Abstract
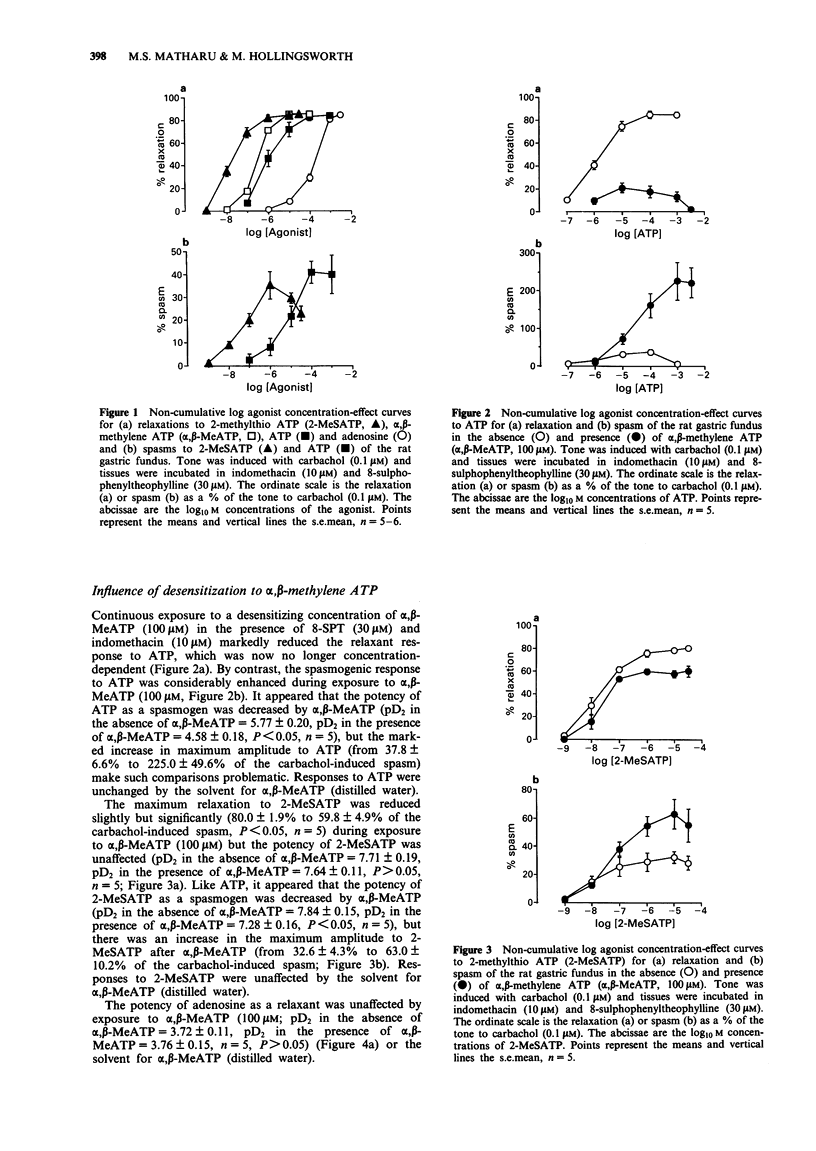
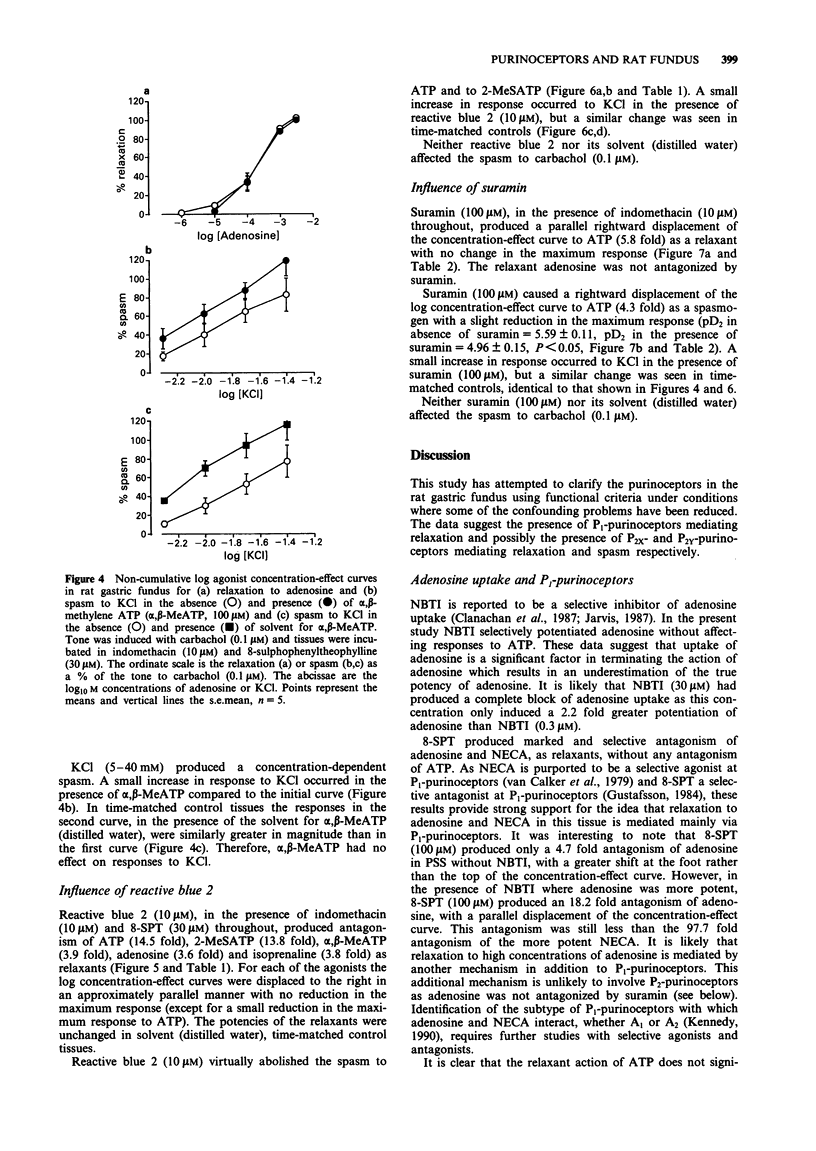
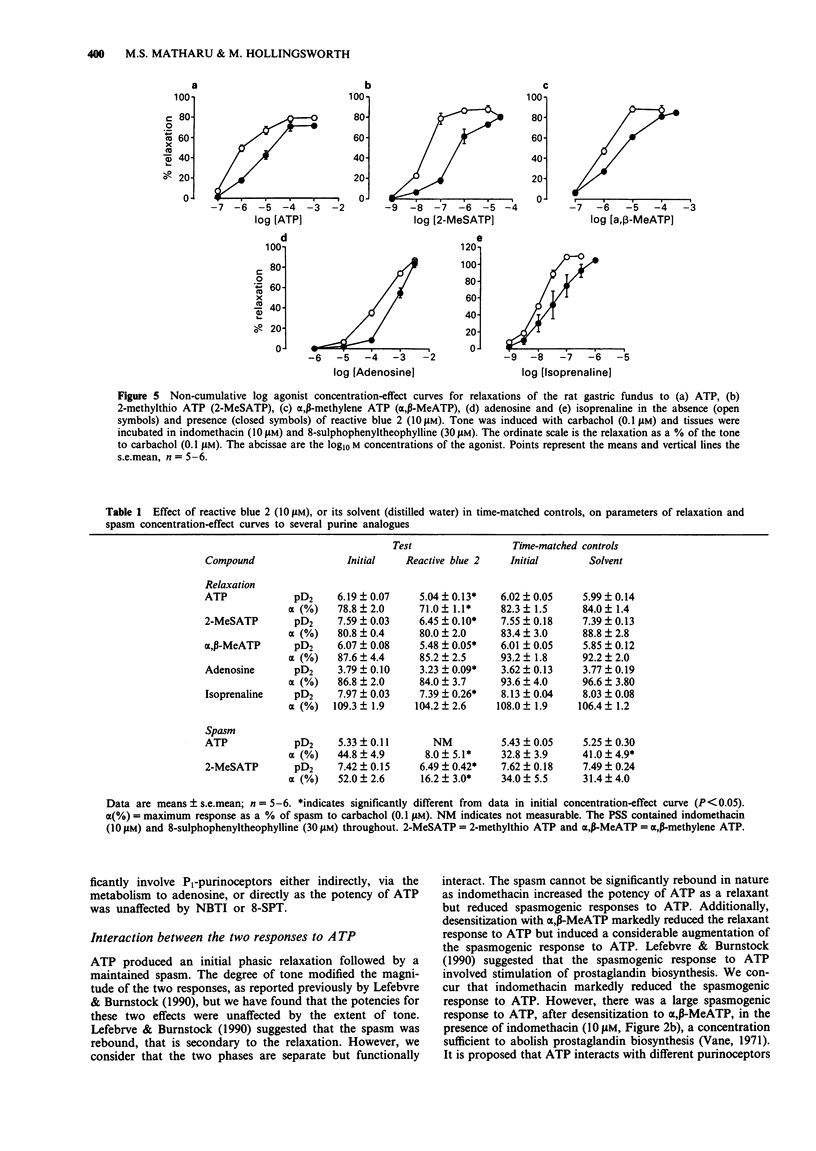
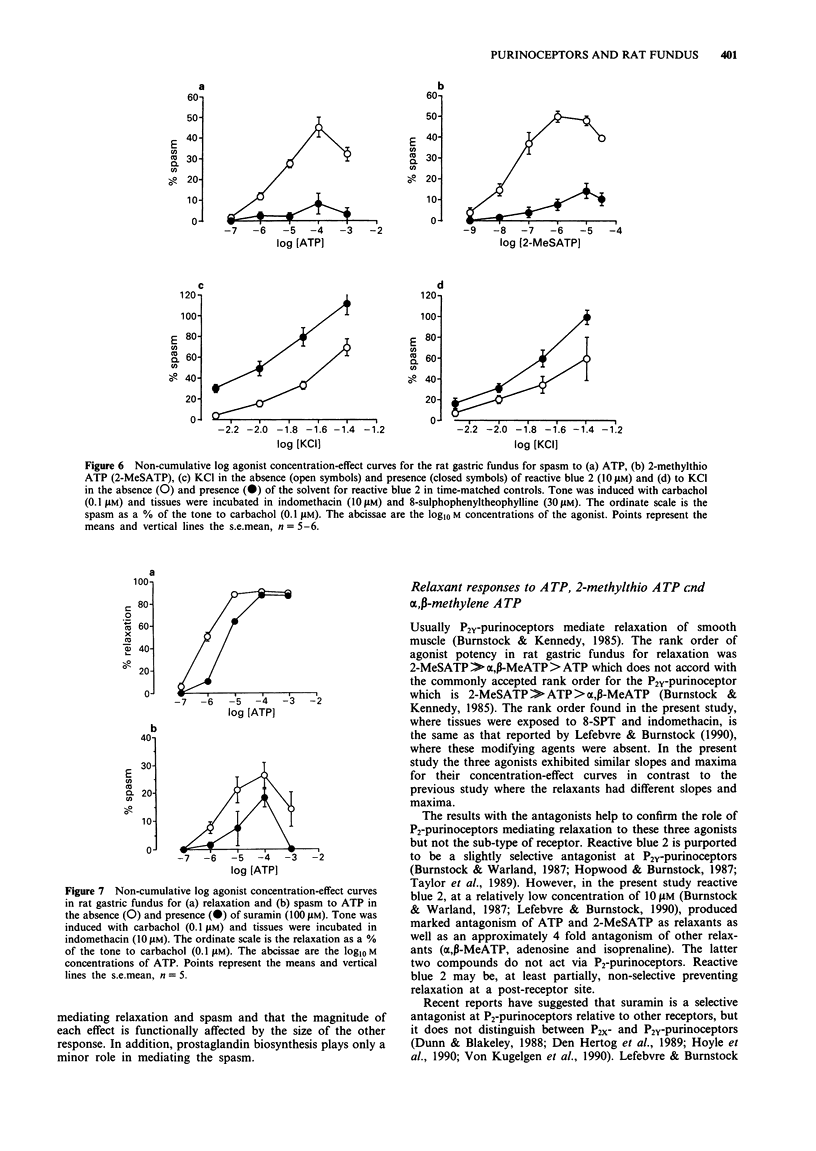
1. The relaxant and spasmogenic effects of purines and analogues were studied in longitudinal strips of rat gastric fundus to characterize the purinoceptors involved. Classification was studied by use of agonist potency orders and of antagonists in circumstances where the influence of confounding factors was reduced. In general tone was raised by carbachol (0.1 microM). 2. Adenosine produced relaxation and was potentiated by nitrobenzylthioinosine (NBTI, 0.3 and 30 microM), an adenosine-uptake inhibitor. 8-Sulphophenyl-theophylline (8-SPT, 30 microM), a selective P1-purinoceptor antagonist, antagonized adenosine and 5'-N-ethylcarboxamidoadenosine (NECA), a selective agonist at P1-purinoceptors. 3. At resting tone, adenosine 5'-triphosphate (ATP) induced a small, phasic relaxation followed by a maintained spasm. When tone was raised by carbachol, ATP induced a larger relaxation followed by a smaller spasm. NBTI did not potentiate ATP, nor did 8-SPT antagonize ATP, suggesting that ATP does not act directly or indirectly at P1-purinoceptors. 4. With raised tone, and in the presence of indomethacin (10 microM) and 8-SPT (30 microM), 2-methylthio ATP (2-MeSATP) and ATP produced relaxations followed by spasms while alpha,beta-methylene ATP (alpha,beta-MeATP) induced only relaxation; all responses were concentration-dependent. The compounds had similar slopes and maxima for relaxation and spasm. The rank orders of potency were 2-MeSATP much greater than alpha,beta-MeATP greater than ATP for relaxation and 2-MeSATP much greater than ATP for spasm.(ABSTRACT TRUNCATED AT 250 WORDS)
