Abstract
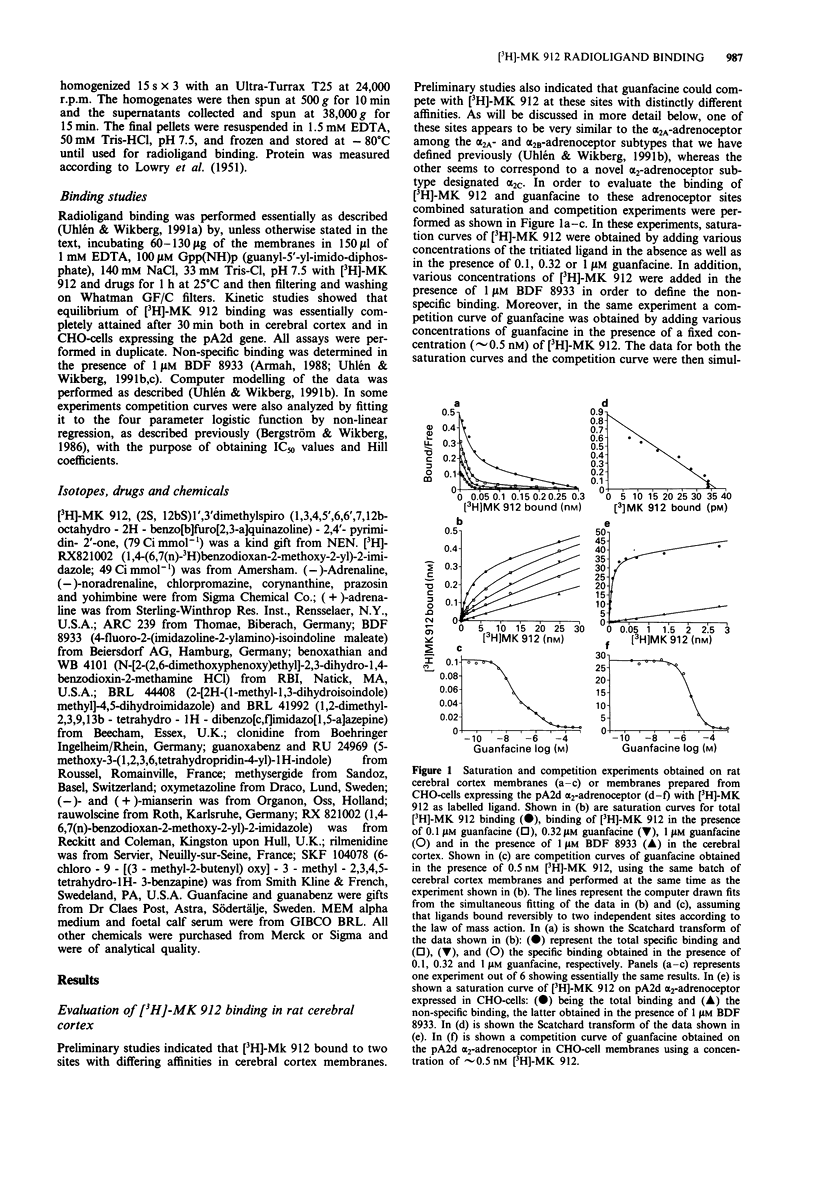
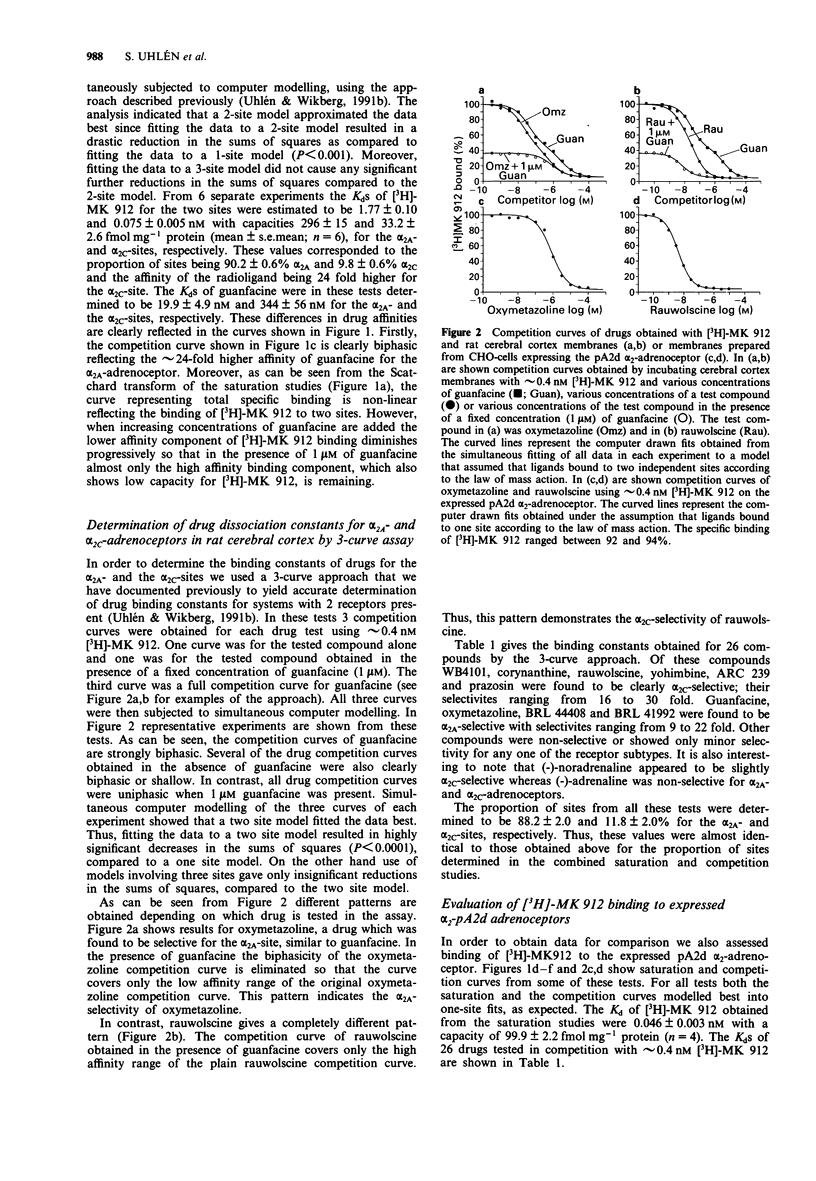
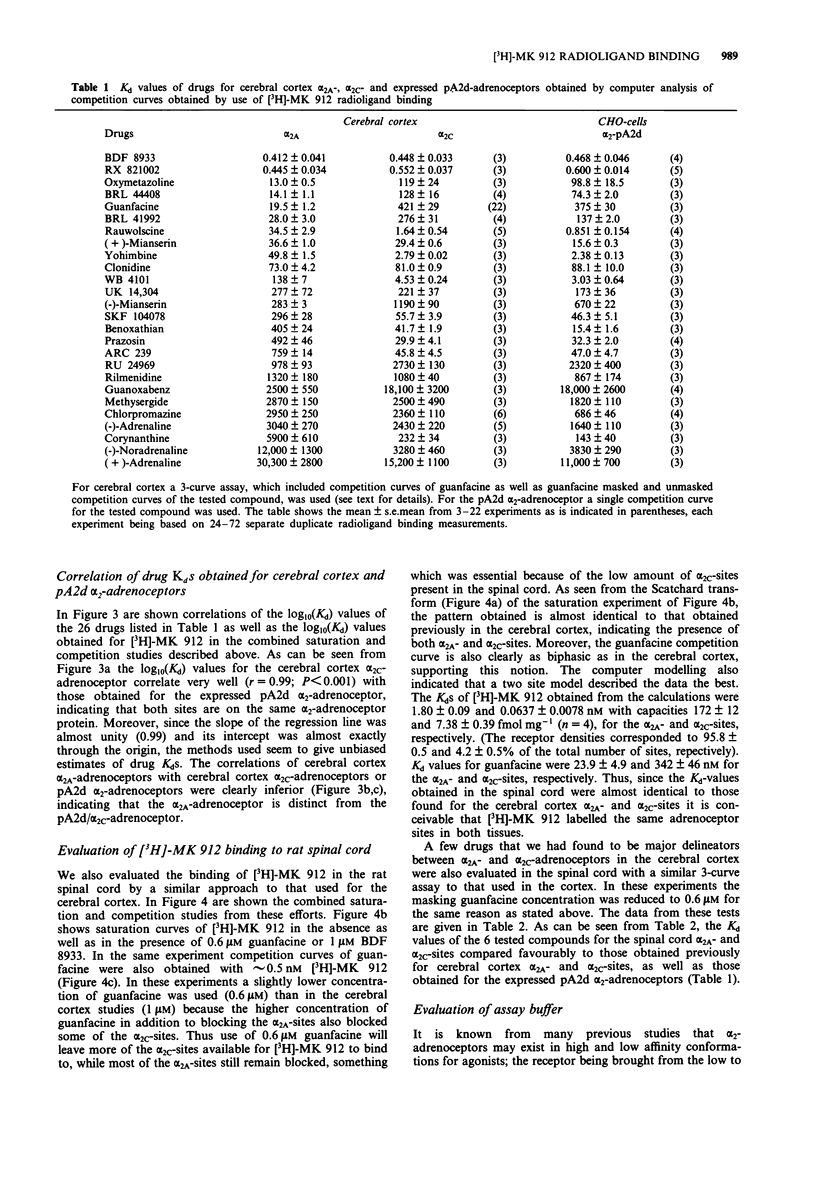
1. Simultaneous computer modelling of control and guanfacine-masked [3H]-MK 912 saturation curves as well as guanfacine competition curves revealed that the drugs bound to two alpha 2-adrenoceptor subtypes in the rat cerebral cortex with very different selectivities. These alpha 2-adrenoceptor subtypes were designated alpha 2A and alpha 2C. The Kd value of [3H]-MK 912 for the alpha 2A-subtype was 1.77 nM and for the alpha 2C-subtype 0.075 nM; the receptor sites showing capacities 296 and 33 fmol mg-1 protein, respectively. The Kds of guanfacine were 19.9 and 344 nM, respectively. 