Abstract
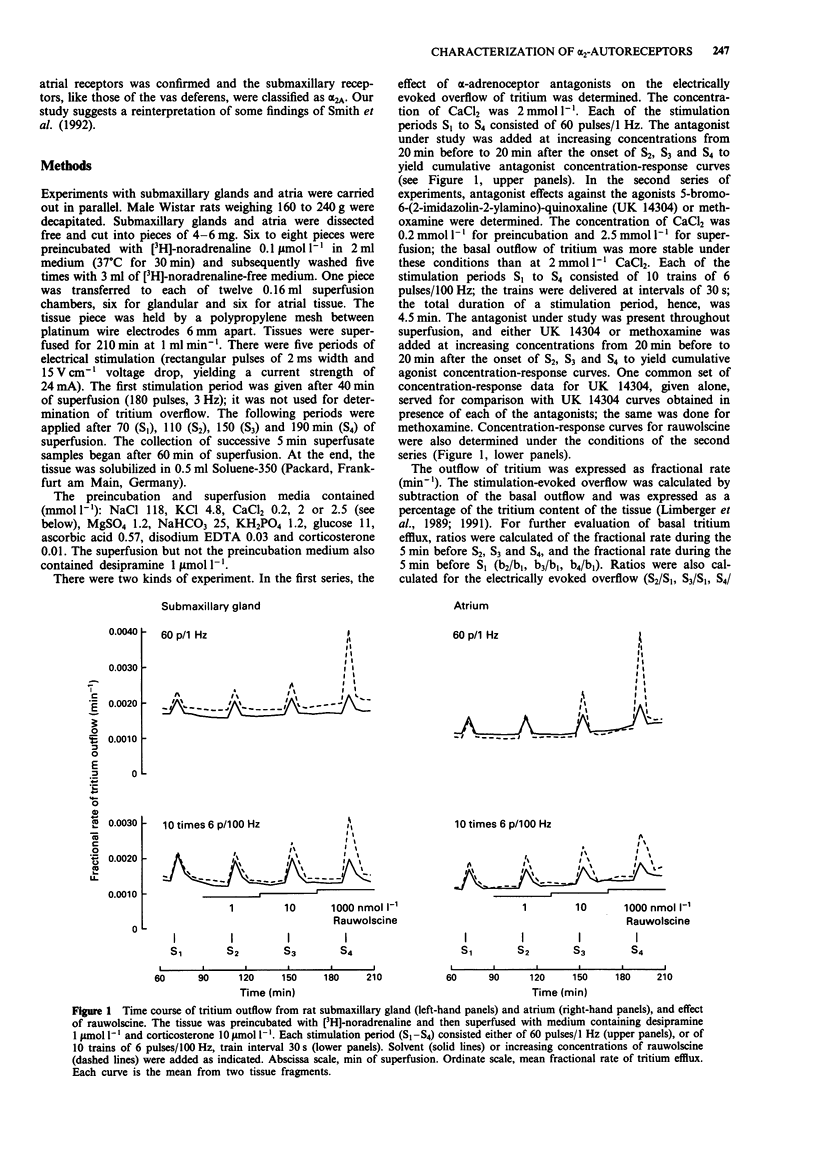
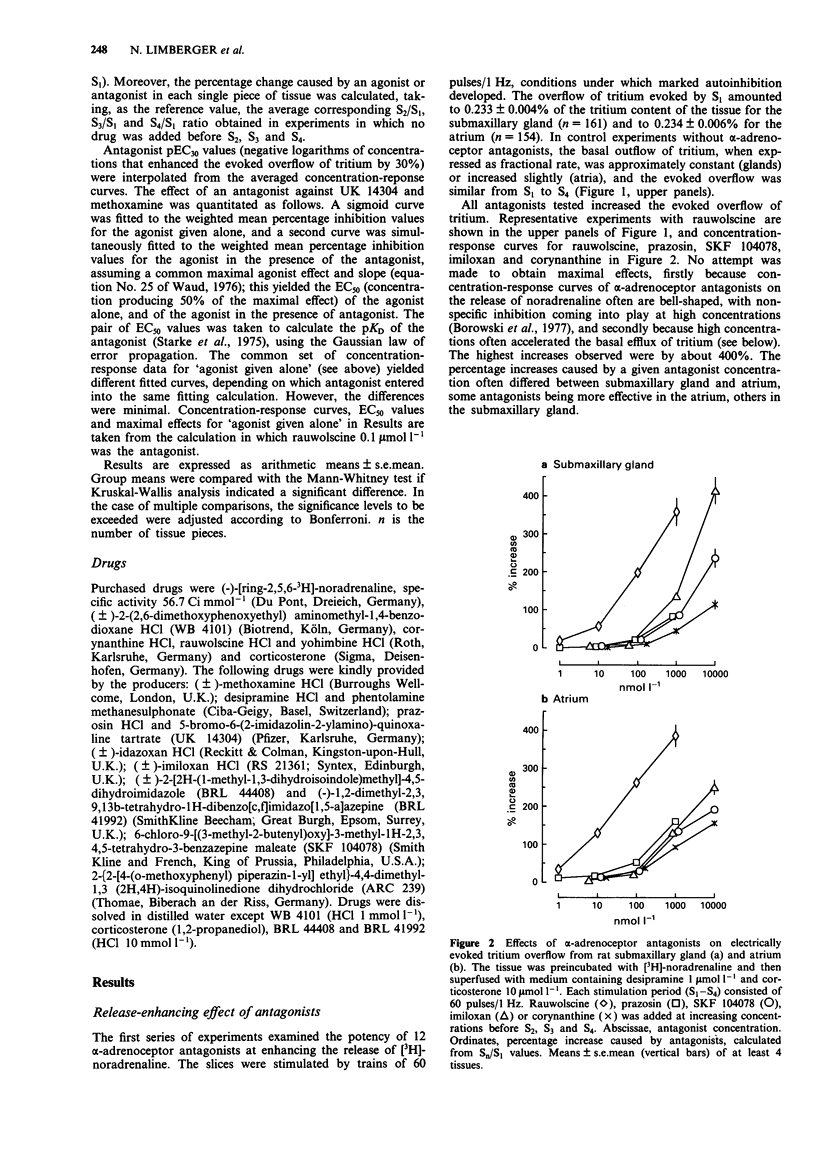
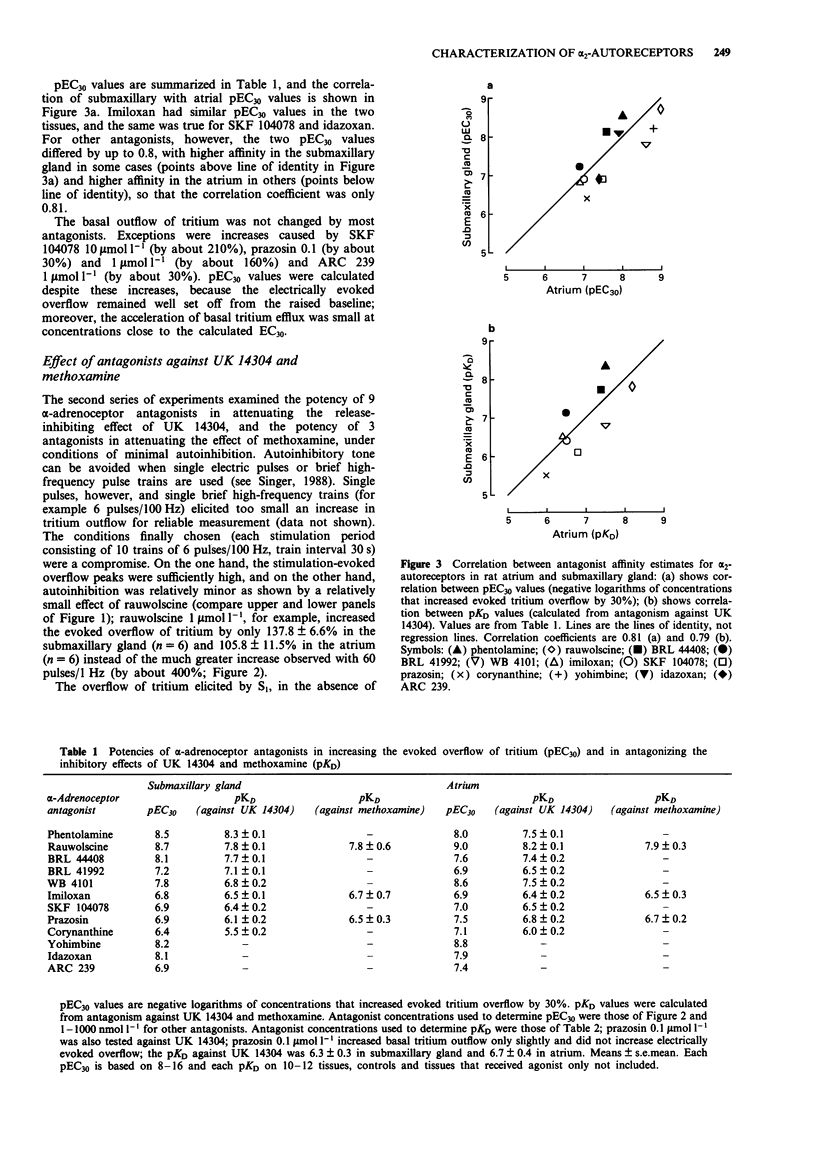
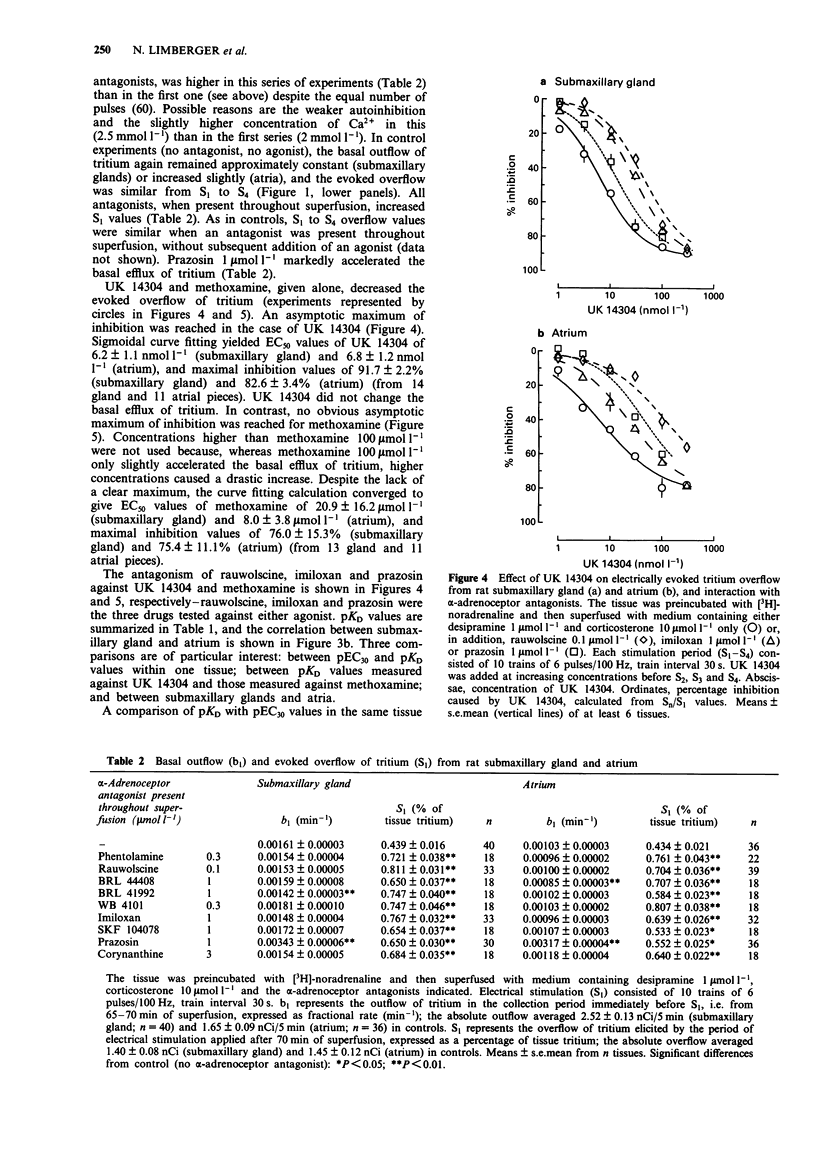
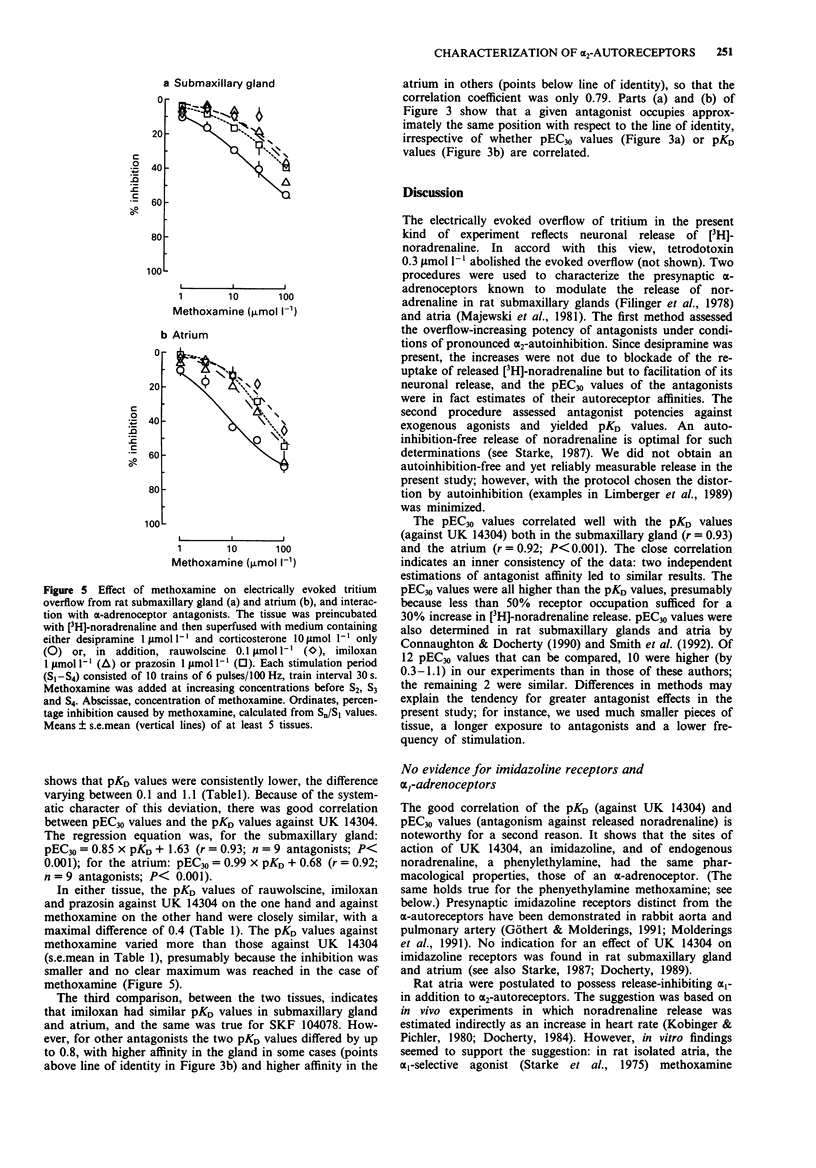
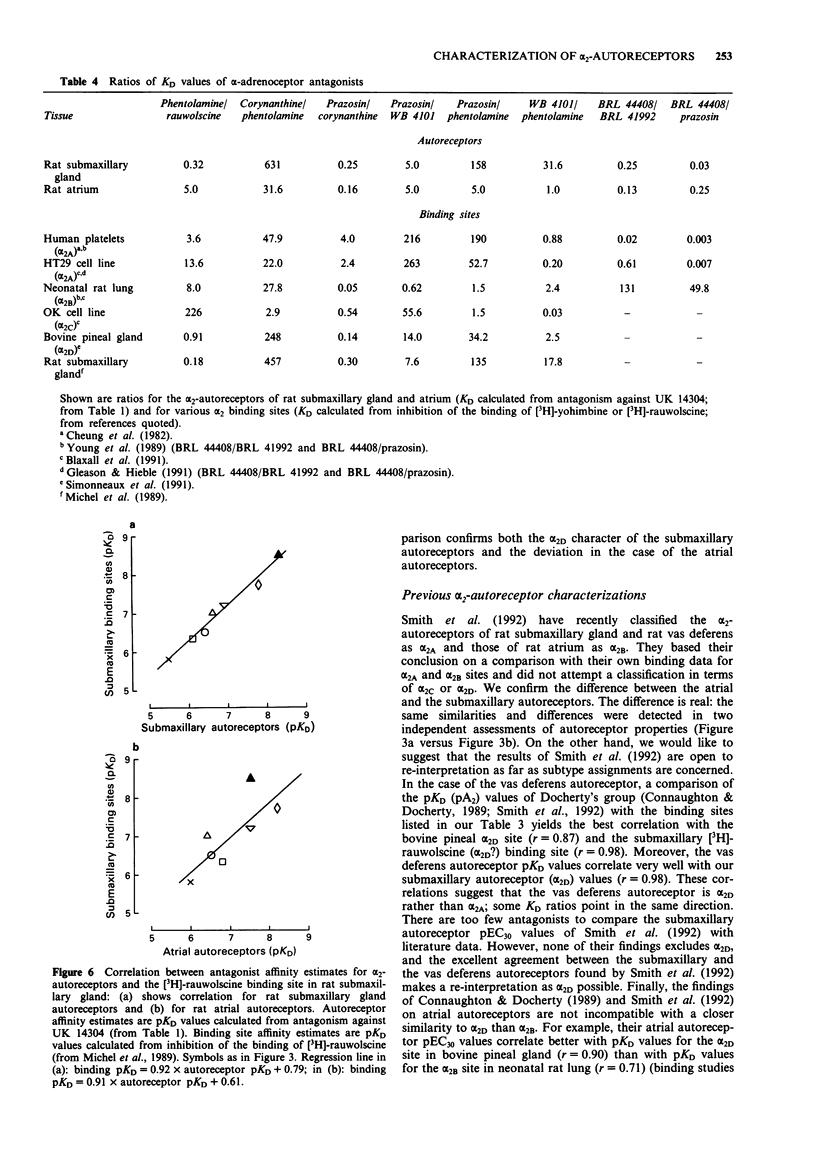
1. The pharmacological properties of presynaptic alpha 2-autoreceptors were studied in rat isolated submaxillary glands and atria. Tissue pieces were preincubated with [3H]-noradrenaline, then superfused with medium containing desipramine, and stimulated electrically. In one series of experiments, pEC30 values of 12 alpha-adrenoceptor antagonists were determined, i.e., negative logarithms of concentrations that increased the electrically evoked overflow of tritium by 30%. In another series, pKD values of 9 alpha-adrenoceptor antagonists against the release-inhibiting effect of 5-bromo-6-(2-imidazolin-2-ylamino)-quinoxaline (UK 14304), and of 3 antagonists against the release-inhibiting effect of methoxamine, were determined. 2. In submaxillary glands, the pEC30 values of the antagonists correlated well with their pKD values against UK 14304 (r = 0.93). The same was true for atria (r = 0.92). 3. In submaxillary glands, the pKD values of 3 antagonists against UK14304 were very similar to their pKD values against methoxamine, with a maximal difference of 0.4. The same was true for atria where the maximal difference was 0.3. 4. The pEC30 values obtained in submaxillary glands correlated significantly with those obtained in atria (r = 0.81). The same was true for the pKD values (r = 0.79). However, the pEC30 and pKD values also indicated consistent differences between the two tissues. 5. It is concluded that the sites of action of the imidazoline UK 14304 (alpha 2-selective), the phenylethylamine noradrenaline, and the phenylethylamine methoxamine (alpha 1-selective) are exclusively alpha 2-adrenoceptors. There is no indication for presynaptic alpha 1-adrenoceptors or for an effect of UK 14304 mediated by presynaptic imidazoline receptors.(ABSTRACT TRUNCATED AT 250 WORDS)
