Abstract
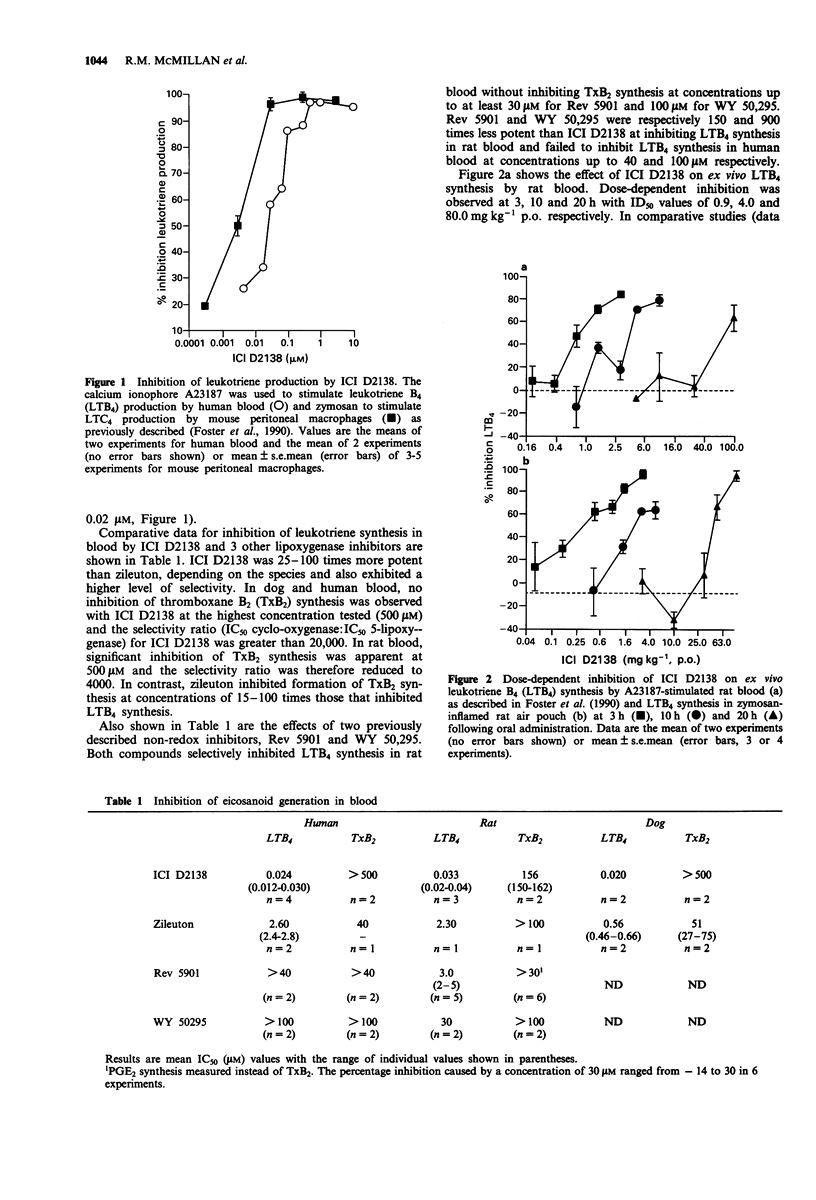
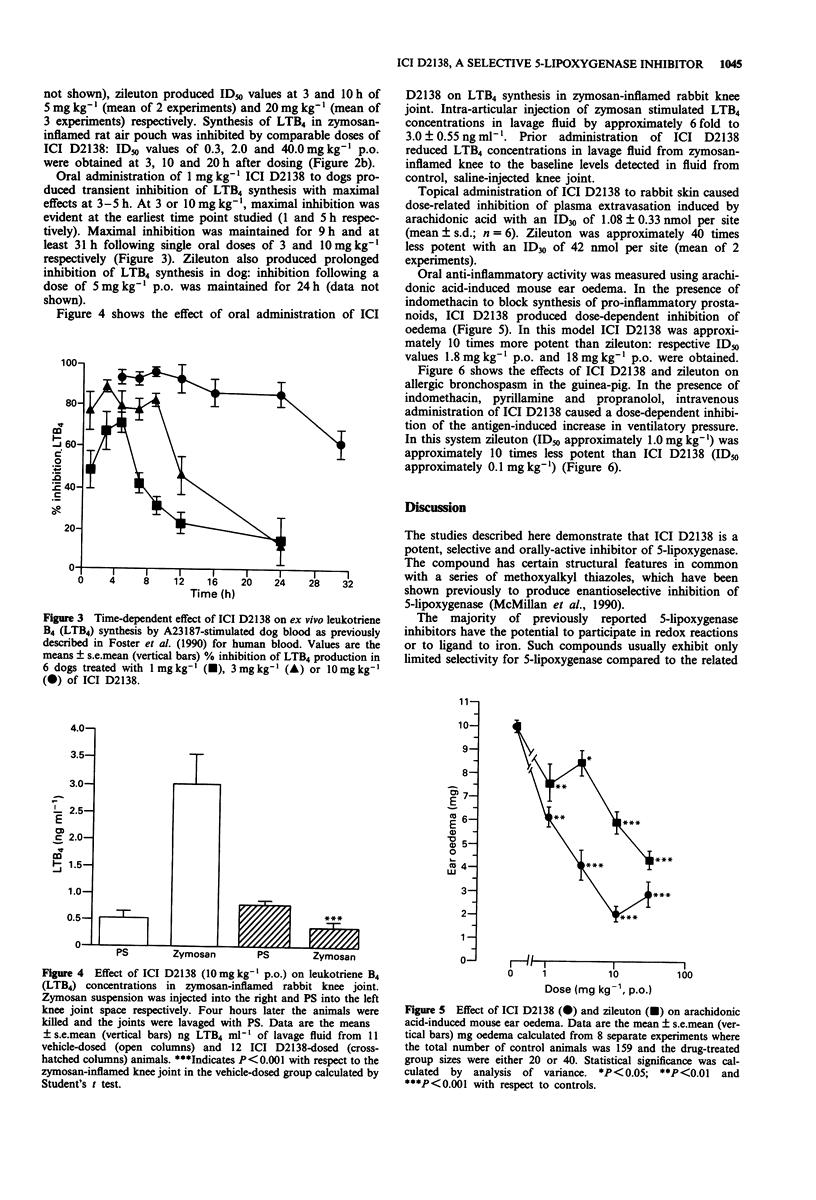
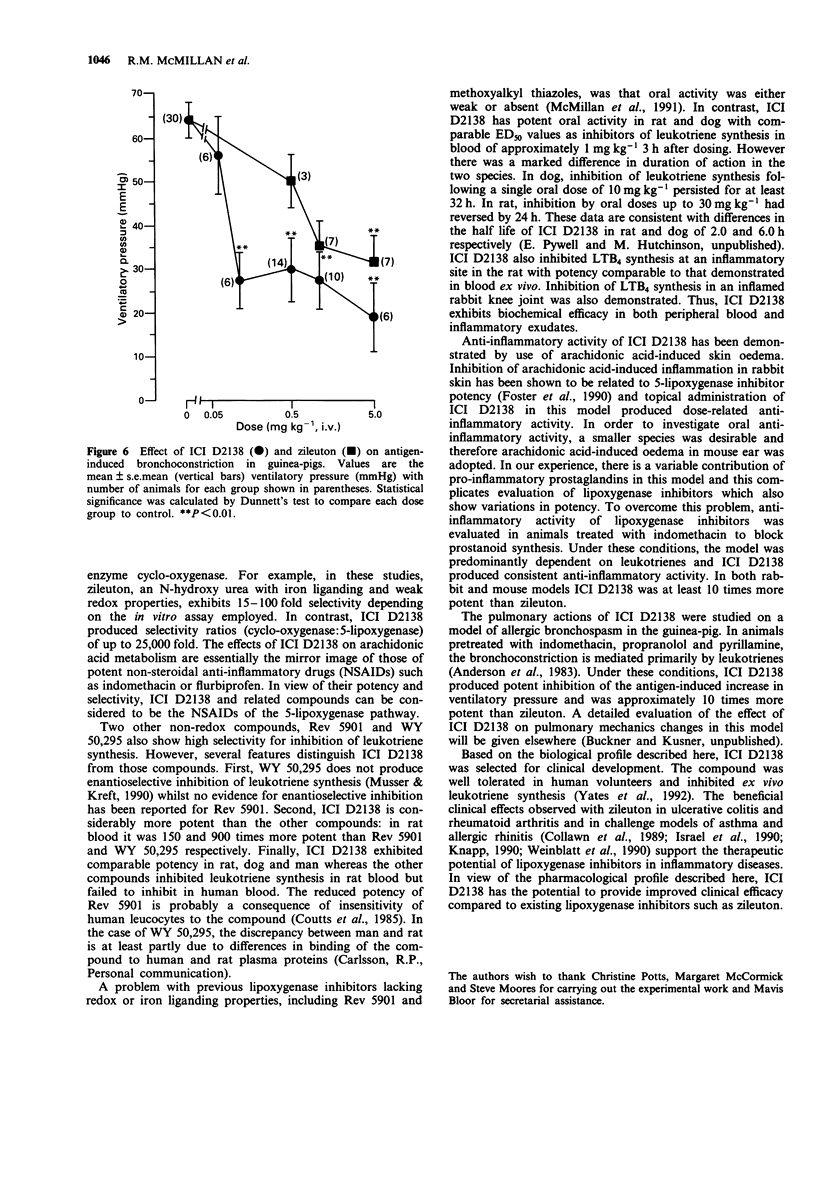
1. This paper describes the pre-clinical pharmacology of ICI D2138, a potent orally-active non-redox inhibitor of 5-lipoxygenase which is undergoing clinical evaluation. 2. ICI D2138 potently inhibited leukotriene synthesis in murine peritoneal macrophages (IC50 = 3 nM) and human blood (IC50 = 20 nM). In human and dog blood, ICI D2138 did not inhibit thromboxane B2 synthesis at a concentration of 500 microM, thus the selectivity ratio (cyclo-oxygenase: 5-lipoxygenase) was greater than 20,000. In contrast, zileuton (a 5-lipoxygenase inhibitor also undergoing clinical evaluation) exhibited a selectivity ratio of 15-100. 3. ICI D2138 potently and dose-dependently inhibited ex vivo leukotriene B4 (LTB4) synthesis by rat blood with ED50 values of 0.9, 4.0 and 80.0 mg kg-1 p.o. at 3, 10 and 20 h respectively after dosing. Similar activity was observed for inhibition of LTB4 production in a zymosan-inflamed rat air pouch model. Zileuton produced ED50 values of 5 and 20 mg kg-1 at 3 and 10 h respectively. 4. Oral administration of 1, 3 or 10 mg kg-1 ICI D2138 to dogs produced maximal inhibition of ex vivo LTB4 synthesis by blood for 5, 9 and 31 h respectively. A dose of 5 mg kg-1 p.o. of zileuton caused maximal inhibition of LTB4 for 24 h. 5. Oral administration of 10 mg kg-1 ICI D2138 caused total inhibition of LTB4 production in zymosan-inflamed rabbit knee joint. 6. Topical administration of ICI D2138 to rabbit skin caused a dose-related inhibition of arachidonic acid-induced plasma extravasation with an ID30 of 1.08 nmol per site.(ABSTRACT TRUNCATED AT 250 WORDS)
