Abstract
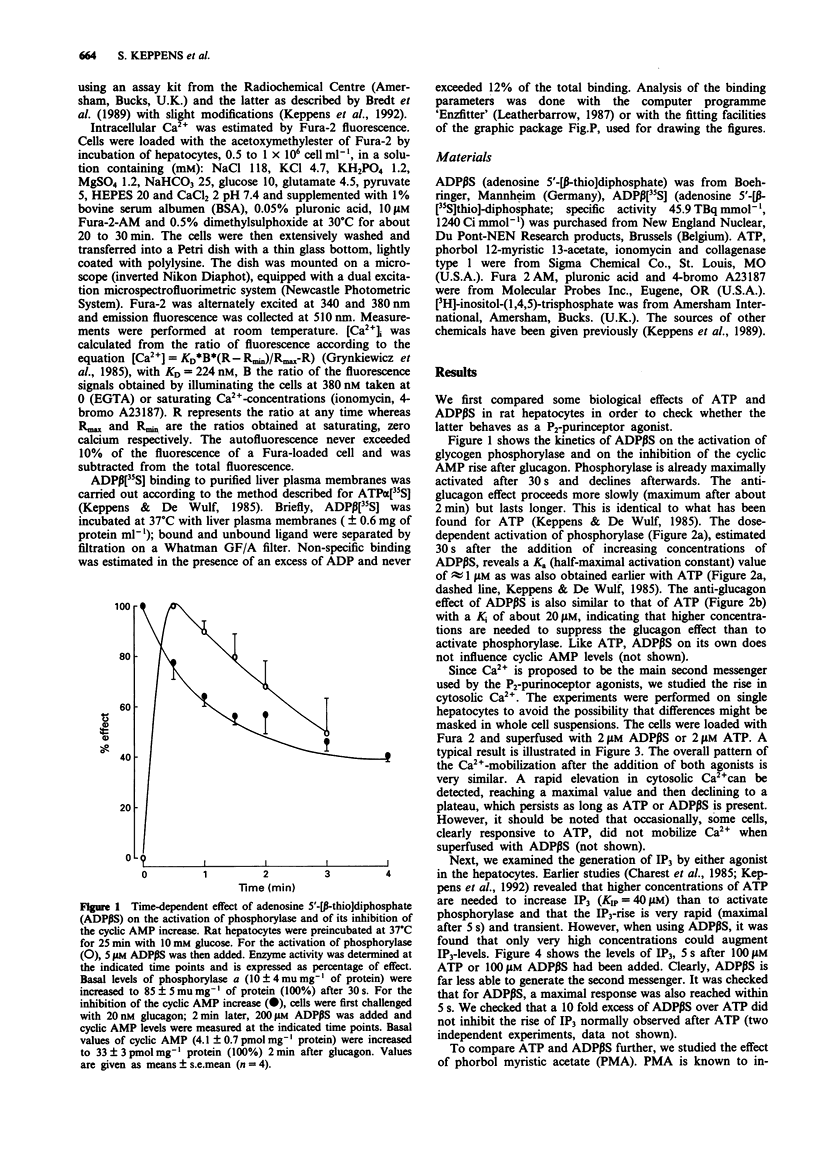
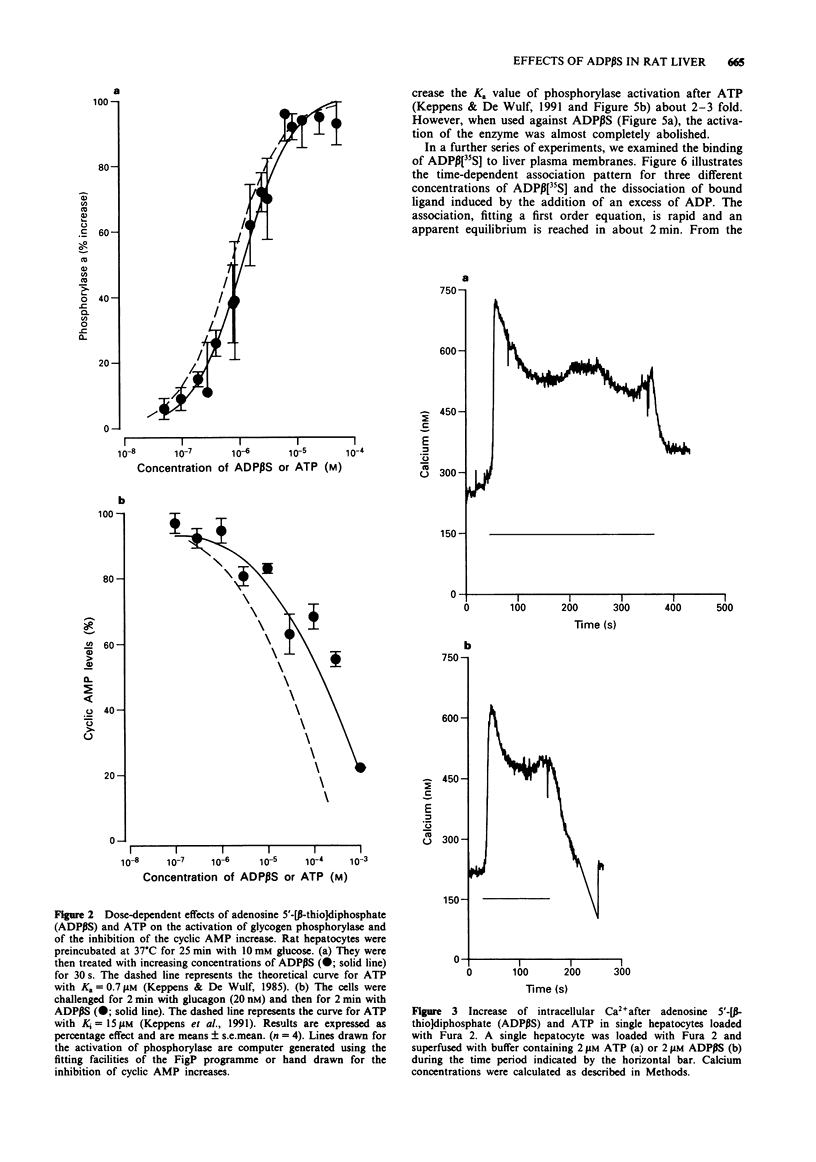
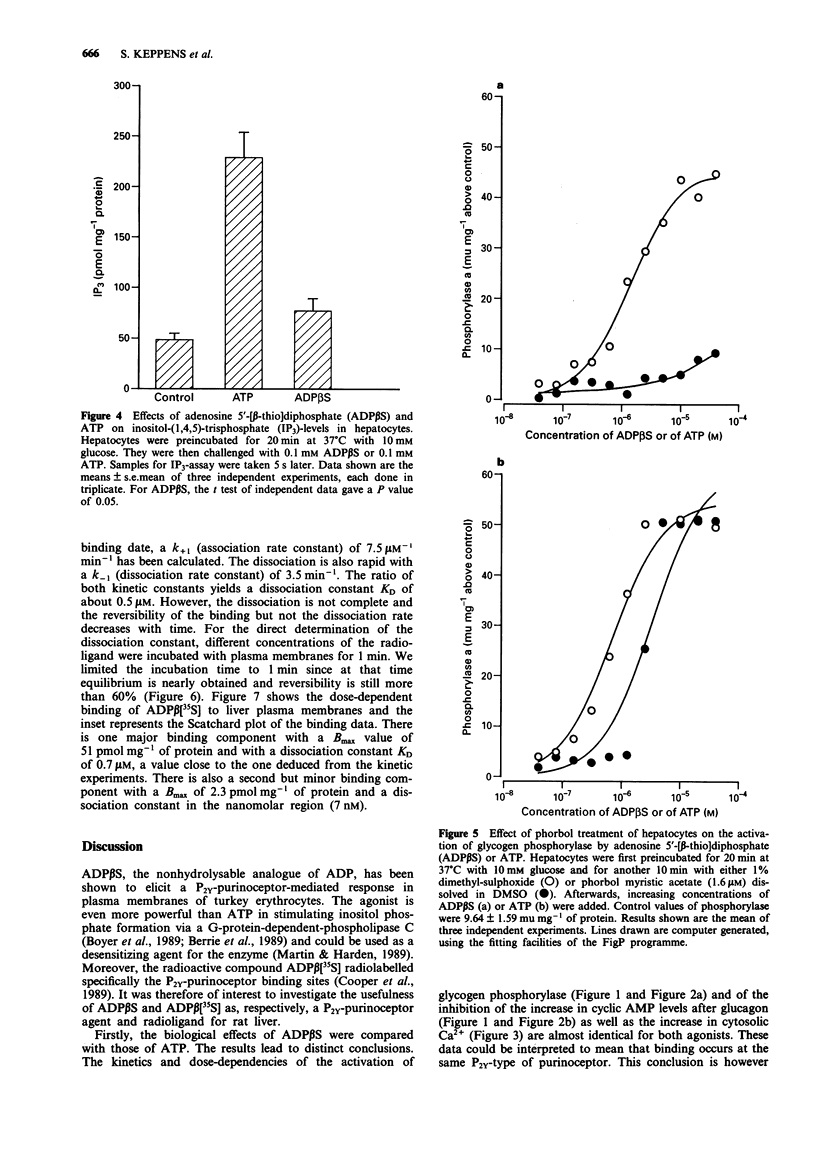
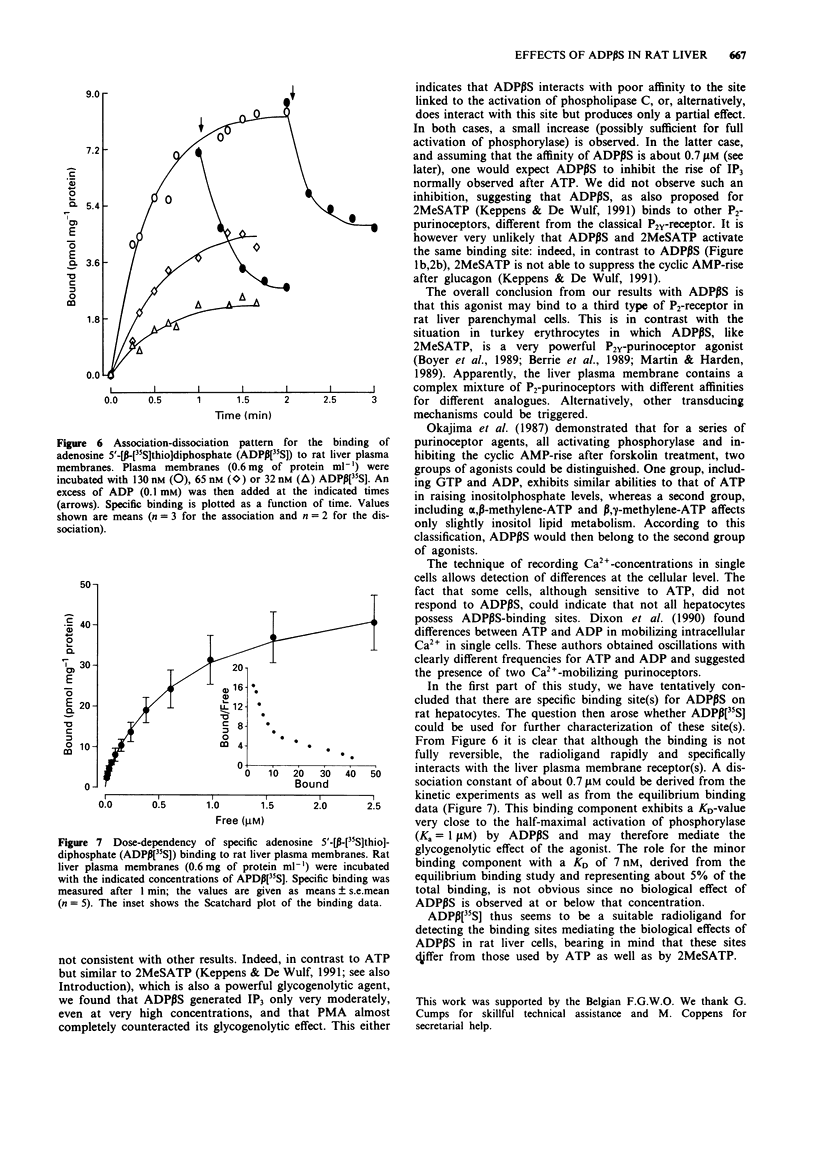
1. In rat liver cells micromolar concentrations of adenosine 5'-[beta-thio]diphosphate (ADP beta S), activate glycogen phosphorylase by an adenosine 3':5'-cyclic monophosphate (cyclic AMP)- independent mechanism. 2. As with adenosine 5'-triphosphate (ATP), ADP beta S also inhibits the rise in cyclic AMP after glucagon. 3. Cytosolic Ca2+ measured in single cells is rapidly increased with a pattern similar for ADP beta S and for ATP. 4. At variance with ATP, ADP beta S hardly increases inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate (IP3) levels. 5. Phorbol myristic acetate, which inhibits only slightly the glycogenolytic effect of ATP, almost completely abolishes this effect of ADP beta S. 6. With adenosine 5'-[beta-[35S]thio]diphosphate (ADP beta[35S]) as radioligand, we detected specific purinoceptors on rat liver plasma membranes. Binding consists of a major binding component with KD = 0.7 microM and Bmax = 51 pmol mg-1 of protein, probably mediating the activation of glycogen phosphorylase, and a minor high affinity, low capacity binding component with no obvious function. 7. It is concluded that the differences in biological effects between ATP and ADP beta S may involve different receptors and/or different transduction mechanisms and that ADP beta[35S] can be used to detect the specific binding sites for ADP beta S.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Berrie C. P., Hawkins P. T., Stephens L. R., Harden T. K., Downes C. P. Phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate hydrolysis in turkey erythrocytes is regulated by P2y purinoceptors. Mol Pharmacol. 1989 Apr;35(4):526–532. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boyer J. L., Downes C. P., Harden T. K. Kinetics of activation of phospholipase C by P2Y purinergic receptor agonists and guanine nucleotides. J Biol Chem. 1989 Jan 15;264(2):884–890. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bredt D. S., Mourey R. J., Snyder S. H. A simple, sensitive, and specific radioreceptor assay for inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate in biological tissues. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1989 Mar 31;159(3):976–982. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(89)92204-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burnstock G., Kennedy C. Is there a basis for distinguishing two types of P2-purinoceptor? Gen Pharmacol. 1985;16(5):433–440. doi: 10.1016/0306-3623(85)90001-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Charest R., Blackmore P. F., Exton J. H. Characterization of responses of isolated rat hepatocytes to ATP and ADP. J Biol Chem. 1985 Dec 15;260(29):15789–15794. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooper C. L., Morris A. J., Harden T. K. Guanine nucleotide-sensitive interaction of a radiolabeled agonist with a phospholipase C-linked P2y-purinergic receptor. J Biol Chem. 1989 Apr 15;264(11):6202–6206. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dixon C. J., Woods N. M., Cuthbertson K. S., Cobbold P. H. Evidence for two Ca2(+)-mobilizing purinoceptors on rat hepatocytes. Biochem J. 1990 Jul 15;269(2):499–502. doi: 10.1042/bj2690499. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilman A. G. A protein binding assay for adenosine 3':5'-cyclic monophosphate. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1970 Sep;67(1):305–312. doi: 10.1073/pnas.67.1.305. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grynkiewicz G., Poenie M., Tsien R. Y. A new generation of Ca2+ indicators with greatly improved fluorescence properties. J Biol Chem. 1985 Mar 25;260(6):3440–3450. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keppens S., De Wulf H. Characterization of the biological effects of 2-methylthio-ATP on rat hepatocytes: clear-cut differences with ATP. Br J Pharmacol. 1991 Oct;104(2):301–304. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1991.tb12426.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keppens S., De Wulf H. Characterization of the liver P2-purinoceptor involved in the activation of glycogen phosphorylase. Biochem J. 1986 Dec 1;240(2):367–371. doi: 10.1042/bj2400367. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keppens S., De Wulf H. P2-purinergic control of liver glycogenolysis. Biochem J. 1985 Nov 1;231(3):797–799. doi: 10.1042/bj2310797. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keppens S., Vandekerckhove A., De Wulf H. Characterization of purinoceptors present on human liver plasma membranes. FEBS Lett. 1989 May 8;248(1-2):137–140. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(89)80448-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keppens S., Vandekerckhove A., De Wulf H. Characterization of the purinoceptors present in rabbit and guinea pig liver. Eur J Pharmacol. 1990 Jun 21;182(1):149–153. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(90)90504-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keppens S., Vandekerckhove A., De Wulf H. Extracellular ATP and UTP exert similar effects on rat isolated hepatocytes. Br J Pharmacol. 1992 Feb;105(2):475–479. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1992.tb14278.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin M. W., Harden T. K. Agonist-induced desensitization of a P2Y-purinergic receptor-regulated phospholipase C. J Biol Chem. 1989 Nov 25;264(33):19535–19539. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Connor S. E., Dainty I. A., Leff P. Further subclassification of ATP receptors based on agonist studies. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 1991 Apr;12(4):137–141. doi: 10.1016/0165-6147(91)90530-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Connor S. E. Recent developments in the classification and functional significance of receptors for ATP and UTP, evidence for nucleotide receptors. Life Sci. 1992;50(22):1657–1664. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(92)90420-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okajima F., Tokumitsu Y., Kondo Y., Ui M. P2-purinergic receptors are coupled to two signal transduction systems leading to inhibition of cAMP generation and to production of inositol trisphosphate in rat hepatocytes. J Biol Chem. 1987 Oct 5;262(28):13483–13490. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pilkis S. J., Exton J. H., Johnson R. A., Park C. R. Effects of glucagon on cyclic AMP and carbohydrate metabolism in livers from diabetic rats. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1974 Mar 20;343(1):250–267. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(74)90258-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sistare F. D., Picking R. A., Haynes R. C., Jr Sensitivity of the response of cytosolic calcium in Quin-2-loaded rat hepatocytes to glucagon, adenine nucleosides, and adenine nucleotides. J Biol Chem. 1985 Oct 15;260(23):12744–12747. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vandenheede J. R., Keppens S., De Wulf H. The activation of liver phosphorylase b kinase by glucagon. FEBS Lett. 1976 Jan 15;61(2):213–217. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(76)81040-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


