Abstract
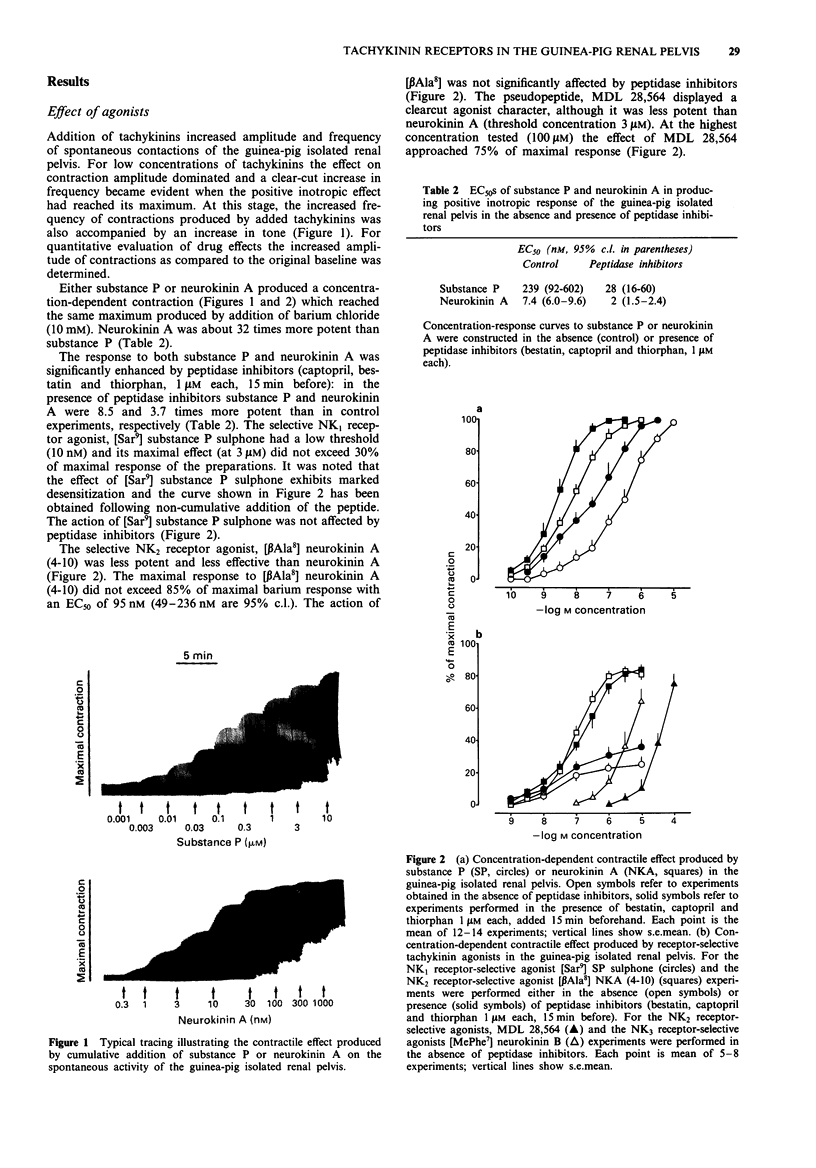
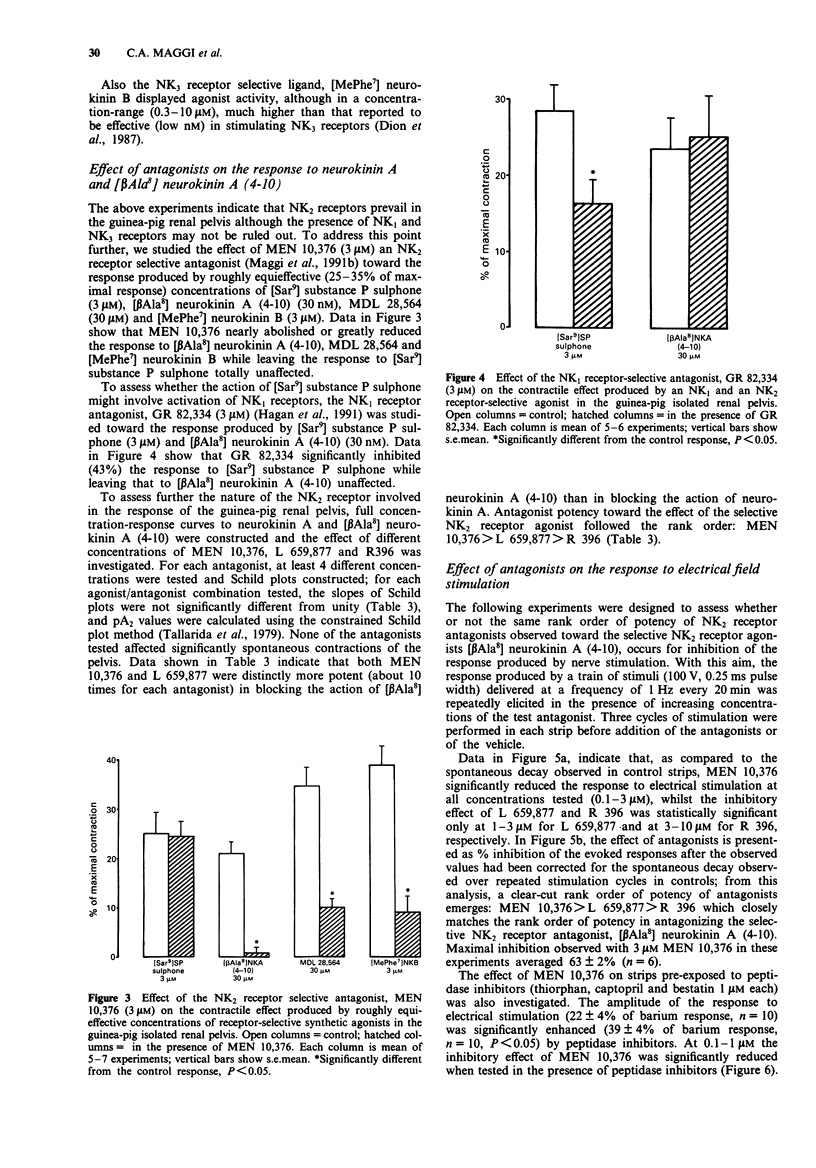
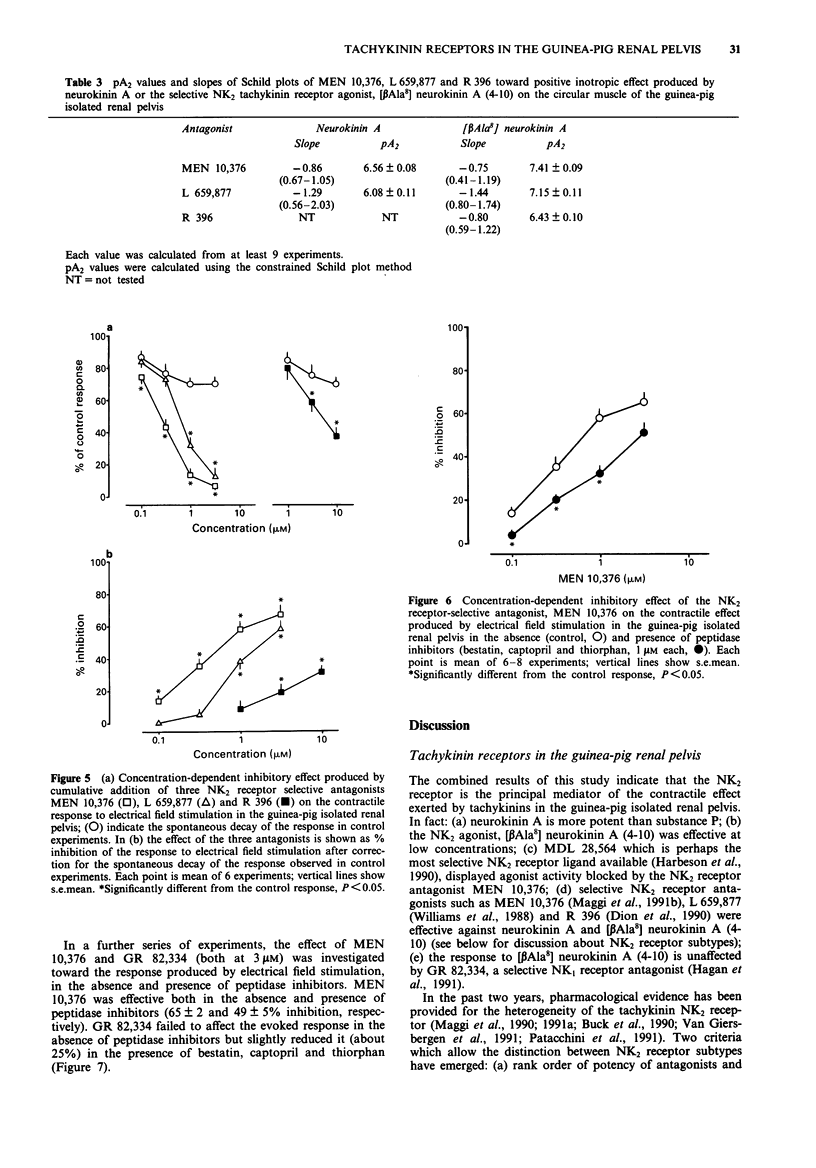
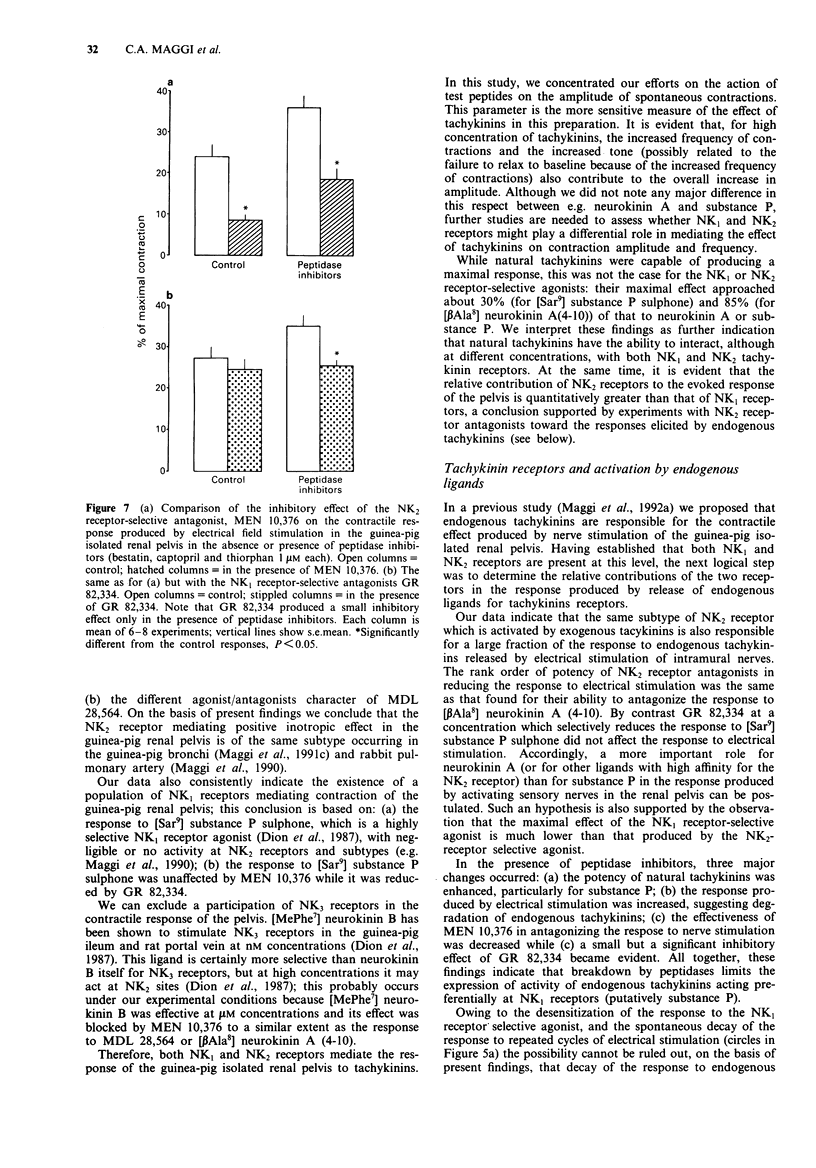
1. The contractile response to substance P, neurokinin A, selective agonists for the NK1, NK2 and NK3 tachykinin receptors and the activity of receptor-selective antagonists has been investigated in circular muscle strips of the guinea-pig isolated renal pelvis in the presence of indomethacin (3 microM). 2. Neurokinin A was the most potent agonist tested, being about 32 times more potent than substance P. The action of both substance P and neurokinin A was enhanced by peptidase inhibitors (bestatin, captopril and thiorphan, 1 microM each). The selective NK2 receptor agonist [beta Ala8] neurokinin A (4-10), was slightly less potent and effective than neurokinin A itself. The selective NK1 receptor agonist [Sar9] substance P sulphone was effective at low (nM) concentrations but its maximal effect did not exceed 30% of maximal response to substance P or neurokinin A. The NK3-selective agonist [MePhe7] neurokinin B was effective only at high (microM) concentrations. 3. The pseudopeptide derivative of neurokinin A(4-10), MDL 28,564, displayed a clear-cut agonist character, although it was less potent than neurokinin A. 4. The responses to roughly equieffective (25-35% of maximal response) concentrations of [beta Ala8] neurokinin A (4-10), MDL 28,564 and [MePhe7] neurokinin B were antagonized to a similar extent by MEN 10,376 (3 microM), a selective NK2 tachykinin receptor antagonist, while the response to [Sar9] substance P sulphone was unchanged. 5. The response to [Sar9] substance P sulphone was inhibited by the NK1 receptor-selective antagonist, GR 82,334 (3 microM) while the response to [beta Ala8] neurokinin A (4-10) was unchanged.(ABSTRACT TRUNCATED AT 250 WORDS)