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anderson W. H., O'Donnell M., Simko B. A., Welton A. F. An in vivo model for measuring antigen-induced SRS-A-mediated bronchoconstriction and plasma SRS-A levels in the guinea-pig. Br J Pharmacol. 1983 Jan;78(1):67–74. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1983.tb09363.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carter G. W., Young P. R., Albert D. H., Bouska J., Dyer R., Bell R. L., Summers J. B., Brooks D. W. 5-lipoxygenase inhibitory activity of zileuton. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1991 Mar;256(3):929–937. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Foster S. J., Bruneau P., Walker E. R., McMillan R. M. 2-substituted indazolinones: orally active and selective 5-lipoxygenase inhibitors with anti-inflammatory activity. Br J Pharmacol. 1990 Jan;99(1):113–118. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1990.tb14663.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Israel E., Dermarkarian R., Rosenberg M., Sperling R., Taylor G., Rubin P., Drazen J. M. The effects of a 5-lipoxygenase inhibitor on asthma induced by cold, dry air. N Engl J Med. 1990 Dec 20;323(25):1740–1744. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199012203232505. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knapp H. R. Reduced allergen-induced nasal congestion and leukotriene synthesis with an orally active 5-lipoxygenase inhibitor. N Engl J Med. 1990 Dec 20;323(25):1745–1748. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199012203232506. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McMillan R. M., Bird T. G., Crawley G. C., Edwards M. P., Girodeau J. M., Kingston J. F., Foster S. J. Methoxyalkyl thiazoles: a novel series of potent, orally active and enantioselective inhibitors of 5-lipoxygenase. Agents Actions. 1991 Sep;34(1-2):110–112. doi: 10.1007/BF01993252. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McMillan R. M., Girodeau J. M., Foster S. J. Selective chiral inhibitors of 5-lipoxygenase with anti-inflammatory activity. Br J Pharmacol. 1990 Nov;101(3):501–503. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1990.tb14111.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Opas E. E., Bonney R. J., Humes J. L. Prostaglandin and leukotriene synthesis in mouse ears inflamed by arachidonic acid. J Invest Dermatol. 1985 Apr;84(4):253–256. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12265320. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salmon J. A., Garland L. G. Leukotriene antagonists and inhibitors of leukotriene biosynthesis as potential therapeutic agents. Prog Drug Res. 1991;37:9–90. doi: 10.1007/978-3-0348-7139-6_1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