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bailey S. J., Hourani S. M. A study of the purinoceptors mediating contraction in the rat colon. Br J Pharmacol. 1990 Aug;100(4):753–756. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1990.tb14087.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berrie C. P., Hawkins P. T., Stephens L. R., Harden T. K., Downes C. P. Phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate hydrolysis in turkey erythrocytes is regulated by P2y purinoceptors. Mol Pharmacol. 1989 Apr;35(4):526–532. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burnstock G., Campbell G., Satchell D., Smythe A. Evidence that adenosine triphosphate or a related nucleotide is the transmitter substance released by non-adrenergic inhibitory nerves in the gut. Br J Pharmacol. 1970 Dec;40(4):668–688. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1970.tb10646.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burnstock G., Kennedy C. Is there a basis for distinguishing two types of P2-purinoceptor? Gen Pharmacol. 1985;16(5):433–440. doi: 10.1016/0306-3623(85)90001-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burnstock G., Warland J. J. P2-purinoceptors of two subtypes in the rabbit mesenteric artery: reactive blue 2 selectively inhibits responses mediated via the P2y-but not the P2x-purinoceptor. Br J Pharmacol. 1987 Feb;90(2):383–391. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1987.tb08968.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunn P. M., Blakeley A. G. Suramin: a reversible P2-purinoceptor antagonist in the mouse vas deferens. Br J Pharmacol. 1988 Feb;93(2):243–245. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1988.tb11427.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gustafsson L. E. Adenosine antagonism and related effects of theophylline derivatives in guinea pig ileum longitudinal muscle. Acta Physiol Scand. 1984 Oct;122(2):191–198. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1984.tb07498.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HELLER H., ZAIDI S. M. The metabolism of exogenous and endogenous antidiuretic hormone in the kidney and liver in vivo. Br J Pharmacol Chemother. 1957 Sep;12(3):284–292. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1957.tb00136.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hopwood A. M., Burnstock G. ATP mediates coronary vasoconstriction via P2x-purinoceptors and coronary vasodilatation via P2y-purinoceptors in the isolated perfused rat heart. Eur J Pharmacol. 1987 Apr 7;136(1):49–54. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(87)90777-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoyle C. H., Knight G. E., Burnstock G. Suramin antagonizes responses to P2-purinoceptor agonists and purinergic nerve stimulation in the guinea-pig urinary bladder and taenia coli. Br J Pharmacol. 1990 Mar;99(3):617–621. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1990.tb12979.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kennedy C. P1- and P2-purinoceptor subtypes--an update. Arch Int Pharmacodyn Ther. 1990 Jan-Feb;303:30–50. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lefebvre R. A., Burnstock G. Effect of adenosine triphosphate and related purines in the rat gastric fundus. Arch Int Pharmacodyn Ther. 1990 Jan-Feb;303:199–215. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leff P., Wood B. E., O'Connor S. E. Suramin is a slowly-equilibrating but competitive antagonist at P2x-receptors in the rabbit isolated ear artery. Br J Pharmacol. 1990 Nov;101(3):645–649. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1990.tb14134.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Connor S. E., Dainty I. A., Leff P. Further subclassification of ATP receptors based on agonist studies. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 1991 Apr;12(4):137–141. doi: 10.1016/0165-6147(91)90530-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Connor S. E., Wood B. E., Leff P. Characterization of P2x-receptors in rabbit isolated ear artery. Br J Pharmacol. 1990 Nov;101(3):640–644. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1990.tb14133.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor E. M., Parsons M. E., Wright P. W., Pipkin M. A., Howson W. The effects of adenosine triphosphate and related purines on arterial resistance vessels in vitro and in vivo. Eur J Pharmacol. 1989 Feb 28;161(2-3):121–133. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(89)90834-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vane J. R. Inhibition of prostaglandin synthesis as a mechanism of action for aspirin-like drugs. Nat New Biol. 1971 Jun 23;231(25):232–235. doi: 10.1038/newbio231232a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiklund N. P., Gustafsson L. E. Indications for P2-purinoceptor subtypes in guinea pig smooth muscle. Eur J Pharmacol. 1988 Apr 13;148(3):361–370. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(88)90114-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- den Hertog A., Nelemans A., Van den Akker J. The inhibitory action of suramin on the P2-purinoceptor response in smooth muscle cells of guinea-pig taenia caeci. Eur J Pharmacol. 1989 Aug 3;166(3):531–534. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(89)90370-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Calker D., Müller M., Hamprecht B. Adenosine regulates via two different types of receptors, the accumulation of cyclic AMP in cultured brain cells. J Neurochem. 1979 Nov;33(5):999–1005. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1979.tb05236.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- von Kügelgen I., Bültmann R., Starke K. Interaction of adenine nucleotides, UTP and suramin in mouse vas deferens: suramin-sensitive and suramin-insensitive components in the contractile effect of ATP. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1990 Aug;342(2):198–205. doi: 10.1007/BF00166965. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


