Abstract
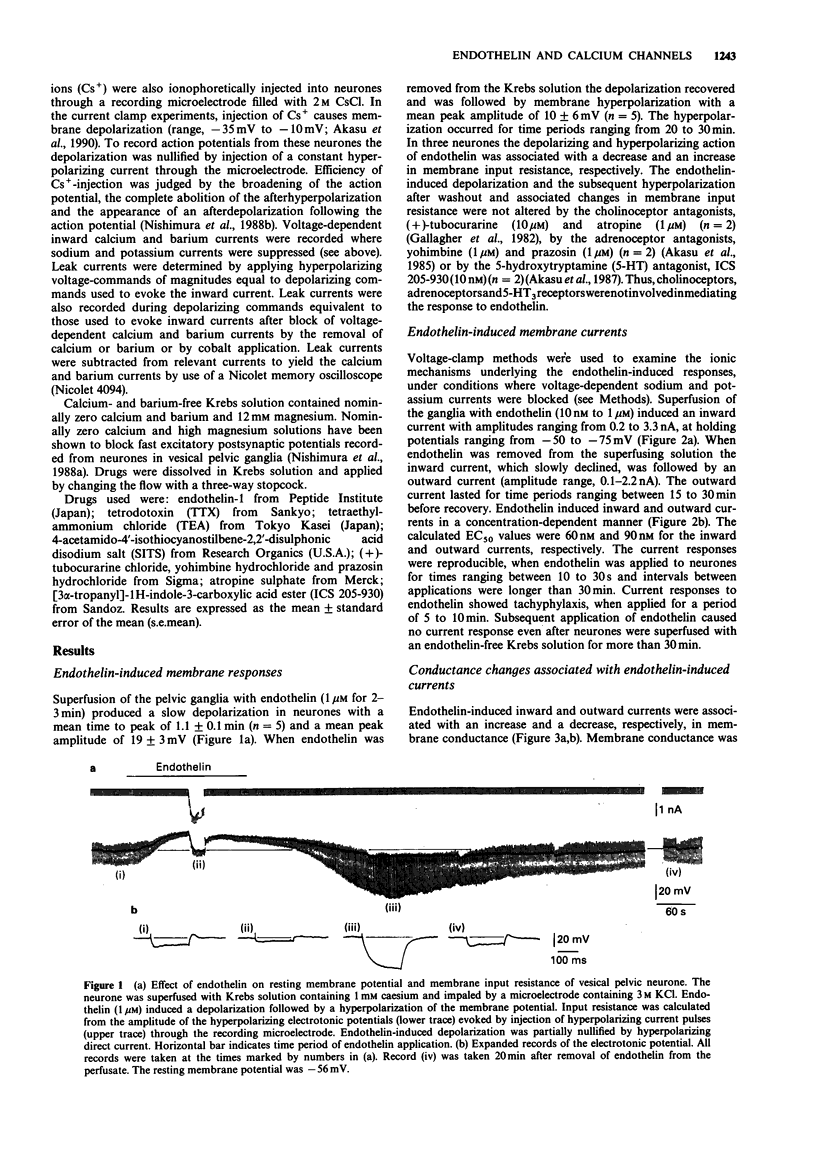
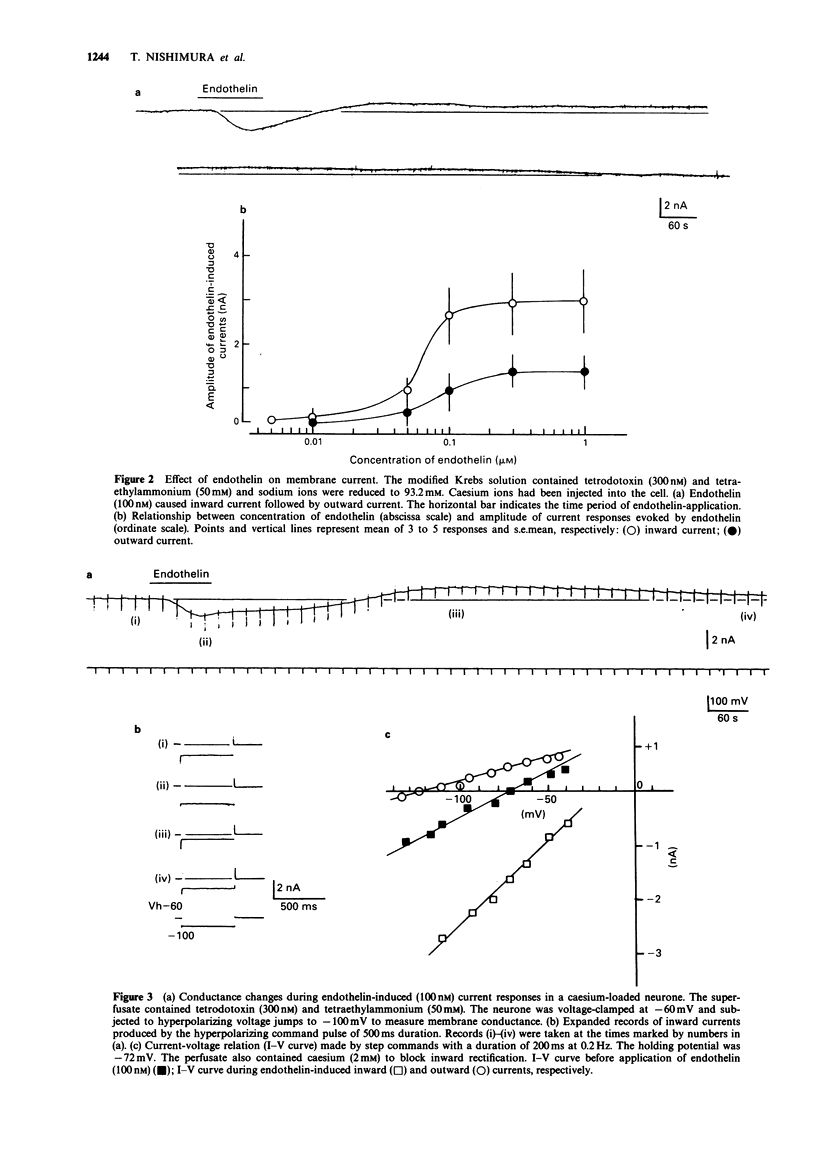
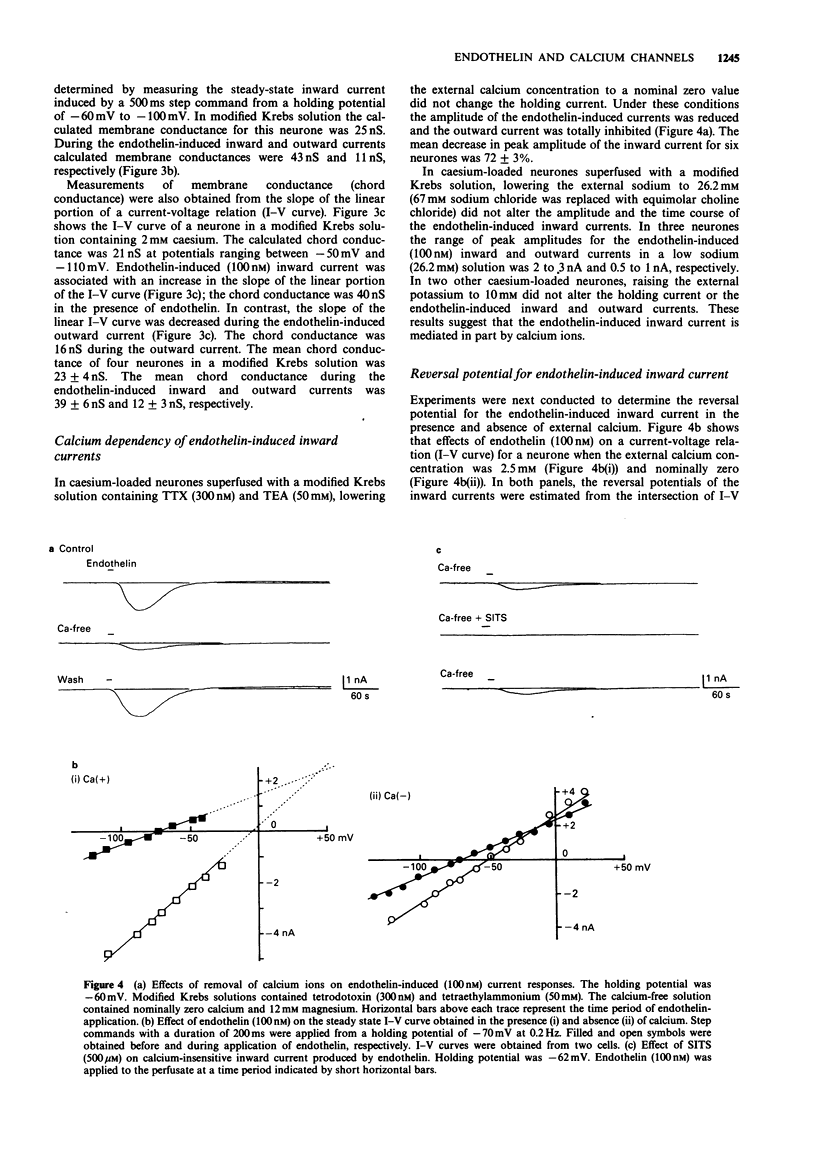
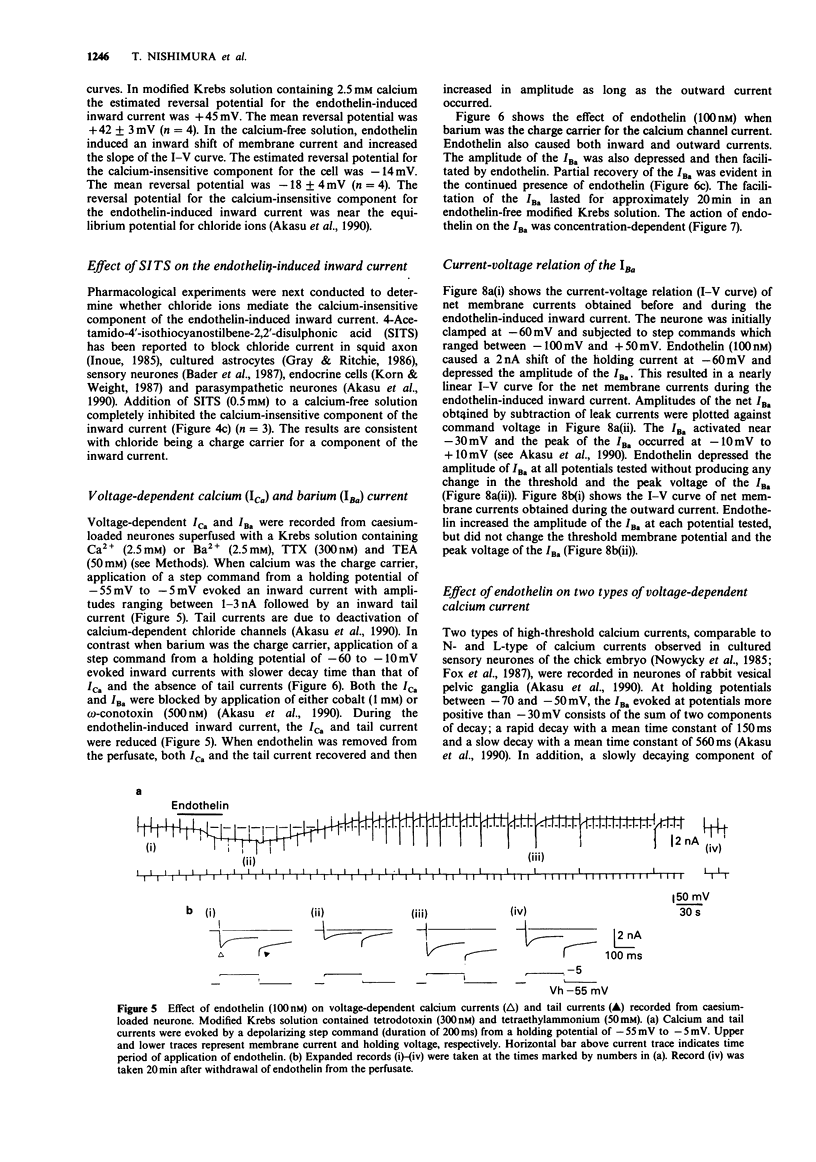
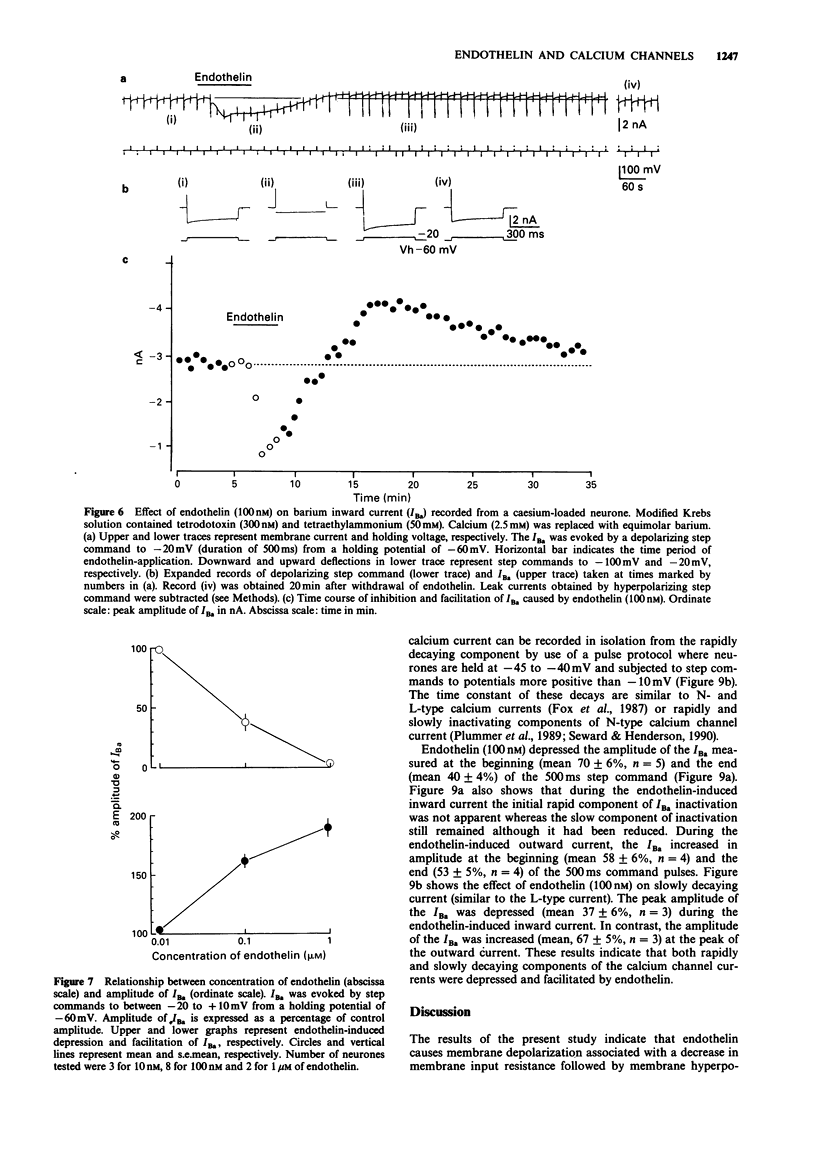
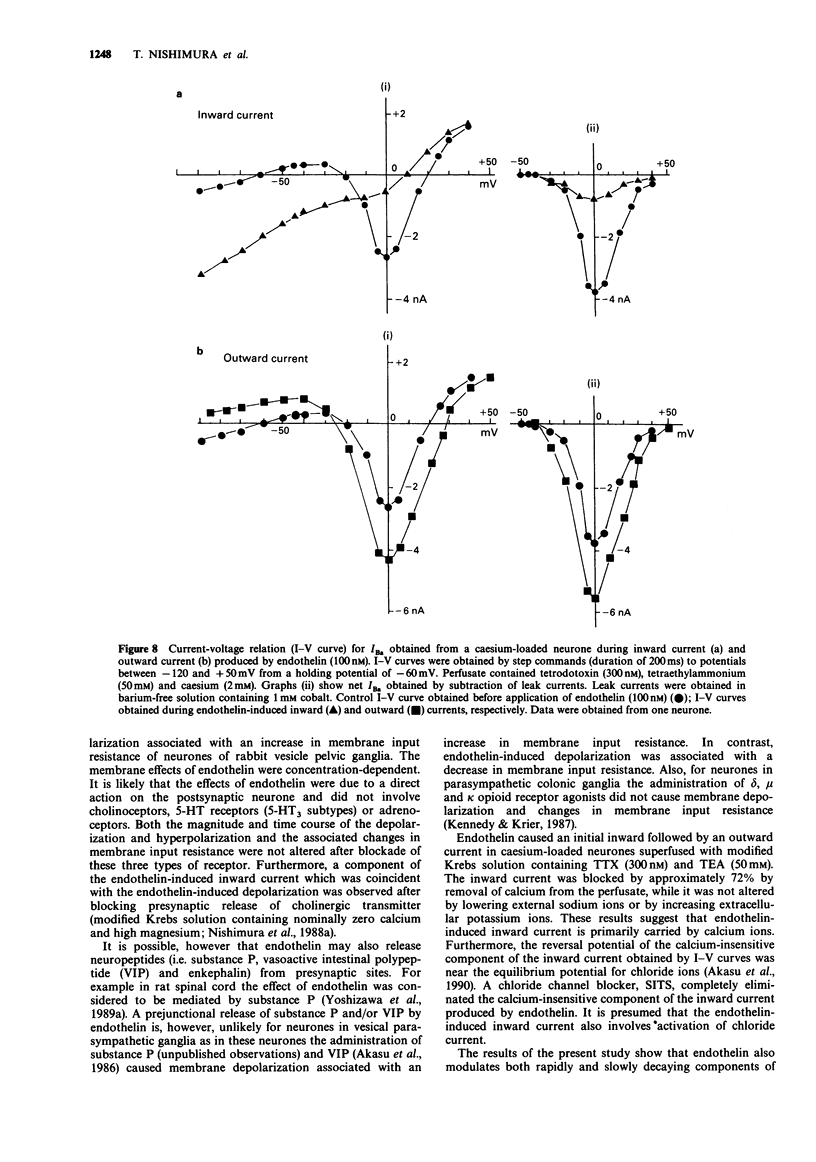
1. The effects of endothelin were studied, in vitro, on neurones contained in the rabbit vesical pelvic ganglion by use of intracellular and single-electrode voltage clamp techniques under conditions where sodium and potassium channels were blocked. 2. In the current-clamp experiments, endothelin (1 microM) caused a depolarization followed by a hyperpolarization of the membrane potential. In the voltage-clamp experiments, endothelin (0.01-1 microM) caused an inward current followed by an outward current in a concentration-dependent manner. 3. Membrane conductance was increased during the endothelin-induced depolarization and inward current. Membrane conductance was decreased during the endothelin-induced hyperpolarization and outward current. 4. The endothelin-induced inward and outward currents were not altered by lowering external sodium concentration or raising external potassium concentration. 5. The endothelin-induced inward current was depressed (mean 72%) in a Krebs solution containing nominally zero calcium and high magnesium. These results suggest that a predominent component of the endothelin-induced inward current is mediated by calcium ions. 6. The calcium-insensitive component of the inward current was abolished by a chloride channel blocker, 4-acetamide-4'-isothiocyanostilbene-2,2'-disulphonic acid. The mean reversal potential for the calcium-insensitive component of the inward current was -18 mV. This value is near the equilibrium potential for chloride. Thus, it