Abstract
1. It has been demonstrated previously that conversion of big endothelin-1 (bET-1) to endothelin-1 (ET-1) is inhibited in vitro and in vivo by phosphoramidon. In addition, ET-1 binding sites and mRNA have been shown within the brain. Here we expand upon our previous observation that rat brain contains phosphoramidon-inhibitable endothelin converting enzyme (ECE) and show that this activity is not uniformly distributed throughout the brain. 2. ECE activity was detected by a bioassay which depended upon the 10,000 fold difference in potency between bET-1 and ET-1 as stimulants of guanosine 3':5'-cyclic monophosphate (cyclic GMP) accumulation in kidney epithelial (PK1) cells of the pig. Data were confirmed by specific enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) employing antibody directed against ET-1/3(17-21). 3. Following homogenization of the whole brain and ultracentrifugation the 100,000 g pellet contained greater than 4 times more ECE activity than the cytosol. Washing of the pellet with KCl (1 M) and extraction with the detergent CHAPS (20 mM) revealed a phosphoramidon-inhibitable ECE within the residual particulate fraction (nominally classified as the cytoskeletal fraction). Phosphoramidon (IC50, approx. 5 microM) or EDTA inhibited the conversion of bET-1 to ET-1 by the cytoskeletal fraction of rat brain by more than 60%.2+ 4. Following dissection of rat brain into olfactory bulb, cerebral cortex, striatum, hippocampus, cerebellum, midbrain (including thalamus), hypothalamus and medulla oblongata (including pons) the greatest ECE was detected in the hypothalamus and medulla oblongata.(ABSTRACT TRUNCATED AT 250 WORDS)
Full text
PDF

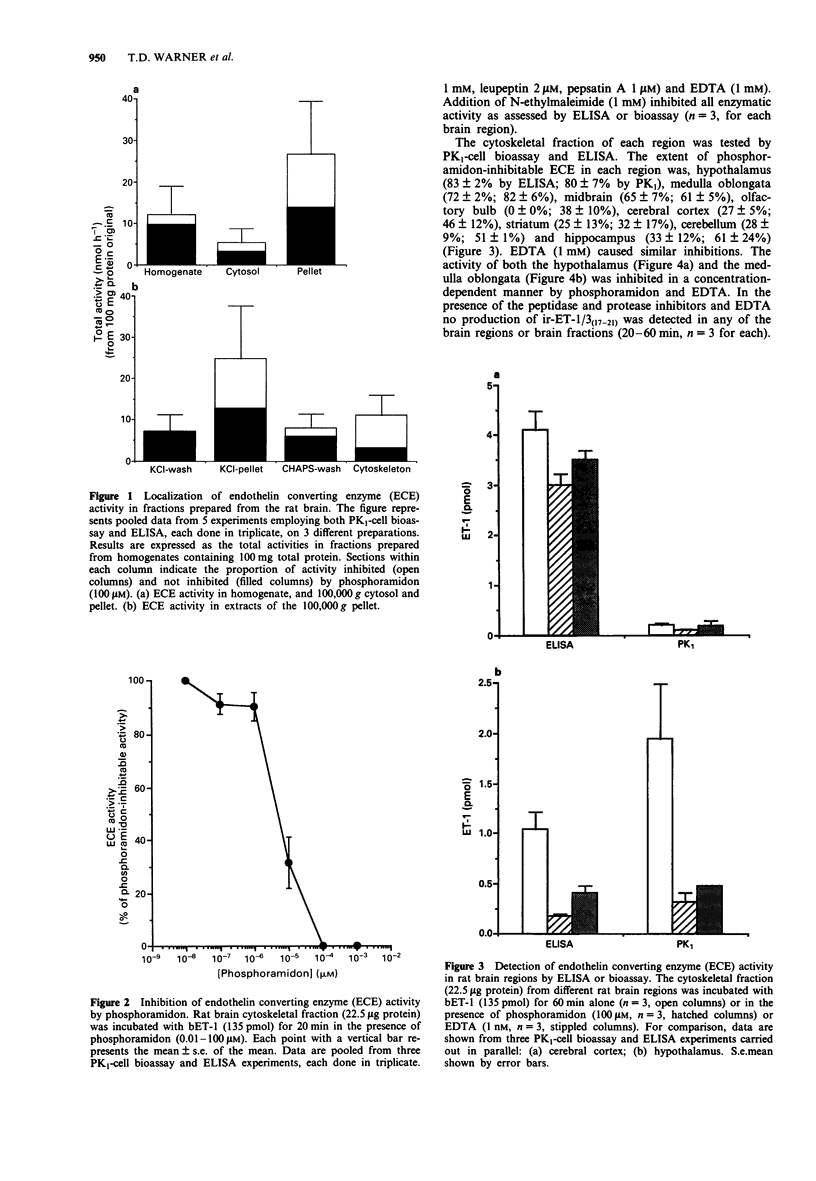
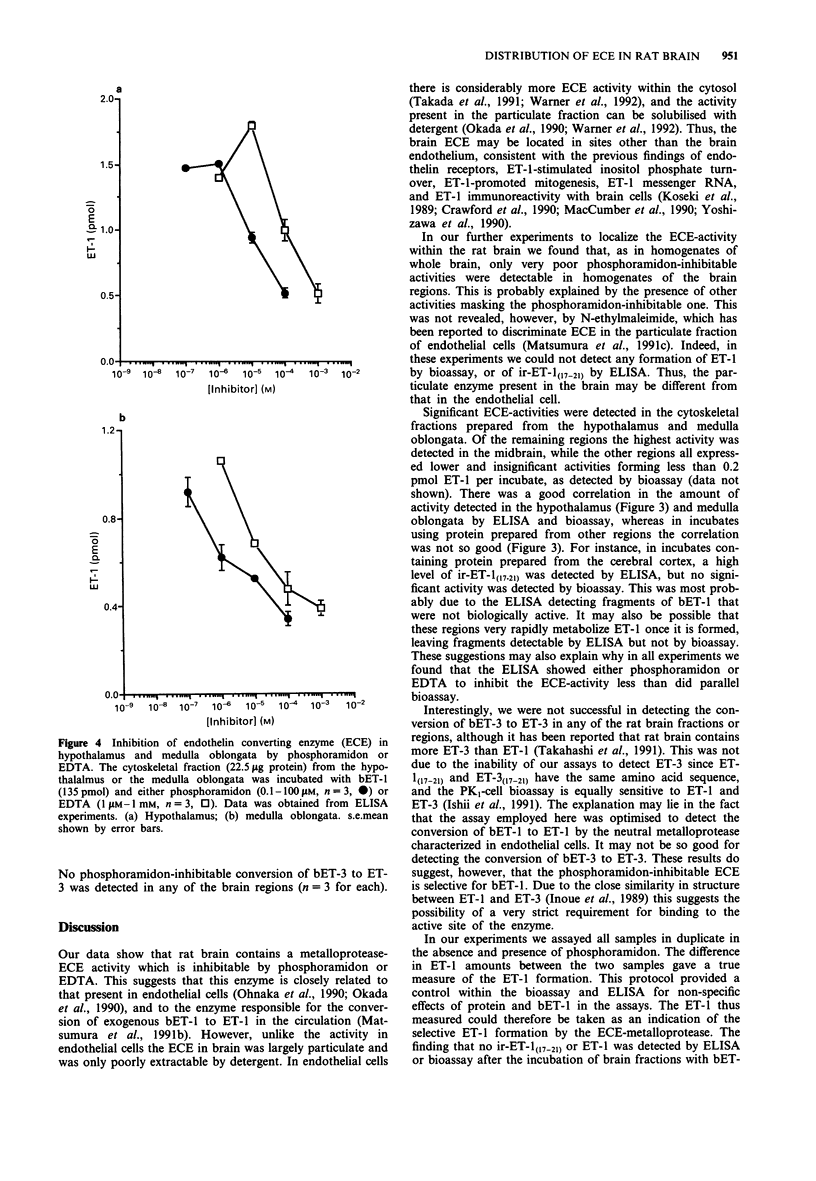

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Crawford M. L., Hiley C. R., Young J. M. Characteristics of endothelin-1 and endothelin-3 stimulation of phosphoinositide breakdown differ between regions of guinea-pig and rat brain. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1990 Mar;341(3):268–271. doi: 10.1007/BF00169742. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Förstermann U., Gorsky L. D., Pollock J. S., Schmidt H. H., Heller M., Murad F. Regional distribution of EDRF/NO-synthesizing enzyme(s) in rat brain. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1990 Apr 30;168(2):727–732. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(90)92382-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glowinski J., Iversen L. L. Regional studies of catecholamines in the rat brain. I. The disposition of [3H]norepinephrine, [3H]dopamine and [3H]dopa in various regions of the brain. J Neurochem. 