Abstract
1. The possibility that bradykinin- or histamine-stimulated inositol polyphosphate accumulation may be regulated by protein kinase C (PKC) in bovine adrenal chromaffin cells has been addressed. 2. Initial experiments confirmed that the phorbol ester 12-O-tetradecanoyl-phorbol 13-acetate (TPA) dramatically inhibited agonist-stimulated [3H]-inositol phosphate accumulations in [3H]-inositol prelabelled cells. In contrast, the PKC inhibitor, Ro 31-8220, did not affect this response. 3. Histamine (100 microM) or bradykinin (100 nM) evoked rapid increases in inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate (Ins(1,4,5)P3) and inositol 1,3,4,5-tetrakisphosphate (Ins(1,3,4,5)P4) mass accumulations (maximal accumulations within 10 s and 30 s, respectively) which declined towards basal values over a 10 min incubation period. TPA (1 microM) significantly attenuated the peak Ins(1,4,5)P3 response to bradykinin and histamine by 30% and 70% respectively. In contrast, TPA did not significantly affect agonist-stimulated Ins(1,3,4,5)P4 responses. 4. Ro 31-8220 (10 microM) significantly enhanced the maximal Ins(1,4,5)P3 accumulations elicited by both bradykinin and histamine. 5. The results indicate that the initial Ins(1,4,5)P3 response to either bradykinin or histamine in bovine adrenal chromaffin cells can be attenuated by PKC activation by phorbol ester and enhanced by PKC inhibition by Ro 31-8220. In contrast, agonist-stimulated Ins(1,3,4,5)P4 accumulation does not appear to be affected by these manipulations of PKC activity. Possible bases for differential modulation of Ins(1,4,5)P3 and Ins(1,3,4,5)P4 are discussed.
Full text
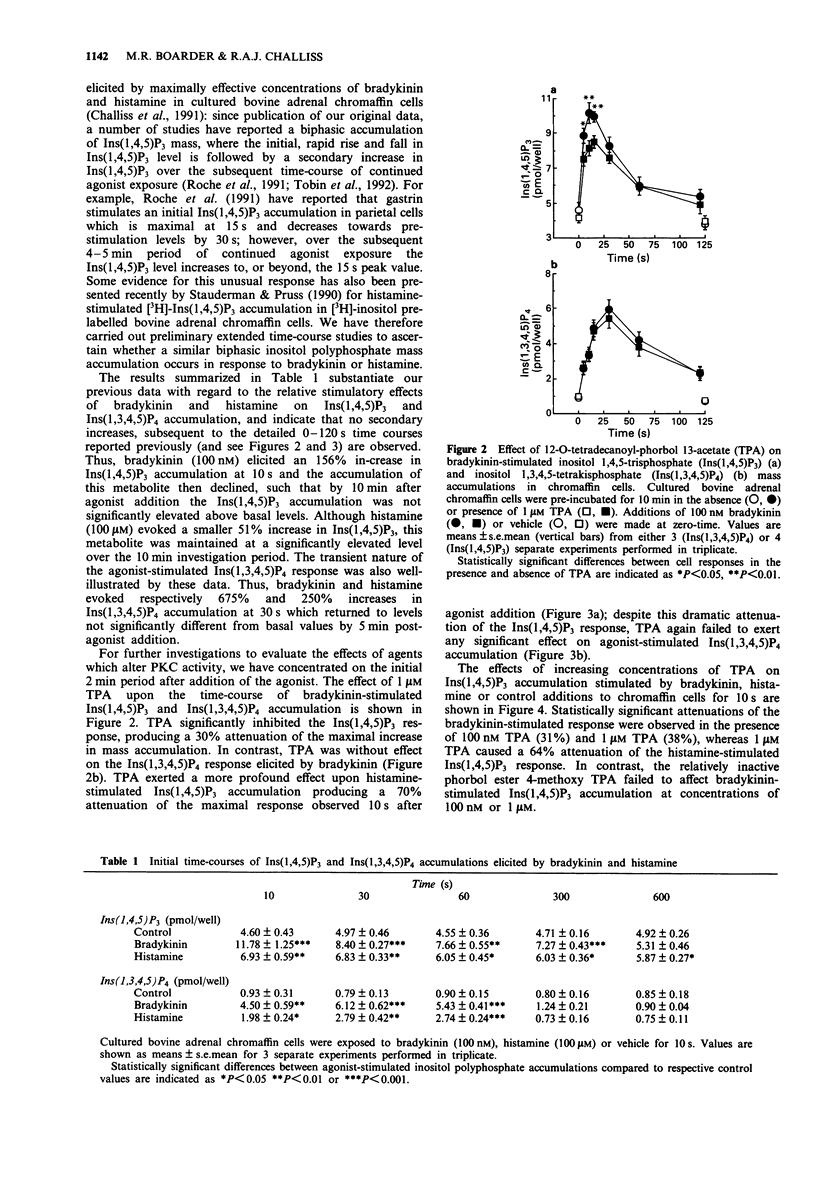
PDF
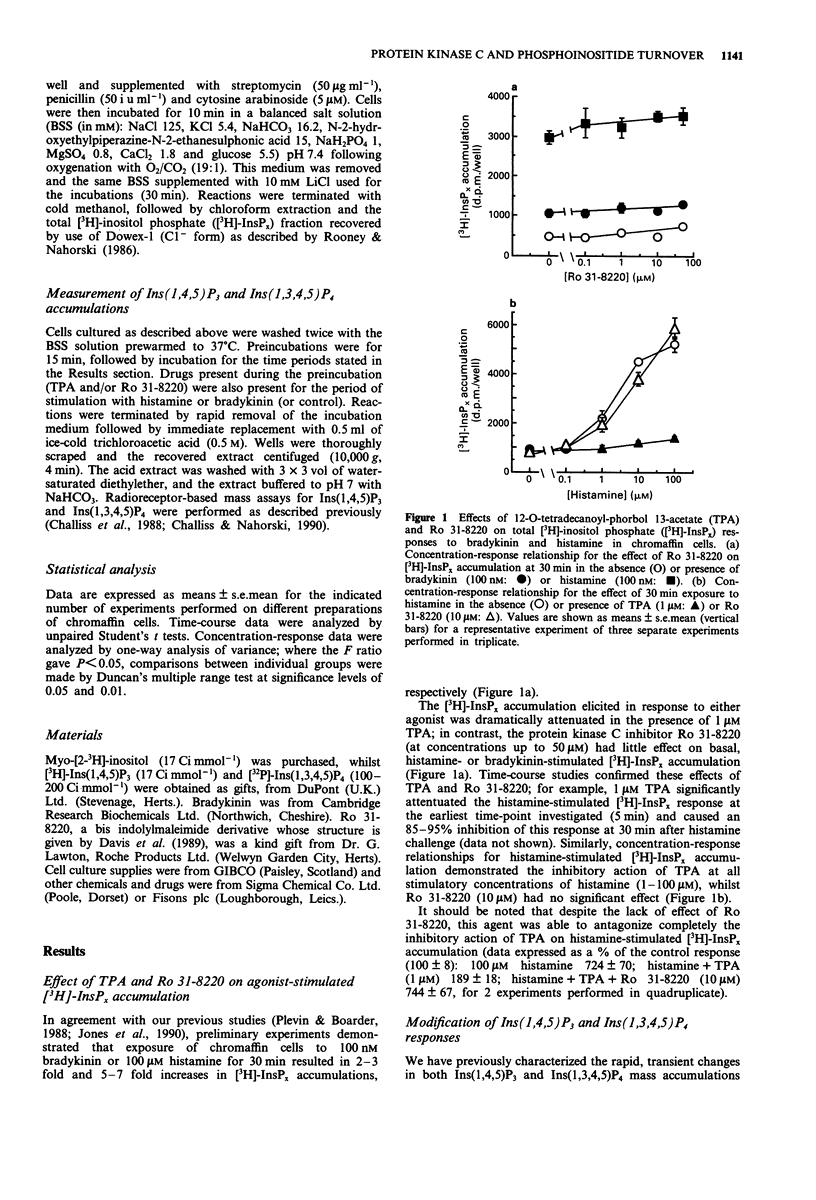
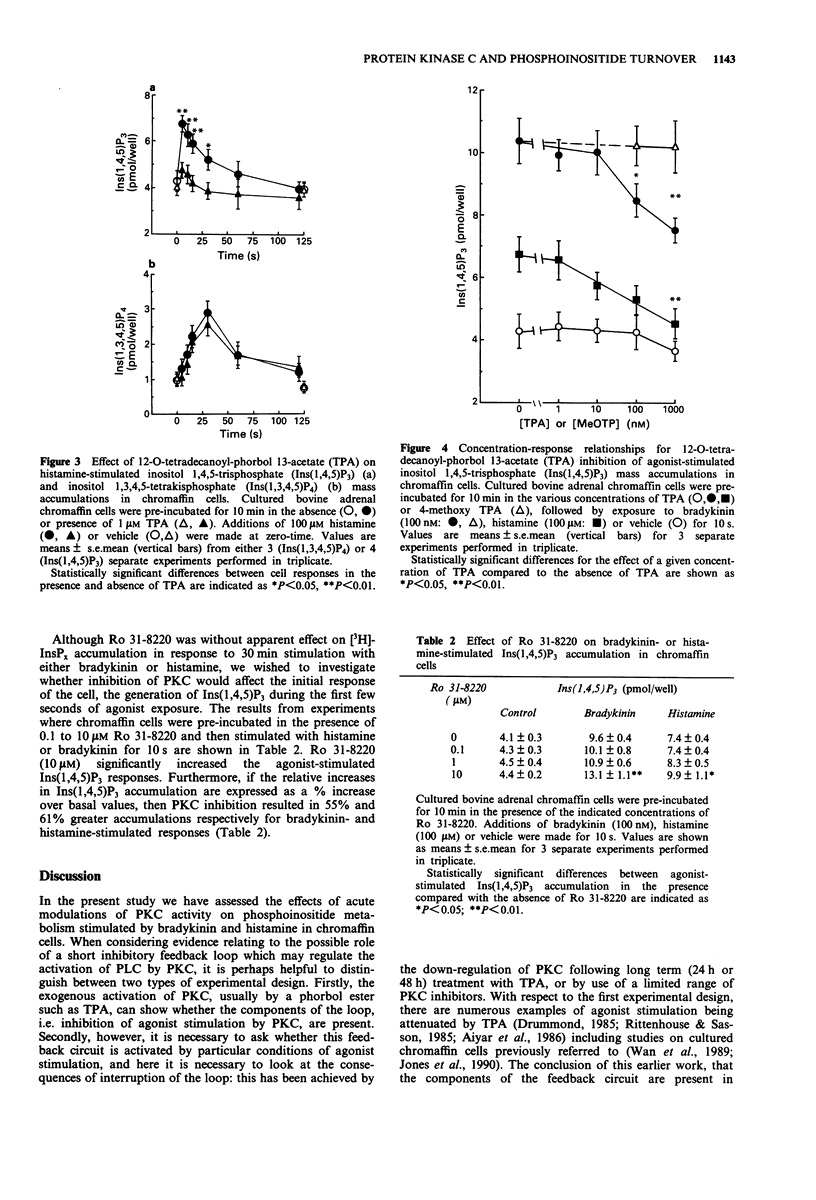


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Burgoyne R. D. Control of exocytosis in adrenal chromaffin cells. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1991 Jul 22;1071(2):174–202. doi: 10.1016/0304-4157(91)90024-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Challis R. A., Jones J. A., Owen P. J., Boarder M. R. Changes in inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate and inositol 1,3,4,5- tetrakisphosphate mass accumulations in cultured adrenal chromaffin cells in response to bradykinin and histamine. J Neurochem. 1991 Mar;56(3):1083–1086. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1991.tb02033.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Challiss R. A., Batty I. H., Nahorski S. R. Mass measurements of inositol(1,4,5)trisphosphate in rat cerebral cortex slices using a radioreceptor assay: effects of neurotransmitters and depolarization. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1988 Dec 15;157(2):684–691. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(88)80304-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Challiss R. A., Nahorski S. R. Neurotransmitter and depolarization-stimulated accumulation of inositol 1,3,4,5-tetrakisphosphate mass in rat cerebral cortex slices. J Neurochem. 1990 Jun;54(6):2138–2141. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1990.tb04920.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis P. D., Hill C. H., Keech E., Lawton G., Nixon J. S., Sedgwick A. D., Wadsworth J., Westmacott D., Wilkinson S. E. Potent selective inhibitors of protein kinase C. FEBS Lett. 1989 Dec 18;259(1):61–63. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(89)81494-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eberhard D. A., Holz R. W. Cholinergic stimulation of inositol phosphate formation in bovine adrenal chromaffin cells: distinct nicotinic and muscarinic mechanisms. J Neurochem. 1987 Nov;49(5):1634–1643. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1987.tb01037.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hepler J. R., Earp H. S., Harden T. K. Long-term phorbol ester treatment down-regulates protein kinase C and sensitizes the phosphoinositide signaling pathway to hormone and growth factor stimulation. Evidence for a role of protein kinase C in agonist-induced desensitization. J Biol Chem. 1988 Jun 5;263(16):7610–7619. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones J. A., Owen P. J., Boarder M. R. Influence of phorbol esters, and diacylglycerol kinase and lipase inhibitors on noradrenaline release and phosphoinositide hydrolysis in chromaffin cells. Br J Pharmacol. 1990 Nov;101(3):521–526. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1990.tb14114.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- King W. G., Rittenhouse S. E. Inhibition of protein kinase C by staurosporine promotes elevated accumulations of inositol trisphosphates and tetrakisphosphate in human platelets exposed to thrombin. J Biol Chem. 1989 Apr 15;264(11):6070–6074. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Livett B. G., Marley P. D. Effects of opioid peptides and morphine on histamine-induced catecholamine secretion from cultured, bovine adrenal chromaffin cells. Br J Pharmacol. 1986 Oct;89(2):327–334. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1986.tb10264.