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alabaster V. A., Keir R. F., Peters C. J. Comparison of potency of alpha 2-adrenoceptor antagonists in vitro: evidence for heterogeneity of alpha 2-adrenoceptors. Br J Pharmacol. 1986 Jul;88(3):607–614. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1986.tb10241.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alberts P. Subtype classification of the presynaptic alpha-adrenoceptors which regulate [3H]-noradrenaline secretion in guinea-pig isolated urethra. Br J Pharmacol. 1992 Jan;105(1):142–146. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1992.tb14225.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blaxall H. S., Murphy T. J., Baker J. C., Ray C., Bylund D. B. Characterization of the alpha-2C adrenergic receptor subtype in the opossum kidney and in the OK cell line. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1991 Oct;259(1):323–329. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borowski E., Starke K., Ehrl H., Endo T. A comparison of pre- and postsynaptic effects of alpha-adrenolytic drugs in the pulmonary artery of the rabbit. Neuroscience. 1977;2(2):285–296. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(77)90095-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bylund D. B. Heterogeneity of alpha-2 adrenergic receptors. Pharmacol Biochem Behav. 1985 May;22(5):835–843. doi: 10.1016/0091-3057(85)90536-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bylund D. B., Ray-Prenger C., Murphy T. J. Alpha-2A and alpha-2B adrenergic receptor subtypes: antagonist binding in tissues and cell lines containing only one subtype. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1988 May;245(2):600–607. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bylund D. B. Subtypes of alpha 2-adrenoceptors: pharmacological and molecular biological evidence converge. