent on divalent cations and intact surface proteins but is independent of temperature, cell metabolism, and intact microtubules and does not appear to be mediated by Fc gamma receptors or IgG. These characteristics distinguish it from immune T-cell/target-cell binding and from antigen-independent T-cell/macrophage or T-cell/B-lymphoblast binding. Contrary to previous suggestions, this interaction is not related to a cytotoxic attack. The lack of similarities with other lymphocyte adherence systems leads the authors to suggest that a unique receptor system is involved.
Full text
PDF










Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Archibald R. B., Frenster J. H. Quantitative ultrastructural analysis of in vivo lymphocyte-Reed-Sternberg cell interactions in Hodgkin's disease. Natl Cancer Inst Monogr. 1973 May;36:239–245. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berke G., Gabison D. Energy requirements of the binding and lytic steps of T lymphocyte-mediated cytolysis of leukemic cells in vitro. Eur J Immunol. 1975 Oct;5(10):671–675. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830051004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Biberfeld P. Uropod formation in phytohaemagglutinin (PHA) stimulated lymphocytes. Exp Cell Res. 1971 Jun;66(2):433–445. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(71)90698-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boecker W. R., Hossfeld D. K., Gallmeier W. M., Schmidt C. G. Clonal growth of Hodgkin cells. Nature. 1975 Nov 20;258(5532):235–236. doi: 10.1038/258235a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galili U., Galili N., Vánky F., Klein E. Natural species-restricted attachment of human and murine T lymphocytes to various cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 May;75(5):2396–2400. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.5.2396. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Golstein P., Smith E. T. Mechanism of T-cell-mediated cytolysis: the lethal hit stage. Contemp Top Immunobiol. 1977;7:273–300. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4684-3054-7_8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grossi C. E., Webb S. R., Zicca A., Lydyard P. M., Moretta L., Mingari M. C., Cooper M. D. Morphological and histochemical analyses of two human T-cell subpopulations bearing receptors for IgM or IgG. J Exp Med. 1978 May 1;147(5):1405–1417. doi: 10.1084/jem.147.5.1405. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henney C. S., Bubbers J. E. Antigen-T lymphocyte interactions: inhibition by cytochalasin B. J Immunol. 1973 Jul;111(1):85–90. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henney C. S. T-Cell-mediated cytolysis: an overview of some current issues. Contemp Top Immunobiol. 1977;7:245–272. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4684-3054-7_7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horwitz D. A., Allison A. C., Ward P., Kight N. Identification of human mononuclear leucocyte populations by esterase staining. Clin Exp Immunol. 1977 Nov;30(2):289–298. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huber C., Michlmayr G., Falkensamer M., Fink U., Zur Nedden G., Braunsteiner H., Huber H. Increased proliferation of T lymphocytes in the blood of patients with Hodgkin's disease. Clin Exp Immunol. 1975 Jul;21(1):47–53. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jondal M., Klein E., Yefenof E. Surface markers on human B and T lymphocytes. VII. Rosette formation between peripheral T lymphocytes and lymphoblastoid B-cell lines. Scand J Immunol. 1975;4(3):259–266. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1975.tb02625.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kadin M. E., Newcom S. R., Gold S. B., Stites D. P. Letter: Origin of Hodgkin's cell. Lancet. 1974 Jul 20;2(7873):167–168. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(74)91602-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kadin M. E., Stites D. P., Levy R., Warnke R. Exogenous immunoglobulin and the macrophage origin of Reed-Sternberg cells in Hodgkin's disease. N Engl J Med. 1978 Nov 30;299(22):1208–1214. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197811302992203. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaplan H. S., Gartner S. "Sternberg-reed" giant cells of Hodgkin's Disease: cultivation in vitro, heterotransplantation, and characterization as neoplastic macrophages. Int J Cancer. 1977 Apr 15;19(4):511–525. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910190412. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kay M. M. Hodgkin's disease: a war between T-lymphocytes and transformed macrophages? Recent Results Cancer Res. 1976;(56):111–121. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-81049-7_15. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koren H. S., Ax W., Freund-Moelbert E. Morphological observations on the contact-induced lysis of target cells. Eur J Immunol. 1973 Jan;3(1):32–37. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830030108. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lipscomb M. F., Ben-Sasson S. Z., Uhr J. W. Specific binding of T lymphocytes to macrophages. I. Kinetics of binding. J Immunol. 1977 May;118(5):1748–1754. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lipsky P. E., Rosenthal A. S. Macrophage-lymphocyte interaction. I. Characteristics of the antigen-independent-binding of guinea pig thymocytes and lymphocytes to syngeneic macrophages. J Exp Med. 1973 Oct 1;138(4):900–924. doi: 10.1084/jem.138.4.900. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Long J. C., Zamecnik P. C., Aisenberg A. C., Atkins L. Tissue culture studies in Hodgkin's disease: Morphologic, cytogenetic, cell surface, and enzymatic properties of cultures derived from splenic tumors. J Exp Med. 1977 Jun 1;145(6):1484–1500. doi: 10.1084/jem.145.6.1484. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lukes R. J., Butler J. J. The pathology and nomenclature of Hodgkin's disease. Cancer Res. 1966 Jun;26(6):1063–1083. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McFarland W., Heilman D. H., Moorhead J. F. Functional anatomy of the lymphocyte in immunological reactions in vitro. J Exp Med. 1966 Nov 1;124(5):851–858. doi: 10.1084/jem.124.5.851. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moretta L., Ferrarini M., Cooper M. D. Characterization of human T-cell subpopulations as defined by specific receptors for immunoglobulins. Contemp Top Immunobiol. 1978;8:19–53. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4684-0922-2_2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moretta L., Webb S. R., Grossi C. E., Lydyard P. M., Cooper M. D. Functional analysis of two human T-cell subpopulations: help and suppression of B-cell responses by T cells bearing receptors for IgM or IgG. J Exp Med. 1977 Jul 1;146(1):184–200. doi: 10.1084/jem.146.1.184. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moroz C., Lahat N., Biniaminov M., Ramot B. Ferritin on the surface of lymphocytes in Hodgkin's disease patients. A possible blocking substance removed by levamisole. Clin Exp Immunol. 1977 Jul;29(1):30–35. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nielsen M. H., Jensen H., Braendstrup O., Werdelin O. Macrophage-lymphocyte clusters in the immune response to soluble protein antigen in vitro. II. Ultrastructure of clusters formed during the early response. J Exp Med. 1974 Nov 1;140(5):1260–1272. doi: 10.1084/jem.140.5.1260. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Order S. E., Hellman S. Pathogenesis of Hodgkin's disease. Lancet. 1972 Mar 11;1(7750):571–573. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(72)90360-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PULVERTAFT R. J. Cellular associations in normal and abnormal lymphocytes. Proc R Soc Med. 1959 May;52(5):315–322. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Payne S. V., Jones D. B., Haegert D. G., Smith J. L., Wright D. H. T and B lymphocytes and Reed-Sternberg cells in Hodgkin's disease lymph nodes and spleens. Clin Exp Immunol. 1976 May;24(2):280–286. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
