Full text
PDF







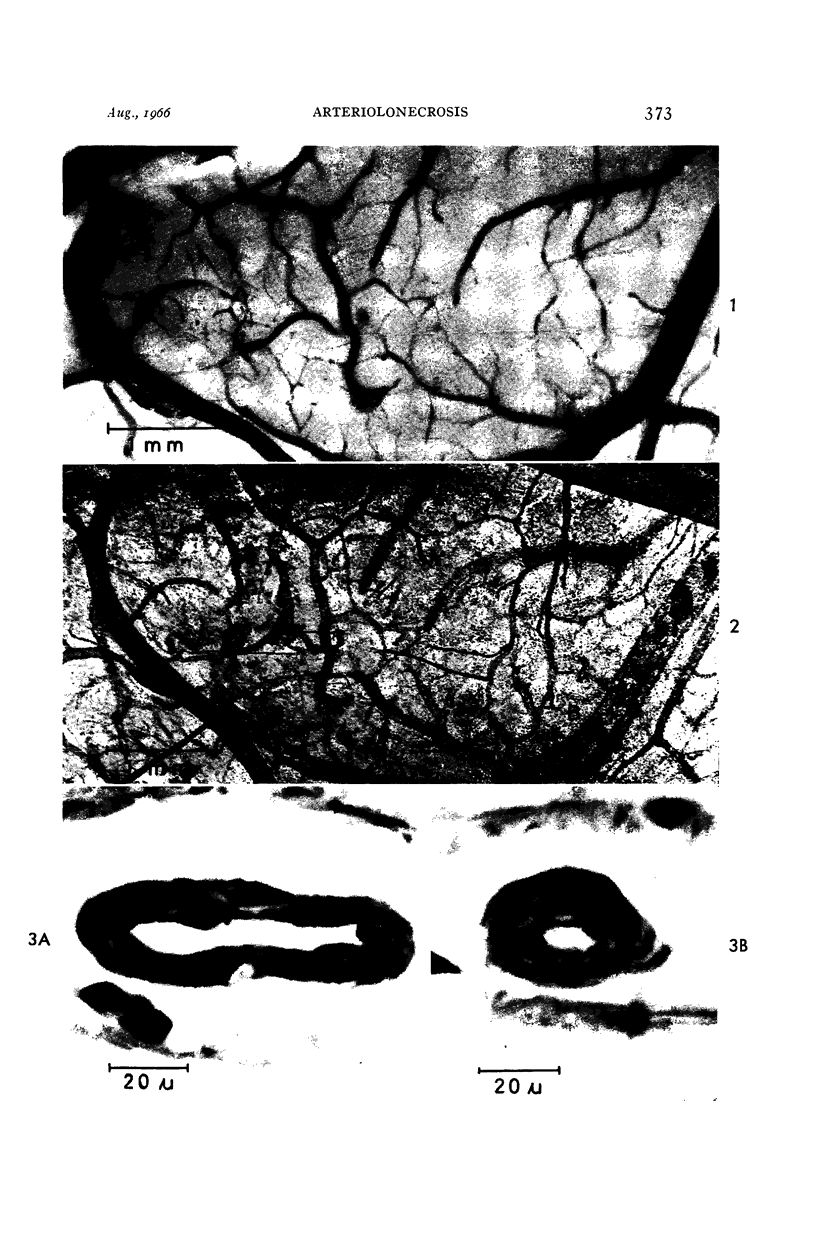

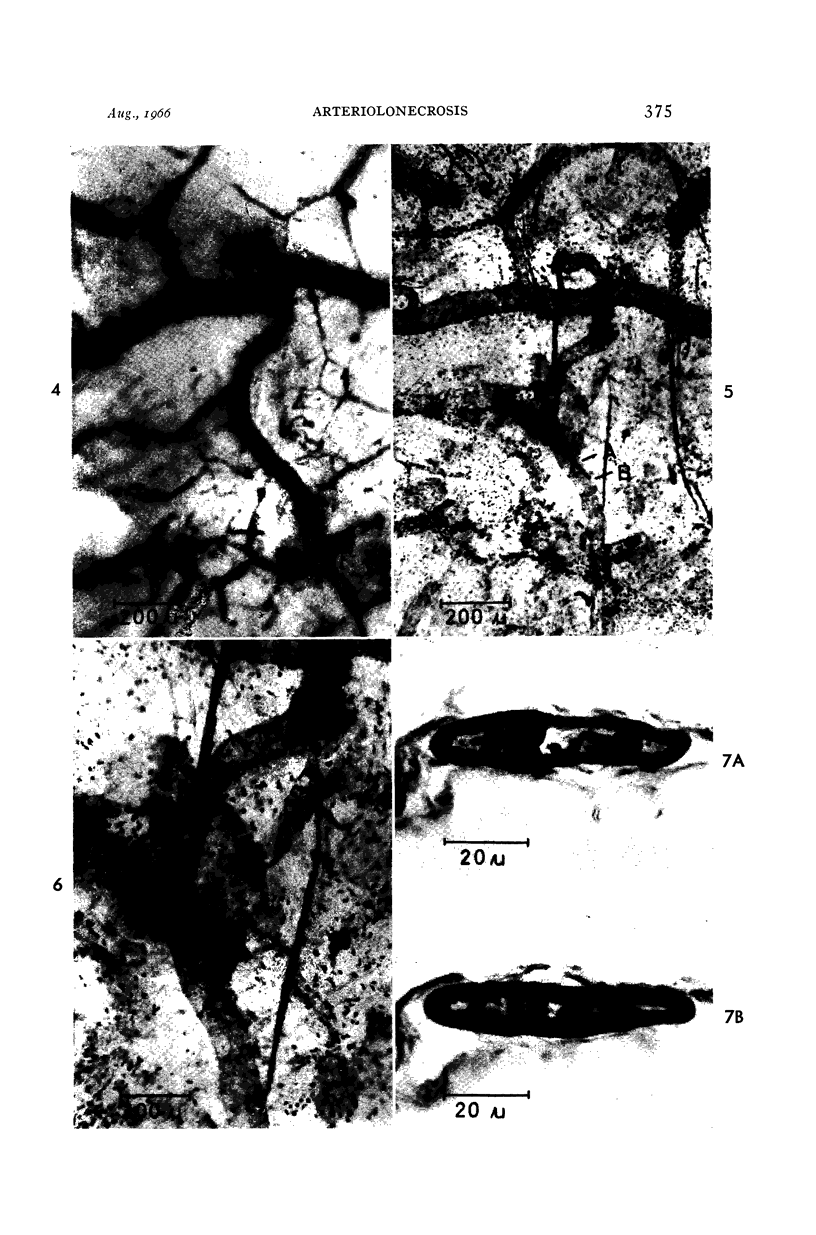

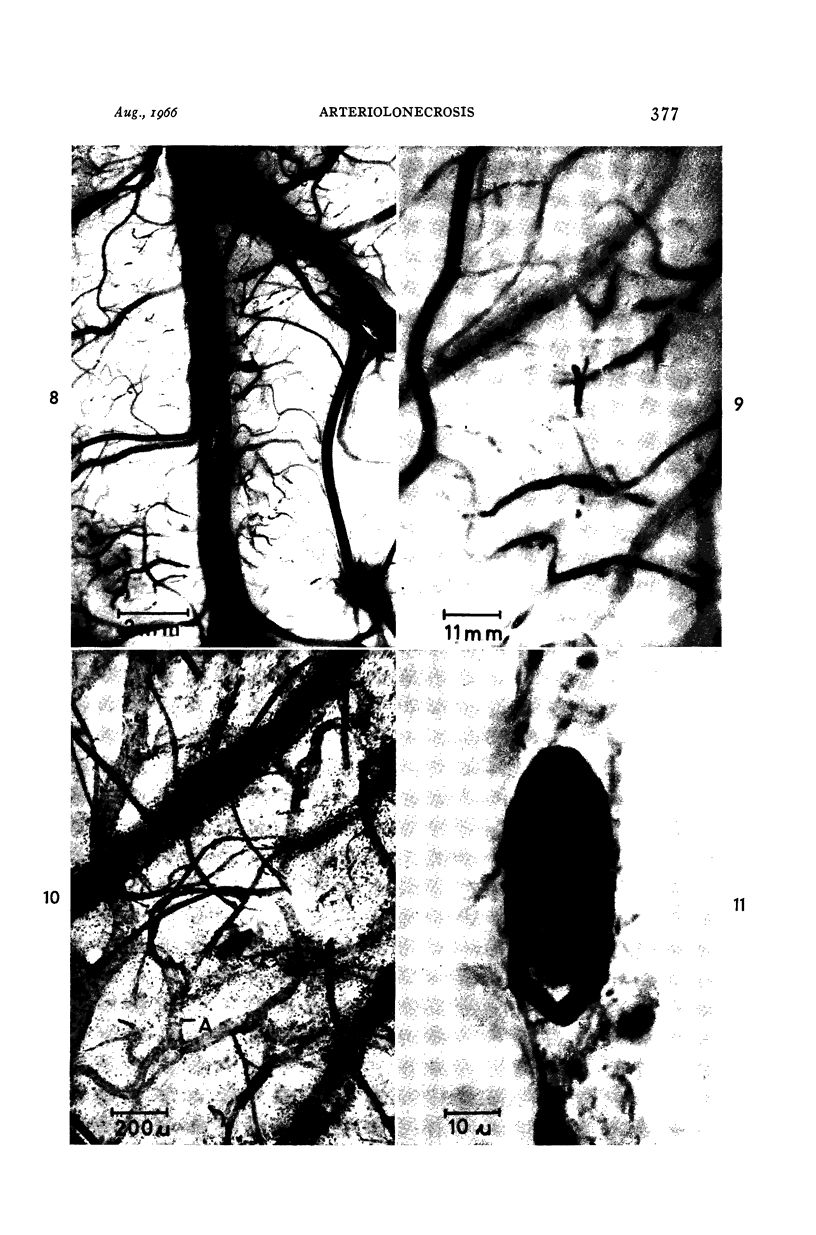

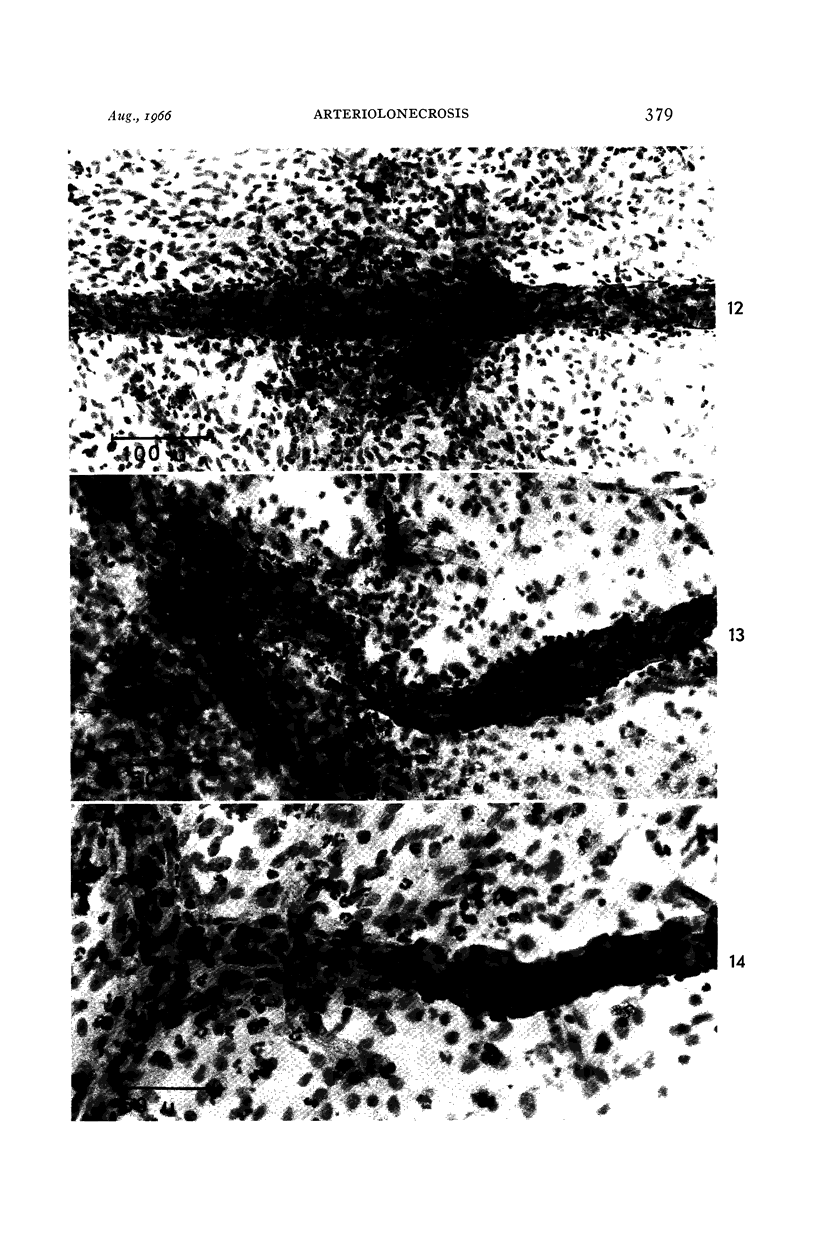

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BYROM F. B. The pathogenesis of hypertensive encephalopathy and its relation to the malignant phase of hypertension; experimental evidence from the hypertensive rat. Lancet. 1954 Jul 31;267(6831):201–211. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(54)91821-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DENNY-BROWN D., MEYER J. S. The cerebral collateral circulation. II. Production of cerebral infarction by ischemic anoxia and its reversibility in early stages. Neurology. 1957 Aug;7(8):567–579. doi: 10.1212/wnl.7.8.567. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
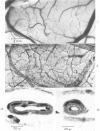
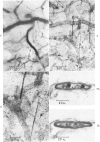
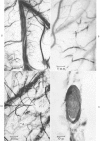
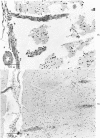
- Rodda R., Denny-Brown D. The cerebral arterioles in experimental hypertension. I. The nature of arteriolar constriction and its effects on the collateral circulation. Am J Pathol. 1966 Jul;49(1):53–76. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]