Abstract
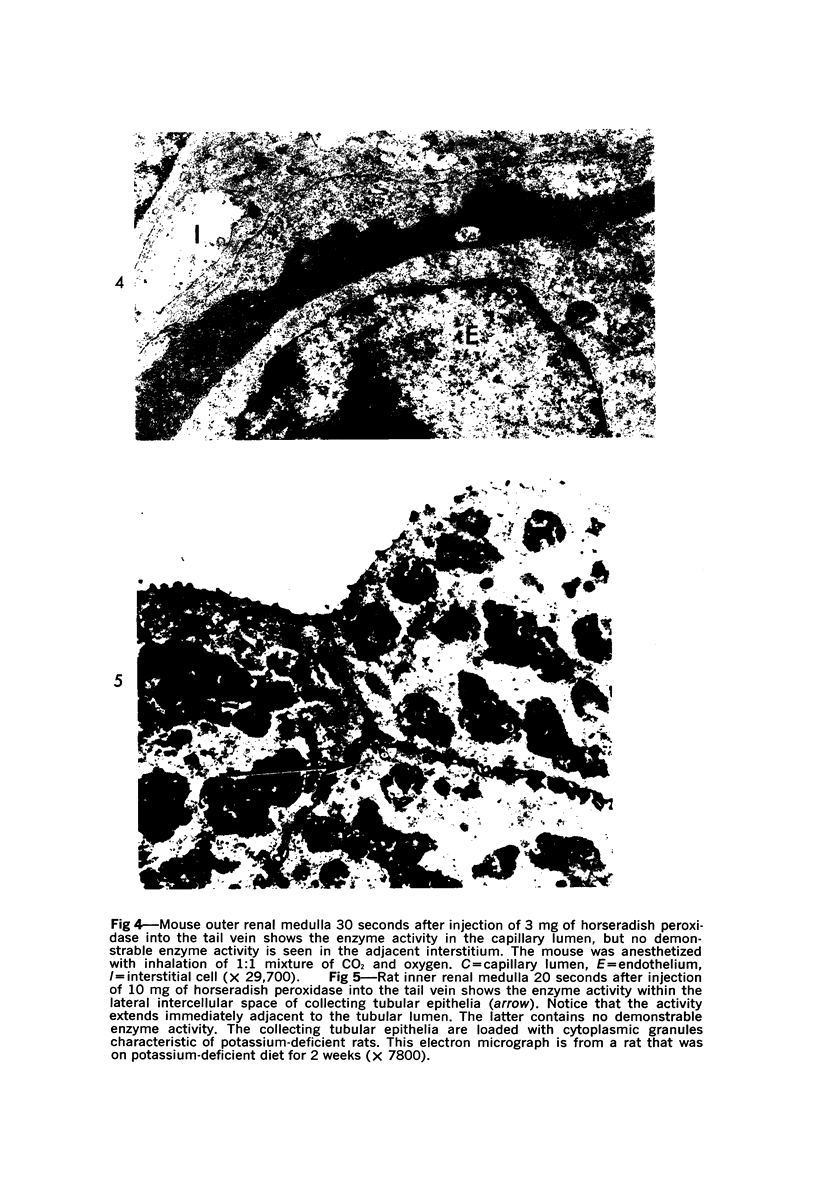
The vascular permeability of the vessels of the renal medulla of normal rats and mice and potassium-deficient rats was studied by using ferritin, horseradish peroxidase and carbon particles as markers. Fenestrated endothelia are more permeable to ferritin and horseradish peroxidase than nonfenestrated endothelia. The ease with which the tracers are able to pass from the vascular lumina through the endothelia into the interstitium is directly related to the size of the tracers (horseradish peroxidase permeates most readily, followed by ferritin and carbon particles, in this order), suggesting the presence of a molecular sieving mechanism for the passage of substances through the capillary walls of the renal medulla. At the initial stage after injection of horseradish peroxidase and ferritin, these tracers pass from the medullary vascular lumina into the interstitium, not from the tubular lumina into the interstitium. It appears that the passage of ferritin and horseradish peroxidase through the vascular wall is enhanced in potassium-deficient rats.
Full text
PDF










Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Beeuwkes R., 3rd Efferent vascular patterns and early vascular-tubular relations in the dog kidney. Am J Physiol. 1971 Nov;221(5):1361–1374. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1971.221.5.1361. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berliner R. W., Bennett C. M. Concentration of urine in the mammalian kidney. Am J Med. 1967 May;42(5):777–789. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(67)90095-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FARQUHAR M. G., PALADE G. E. Glomerular permeability. II. Ferritin transfer across the glomerular capillary wall in nephrotic rats. J Exp Med. 1961 Nov 1;114:699–716. doi: 10.1084/jem.114.5.699. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GOTTSCHALK C. W., MYLLE M. Micropuncture study of the mammalian urinary concentrating mechanism: evidence for the countercurrent hypothesis. Am J Physiol. 1959 Apr;196(4):927–936. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1959.196.4.927. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GOTTSCHALK C. W. OSMOTIC CONCENTRATION AND DILUTION OF THE URINE. Am J Med. 1964 May;36:670–685. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(64)90179-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graham R. C., Jr, Karnovsky M. J. The early stages of absorption of injected horseradish peroxidase in the proximal tubules of mouse kidney: ultrastructural cytochemistry by a new technique. J Histochem Cytochem. 1966 Apr;14(4):291–302. doi: 10.1177/14.4.291. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kokko J. P., Rector F. C., Jr Countercurrent multiplication system without active transport in inner medulla. Kidney Int. 1972 Oct;2(4):214–223. doi: 10.1038/ki.1972.97. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LONGLEY J. B., BANFIELD W. G., BRINDLEY D. C. Structure of the rete mirabile in the kidney of the rat as seen with the electron microscope. J Biophys Biochem Cytol. 1960 Feb;7:103–106. doi: 10.1083/jcb.7.1.103. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MOFFAT D. B., FOURMAN J. THE VASCULAR PATTERN OF THE RAT KIDNEY. J Anat. 1963 Oct;97:543–553. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MOLLENHAUER H. H. PLASTIC EMBEDDING MIXTURES FOR USE IN ELECTRON MICROSCOPY. Stain Technol. 1964 Mar;39:111–114. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moffat D. B. Extravascular protein in the renal medulla. Q J Exp Physiol Cogn Med Sci. 1969 Jan;54(1):60–67. doi: 10.1113/expphysiol.1969.sp002006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morrison A. B., Schneeberger-Keeley E. E. The phagocytic role of renal medullary interstitial cells and the effect of potassium deficiency on this function. Nephron. 1969;6(5):584–597. doi: 10.1159/000179757. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHMIDT-NIELSEN B., O'DELL R. Structure and concentrating mechanism in the mammalian kidney. Am J Physiol. 1961 Jun;200:1119–1124. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1961.200.6.1119. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Venkatachalam M. A., Karnovsky M. J. Extravascular protein in the kidney. An ultrastructural study of its relation to renal peritubular capillary permeability using protein tracers. Lab Invest. 1972 Nov;27(5):435–444. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WIRZ H., HARGITAY B., KUHN W. Lokalisation des Konzentrierungsprozesses in der Niere durch direkte Kryoskopie. Helv Physiol Pharmacol Acta. 1951 Jun;9(2):196–207. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]