Abstract
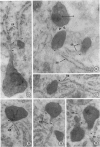
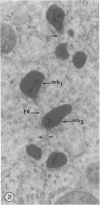
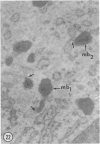
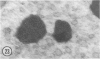
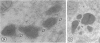
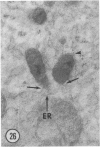
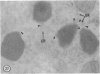
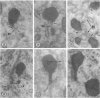
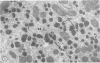
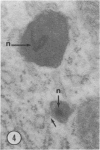
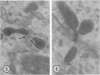
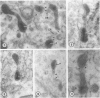
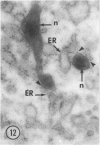
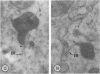
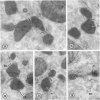
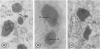
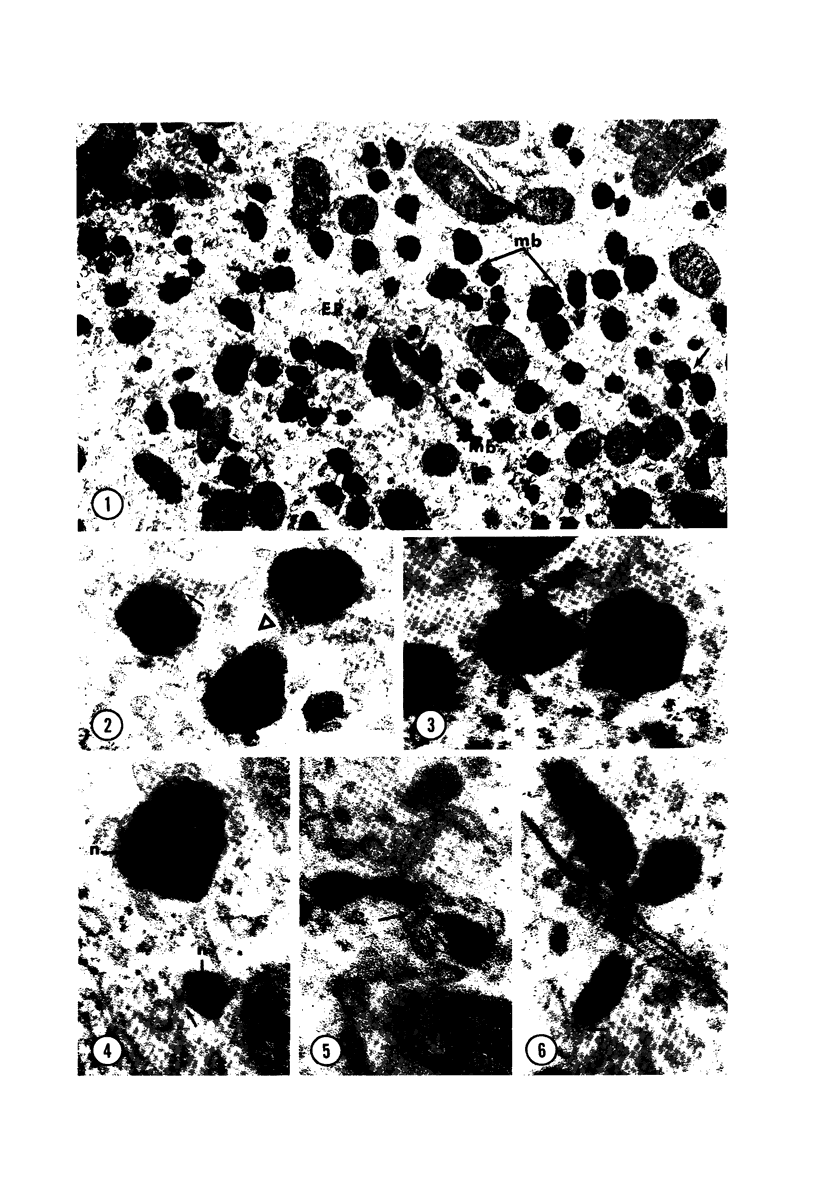
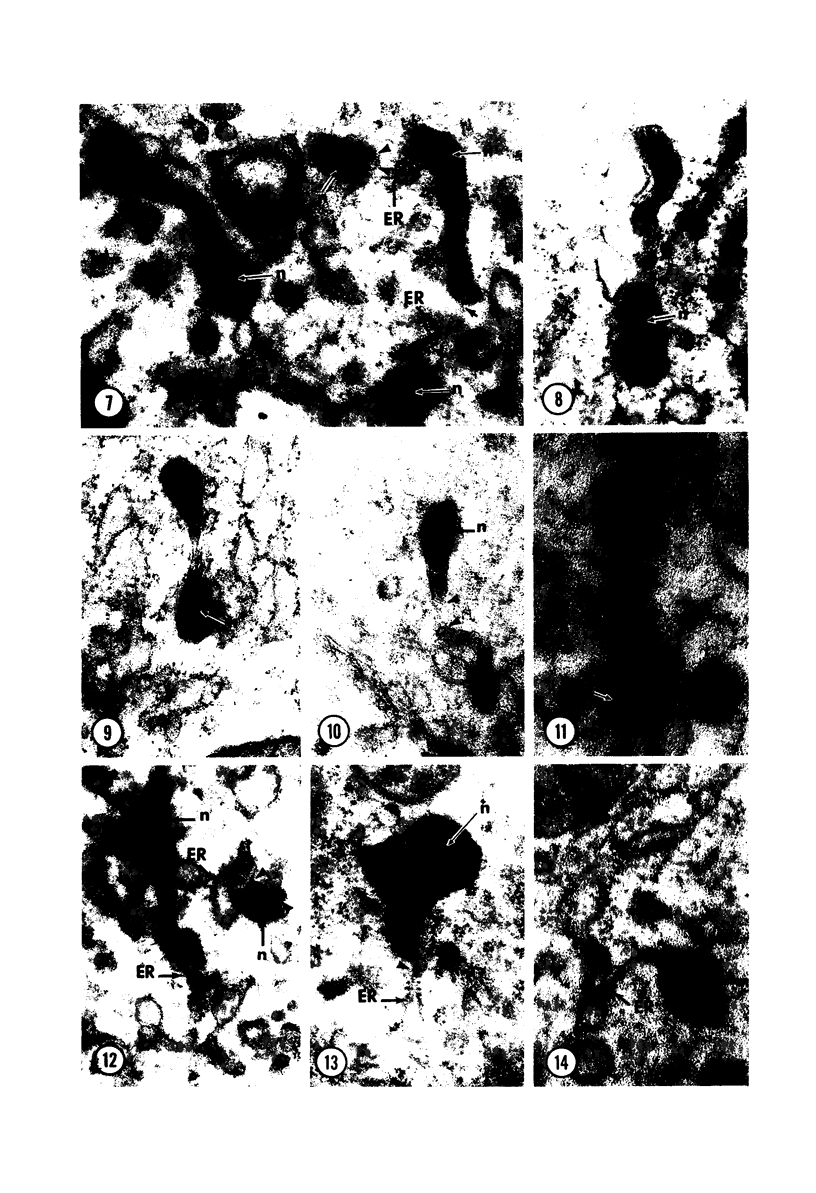
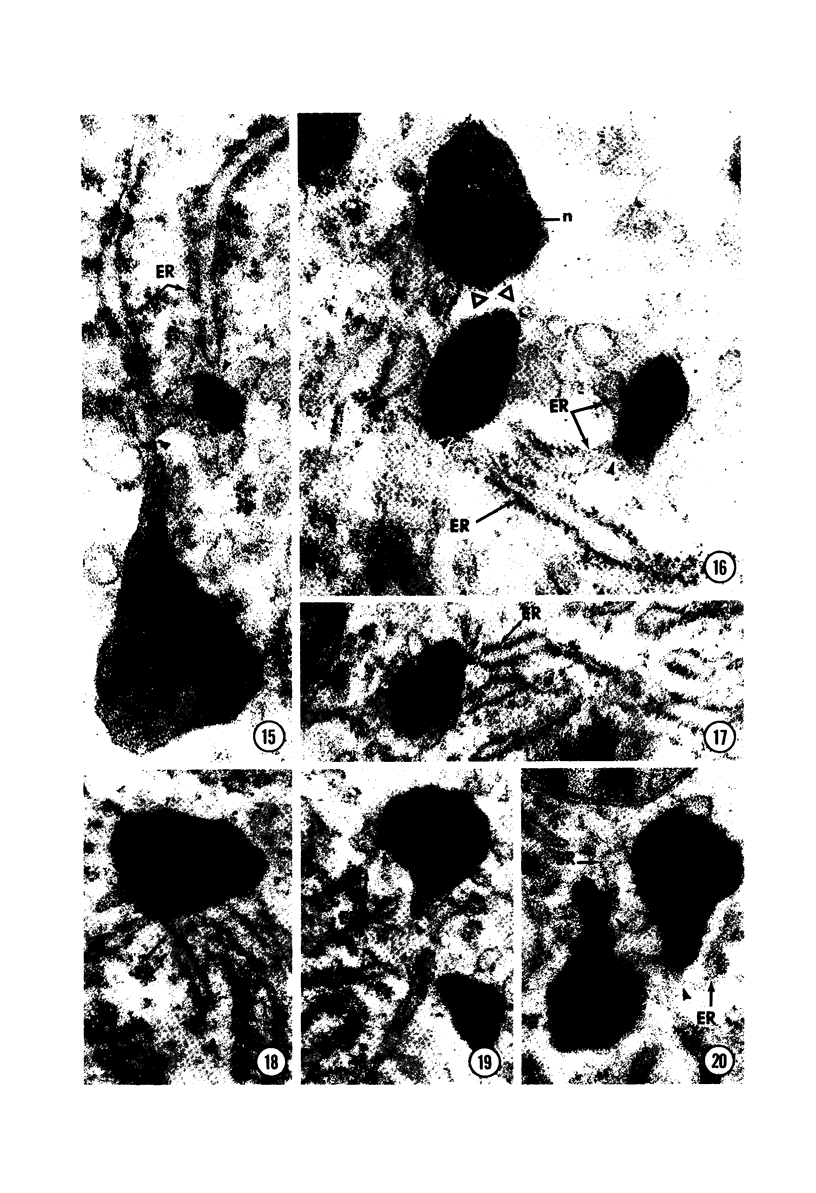
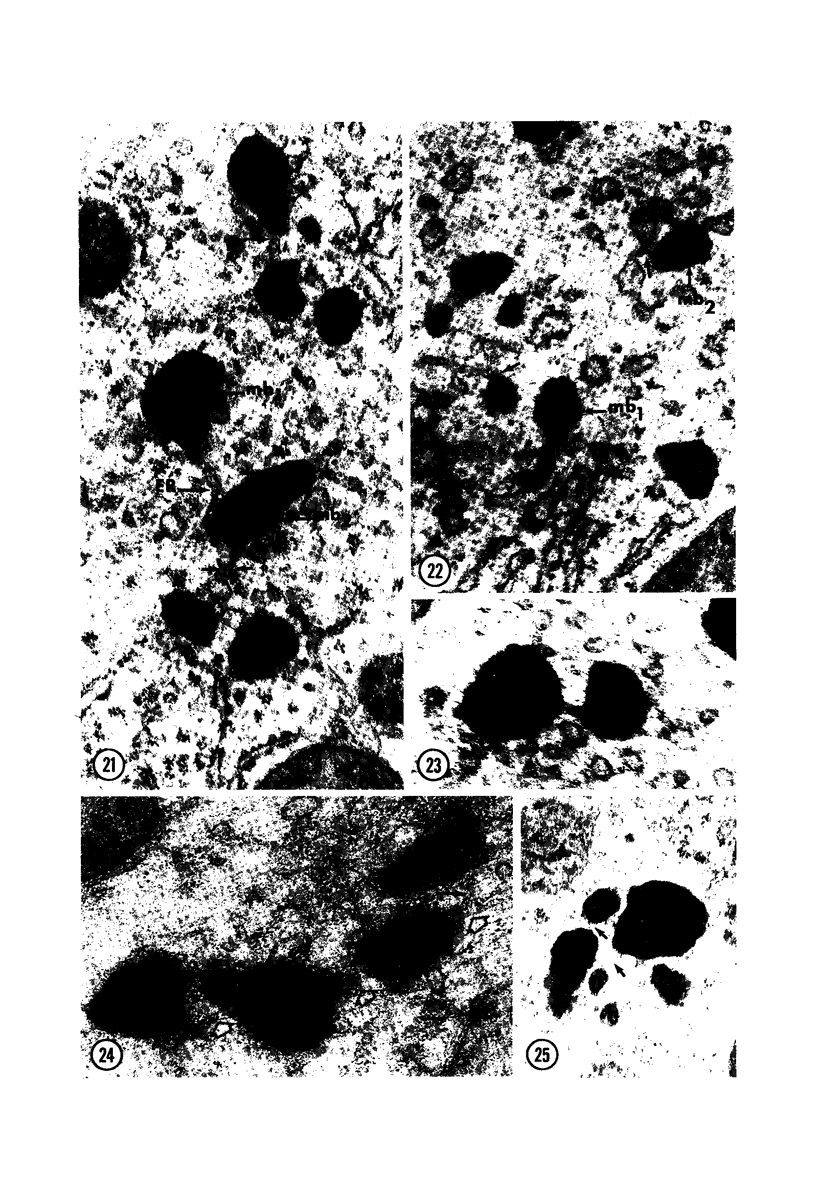
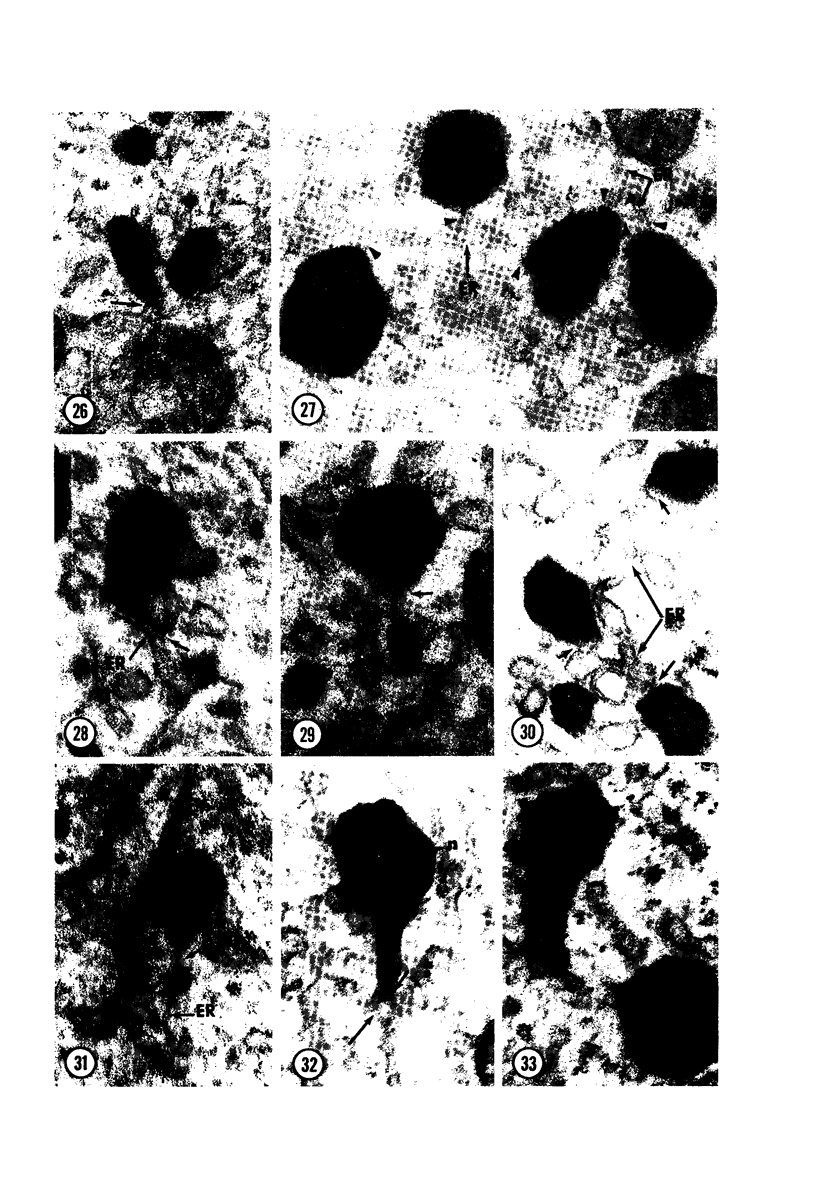
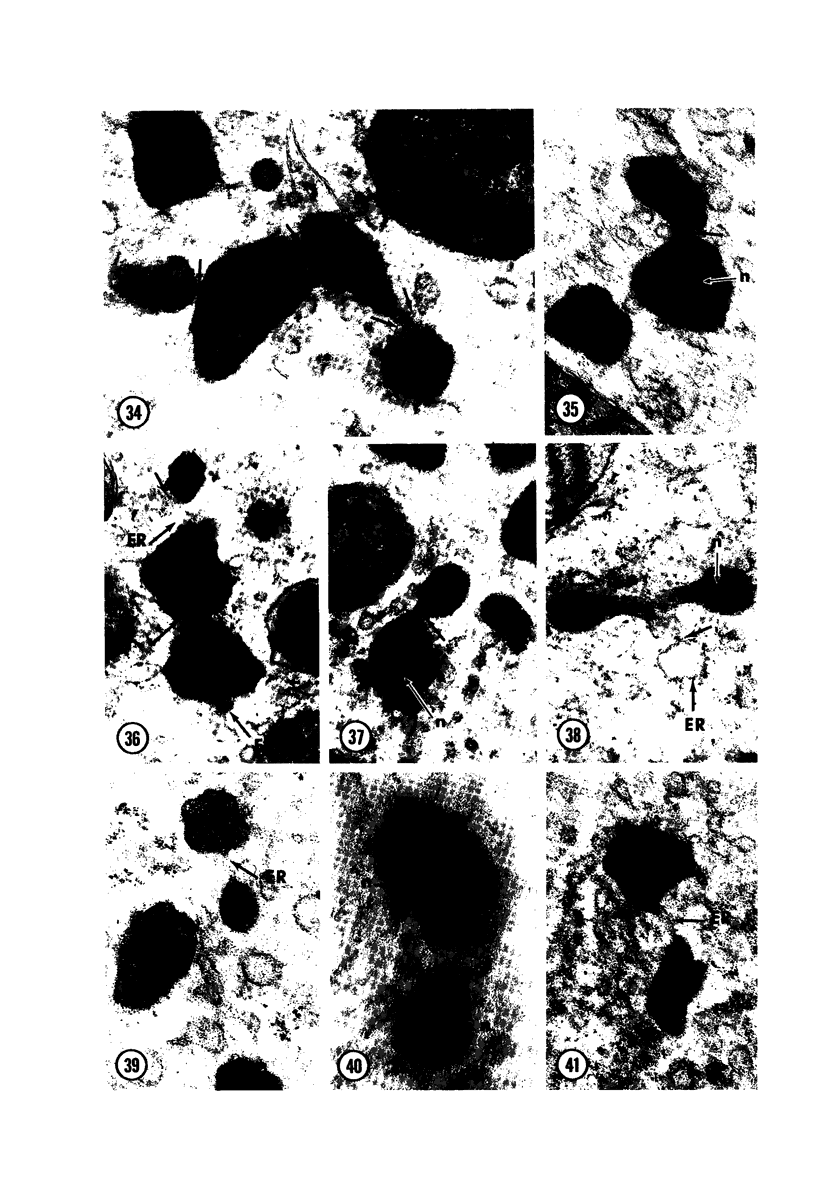
Male wild-type mice (Csa strain) were treated with ethyl-α-p-chlorophenoxyisobutyrate (CPIB), a hypolipidemic drug which enhances hepatic catalase synthesis and induces rapid and significant increase in the number of microbody (peroxisome) profiles in liver cells. Numerous microbody profiles, several of them appearing in clusters and retaining membranous continuities, were observed in liver cells of CPIB-treated mice. They showed a significant variation in size and configuration, and the presence or