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Molina y Vedia L. M., Lapetina E. G. Phorbol 12,13-dibutyrate and 1-oleyl-2-acetyldiacylglycerol stimulate inositol trisphosphate dephosphorylation in human platelets. J Biol Chem. 1986 Aug 15;261(23):10493–10495. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nixon J. S., Bishop J., Bradshaw D., Davis P. D., Hill C. H., Elliott L. H., Kumar H., Lawton G., Lewis E. J., Mulqueen M. The design and biological properties of potent and selective inhibitors of protein kinase C. Biochem Soc Trans. 1992 May;20(2):419–425. doi: 10.1042/bst0200419. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Sullivan A. J., Burgoyne R. D. A comparison of bradykinin, angiotensin II and muscarinic stimulation of cultured bovine adrenal chromaffin cells. Biosci Rep. 1989 Apr;9(2):243–252. doi: 10.1007/BF01116001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Owen P. J., Boarder M. R. Influence of bradykinin on diacylglycerol and phosphatidic acid accumulation in cultured bovine adrenal chromaffin cells. J Neurochem. 1991 Sep;57(3):760–768. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1991.tb08217.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Owen P. J., Plevin R., Boarder M. R. Characterization of bradykinin-stimulated release of noradrenaline from cultured bovine adrenal chromaffin cells. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1989 Mar;248(3):1231–1236. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pfeilschifter J., Ochsner M., Whitebread S., De Gasparo M. Down-regulation of protein kinase C potentiates angiotensin II-stimulated polyphosphoinositide hydrolysis in vascular smooth-muscle cells. Biochem J. 1989 Aug 15;262(1):285–291. doi: 10.1042/bj2620285. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plevin R., Boarder M. R. Stimulation of formation of inositol phosphates in primary cultures of bovine adrenal chromaffin cells by angiotensin II, histamine, bradykinin, and carbachol. J Neurochem. 1988 Aug;51(2):634–641. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1988.tb01085.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plevin R., Owen P. J., Marriott D. B., Jones J. A., Boarder M. R. Role of phosphoinositide turnover and cyclic AMP accumulation in prostaglandin-stimulated noradrenaline release from cultured adrenal chromaffin cells. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1990 Mar;252(3):1296–1303. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Purkiss J., Murrin R. A., Owen P. J., Boarder M. R. Lack of phospholipase D activity in chromaffin cells: bradykinin-stimulated phosphatidic acid formation involves phospholipase C in chromaffin cells but phospholipase D in PC12 cells. J Neurochem. 