is presumed that the calcium-insensitive component of the inward current is carried by chloride ions. 7. Endothelin caused an initial depression followed by a long lasting facilitation of both rapidly and slowly decaying components of high-threshold calcium channel currents (N- and L-type).(ABSTRACT TRUNCATED AT 250 WORDS)
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Akasu T., Gallagher J. P., Hirai K., Shinnick-Gallagher P. Vasoactive intestinal polypeptide depolarizations in cat bladder parasympathetic ganglia. J Physiol. 1986 May;374:457–473. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1986.sp016091. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Akasu T., Gallagher J. P., Nakamura T., Shinnick-Gallagher P., Yoshimura M. Noradrenaline hyperpolarization and depolarization in cat vesical parasympathetic neurones. J Physiol. 1985 Apr;361:165–184. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1985.sp015639. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Akasu T., Hasuo H., Tokimasa T. Activation of 5-HT3 receptor subtypes causes rapid excitation of rabbit parasympathetic neurones. Br J Pharmacol. 1987 Jul;91(3):453–455. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1987.tb11236.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Akasu T., Nishimura T., Tokimasa T. Calcium-dependent chloride current in neurones of the rabbit pelvic parasympathetic ganglia. J Physiol. 1990 Mar;422:303–320. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1990.sp017985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bader C. R., Bertrand D., Schlichter R. Calcium-activated chloride current in cultured sensory and parasympathetic quail neurones. J Physiol. 1987 Dec;394:125–148. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1987.sp016863. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brehm P., Eckert R. Calcium entry leads to inactivation of calcium channel in Paramecium. Science. 1978 Dec 15;202(4373):1203–1206. doi: 10.1126/science.103199. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fox A. P., Nowycky M. C., Tsien R. W. Kinetic and pharmacological properties distinguishing three types of calcium currents in chick sensory neurones. J Physiol. 1987 Dec;394:149–172. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1987.sp016864. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gallagher J. P., Griffith W. H., Shinnick-Gallagher P. Cholinergic transmission in cat parasympathetic ganglia. J Physiol. 1982 Nov;332:473–486. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1982.sp014425. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giaid A., Gibson S. J., Ibrahim B. N., Legon S., Bloom S. R., Yanagisawa M., Masaki T., Varndell I. M., Polak J. M. Endothelin 1, an endothelium-derived peptide, is expressed in neurons of the human spinal cord and dorsal root ganglia. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Oct;86(19):7634–7638. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.19.7634. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goto K., Kasuya Y., Matsuki N., Takuwa Y., Kurihara H., Ishikawa T., Kimura S., Yanagisawa M., Masaki T. Endothelin activates the dihydropyridine-sensitive, voltage-dependent Ca2+ channel in vascular smooth muscle. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 May;86(10):3915–3918. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.10.3915. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gray P. T., Ritchie J. M. A voltage-gated chloride conductance in rat cultured astrocytes. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1986 Aug 22;228(1252):267–288. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1986.0055. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inoue I. Voltage-dependent chloride conductance of the squid axon membrane and its blockade by some disulfonic stilbene derivatives. J Gen Physiol. 1985 Apr;85(4):519–537. doi: 10.1085/jgp.85.4.519. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inoue Y., Oike M., Nakao K., Kitamura K., Kuriyama H. Endothelin augments unitary calcium channel currents on the smooth muscle cell membrane of guinea-pig portal vein. J Physiol. 1990 Apr;423:171–191. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1990.sp018017. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Itoh Y., Yanagisawa M., Ohkubo S., Kimura C., Kosaka T., Inoue A., Ishida N., Mitsui Y., Onda H., Fujino M. Cloning and sequence analysis of cDNA encoding the precursor of a human endothelium-derived vasoconstrictor peptide, endothelin: identity of human and porcine endothelin. FEBS Lett. 1988 Apr 25;231(2):440–444. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(88)80867-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kennedy C., Krier J. Delta-opioid receptors mediate inhibition of fast excitatory postsynaptic potentials in cat parasympathetic colonic ganglia. Br J Pharmacol. 1987 Oct;92(2):437–443. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1987.tb11340.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Korn S. J., Weight F. F. Patch-clamp study of the calcium-dependent chloride current in AtT-20 pituitary cells. J Neurophysiol. 1987 Dec;58(6):1431–1451. doi: 10.1152/jn.1987.58.6.1431. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koseki C., Imai M., Hirata Y., Yanagisawa M., Masaki T. Autoradiographic distribution in rat tissues of binding sites for endothelin: a neuropeptide? Am J Physiol. 1989 Apr;256(4 Pt 2):R858–R866. doi: 10.1152/ajpregu.1989.256.4.R858. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee K. S., Marban E., Tsien R. W. Inactivation of calcium channels in mammalian heart cells: joint dependence on membrane potential and intracellular calcium. J Physiol. 1985 Jul;364:395–411. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1985.sp015752. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacCumber M. W., Ross C. A., Snyder S. H. Endothelin in brain: receptors, mitogenesis, and biosynthesis in glial cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Mar;87(6):2359–2363. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.6.2359. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Masaki T. The discovery, the present state, and the future prospects of endothelin. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol. 1989;13 (Suppl 5):S1–S18. doi: 10.1097/00005344-198900135-00002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller R. J. Multiple calcium channels and neuronal function. Science. 1987 Jan 2;235(4784):46–52. doi: 10.1126/science.2432656. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishimura T., Tokimasa T., Akasu T. 5-hydroxytryptamine inhibits cholinergic transmission through 5-HT1A receptor subtypes in rabbit vesical parasympathetic ganglia. Brain Res. 1988 Mar 1;442(2):399–402. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(88)91534-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishimura T., Tokimasa T., Akasu T. Calcium-dependent potassium conductance in neurons of rabbit vesical pelvic ganglia. J Auton Nerv Syst. 1988 Sep;24(1-2):133–145. doi: 10.1016/0165-1838(88)90142-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nowycky M. C., Fox A. P., Tsien R. W. Three types of neuronal calcium channel with different calcium agonist sensitivity. Nature. 1985 Aug 1;316(6027):440–443. doi: 10.1038/316440a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plummer M. R., Logothetis D. E., Hess P. Elementary properties and pharmacological sensitivities of calcium channels in mammalian peripheral neurons. Neuron. 1989 May;2(5):1453–1463. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(89)90191-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scott R. H., McGuirk S. M., Dolphin A. C. Modulation of divalent cation-activated chloride ion currents. Br J Pharmacol. 1988 Jul;94(3):653–662. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1988.tb11572.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seward E. P., Henderson G. Characterization of two components of the N-like, high-threshold-activated calcium channel current in differentiated SH-SY5Y cells. Pflugers Arch. 1990 Oct;417(2):223–230. doi: 10.1007/BF00370703. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silberberg S. D., Poder T. C., Lacerda A. E. Endothelin increases single-channel calcium currents in coronary arterial smooth muscle cells. FEBS Lett. 1989 Apr 10;247(1):68–72. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(89)81242-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stojilković S. S., Merelli F., Iida T., Krsmanović L. Z., Catt K. J. Endothelin stimulation of cytosolic calcium and gonadotropin secretion in anterior pituitary cells. Science. 