1966 Aug;13(8):655–669. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1966.tb09873.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hashim M. A., Tadepalli A. S. Functional evidence for the presence of a phosphoramidon-sensitive enzyme in rat brain that converts big endothelin-1 to endothelin-1. Life Sci. 1991;49(24):PL207–PL211. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(91)90491-s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hisaki K., Matsumura Y., Ikegawa R., Nishiguchi S., Hayashi K., Takaoka M., Morimoto S. Evidence for phosphoramidon-sensitive conversion of big endothelin-1 to endothelin-1 in isolated rat mesenteric artery. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1991 Jun 28;177(3):1127–1132. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(91)90656-r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ikegawa R., Matsumura Y., Tsukahara Y., Takaoka M., Morimoto S. Phosphoramidon, a metalloproteinase inhibitor, suppresses the secretion of endothelin-1 from cultured endothelial cells by inhibiting a big endothelin-1 converting enzyme. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1990 Sep 14;171(2):669–675. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(90)91198-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inoue A., Yanagisawa M., Kimura S., Kasuya Y., Miyauchi T., Goto K., Masaki T. The human endothelin family: three structurally and pharmacologically distinct isopeptides predicted by three separate genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Apr;86(8):2863–2867. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.8.2863. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishii K., Warner T. D., Sheng H., Murad F. Endothelin-1 stimulates cyclic GMP formation in porcine kidney epithelial cells via activation of the L-arginine-dependent soluble guanylate cyclase pathway. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol. 1991;17 (Suppl 7):S246–S250. doi: 10.1097/00005344-199100177-00071. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koseki C., Imai M., Hirata Y., Yanagisawa M., Masaki T. Autoradiographic distribution in rat tissues of binding sites for endothelin: a neuropeptide? Am J Physiol. 1989 Apr;256(4 Pt 2):R858–R866. doi: 10.1152/ajpregu.1989.256.4.R858. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lecci A., Maggi C. A., Rovero P., Giachetti A., Meli A. Effect of endothelin-1, endothelin-3 and C-terminal hexapeptide, endothelin (16-21) on motor activity in rats. Neuropeptides. 