2. Binding constants of 26 compounds for the two rat cerebral cortex alpha 2-adrenoceptor subtypes were determined by simultaneous computer modelling of control and guanfacine-masked drug competition curves as well as plain guanfacine competition curves using [3H]-MK912 as labelled ligand (i.e. a '3-curve assay'). Of the tested drugs WB4101, corynanthine, rauwolscine, yohimbine, ARC 239 and prazosin were found to be clearly alpha 2C-selective with selectivities ranging from 16 to 30 fold whereas guanfacine, oxymetazoline, BRL 44408 and BRL 41992 were found to be alpha 2A-selective with selectivities ranging from 9 to 22 fold. 3. The Kds of compounds obtained for the cerebral cortex alpha 2C-adrenoceptors showed an almost 1:1 correlation with the corresponding Kds for alpha 2-adrenoceptors expressed by the pA2d-gene (the rat 'alpha 2-C4' adrenoceptor) in CHO-cells. The cerebral cortex alpha 2A-adrenoceptors did not correlate well with the pA2d alpha 2-adrenoceptor Kds. 4. In the rat spinal cord [3H]-MK 912 bound to alpha 2A- and alpha 2C-adrenoceptor sites with similar affinities as in the cerebral cortex and with densities 172 and 7.4 fmol mg-1 protein, respectively. Drug affinities for some compounds showing major selectivity for alpha 2A- and alpha 2C-adrenoceptors were fully compatible with the notion that the spinal cord sites were alpha 2A- and alpha 2C-adrenoceptors.