absence of the nucleoid or core did not appear to bear any relation to the size or shape of microbody profiles. Nucleoids were encountered frequently in microbody profiles measuring as small as 0.1 μ in diameter. Numerous continuities between two or more anucleoid and/or nucleoid-containing microbody profiles of different sizes and shapes were seen. These findings are inconsistent with the concept that the smaller peroxisomes are the possible precursors or progenitors of their larger counterparts. Detailed examination of numerous electron micrographs revealed irregular dilatations and tortuosities of the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) containing electron-opaque peroxisomal material displaying the characteristic appearance of matrix and usually containing irregular cores. Transitions of rough ER to smooth ER in which microbody proteins accumulated were also apparent. Numerous continuities between several microbody profiles and continuities between microbody profiles and ER are interpreted as accumulations of peroxisomal proteins in dilated tortuous channels of ER. These observations strongly suggest that the microbody proteins constitute a common pool, circulating constantly in the dilated ER channels. The size, shape and number of microbody profiles appear to reflect the amount of peroxisomal proteins present in the pool. These observations clearly suggest that the microbodies do not exist as individual entities.
Full text
PDF











Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ahlabo I., Barnard T. Observations on peroxisomes in brown adipose tissue of the rat. J Histochem Cytochem. 1971 Nov;19(11):670–675. doi: 10.1177/19.11.670. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Azarnoff D. L., Svoboda D. J. Microbodies in experimentally altered cells. VI. Thyroxine displacement from plasma proteins and clofibrate effect. Arch Int Pharmacodyn Ther. 1969 Oct;181(2):386–393. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beard M. E. Identification of peroxisomes in the rat adrenal cortex. J Histochem Cytochem. 1972 Mar;20(3):173–179. doi: 10.1177/20.3.173. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beard M. E., Novikoff A. B. Distribution of peroxisomes (microbodies) in the nephron of the rat: a cytochemical study. J Cell Biol. 1969 Aug;42(2):501–518. doi: 10.1083/jcb.42.2.501. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Essner E. Endoplasmic reticulum and the origin of microbodies in fetal mouse liver. Lab Invest. 1967 Jul;17(1):71–87. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinstein R. N., Braun J. T., Howard J. B. Acatalasemic and hypocathalasemic mouse mutants. II. Mutational variations in blood and solid tissue catalases. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1967 Apr;120(1):165–169. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(67)90609-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hess R., Stäubli W., Riess W. Nature of the hepatomegalic effect produced by ethyl-chlorophenoxy-isobutyrate in the rat. Nature. 1965 Nov 27;208(5013):856–858. doi: 10.1038/208856a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hruban Z., Vigil E. L., Slesers A., Hopkins E. Microbodies: constituent organelles of animal cells. Lab Invest. 1972 Aug;27(2):184–191. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KARNOVSKY M. J. Simple methods for "staining with lead" at high pH in electron microscopy. J Biophys Biochem Cytol. 1961 Dec;11:729–732. doi: 10.1083/jcb.11.3.729. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuhn C. Particles resembling microbodies in normal and neoplastic perianal glands of dogs. Z Zellforsch Mikrosk Anat. 1968;90(4):554–562. doi: 10.1007/BF00339503. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Langer K. H. Feinstrukturen der Mikrokörper (Microbodies) des proximalen Nierentubulus. Z Zellforsch Mikrosk Anat. 1968;90(3):432–446. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Legg P. G., Wood R. L. New observations on microbodies. A cytochemical study on CPIB-treated rat liver. J Cell Biol. 1970 Apr;45(1):118–129. doi: 10.1083/jcb.45.1.118. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leighton F., Poole B., Lazarow P. B., De Duve C. The synthesis and turnover of rat liver peroxisomes. I. Fractionation of peroxisome proteins. J Cell Biol. 1969 May;41(2):521–535. doi: 10.1083/jcb.41.2.521. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Magalhäes M. M., Magalhäes M. C. Microbodies (peroxisomes) in rat adrenal cortex. J Ultrastruct Res. 1971 Dec;37(5):563–573. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5320(71)80025-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Novikoff P. M., Novikoff A. B. Peroxisomes in absorptive cells of mammalian small intestine. J Cell Biol. 1972 May;53(2):532–560. doi: 10.1083/jcb.53.2.532. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petrik P. Fine structural identification of peroxisomes in mouse and rat bronchiolar and alveolar epithelium. J Histochem Cytochem. 1971 Jun;19(6):339–348. doi: 10.1177/19.6.339. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Platt D. S., Cockrill B. L. Changes in the liver concentrations of the nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide coenzymes and in the activities of oxidoreductase enzymes following treatment of the rat with ethyl chlorophenoxyisobutyrate (Atromid-S). Biochem Pharmacol. 1966 Jul;15(7):927–935. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(66)90169-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poole B., Higashi T., De Duve C. The synthesis and turnover of rat liver peroxisomes. 