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Buck S. H., Harbeson S. L., Hassmann C. F., 3rd, Shatzer S. A., Rouissi N., Nantel F., van Giersbergen P. L. [Leu9 psi(CH2NH)Leu10]-neurokinin A (4-10) (MDL 28,564) distinguishes tissue tachykinin peptide NK2 receptors. Life Sci. 1990;47(10):PL37–PL41. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(90)90605-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cervero F., Sann H. Mechanically evoked responses of afferent fibres innervating the guinea-pig's ureter: an in vitro study. J Physiol. 1989 May;412:245–266. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1989.sp017613. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dion S., D'Orléans-Juste P., Drapeau G., Rhaleb N. E., Rouissi N., Tousignant C., Regoli D. Characterization of neurokinin receptors in various isolated organs by the use of selective agonists. Life Sci. 1987 Nov 16;41(20):2269–2278. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(87)90538-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dion S., Rouissi N., Nantel F., Jukic D., Rhaleb N. E., Tousignant C., Télémaque S., Drapeau G., Regoli D., Naline E. Structure-activity study of neurokinins: antagonists for the neurokinin-2 receptor. Pharmacology. 1990;41(4):184–194. doi: 10.1159/000138717. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Golenhofen K., Hannappel J. Normal spontaneous activity of the pyeloureteral system in the guinea-pig. Pflugers Arch. 1973 Jul 6;341(3):257–270. doi: 10.1007/BF00592794. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maggi C. A., Giuliani S., Ballati L., Lecci A., Manzini S., Patacchini R., Renzetti A. R., Rovero P., Quartara L., Giachetti A. In vivo evidence for tachykininergic transmission using a new NK-2 receptor-selective antagonist, MEN 10,376. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1991 Jun;257(3):1172–1178. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maggi C. A., Giuliani S., Patacchini R., Santicioli P., Theodorsson E., Barbanti G., Turini D., Giachetti A. Tachykinin antagonists inhibit nerve-mediated contractions in the circular muscle of the human ileum. Involvement of neurokinin-2 receptors. Gastroenterology. 1992 Jan;102(1):88–96. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(92)91787-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maggi C. A., Giuliani S. The neurotransmitter role of calcitonin gene-related peptide in the rat and guinea-pig ureter: effect of a calcitonin gene-related peptide antagonist and species-related differences in the action of omega conotoxin on calcitonin gene-related peptide release from primary afferents. Neuroscience. 1991;43(1):261–268. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(91)90433-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maggi C. A., Patacchini R., Astolfi M., Rovero P., Giuliani S., Giachetti A. NK-2 receptor agonists and antagonists. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1991;632:184–191. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1991.tb33106.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maggi C. A., Patacchini R., Quartara L., Rovero P., Santicioli P. Tachykinin receptors in the guinea-pig isolated bronchi. Eur J Pharmacol. 1991 May 17;197(2-3):167–174. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(91)90517-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maggi C. A., Theodorsson E., Santicioli P., Giuliani S. Tachykinins and calcitonin gene-related peptide as co-transmitters in local motor responses produced by sensory nerve activation in the guinea-pig isolated renal pelvis. Neuroscience. 1992;46(3):549–559. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(92)90143-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patacchini R., Astolfi M., Quartara L., Rovero P., Giachetti A., Maggi C. A. Further evidence for the existence of NK2 tachykinin receptor subtypes. Br J Pharmacol. 1991 Sep;104(1):91–96. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1991.tb12390.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tallarida R. J., Cowan A., Adler M. W. pA2 and receptor differentiation: a statistical analysis of competitive antagonism. Life Sci. 1979 Aug 20;25(8):637–654. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(79)90505-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Giersbergen P. L., Shatzer S. A., Henderson A. K., Lai J., Nakanishi S., Yamamura H. I., Buck S. H. Characterization of a tachykinin peptide NK2 receptor transfected into murine fibroblast B82 cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Mar 1;88(5):1661–1665. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.5.1661. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


