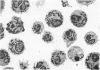
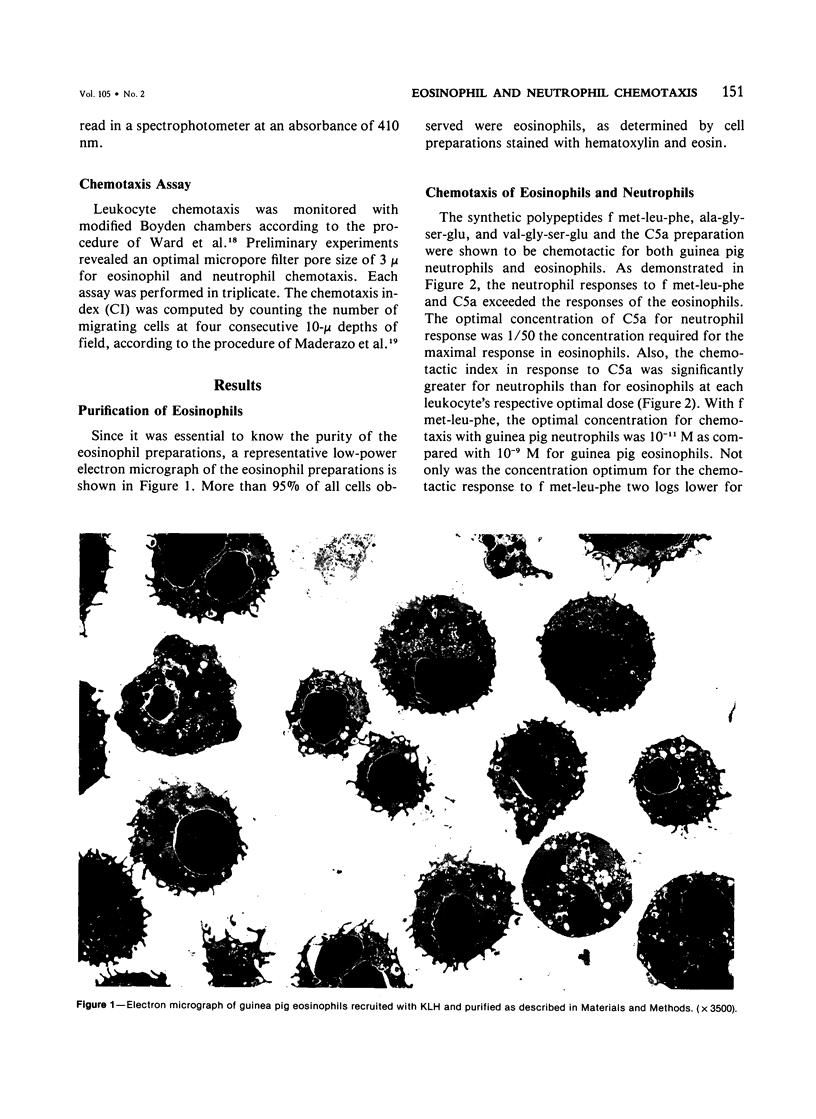
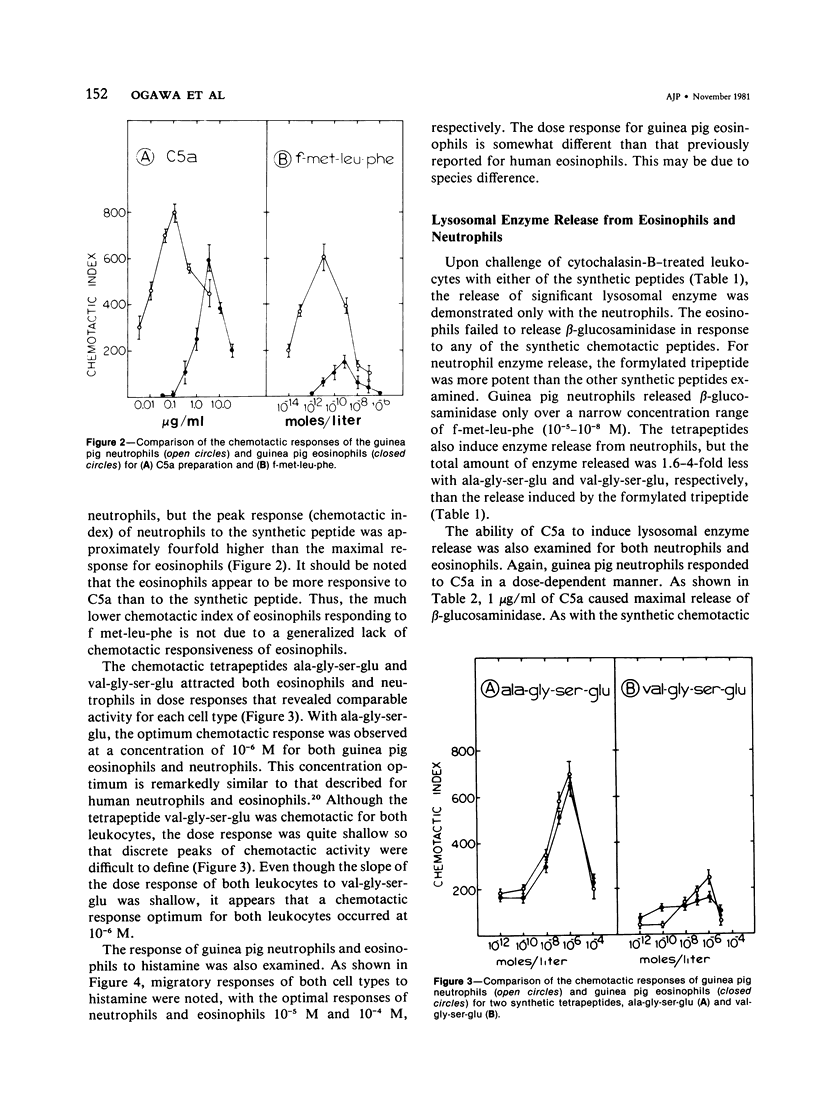
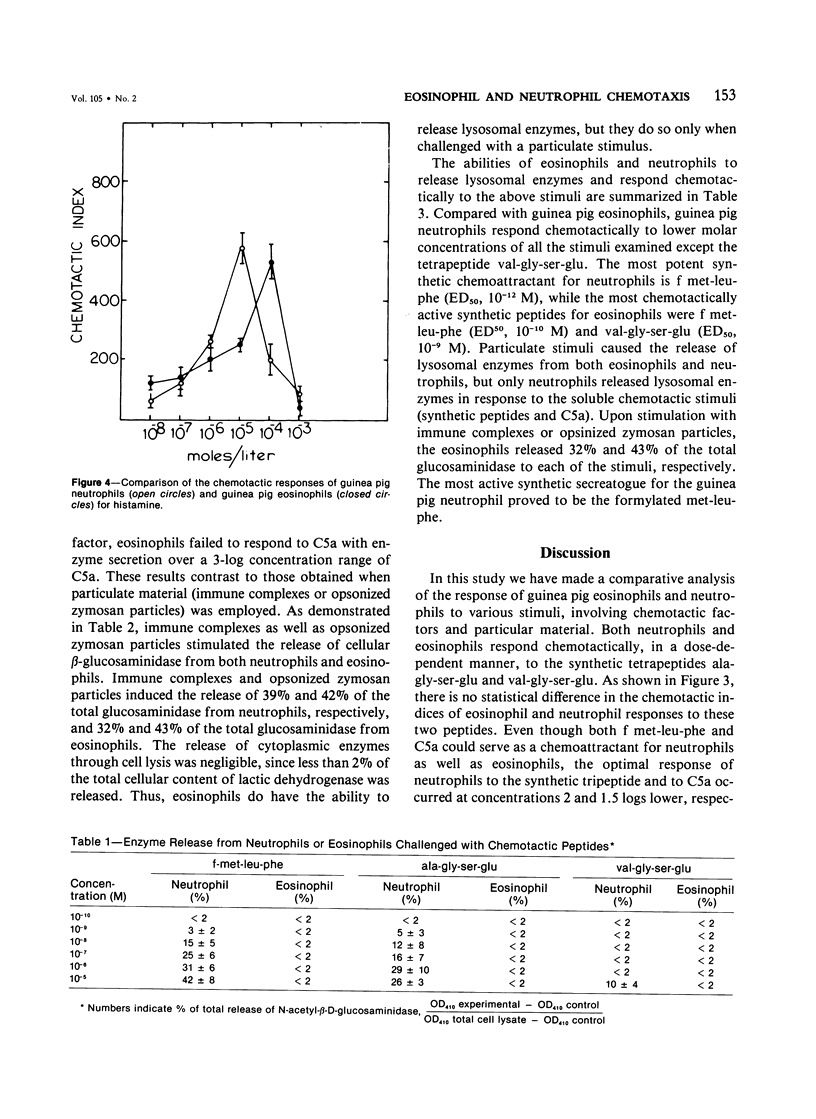
Abstract
It has been well documented that both natural and synthetic chemotactic peptides can induce lysosomal enzyme release from neutrophils treated with cytochalasin B. These same peptides are also potent inducers of unidirectional movement, as demonstrated by the chemotactic response in Boyden chambers. In this study, the ability of another family of leukocytes, eosinophils, to release lysosomal enzymes and exhibit a chemotactic response to both natural and synthetic chemotactic peptides was examined. A striking fundamental difference between neutrophil and eosinophil chemotaxis and enzyme release was shown using C5a, formyl met-leu-phe (FMLP), and ala-gly-ser-glu (AGSG) peptides. The 50% effective doses (ED50) for chemotactic responses to C5a, FMLP, or AGSG by neutrophils and eosinophils were 0.05 microgram/ml and 1.0 microgram/ml, 10(-12) M and 10(-10) M, and 10(-7) M and 10(-7) M, respectively. At the same concentrations, these peptides (C5a, f met-leu-phe, and ala-gly-ser-glu) induced the following release of glucosaminidase from neutrophils and eosinophils, respectively: 42% and 2%, 42% and 2%, and 29% and 2%. In striking contrast, immune complexes and opsonized zymosan particles induced the release of 39% and 42% of the total glucosaminidase from neutrophils, while eosinophils released 32% and 43% of the total glucosaminidase from immune complexes and opsonized zymosan particles, respectively. These data indicate fundamental differences between neutrophils and eosinophils in unidirectional movement induced by chemotactic factors and enzyme release mechanism(s).