1991 Sep;57(3):1084–1087. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1991.tb08262.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rittenhouse S. E., Sasson J. P. Mass changes in myoinositol trisphosphate in human platelets stimulated by thrombin. Inhibitory effects of phorbol ester. J Biol Chem. 1985 Jul 25;260(15):8657–8660. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roche S., Gusdinar T., Bali J. P., Magous R. Biphasic kinetics of inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate accumulation in gastrin-stimulated parietal cells. Effects of pertussis toxin and extracellular calcium. FEBS Lett. 1991 Apr 22;282(1):147–151. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(91)80465-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rooney T. A., Nahorski S. R. Regional characterization of agonist and depolarization-induced phosphoinositide hydrolysis in rat brain. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1986 Dec;239(3):873–880. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rüegg U. T., Burgess G. M. Staurosporine, K-252 and UCN-01: potent but nonspecific inhibitors of protein kinases. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 1989 Jun;10(6):218–220. doi: 10.1016/0165-6147(89)90263-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shears S. B. Regulation of the metabolism of 1,2-diacylglycerols and inositol phosphates that respond to receptor activation. Pharmacol Ther. 1991;49(1-2):79–104. doi: 10.1016/0163-7258(91)90023-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sim S. S., Kim J. W., Rhee S. G. Regulation of D-myo-inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate 3-kinase by cAMP-dependent protein kinase and protein kinase C. J Biol Chem. 1990 Jun 25;265(18):10367–10372. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stauderman K. A., Pruss R. M. Different patterns of agonist-stimulated increases of 3H-inositol phosphate isomers and cytosolic Ca2+ in bovine adrenal chromaffin cells: comparison of the effects of histamine and angiotensin II. J Neurochem. 1990 Mar;54(3):946–953. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1990.tb02342.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wan D. C., Bunn S. J., Livett B. G. Effects of phorbol esters and forskolin on basal and histamine-induced accumulation of inositol phosphates in cultured bovine adrenal chromaffin cells. J Neurochem. 1989 Oct;53(4):1219–1227. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1989.tb07418.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


