Abstract
1. The antinociceptive activity of the bradykinin (BK) BK2 receptor antagonist D-Arg-[Hyp3,Thi5D-Tic7,Oic8]BK (Hoe 140) was determined in a range of mouse abdominal constriction assays. 2. Hoe 140 potently inhibited the response induced by i.p. injection of 10 micrograms BK/mouse, and 1 microgram BK/mouse in mice pre-sensitized by i.p. injection of prostaglandin E2 (PGE2). The ED50 values in these assays were 1.9 and 3.7 micrograms kg-1 respectively. This confirms that Hoe 140 is a potent antagonist of BK in vivo. 3. Hoe 140 produced potent, but incomplete inhibition of the responses evoked by i.p. injection of kaolin or 0.25% acetic acid. ED25 values in these assays were 2.7 and 16.1 micrograms kg-1, and the maximum inhibition produced was 60% and 70% respectively. 4. At doses up to 1 mg kg-1, Hoe 140 was completely ineffective against the abdominal constriction response induced by zymosan. In contrast, morphine, ibuprofen and indomethacin had similar potencies against zymosan, kaolin and acetic acid-induced abdominal constriction. 5. Although zymosan, acetic acid and kaolin all produce qualitatively similar responses, it is appears that they achieve this by different mechanisms. The extent to which BK is involved as a mediator differs between the various types of abdominal constriction assay.
Full text
PDF
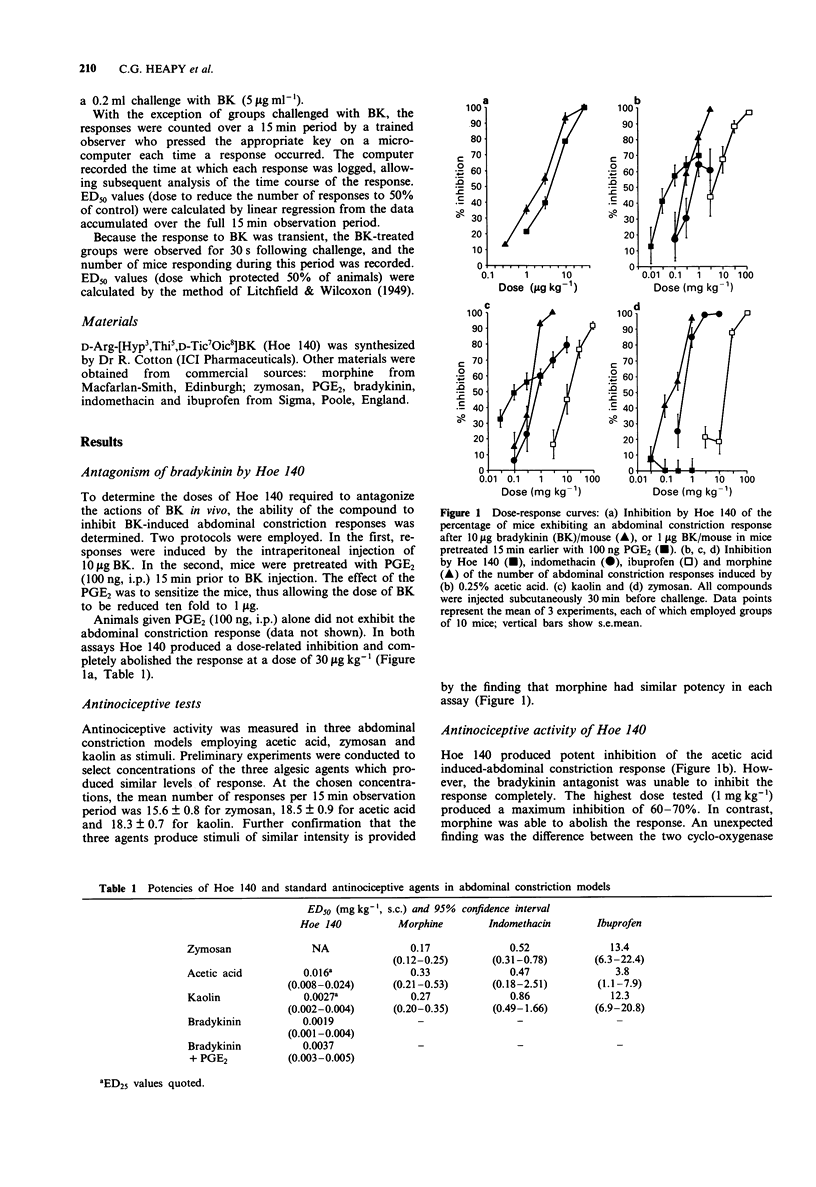
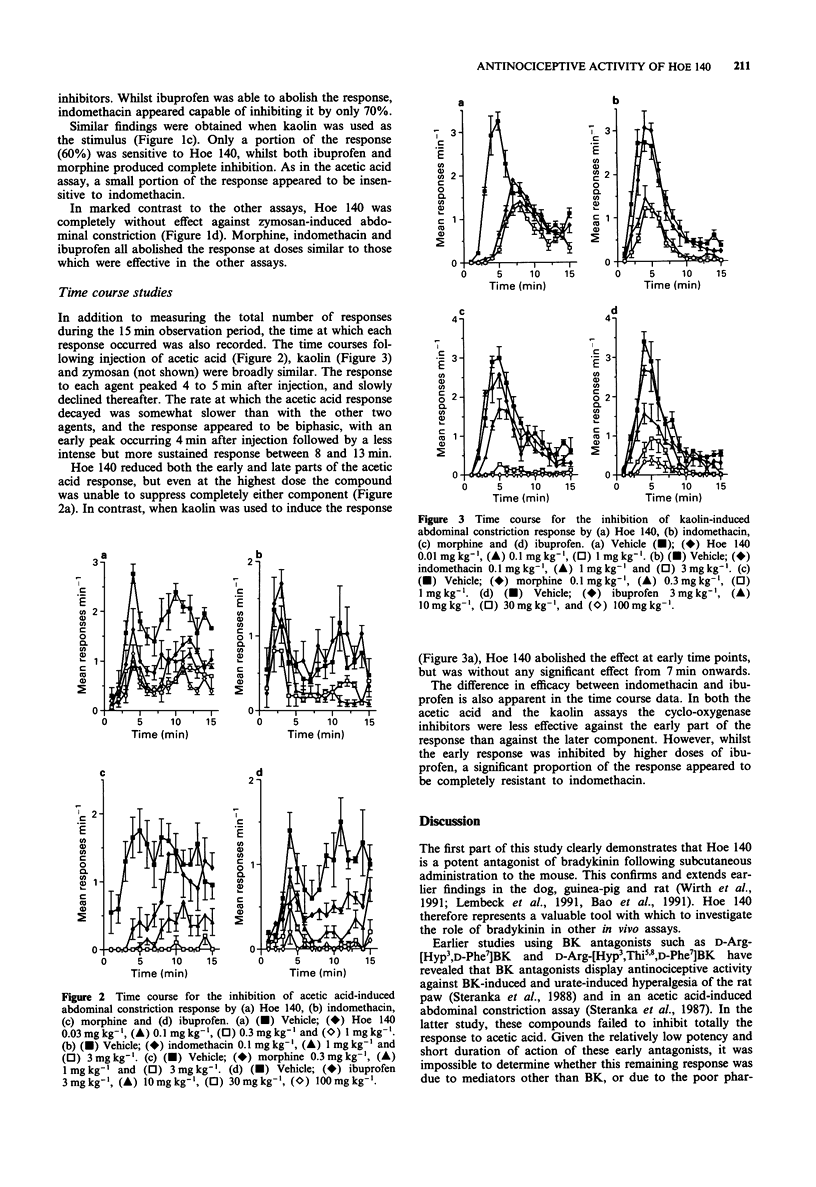


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bao G., Qadri F., Stauss B., Stauss H., Gohlke P., Unger T. HOE 140, a new highly potent and long-acting bradykinin antagonist in conscious rats. Eur J Pharmacol. 1991 Jul 23;200(1):179–182. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(91)90684-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Damas J., Bourdon V., Remacle-Volon G., Adam A. Kinins and peritoneal exudates induced by carrageenin and zymosan in rats. Br J Pharmacol. 1990 Oct;101(2):418–422. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1990.tb12724.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deraedt R., Jouquey S., Delevallée F., Flahaut M. Release of prostaglandins E and F in an algogenic reaction and its inhibition. Eur J Pharmacol. 1980 Jan 11;61(1):17–24. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(80)90377-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doherty N. S., Beaver T. H., Chan K. Y., Coutant J. E., Westrich G. L. The role of prostaglandins in the nociceptive response induced by intraperitoneal injection of zymosan in mice. Br J Pharmacol. 