1990 Jun 29;248(4963):1663–1666. doi: 10.1126/science.2163546. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tillotson D. Inactivation of Ca conductance dependent on entry of Ca ions in molluscan neurons. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Mar;76(3):1497–1500. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.3.1497. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yanagisawa M., Kurihara H., Kimura S., Tomobe Y., Kobayashi M., Mitsui Y., Yazaki Y., Goto K., Masaki T. A novel potent vasoconstrictor peptide produced by vascular endothelial cells. Nature. 1988 Mar 31;332(6163):411–415. doi: 10.1038/332411a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshizawa T., Kimura S., Kanazawa I., Uchiyama Y., Yanagisawa M., Masaki T. Endothelin localizes in the dorsal horn and acts on the spinal neurones: possible involvement of dihydropyridine-sensitive calcium channels and substance P release. Neurosci Lett. 1989 Jul 31;102(2-3):179–184. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(89)90075-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshizawa T., Shinmi O., Giaid A., Yanagisawa M., Gibson S. J., Kimura S., Uchiyama Y., Polak J. M., Masaki T., Kanazawa I. Endothelin: a novel peptide in the posterior pituitary system. Science. 1990 Jan 26;247(4941):462–464. doi: 10.1126/science.2405487. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang W., Sakai N., Yamada H., Fu T., Nozawa Y. Endothelin-1 induces intracellular calcium rise and inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate formation in cultured rat and human glioma cells. Neurosci Lett. 1990 May 4;112(2-3):199–204. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(90)90203-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