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 1988 Oct;9(10):356–361. doi: 10.1016/0165-6147(88)90254-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cambridge D. UK-14,304, a potent and selective alpha2-agonist for the characterisation of alpha-adrenoceptor subtypes. Eur J Pharmacol. 1981 Jul 10;72(4):413–415. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(81)90588-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheung Y. D., Barnett D. B., Nahorski S. R. [3H]Rauwolscine and [3H]yohimbine binding to rat cerebral and human platelet membranes: possible heterogeneity of alpha 2-adrenoceptors. Eur J Pharmacol. 1982 Oct 15;84(1-2):79–85. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(82)90159-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Connaughton S., Docherty J. R. Functional evidence for heterogeneity of peripheral prejunctional alpha 2-adrenoceptors. Br J Pharmacol. 1990 Oct;101(2):285–290. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1990.tb12702.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Docherty J. R. An investigation of presynaptic alpha-adrenoceptor subtypes in the pithed rat heart and in the rat isolated vas deferens. Br J Pharmacol. 1984 May;82(1):15–23. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1984.tb16437.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Docherty J. R. The pharmacology of alpha 1- and alpha 2-adrenoceptors: evidence for and against a further subdivision. Pharmacol Ther. 1989;44(2):241–284. doi: 10.1016/0163-7258(89)90067-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doxey J. C., Everitt J. Inhibitory effects of clonidine on responses to sympathetic nerve stimulation in the pithed rat. Br J Pharmacol. 1977 Dec;61(4):559–566. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1977.tb07548.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Filinger E. J., Langer S. Z., Perec C. J., Stefano F. J. Evidence for the presynaptic location of the alpha-adrenoceptors which regulate noradrenaline release in the rat submaxillary gland. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1978 Aug;304(1):21–26. doi: 10.1007/BF00501373. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gleason M. M., Hieble J. P. Ability of SK&F 104078 and SK&F 104856 to identify alpha-2 adrenoceptor subtypes in NCB20 cells and guinea pig lung. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1991 Dec;259(3):1124–1132. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gobbi M., Frittoli E., Mennini T. The modulation of [3H]noradrenaline and [3H]serotonin release from rat brain synaptosomes is not mediated by the alpha 2B-adrenoceptor subtype. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1990 Oct;342(4):382–386. doi: 10.1007/BF00169453. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guimarães S., Paiva M. Q., Moura D. Alpha 2-adrenoceptor-mediated responses to so-called selective alpha 1-adrenoceptor agonists after partial blockade of alpha 1-adrenoceptors. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1987 Apr;335(4):397–402. doi: 10.1007/BF00165554. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Göthert M., Molderings G. J. Involvement of presynaptic imidazoline receptors in the alpha 2-adrenoceptor-independent inhibition of noradrenaline release by imidazoline derivatives. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1991 Mar;343(3):271–282. doi: 10.1007/BF00251126. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kobinger W., Pichler L. Investigation into different types of post- and presynaptic alpha-adrenoceptors at cardiovascular sites in rats. Eur J Pharmacol. 1980 Aug 8;65(4):393–402. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(80)90343-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Langer S. Z. Presynaptic regulation of catecholamine release. Biochem Pharmacol. 1974 Jul 1;23(13):1793–1800. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(74)90187-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lanier S. M., Downing S., Duzic E., Homcy C. J. Isolation of rat genomic clones encoding subtypes of the alpha 2-adrenergic receptor. Identification of a unique receptor subtype. J Biol Chem. 1991 Jun 5;266(16):10470–10478. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lattimer N., Rhodes K. F. A difference in the affinity of some selective alpha 2-adrenoceptor antagonists when compared on isolated vasa deferentia of rat and rabbit. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1985 May;329(3):278–281. doi: 10.1007/BF00501880. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Limberger N., Mayer A., Zier G., Valenta B., Starke K., Singer E. A. Estimation of pA2 values at presynaptic alpha 2-autoreceptors in rabbit and rat brain cortex in the absence of autoinhibition. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1989 Dec;340(6):639–647. doi: 10.1007/BF00717739. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Limberger N., Späth L., Starke K. Subclassification of the presynaptic alpha 2-autoreceptors in rabbit brain cortex. Br J Pharmacol. 1991 May;103(1):1251–1255. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1991.tb12332.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Majewski H., Rand M. J., Tung L. H. Activation of prejunctional beta-adrenoceptors in rat atria by adrenaline applied exogenously or released as a co-transmitter. Br J Pharmacol. 1981 Jul;73(3):669–679. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1981.tb16802.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michel A. D., Loury D. N., Whiting R. L. Differences between the alpha 2-adrenoceptor in rat submaxillary gland and the alpha 2A-and alpha 2B-adrenoceptor subtypes. Br J Pharmacol. 1989 Nov;98(3):890–897. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1989.tb14618.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Molderings G. J., Hentrich F., Göthert M. Pharmacological characterization of the imidazoline receptor which mediates inhibition of noradrenaline release in the rabbit pulmonary artery. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1991 Dec;344(6):630–638. doi: 10.1007/BF00174746. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paris H., Voisin T., Remaury A., Rouyer-Fessard C., Daviaud D., Langin D., Laburthe M. Alpha-2 adrenoceptor in rat jejunum epithelial cells: characterization with [3H]RX821002 and distribution along the villus-crypt axis. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1990 Sep;254(3):888–893. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reichenbacher D., Reimann W., Starke K. alpha-Adrenoceptor-mediated inhibition of noradrenaline release in rabbit brain cortex slices. Receptor properties and role of the biophase concentration of noradrenaline. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1982 Apr;319(1):71–77. doi: 10.1007/BF00491481. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruffolo R. R., Jr, Nichols A. J., Stadel J. M., Hieble J. P. Structure and function of alpha-adrenoceptors. Pharmacol Rev. 1991 Dec;43(4):475–505. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shinozuka K., Sedaa K. O., Bjur R. A., Westfall D. P. Participation by purines in the modulation of norepinephrine release by methoxamine. Eur J Pharmacol. 1991 Jan 17;192(3):431–434. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(91)90236-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simonneaux V., Ebadi M., Bylund D. B. Identification and characterization of alpha 2D-adrenergic receptors in bovine pineal gland. Mol Pharmacol. 1991 Aug;40(2):235–241. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singer E. A. Transmitter release from brain slices elicited by single pulses: a powerful method to study presynaptic mechanisms. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 1988 Aug;9(8):274–276. doi: 10.1016/0165-6147(88)90004-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith K., Connaughton S., Docherty J. R. Investigations of prejunctional alpha 2-adrenoceptors in rat atrium, vas deferens and submandibular gland. Eur J Pharmacol. 