1987 May;91(1):39–47. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1987.tb08981.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunn P. M., Rang H. P. Bradykinin-induced depolarization of primary afferent nerve terminals in the neonatal rat spinal cord in vitro. Br J Pharmacol. 1990 Jul;100(3):656–660. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1990.tb15863.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferreira S. H., Moncada S., Vane J. R. Prostaglandins and the mechanism of analgesia produced by aspirin-like drugs. Br J Pharmacol. 1973 Sep;49(1):86–97. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1973.tb08270.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujiyoshi T., Dozen M., Iida H., Ikeda K., Hayashi I., Oh-ishi S. Demonstration of kinin-release in the peritoneal exudate of kaolin-induced writhing in mice. Jpn J Pharmacol. 1990 Jun;53(2):255–258. doi: 10.1254/jjp.53.255. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujiyoshi T., Dozen M., Ikeda K., Oh-ishi S. Involvement of prostaglandins in kaolin-induced writhing reaction in mice. J Pharmacobiodyn. 1989 Aug;12(8):476–482. doi: 10.1248/bpb1978.12.476. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujiyoshi T., Hayashi I., Oh-ishi S. Kaolin-induced writhing response in mice: activation of the plasma kallikrein-kinin system by kaolin. J Pharmacobiodyn. 1989 Aug;12(8):483–487. doi: 10.1248/bpb1978.12.483. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujiyoshi T., Kuwashima M., Iida H., Uematsu T. A new writhing model of factor XII activator-induced pain for assessment of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory agents. I. Kaolin-induced writhing in mice. J Pharmacobiodyn. 1989 Mar;12(3):132–136. doi: 10.1248/bpb1978.12.132. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hock F. J., Wirth K., Albus U., Linz W., Gerhards H. J., Wiemer G., Henke S., Breipohl G., König W., Knolle J. Hoe 140 a new potent and long acting bradykinin-antagonist: in vitro studies. Br J Pharmacol. 1991 Mar;102(3):769–773. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1991.tb12248.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lembeck F., Griesbacher T., Eckhardt M., Henke S., Breipohl G., Knolle J. New, long-acting, potent bradykinin antagonists. Br J Pharmacol. 