1990 May;16(1):21–24. doi: 10.1016/0143-4179(90)90025-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee M. E., de la Monte S. M., Ng S. C., Bloch K. D., Quertermous T. Expression of the potent vasoconstrictor endothelin in the human central nervous system. J Clin Invest. 1990 Jul;86(1):141–147. doi: 10.1172/JCI114677. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacCumber M. W., Ross C. A., Snyder S. H. Endothelin in brain: receptors, mitogenesis, and biosynthesis in glial cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Mar;87(6):2359–2363. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.6.2359. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsumura Y., Hisaki K., Takaoka M., Morimoto S. Phosphoramidon, a metalloproteinase inhibitor, suppresses the hypertensive effect of big endothelin-1. Eur J Pharmacol. 1990 Aug 21;185(1):103–106. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(90)90216-s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsumura Y., Ikegawa R., Tsukahara Y., Takaoka M., Morimoto S. Conversion of big endothelin-1 to endothelin-1 by two-types of metalloproteinases of cultured porcine vascular smooth muscle cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1991 Aug 15;178(3):899–905. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(91)90976-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsumura Y., Ikegawa R., Tsukahara Y., Takaoka M., Morimoto S. N-ethylmaleimide differentiates endothelin converting activity by two types of metalloproteinases derived from vascular endothelial cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1991 Jul 31;178(2):531–538. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(91)90140-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohnaka K., Takayanagi R., Yamauchi T., Okazaki H., Ohashi M., Umeda F., Nawata H. Identification and characterization of endothelin converting activity in cultured bovine endothelial cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1990 May 16;168(3):1128–1136. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(90)91146-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okada K., Miyazaki Y., Takada J., Matsuyama K., Yamaki T., Yano M. Conversion of big endothelin-1 by membrane-bound metalloendopeptidase in cultured bovine endothelial cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1990 Sep 28;171(3):1192–1198. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(90)90811-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shinyama H., Uchida T., Kido H., Hayashi K., Watanabe M., Matsumura Y., Ikegawa R., Takaoka M., Morimoto S. Phosphoramidon inhibits the conversion of intracisternally administered big endothelin-1 to endothelin-1. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1991 Jul 15;178(1):24–30. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(91)91774-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steiner A. L., Parker C. W., Kipnis D. M. Radioimmunoassay for cyclic nucleotides. I. Preparation of antibodies and iodinated cyclic nucleotides. J Biol Chem. 1972 Feb 25;247(4):1106–1113. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takada J., Okada K., Ikenaga T., Matsuyama K., Yano M. Phosphoramidon-sensitive endothelin-converting enzyme in the cytosol of cultured bovine endothelial cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1991 Apr 30;176(2):860–865. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(05)80265-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takahashi K., Ghatei M. A., Jones P. M., Murphy J. K., Lam H. C., O'Halloran D. J., Bloom S. R. Endothelin in human brain and pituitary gland: comparison with rat. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol. 1991;17 (Suppl 7):S101–S103. doi: 10.1097/00005344-199100177-00026. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Télémaque S., D'Orléans-Juste P. Presence of a phosphoramidon-sensitive endothelin-converting enzyme which converts big-endothelin-1, but not big-endothelin-3, in the rat vas deferens. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1991 Oct;344(4):505–507. doi: 10.1007/BF00172593. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Warner T. D., Mitchell J. A., D'Orleans-Juste P., Ishii K., Förstermann U., Murad F. Characterization of endothelin-converting enzyme from endothelial cells and rat brain: detection of the formation of biologically active endothelin-1 by rapid bioassay. Mol Pharmacol. 1992 Feb;41(2):399–403. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yanagisawa M., Kurihara H., Kimura S., Tomobe Y., Kobayashi M., Mitsui Y., Yazaki Y., Goto K., Masaki T. A novel potent vasoconstrictor peptide produced by vascular endothelial cells. Nature. 1988 Mar 31;332(6163):411–415. doi: 10.1038/332411a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshimi H., Kawano Y., Akabane S., Ashida T., Yoshida K., Kinoshita O., Kuramochi M., Omae T. Immunoreactive endothelin-1 contents in brain regions from spontaneously hypertensive rats. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol. 1991;17 (Suppl 7):S417–S419. doi: 10.1097/00005344-199100177-00118. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshizawa T., Shinmi O., Giaid A., Yanagisawa M., Gibson S. J., Kimura S., Uchiyama Y., Polak J. M., Masaki T., Kanazawa I. Endothelin: a novel peptide in the posterior pituitary system. Science. 1990 Jan 26;247(4941):462–464. doi: 10.1126/science.2405487. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