Full text
PDF
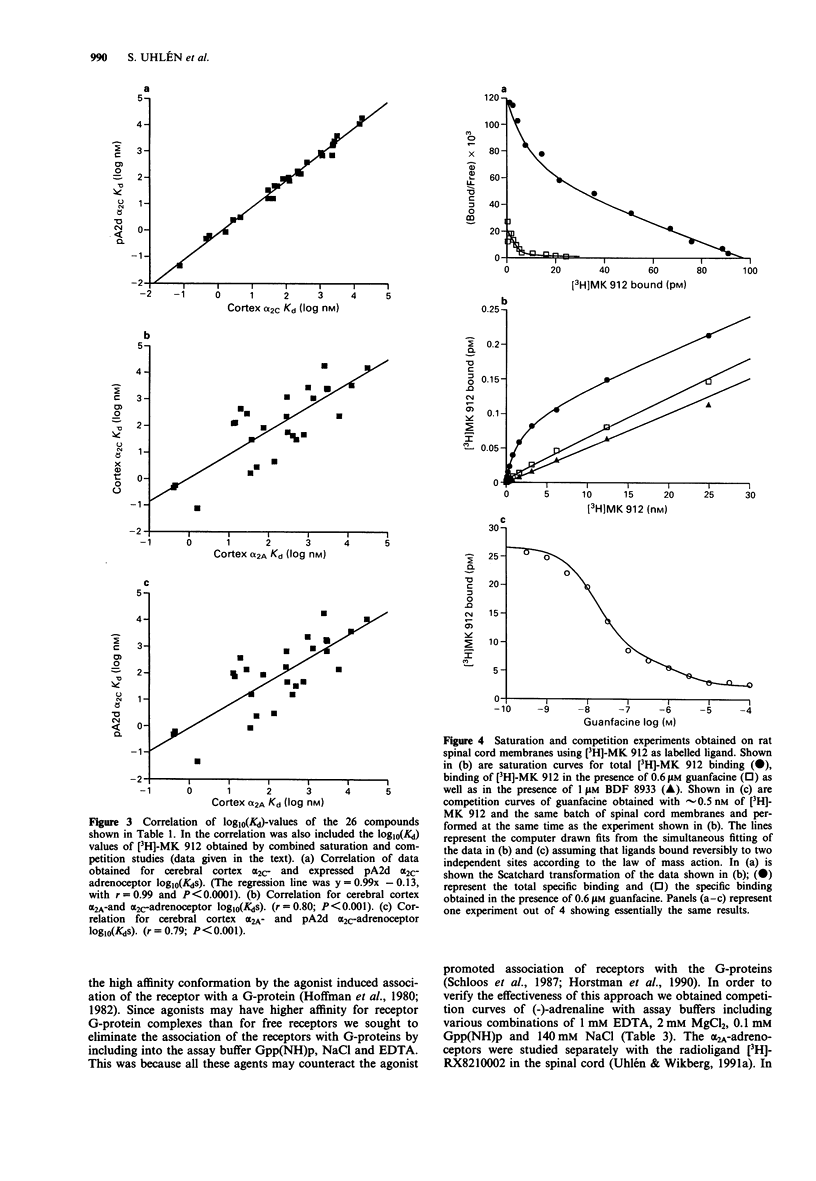




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bergström A., Wikberg J. E. Structural and pharmacological differences between codfish and rat brain alpha 1-adrenergic receptors revealed by photoaffinity labeling with 125I-APDQ. Acta Pharmacol Toxicol (Copenh) 1986 Feb;58(2):148–155. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0773.1986.tb00085.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berthelsen S., Pettinger W. A. A functional basis for classification of alpha-adrenergic receptors. Life Sci. 1977 Sep 1;21(5):595–606. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(77)90066-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blaxall H. S., Murphy T. J., Baker J. C., Ray C., Bylund D. B. Characterization of the alpha-2C adrenergic receptor subtype in the opossum kidney and in the OK cell line. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1991 Oct;259(1):323–329. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Broadhurst A. M., Alexander B. S., Wood M. D. Heterogeneous 3H-rauwolscine binding sites in rat cortex: two alpha 2-adrenoceptor subtypes or an additional non-adrenergic interaction? Life Sci. 1988;43(1):83–92. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(88)90240-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown C. M., MacKinnon A. C., McGrath J. C., Spedding M., Kilpatrick A. T. Heterogeneity of alpha 2-adrenoceptors in rat cortex but not human platelets can be defined by 8-OH-DPAT, RU 24969 and methysergide. Br J Pharmacol. 1990 Mar;99(3):481–486. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1990.tb12954.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bylund D. B. Heterogeneity of alpha-2 adrenergic receptors. Pharmacol Biochem Behav. 1985 May;22(5):835–843. doi: 10.1016/0091-3057(85)90536-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bylund D. B., Ray-Prenger C., Murphy T. J. Alpha-2A and alpha-2B adrenergic receptor subtypes: antagonist binding in tissues and cell lines containing only one subtype. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1988 May;245(2):600–607. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chalberg S. C., Duda T., Rhine J. A., Sharma R. K. Molecular cloning, sequencing and expression of an alpha 2-adrenergic receptor complementary DNA from rat brain. Mol Cell Biochem. 1990 Sep 21;97(2):161–172. doi: 10.1007/BF00221058. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harrison J. K., D'Angelo D. D., Zeng D. W., Lynch K. R. Pharmacological characterization of rat alpha 2-adrenergic receptors. Mol Pharmacol. 1991 Sep;40(3):407–412. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harrison J. K., Pearson W. R., Lynch K. R. Molecular characterization of alpha 1- and alpha 2-adrenoceptors. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 1991 Feb;12(2):62–67. doi: 10.1016/0165-6147(91)90499-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoffman B. B., Michel T., Brenneman T. B., Lefkowitz R. J. Interactions of agonists with platelet alpha 2-adrenergic receptors. Endocrinology. 1982 Mar;110(3):926–932. doi: 10.1210/endo-110-3-926. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoffman B. B., Michel T., Kilpatrick D. M., Lefkowitz R. J., Tolbert M. E., Gilman H., Fain J. N. Agonist versus antagonist binding to alpha-adrenergic receptors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Aug;77(8):4569–4573. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.8.4569. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horstman D. A., Brandon S., Wilson A. L., Guyer C. A., Cragoe E. J., Jr, Limbird L. E. An aspartate conserved among G-protein receptors confers allosteric regulation of alpha 2-adrenergic receptors by sodium. J Biol Chem. 1990 Dec 15;265(35):21590–21595. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kobilka B. K., Matsui H., Kobilka T. S., Yang-Feng T. L., Francke U., Caron M. G., Lefkowitz R. J., Regan J. W. Cloning, sequencing, and expression of the gene coding for the human platelet alpha 2-adrenergic receptor. Science. 1987 Oct 30;238(4827):650–656. doi: 10.1126/science.2823383. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lands A. M., Luduena F. P., Buzzo H. J. Differentiation of receptors responsive to isoproterenol. Life Sci. 1967 Nov 1;6(21):2241–2249. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(67)90031-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lanier S. M., Downing S., Duzic E., Homcy C. J. Isolation of rat genomic clones encoding subtypes of the alpha 2-adrenergic receptor. Identification of a unique receptor subtype. J Biol Chem. 1991 Jun 5;266(16):10470–10478. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lomasney J. W., Lorenz W., Allen L. F., King K., Regan J. W., Yang-Feng T. L., Caron M. G., Lefkowitz R. J. Expansion of the alpha 2-adrenergic receptor family: cloning and characterization of a human alpha 2-adrenergic receptor subtype, the gene for which is located on chromosome 2. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Jul;87(13):5094–5098. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.13.5094. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lorenz W., Lomasney J. W., Collins S., Regan J. W., Caron M. G., Lefkowitz R. J. Expression of three alpha 2-adrenergic receptor subtypes in rat tissues: implications for alpha 2 receptor classification. Mol Pharmacol. 1990 Nov;38(5):599–603. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maura G., Gemignani A., Raiteri M. Alpha 2-adrenoceptors in rat hypothalamus and cerebral cortex: functional evidence for pharmacologically distinct subpopulations. Eur J Pharmacol. 1985 Oct 22;116(3):335–339. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(85)90173-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murphy T. J., Bylund D. B. Characterization of alpha-2 adrenergic receptors in the OK cell, an opossum kidney cell line. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1988 Feb;244(2):571–578. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pettibone D. J., Flagg S. D., Totaro J. A., Clineschmidt B. V., Huff J. R., Young S. D., Chen R. [3H]L-657,743 (MK-912): a new, high affinity, selective radioligand for brain alpha 2-adrenoceptors. Life Sci. 1989;44(7):459–467. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(89)90461-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raiteri M., Maura G., Gemignani A., Pittaluga A. Differential blockade by (-)mianserin of the alpha 2-adrenoceptors mediating inhibition of noradrenaline and serotonin release from rat brain synaptosomes. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1983 Mar;322(2):180–182. doi: 10.1007/BF00512394. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Regan J. W., Kobilka T. S., Yang-Feng T. L., Caron M. G., Lefkowitz R. J., Kobilka B. K. Cloning and expression of a human kidney cDNA for an alpha 2-adrenergic receptor subtype. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Sep;85(17):6301–6305. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.17.6301. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schloos J., Wellstein A., Palm D. Agonist binding at alpha 2-adrenoceptors of human platelets using 3H-UK-14,304: regulation by Gpp(NH)p and cations. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1987 Jul;336(1):48–59. doi: 10.1007/BF00177750. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uhlén S., Persson M. L., Alari L., Post C., Axelsson K. L., Wikberg J. E. Antinociceptive actions of alpha 2-adrenoceptor agonists in the rat spinal cord: evidence for antinociceptive alpha 2-adrenoceptor subtypes and dissociation of antinociceptive alpha 2-adrenoceptors from cyclic AMP. J Neurochem. 1990 Dec;55(6):1905–1914. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1990.tb05775.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uhlén S., Wikberg J. E. Delineation of rat kidney alpha 2A- and alpha 2B-adrenoceptors with [3H]RX821002 radioligand binding: computer modelling reveals that guanfacine is an alpha 2A-selective compound. Eur J Pharmacol. 1991 Sep 17;202(2):235–243. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(91)90299-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uhlén S., Wikberg J. E. Delineation of three pharmacological subtypes of alpha 2-adrenoceptor in the rat kidney. Br J Pharmacol. 1991 Nov;104(3):657–664. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1991.tb12485.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uhlén S., Wikberg J. E. Rat spinal cord alpha 2-adrenoceptors are of the alpha 2A-subtype: comparison with alpha 2A- and alpha 2B-adrenoceptors in rat spleen, cerebral cortex and kidney using 3H-RX821002 ligand binding. Pharmacol Toxicol. 1991 Nov;69(5):341–350. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0773.1991.tb01308.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Voigt M. M., McCune S. K., Kanterman R. Y., Felder C. C. The rat alpha 2-C4 adrenergic receptor gene encodes a novel pharmacological subtype. FEBS Lett. 1991 Jan 14;278(1):45–50. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(91)80080-m. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wikberg J. E. Pharmacological classification of adrenergic alpha receptors in the guinea pig. Nature. 1978 May 11;273(5658):164–166. doi: 10.1038/273164a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wikberg J. E., Uhlén S. Further characterization of the guinea pig cerebral cortex idazoxan receptor: solubilization, distinction from the imidazole site, and demonstration of cirazoline as an idazoxan receptor-selective drug. J Neurochem. 1990 Jul;55(1):192–203. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1990.tb08838.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young P., Berge J., Chapman H., Cawthorne M. A. Novel alpha 2-adrenoceptor antagonists show selectivity for alpha 2A- and alpha 2B-adrenoceptor subtypes. Eur J Pharmacol. 1989 Sep 22;168(3):381–386. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(89)90801-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zeng D. W., Harrison J. K., D'Angelo D. D., Barber C. M., Tucker A. L., Lu Z. H., Lynch K. R. Molecular characterization of a rat alpha 2B-adrenergic receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Apr;87(8):3102–3106. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.8.3102. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zeng D. W., Lynch K. R. Distribution of alpha 2-adrenergic receptor mRNAs in the rat CNS. Brain Res Mol Brain Res. 1991 Jun;10(3):219–225. doi: 10.1016/0169-328x(91)90064-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