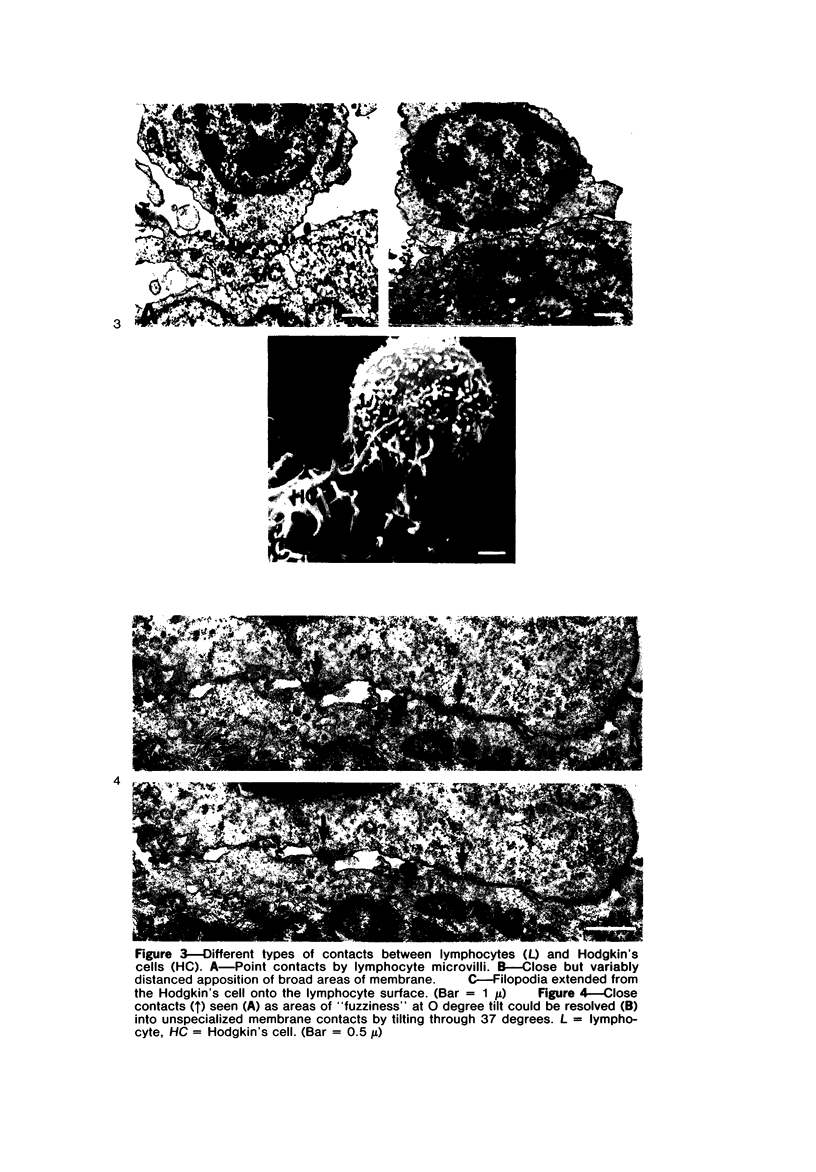
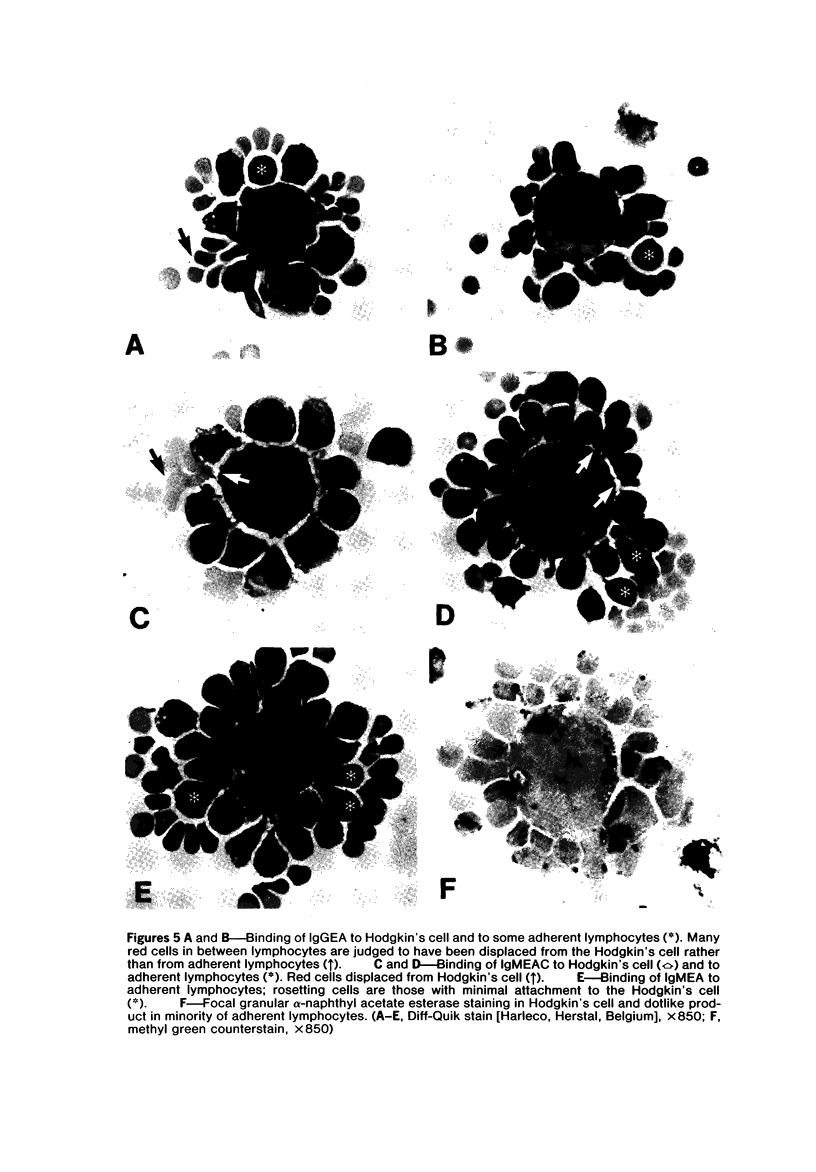
- Payne S. V., Jones D. B., Wright D. H. Reed-Sternberg-cell/lymphocyte interaction. Lancet. 1977 Oct 8;2(8041):768–769. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(77)90281-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pretlow T. G., 2nd, Boone C. W. Separation of mammalian cells using programmed gradient sedimentation. Exp Mol Pathol. 1969 Oct;11(2):139–152. doi: 10.1016/0014-4800(69)90003-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roder J. C., Kiessling R., Biberfeld P., Andersson B. Target-effector interaction in the natural killer (NK) cell system. II. The isolation of NK cells and studies on the mechanism of killing. J Immunol. 1978 Dec;121(6):2509–2517. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanderson C. J., Glauert A. M. The mechanism of T-cell mediated cytotoxicity. VI. T-cell projections and their role in target cell killing. Immunology. 1979 Jan;36(1):119–129. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sarcione E. J., Smalley J. R., Lema M. J., Stutzman L. Increased ferritin synthesis and release by Hodgkin's disease peripheral blood lymphocytes. Int J Cancer. 1977 Sep 15;20(3):339–346. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910200304. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith J. L., Haegert D. B- and T-lymphocyte markers on transformed lymphocytes from mitogen-stimulated cultures of normal and CLL lymphocytes and on tonsil blasts. Clin Exp Immunol. 1974 Aug;17(4):547–560. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stuart A. E., Williams A. R., Habeshaw J. A. Rosetting and other reactions of the Reed-Sternberg cell. J Pathol. 1977 Jun;122(2):81–90. doi: 10.1002/path.1711220205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sundström C., Nilsson K., Ranki A., Häyry P. Presence of alpha-naphthyl acetate esterase activity in human haematopoietic cell lines and in fresh biopsy specimens of lymphoma and myeloma. Scand J Haematol. 1978 Jul;21(1):47–59. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0609.1978.tb02494.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tötterman T. H., Ranki A., Häyry P. Expression of the acid alpha-naphthyl acetate esterase marker by activated and secondary T lymphocytes in man. Scand J Immunol. 1977;6(4):305–310. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1977.tb00398.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]