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Becker E. L., Showell H. J., Henson P. M., Hsu L. S. The ability of chemotactic factors to induce lysosomal enzyme release. I. The characteristics of the release, the importance of surfaces and the relation of enzyme release to chemotactic responsiveness. J Immunol. 1974 Jun;112(6):2047–2054. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Butterworth A. E., Sturrock R. F., Houba V., Mahmoud A. A., Sher A., Rees P. H. Eosinophils as mediators of antibody-dependent damage to schistosomula. Nature. 1975 Aug 28;256(5520):727–729. doi: 10.1038/256727a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chusid M. J., Dale D. C., West B. C., Wolff S. M. The hypereosinophilic syndrome: analysis of fourteen cases with review of the literature. Medicine (Baltimore) 1975 Jan;54(1):1–27. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark R. A., Gallin J. I., Kaplan A. P. The selective eosinophil chemotactic activity of histamine. J Exp Med. 1975 Dec 1;142(6):1462–1476. doi: 10.1084/jem.142.6.1462. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fantone J., Senior R. M., Kreutzer D. L., Jones M., Ward P. A. Biochemical quantitation of the chemotactic factor inactivator activity in human serum. J Lab Clin Med. 1979 Jan;93(1):17–24. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fernandez H. N., Hugli T. E. Partial characterization of human C5a anaphylatoxin. I. Chemical description of the carbohydrate and polypeptide prtions of human C5a. J Immunol. 1976 Nov;117(5 Pt 1):1688–1694. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goetzl E. J., Austen K. F. Purification and synthesis of eosinophilotactic tetrapeptides of human lung tissue: identification as eosinophil chemotactic factor of anaphylaxis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Oct;72(10):4123–4127. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.10.4123. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jong E. C., Henderson W. R., Klebanoff S. J. Bactericidal activity of eosinophil peroxidase. J Immunol. 1980 Mar;124(3):1378–1382. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kay A. B., Shin H. S., Austen K. F. Selective attraction of eosinophils and synergism between eosinophil chemotactic factor of anaphylaxis (ECF-A) and a fragment cleaved from the fifth component of complement (C5a). Immunology. 1973 Jun;24(6):969–976. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kunkel S. L., Kreutzer D. L., Goralnick S., Ward P. A. Purification of the third and fifth components of human complement: application of hydrophobic chromatography. J Immunol Methods. 1980;35(3-4):337–351. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(80)90259-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LITT M. Studies in experimental eosinophilia. I. Repeated quantitation of peritoneal eosinophilia in guinea pigs by a method of peritoneal lavage. Blood. 1960 Sep;16:1318–1329. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pincus S. H. Production of eosinophil-rich guinea pig peritoneal exudates. Blood. 1978 Jul;52(1):127–134. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Showell H. J., Freer R. J., Zigmond S. H., Schiffmann E., Aswanikumar S., Corcoran B., Becker E. L. The structure-activity relations of synthetic peptides as chemotactic factors and inducers of lysosomal secretion for neutrophils. J Exp Med. 1976 May 1;143(5):1154–1169. doi: 10.1084/jem.143.5.1154. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thrall R. S., Phan S. H., Showell H. J., Williams D. J., O'Flaherty J. T., Ward P. A. Membrane protein alterations in the neutrophil in response to chemotactic factors. Mol Immunol. 1980 Feb;17(2):181–190. doi: 10.1016/0161-5890(80)90070-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vitkauskas G., Showell H. J., Becker E. L. Specific binding of synthetic chemotactic peptides to rabbit peritoneal neutrophils: effects on dissociability of bound peptide, receptor activity and subsequent biologic responsiveness (deactivation). Mol Immunol. 1980 Feb;17(2):171–180. doi: 10.1016/0161-5890(80)90069-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WARD P. A., COCHRANE C. G., MUELLER-EBERHARD H. J. THE ROLE OF SERUM COMPLEMENT IN CHEMOTAXIS OF LEUKOCYTES IN VITRO. J Exp Med. 1965 Aug 1;122:327–346. doi: 10.1084/jem.122.2.327. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weller P. F., Goetzl E. J. The regulatory and effector roles of eosinophils. Adv Immunol. 1979;27:339–371. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2776(08)60264-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]