Abstract
1 The aims of the present study were to characterize the cyclic nucleotide phosphodiesterase (PDE) isoenzyme activities present in human bronchi and to examine the ability of selective isoenzyme inhibitors to relax histamine and methacholine precontracted preparations of human bronchi. 2 Three separations of pooled human bronchial tissue samples were performed. Ion-exchange chromatography showed that the soluble fraction of human bronchial preparations contains PDE I, II, III, IV and V isoenzyme activities. Multiple forms of PDE I and PDE IV were observed and PDE IV was the main cyclic AMP hydrolytic activity. 3 3-Isobutyl-l-methylxanthine (IBMX) non-selectively inhibited all separated isoenzyme activities. Zaprinast selectively inhibited PDE V, but also effectively inhibited one of the two PDE I isoforms identified. The PDE IV selective inhibitors rolipram and RO-201724, inhibited the PDE IV activities as did the dual PDE III/IV inhibitor, Org 30029. Org 9935, a PDE III selective inhibitor, potently attenuated part of the PDE IV activity peak in one of three separations performed, indicating that some PDE III activity may co-elute with PDE IV under the experimental conditions employed. 4 PDE IV-selective (rolipram), PDE III-selective (Org 9935) and dual PDE III/IV (Org 30029) inhibitors were effective relaxants of human bronchial smooth muscle. The PDE V/PDE I inhibitor, zaprinast was relatively ineffective. 5 The present study demonstrates in human bronchi, as in animal airways smooth muscle, that inhibitors of PDE III, PDEIV and dual PDE III/IV have potentially useful bronchodilator activity and are worthy of further consideration as anti-asthma drugs.
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Beavo J. A., Reifsnyder D. H. Primary sequence of cyclic nucleotide phosphodiesterase isozymes and the design of selective inhibitors. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 1990 Apr;11(4):150–155. doi: 10.1016/0165-6147(90)90066-H. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
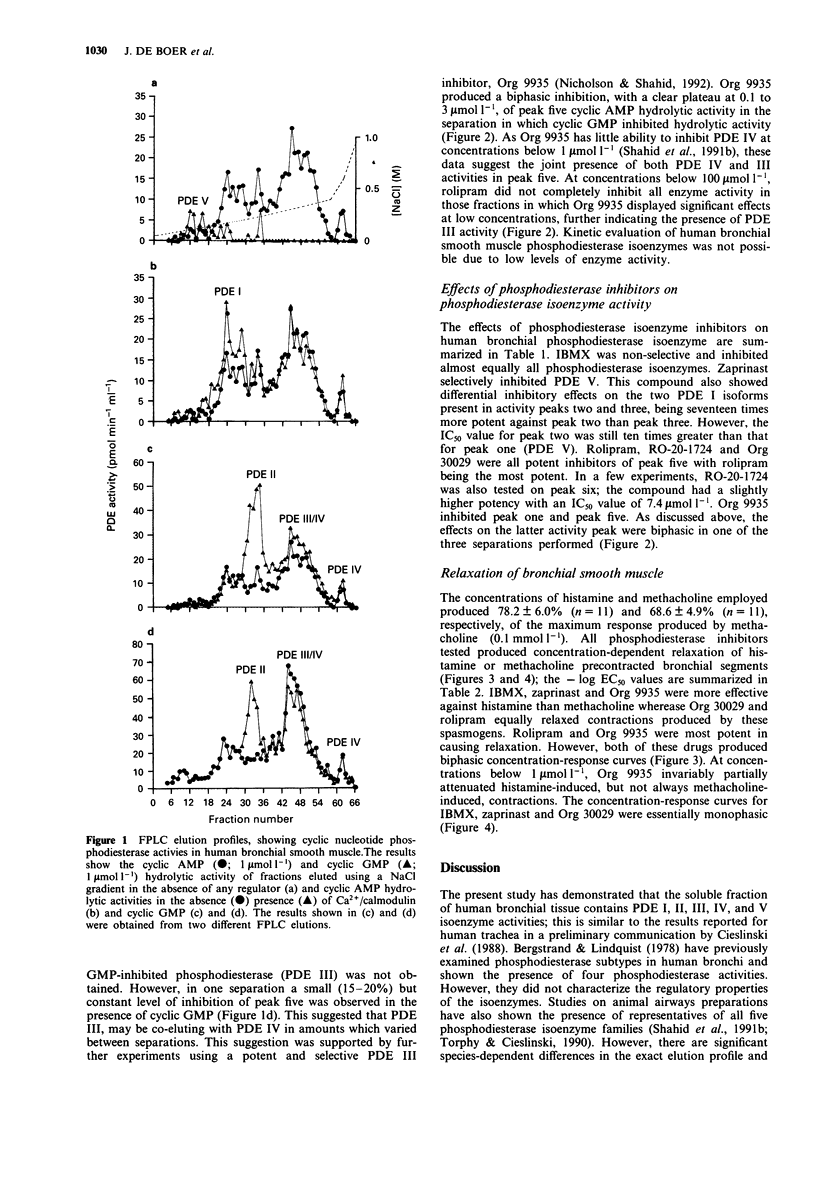
- Bergstrand H., Lundquist B. Partial purification and characterization of cyclic nucleotide phosphodiesterases from human bronchial tissue. Mol Cell Biochem. 1978 Oct 13;21(1):9–15. doi: 10.1007/BF00230191. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bode D. C., Kanter J. R., Brunton L. L. Cellular distribution of phosphodiesterase isoforms in rat cardiac tissue. Circ Res. 1991 Apr;68(4):1070–1079. doi: 10.1161/01.res.68.4.1070. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bosken C. H., Wiggs B. R., Paré P. D., Hogg J. C. Small airway dimensions in smokers with obstruction to airflow. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1990 Sep;142(3):563–570. doi: 10.1164/ajrccm/142.3.563. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dent G., Giembycz M. A., Rabe K. F., Barnes P. J. Inhibition of eosinophil cyclic nucleotide PDE activity and opsonised zymosan-stimulated respiratory burst by 'type IV'-selective PDE inhibitors. Br J Pharmacol. 1991 Jun;103(2):1339–1346. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1991.tb09790.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Downing S. J., Hollingsworth M. One way cross tolerance between cromakalim and salbutamol in the uterus of the rat in vivo. Br J Pharmacol. 1992 Jan;105(1):129–134. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1992.tb14223.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feth F., Rascher W., Michel M. C. Neuropeptide Y (NPY) receptors in HEL cells: comparison of binding and functional parameters for full and partial agonists and a non-peptide antagonist. Br J Pharmacol. 1992 Jan;105(1):71–76. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1992.tb14212.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hall I. P., Donaldson J., Hill S. J. Inhibition of histamine-stimulated inositol phospholipid hydrolysis by agents which increase cyclic AMP levels in bovine tracheal smooth muscle. Br J Pharmacol. 1989 Jun;97(2):603–613. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1989.tb11992.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hall I. P., Donaldson J., Hill S. J. Modulation of carbachol-induced inositol phosphate formation in bovine tracheal smooth muscle by cyclic AMP phosphodiesterase inhibitors. Biochem Pharmacol. 1990 Apr 15;39(8):1357–1363. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(90)90013-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hall I. P., Hill S. J. Beta-adrenoceptor stimulation inhibits histamine-stimulated inositol phospholipid hydrolysis in bovine tracheal smooth muscle. Br J Pharmacol. 1988 Dec;95(4):1204–1212. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1988.tb11757.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harris A. L., Connell M. J., Ferguson E. W., Wallace A. M., Gordon R. J., Pagani E. D., Silver P. J. Role of low Km cyclic AMP phosphodiesterase inhibition in tracheal relaxation and bronchodilation in the guinea pig. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1989 Oct;251(1):199–206. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lavan B. E., Lakey T., Houslay M. D. Resolution of soluble cyclic nucleotide phosphodiesterase isoenzymes, from liver and hepatocytes, identifies a novel IBMX-insensitive form. Biochem Pharmacol. 1989 Nov 15;38(22):4123–4136. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(89)90694-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Madison J. M., Brown J. K. Differential inhibitory effects of forskolin, isoproterenol, and dibutyryl cyclic adenosine monophosphate on phosphoinositide hydrolysis in canine tracheal smooth muscle. J Clin Invest. 1988 Oct;82(4):1462–1465. doi: 10.1172/JCI113752. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicholson C. D., Challiss R. A., Shahid M. Differential modulation of tissue function and therapeutic potential of selective inhibitors of cyclic nucleotide phosphodiesterase isoenzymes. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 1991 Jan;12(1):19–27. doi: 10.1016/0165-6147(91)90484-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nielson C. P., Vestal R. E., Sturm R. J., Heaslip R. Effects of selective phosphodiesterase inhibitors on the polymorphonuclear leukocyte respiratory burst. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1990 Nov;86(5):801–808. doi: 10.1016/s0091-6749(05)80186-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Purvis K., Rui H. High-affinity, calmodulin-dependent isoforms of cyclic nucleotide phosphodiesterase in rat testis. Methods Enzymol. 1988;159:675–685. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(88)59063-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reeves M. L., Leigh B. K., England P. J. The identification of a new cyclic nucleotide phosphodiesterase activity in human and guinea-pig cardiac ventricle. Implications for the mechanism of action of selective phosphodiesterase inhibitors. Biochem J. 1987 Jan 15;241(2):535–541. doi: 10.1042/bj2410535. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robicsek S. A., Blanchard D. K., Djeu J. Y., Krzanowski J. J., Szentivanyi A., Polson J. B. Multiple high-affinity cAMP-phosphodiesterases in human T-lymphocytes. Biochem Pharmacol. 1991 Jul 25;42(4):869–877. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(91)90047-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schneider H. H., Schmiechen R., Brezinski M., Seidler J. Stereospecific binding of the antidepressant rolipram to brain protein structures. Eur J Pharmacol. 1986 Aug 7;127(1-2):105–115. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(86)90210-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shahid M., Nicholson C. D. Comparison of cyclic nucleotide phosphodiesterase isoenzymes in rat and rabbit ventricular myocardium: positive inotropic and phosphodiesterase inhibitory effects of Org 30029, milrinone and rolipram. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1990 Dec;342(6):698–705. doi: 10.1007/BF00175715. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shahid M., van Amsterdam R. G., de Boer J., ten Berge R. E., Nicholson C. D., Zaagsma J. The presence of five cyclic nucleotide phosphodiesterase isoenzyme activities in bovine tracheal smooth muscle and the functional effects of selective inhibitors. Br J Pharmacol. 1991 Oct;104(2):471–477. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1991.tb12453.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharma R. K., Wang J. H. Regulation of cAMP concentration by calmodulin-dependent cyclic nucleotide phosphodiesterase. Biochem Cell Biol. 1986 Nov;64(11):1072–1080. doi: 10.1139/o86-142. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Souness J. E., Carter C. M., Diocee B. K., Hassall G. A., Wood L. J., Turner N. C. Characterization of guinea-pig eosinophil phosphodiesterase activity. Assessment of its involvement in regulating superoxide generation. Biochem Pharmacol. 1991 Jul 25;42(4):937–945. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(91)90056-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Torphy T. J. Action of mediators on airway smooth muscle: functional antagonism as a mechanism for bronchodilator drugs. Agents Actions Suppl. 1988;23:37–53. doi: 10.1007/978-3-0348-9156-1_2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Torphy T. J., Burman M., Huang L. B., Tucker S. S. Inhibition of the low km cyclic AMP phosphodiesterase in intact canine trachealis by SK&F 94836: mechanical and biochemical responses. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1988 Sep;246(3):843–850. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Torphy T. J., Cieslinski L. B. Characterization and selective inhibition of cyclic nucleotide phosphodiesterase isozymes in canine tracheal smooth muscle. Mol Pharmacol. 1990 Feb;37(2):206–214. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Torphy T. J., Undem B. J. Phosphodiesterase inhibitors: new opportunities for the treatment of asthma. Thorax. 1991 Jul;46(7):512–523. doi: 10.1136/thx.46.7.512. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- VAN ROSSUM J. M. Cumulative dose-response curves. II. Technique for the making of dose-response curves in isolated organs and the evaluation of drug parameters. Arch Int Pharmacodyn Ther. 1963;143:299–330. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Amsterdam R. G., Meurs H., Brouwer F., Postema J. B., Timmermans A., Zaagsma J. Role of phosphoinositide metabolism in functional antagonism of airway smooth muscle contraction by beta-adrenoceptor agonists. Eur J Pharmacol. 1989 May 11;172(2):175–183. doi: 10.1016/0922-4106(89)90008-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Amsterdam R. G., Meurs H., Ten Berge R. E., Veninga N. C., Brouwer F., Zaagsma J. Role of phosphoinositide metabolism in human bronchial smooth muscle contraction and in functional antagonism by beta-adrenoceptor agonists. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1990 Nov;142(5):1124–1128. doi: 10.1164/ajrccm/142.5.1124. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