3. The size distribution of peroxisomes and the incorporation of new catalase. J Cell Biol. 1970 May;45(2):408–415. doi: 10.1083/jcb.45.2.408. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reddy J., Bunyaratvej S., Svoboda D. Microbodies in experimentally altered cells. IV. Acatalasemic (CSb) mice treated with CPIB. J Cell Biol. 1969 Aug;42(2):587–596. doi: 10.1083/jcb.42.2.587. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reddy J., Bunyaratvej S., Svoboda D. Microbodies in experimentally altered cells. V. Histochemical and cytochemical studies on the livers of rats and acatalasemic (Csb) mice treated with CPIB. Am J Pathol. 1969 Sep;56(3):351–370. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reddy J., Chiga M., Bunyaratvej S., Svoboda D. Microbodies in experimentally altered cells. VII. CPID-induced hepatic microbody proliferation in the absence of significant catalase synthesis. J Cell Biol. 1970 Jan;44(1):226–234. doi: 10.1083/jcb.44.1.226. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reddy J., Chiga M., Svoboda D. Stimulation of liver catalase synthesis in rats by ethyl-alpha-p-chlorophenoxyisobutyrate. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1971 Apr 16;43(2):318–324. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(71)90755-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reddy J., Svoboda D. Microbodies (peroxisomes) identification in interstitial cells of the testis. J Histochem Cytochem. 