Abstract
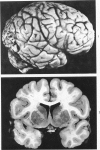
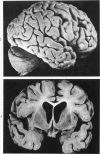
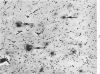
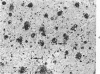
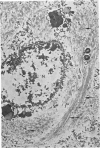
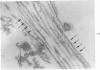
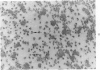
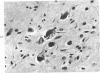
Senile plaques, neurofibrillary change and granulovacuolar degeneration characterize Alzheimer's disease (presenile dementia) and senile dementia and are also seen in the aged human brain. The development of these lesions was studied in 13 patients with Down's syndrome, ages 12 to 65, with the purpose of defining similarities and dissimilarities, if any, between their morphologies in these four conditions. Evaluation by light and, when applied, electron microscopy established apparent identities. The findings suggest that Down's syndrome, with its partially characterized genotypic and phenotypic abnormalities, is an appropriate model for the study of the pathogenesis of these lesions.
Full text
PDF

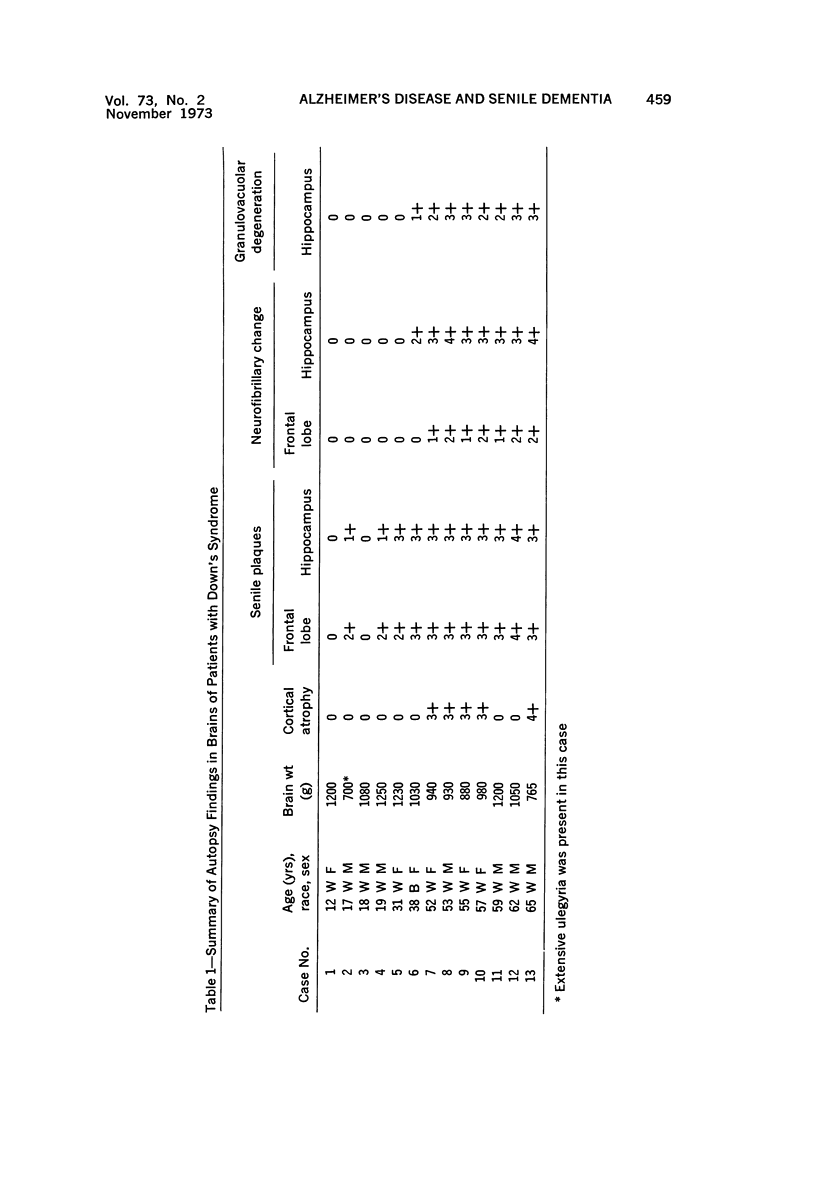









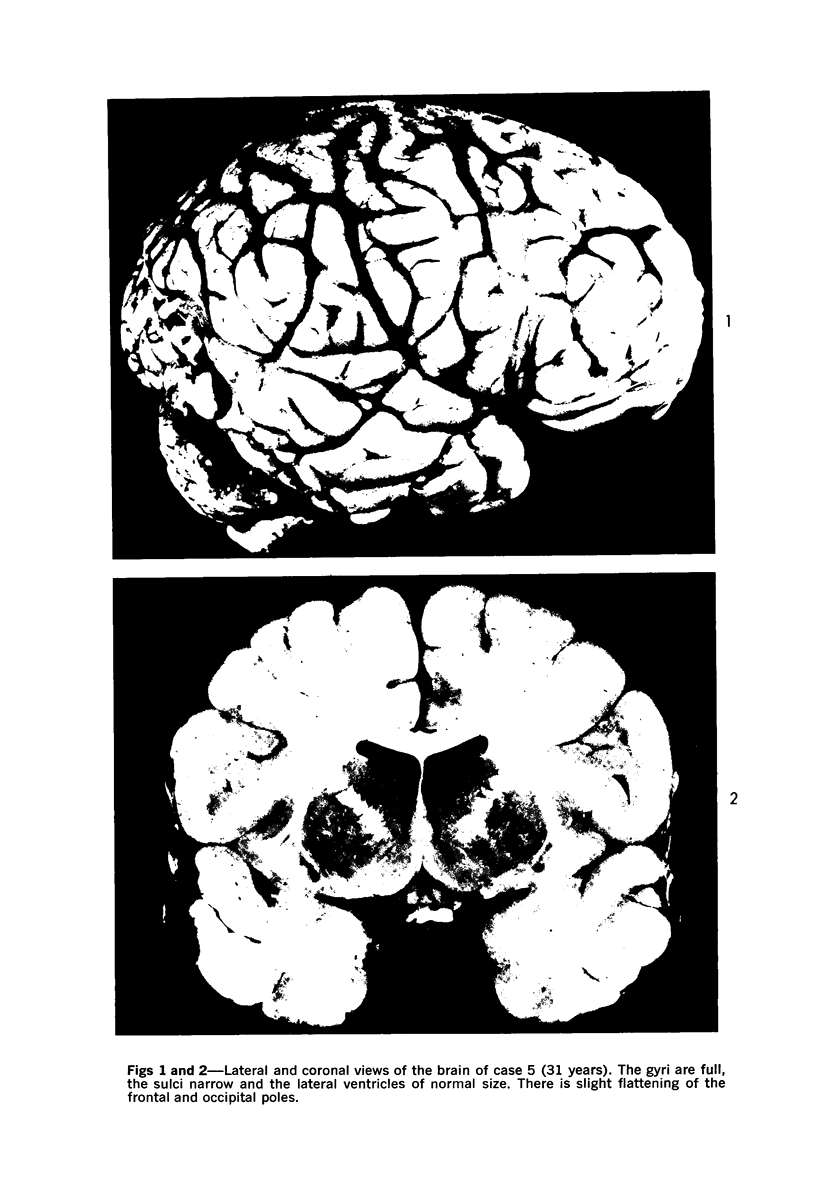
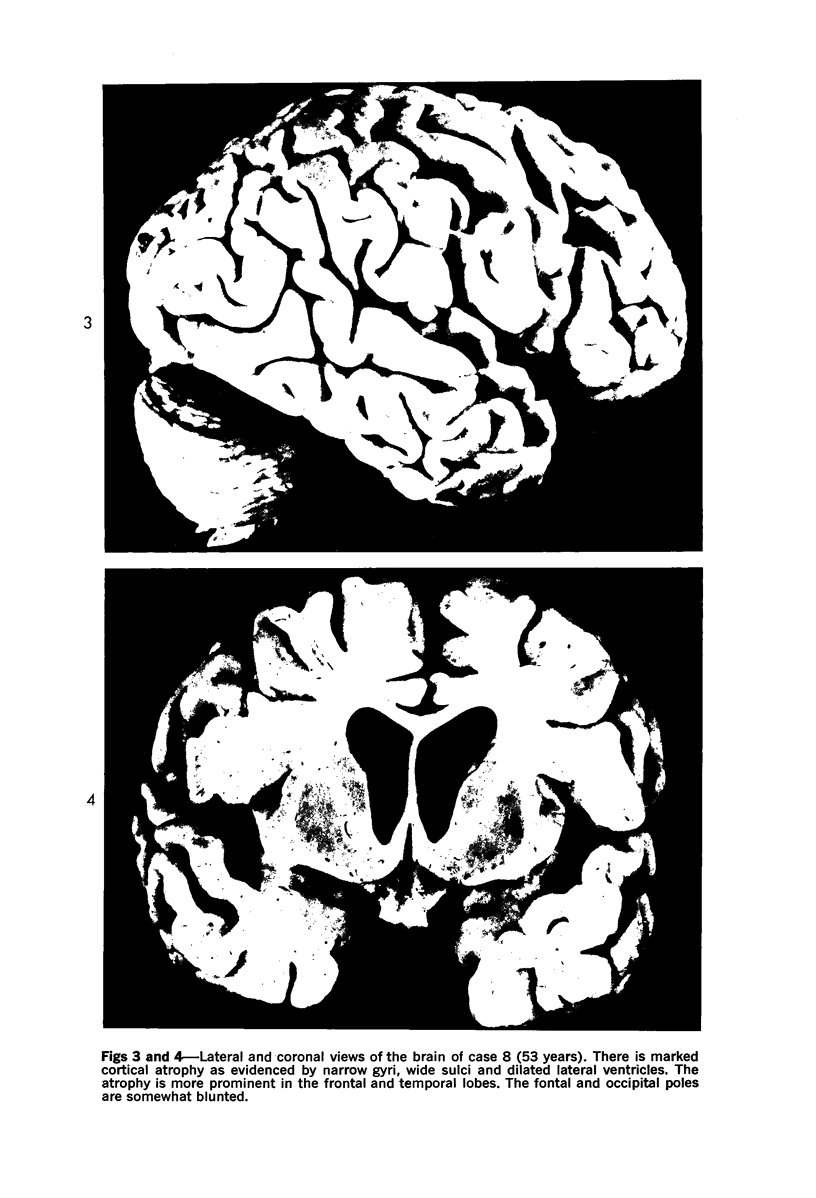

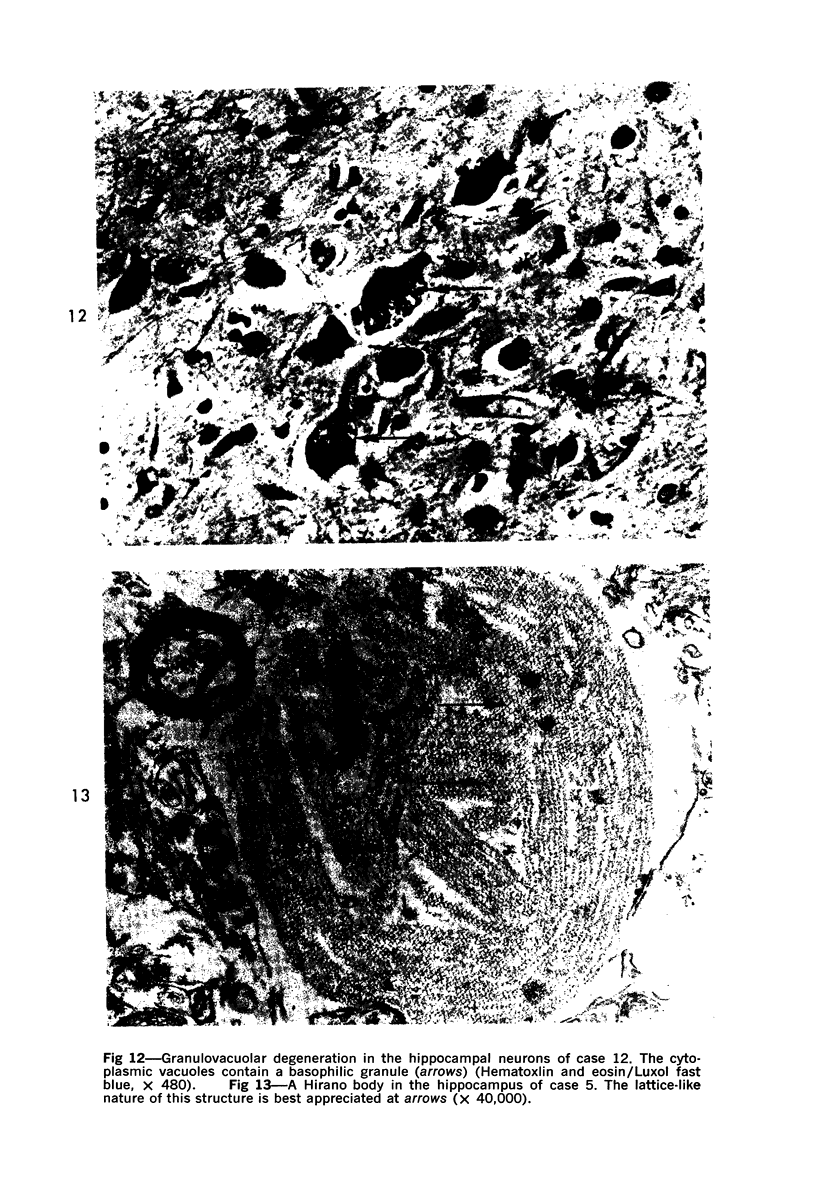
Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Boullin D. J., O'Brien R. A. Abnormalities of 5-hydroxytryptamine uptake and binding by blood platelets from children with Down's syndrome. J Physiol. 1971 Jan;212(2):287–297. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1971.sp009325. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gottfries C. G., Gottfries I., Roos B. E. Homovanillic acid and 5-hydroxyindoleacetic acid in cerebrospinal fluid related to rated mental and motor impairment in senile and presenile dementia. Acta Psychiatr Scand. 1970;46(2):99–105. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gottfries C. G., Gottfries I., Roos B. E. Homovanillic acid and 5-hydroxyindoleacetic acid in the cerebrospinal fluid of patients with senile dementia, presenile dementia and parkinsonism. J Neurochem. 1969 Sep;16(9):1341–1345. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1969.tb05984.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gregory L., Williams R., Thompson E. Leucocyte function in Down's syndrome and acute leukaemia. Lancet. 1972 Jun 24;1(7765):1359–1361. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(72)91093-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirano A., Dembitzer H. M., Kurland L. T., Zimmerman H. M. The fine structure of some intraganglionic alterations. Neurofibrillary tangles, granulovacuolar bodies and "rod-like" structures as seen in Guam amyotrophic lateral sclerosis and parkinsonism-dementia complex. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol. 1968 Apr;27(2):167–182. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hsia D. Y., Smith G. F., Dowben R. M., Justice P. Down's syndrome. A critical review of the biochemical and immunological data. Am J Dis Child. 1971 Feb;121(2):153–161. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KRIGMAN M. R., FELDMAN R. G., BENSCH K. ALZHEIMER'S PRESENILE DEMENTIA. A HISTOCHEMICAL AND ELECTRON MICROSCOPIC STUDY. Lab Invest. 1965 Apr;14:381–396. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Korf J., Van Praag H. M. Amine metabolism in the human brain: further evaluation of the probenecid test. Brain Res. 1971 Dec 10;35(1):221–230. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(71)90607-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lott I. T., Murphy D. L., Chase T. N. Down's syndrome. Central monoamine turnover in patients with diminished platelet serotonin. Neurology. 1972 Sep;22(9):967–972. doi: 10.1212/wnl.22.9.967. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neumann M. A. Langdon Down syndrome and Alzheimer's disease. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol. 1967 Jan;26(1):149–150. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ogata J., Budzilovich G. N., Cravioto H. A study of rod-like structures (Hirano bodies) in 240 normal and pathological brains. Acta Neuropathol. 1972;21(1):61–67. doi: 10.1007/BF00688000. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olson M. I., Shaw C. M. Presenile dementia and Alzheimer's disease in mongolism. Brain. 1969 Mar;92(1):147–156. doi: 10.1093/brain/92.1.147. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Owens D., Dawson J. C., Losin S. Alzheimer's disease in Down's syndrome. Am J Ment Defic. 1971 Mar;75(5):606–612. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schneider E. L., Epstein C. J. Replication rate and lifespan of cultured fibroblasts in Down's syndrome. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1972 Dec;141(3):1092–1094. doi: 10.3181/00379727-141-36940. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schochet S. S., Jr, McCormick W. F. Ultrastructure of Hirano bodies. Acta Neuropathol. 1972;21(1):50–60. doi: 10.1007/BF00687999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shaw D. M., Macsweeney D. A., Johnson A. L., O'Keeffe R., Naidoo D., Macleod D. M., Jog S., Preece J. M., Crowley J. M. Folate and amine metabolites in senile dementia: a combined trial and biochemical study. Psychol Med. 1971 Feb;1(2):166–171. doi: 10.1017/s003329170000009x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Solitare G. B., Lamarche J. B. Alzheimer's disease and senile dementia as seen in mongoloids: neuropathological observations. Am J Ment Defic. 1966 May;70(6):840–848. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Solitare G. B., Lamarche J. B. Brain weight in the adult mongol. J Ment Defic Res. 1967 Jun;11(2):79–84. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2788.1967.tb00207.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sutnick A. I., London W. T., Blumberg B. S. Effects of host and environment on immunoglobulins in Down's syndrome. Arch Intern Med. 1969 Dec;124(6):722–725. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Terry R. D. Neuronal fibrous protein in human pathology. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol. 1971 Jan;30(1):8–19. doi: 10.1097/00005072-197101000-00003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tomlinson B. E., Blessed G., Roth M. Observations on the brains of demented old people. J Neurol Sci. 1970 Sep;11(3):205–242. doi: 10.1016/0022-510x(70)90063-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tomlinson B. E., Blessed G., Roth M. Observations on the brains of non-demented old people. J Neurol Sci. 1968 Sep-Oct;7(2):331–356. doi: 10.1016/0022-510x(68)90154-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wetterberg L., Gustavson K. H., Bäckström M., Ross S. B., Frödén O. Low dopamine-beta-hydroxylase activity in Down's syndrome. Clin Genet. 1972;3(3):152–153. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-0004.1972.tb01451.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiśniewski H., Johnson A. B., Raine C. S., Kay W. J., Terry R. D. Senile plaques and cerebral amyloidosis in aged dogs. A histochemical and ultrastructural study. Lab Invest. 1970 Sep;23(3):287–296. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yokoyama M., Ball C., Lou K., Alepa F. P. Immunogenetic studies on mongolism. Am J Ment Defic. 1967 Jan;71(4):597–601. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]