1991 Feb;102(2):297–304. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1991.tb12169.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luttinger D. Determination of antinociceptive efficacy of drugs in mice using different water temperatures in a tail-immersion test. J Pharmacol Methods. 1985 Jul;13(4):351–357. doi: 10.1016/0160-5402(85)90017-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Melmon K. L., Webster M. E., Goldfinger S. E., Seegmiller J. E. The presence of a kinin in inflammatory synovial effusion from arthritides of varying etiologies. Arthritis Rheum. 1967 Feb;10(1):13–20. doi: 10.1002/art.1780100103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rampart M., Bult H., Herman A. G. Effect of complement activation on the biosynthesis of prostacyclin (PGI2) by rabbit peritoneum in vitro. Arch Int Pharmacodyn Ther. 1981 Oct;253(2):327–329. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steranka L. R., DeHaas C. J., Vavrek R. J., Stewart J. M., Enna S. J., Snyder S. H. Antinociceptive effects of bradykinin antagonists. Eur J Pharmacol. 1987 Apr 14;136(2):261–262. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(87)90723-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steranka L. R., Manning D. C., DeHaas C. J., Ferkany J. W., Borosky S. A., Connor J. R., Vavrek R. J., Stewart J. M., Snyder S. H. Bradykinin as a pain mediator: receptors are localized to sensory neurons, and antagonists have analgesic actions. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 May;85(9):3245–3249. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.9.3245. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whalley E. T., Clegg S., Stewart J. M., Vavrek R. J. The effect of kinin agonists and antagonists on the pain response of the human blister base. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1987 Dec;336(6):652–655. doi: 10.1007/BF00165756. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wirth K., Hock F. J., Albus U., Linz W., Alpermann H. G., Anagnostopoulos H., Henk S., Breipohl G., König W., Knolle J. Hoe 140 a new potent and long acting bradykinin-antagonist: in vivo studies. Br J Pharmacol. 1991 Mar;102(3):774–777. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1991.tb12249.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