1972 Feb;20(2):140–142. doi: 10.1177/20.2.140. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reddy J., Svoboda D. Microbodies (peroxisomes) in the interstitial cells of rodent testes. Lab Invest. 1972 Jun;26(6):657–665. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reddy J., Svoboda D. Microbodies in experimentally altered cells. 8. Continuities between microbodies and their possible biologic significance. Lab Invest. 1971 Jan;24(1):74–81. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Svoboda D. J., Azarnoff D. L. Response of hepatic microbodies to a hypolipidemic agent, ethyl chlorophenoxyisobutyrate (CPIB). J Cell Biol. 1966 Aug;30(2):442–450. doi: 10.1083/jcb.30.2.442. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Svoboda D., Grady H., Azarnoff D. Microbodies in experimentally altered cells. J Cell Biol. 1967 Oct;35(1):127–152. doi: 10.1083/jcb.35.1.127. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Svoboda D., Reddy J. Microbodies in experimentally altered cells. IX. The fate of microbodies. Am J Pathol. 1972 Jun;67(3):541–554. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsukada H., Mochizuki Y., Konishi T. Morphogenesis and development of microbodies of hepatocytes of rats during pre- and postnatal growth. J Cell Biol. 1968 May;37(2):231–243. doi: 10.1083/jcb.37.2.231. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]