1992 Feb 11;211(2):251–256. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(92)90536-d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Starke K. Alpha sympathomimetic inhibition of adrenergic and cholinergic transmission in the rabbit heart. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1972;274(1):18–45. doi: 10.1007/BF00501004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Starke K., Endo T., Taube H. D. Relative pre- and postsynaptic potencies of alpha-adrenoceptor agonists in the rabbit pulmonary artery. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1975;291(1):55–78. doi: 10.1007/BF00510821. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Starke K. Presynaptic alpha-autoreceptors. Rev Physiol Biochem Pharmacol. 1987;107:73–146. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Story D. F., Standford-Starr C. A., Rand M. J. Evidence for the involvement of alpha 1-adrenoceptors in negative feedback regulation of noradrenergic transmitter release in rat atria. Clin Sci (Lond) 1985;68 (Suppl 10):111s–115s. doi: 10.1042/cs068s111. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weitzell R., Tanaka T., Starke K. Pre- and postsynaptic effects of yohimbine stereoisomers on noradrenergic transmission in the pulmonary artery of the rabbit. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1979 Aug;308(2):127–136. doi: 10.1007/BF00499054. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson V. G., Brown C. M., McGrath J. C. Are there more than two types of alpha-adrenoceptors involved in physiological responses? Exp Physiol. 1991 May;76(3):317–346. doi: 10.1113/expphysiol.1991.sp003501. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young P., Berge J., Chapman H., Cawthorne M. A. Novel alpha 2-adrenoceptor antagonists show selectivity for alpha 2A- and alpha 2B-adrenoceptor subtypes. Eur J Pharmacol. 1989 Sep 22;168(3):381–386. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(89)90801-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


