Abstract
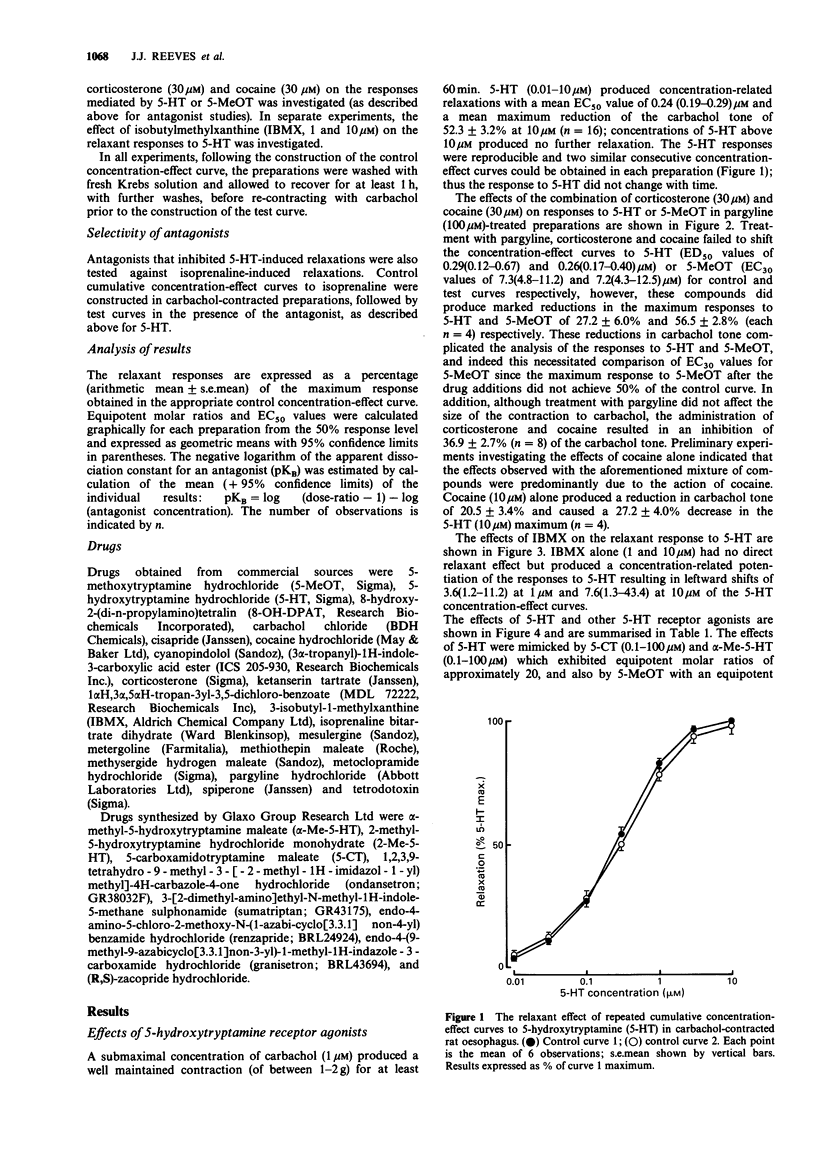
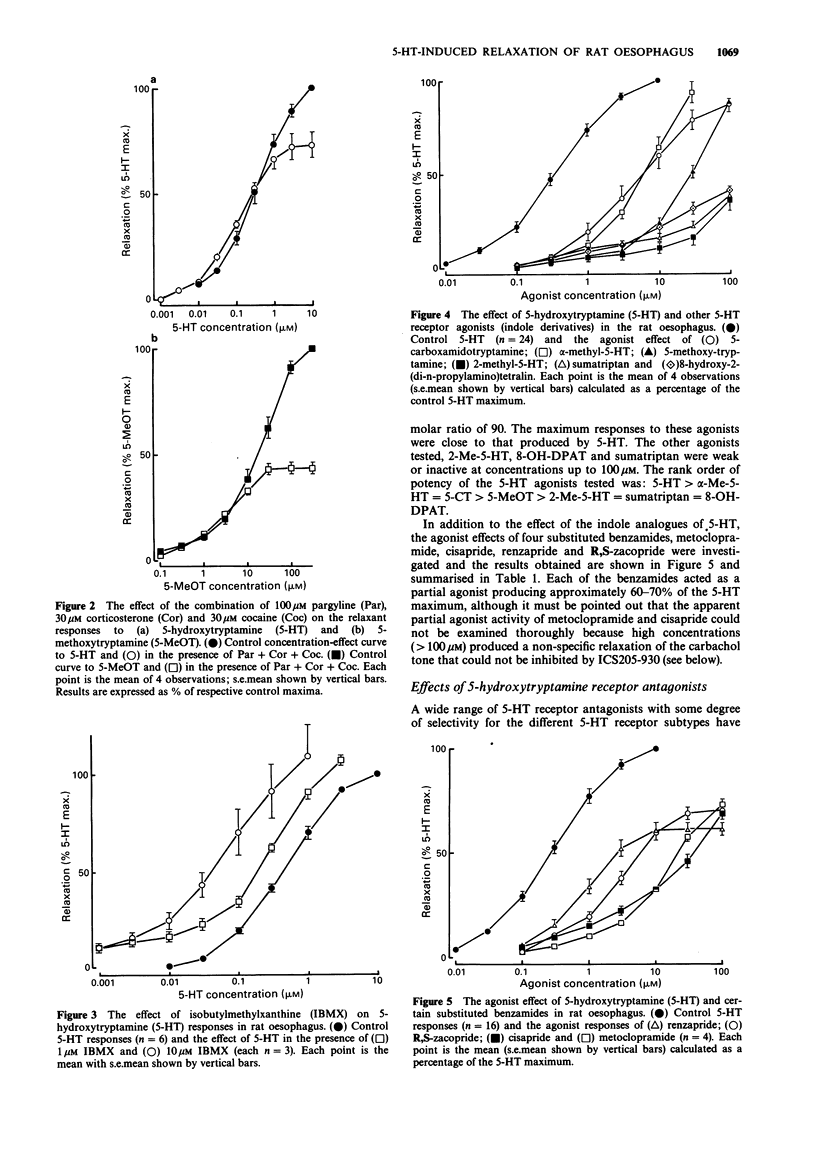
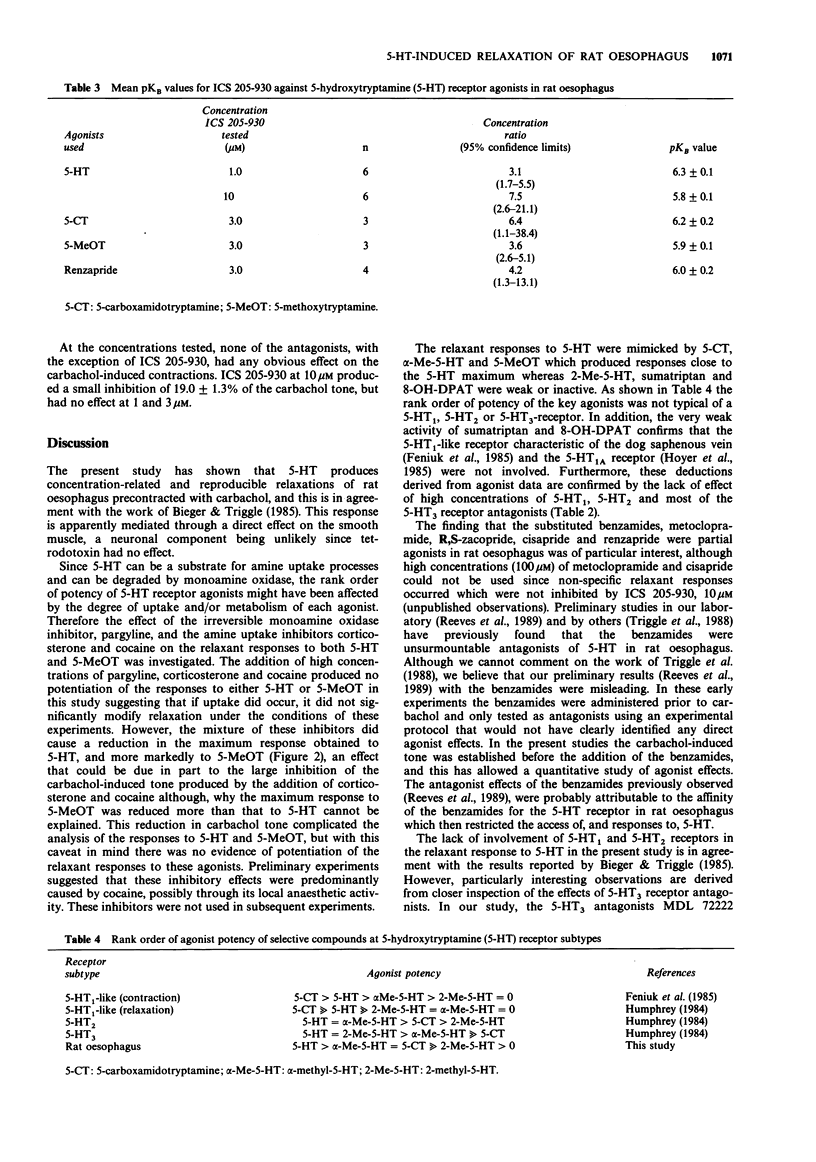
1. An investigation has been made into the 5-hydroxytryptamine (5-HT) receptor mediating relaxation of rat oesophagus in preparations precontracted with carbachol. 2. In tissues treated with pargyline (100 microM) and in the presence of corticosterone (30 microM) and cocaine (30 microM) the potency of 5-HT and 5-methoxytyramine (5-MeOT) was not changed but the maximum response to these agonists was reduced. Thus there was no evidence of metabolism and/or uptake through an amine depleting mechanism. 3. The relaxant concentration-effect curves to 5-HT were shifted to the left in a concentration-related manner by isobutylmethylxanthine (1 and 10 microM), suggesting the involvement of adenosine 3':5'-cyclic monophosphate in these responses. 4. 5-HT produced concentration-related relaxations of rat oesophagus with an EC50 value of 0.24 microM. Several indole agonists were tested and the following rank order of potency of key agonists obtained: 5-HT greater than alpha-methyl-5-hydroxytryptamine = 5-carboxamidotryptamine (5-CT) greater than 5-MeOT. In contrast, 2-methyl-5-hydroxytryptamine, sumatriptan and 8-hydroxy-2-(di-n-propylamino) tetralin were weak or inactive. 5. The substituted benzamides, metoclopramide, cisapride, renzapride and R,S-zacopride acted as partial agonists, producing 60-70% of the 5-HT maximum. 6. The relaxation responses to 5-HT were neither inhibited by antagonists selective for 5-HT1 or 5-HT2 receptors nor by the 5-HT3 receptor antagonists, ondansetron, granisetron or MDL 72222. 7. The relaxation responses induced by 5-HT, 5-CT, 5-MeOT and renzapride were selectively inhibited by high concentrations of ICS 205-930 with pKB values of approximately 6.(ABSTRACT TRUNCATED AT 250 WORDS)
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bieger D., Triggle C. Pharmacological properties of mechanical responses of the rat oesophageal muscularis mucosae to vagal and field stimulation. Br J Pharmacol. 1985 Jan;84(1):93–106. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bockaert J., Sebben M., Dumuis A. Pharmacological characterization of 5-hydroxytryptamine4(5-HT4) receptors positively coupled to adenylate cyclase in adult guinea pig hippocampal membranes: effect of substituted benzamide derivatives. Mol Pharmacol. 1990 Mar;37(3):408–411. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradley P. B., Engel G., Feniuk W., Fozard J. R., Humphrey P. P., Middlemiss D. N., Mylecharane E. J., Richardson B. P., Saxena P. R. Proposals for the classification and nomenclature of functional receptors for 5-hydroxytryptamine. Neuropharmacology. 1986 Jun;25(6):563–576. doi: 10.1016/0028-3908(86)90207-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Butler A., Hill J. M., Ireland S. J., Jordan C. C., Tyers M. B. Pharmacological properties of GR38032F, a novel antagonist at 5-HT3 receptors. Br J Pharmacol. 1988 Jun;94(2):397–412. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1988.tb11542.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clarke D. E., Craig D. A., Fozard J. R. The 5-HT4 receptor: naughty, but nice. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 1989 Oct;10(10):385–386. doi: 10.1016/0165-6147(89)90177-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Craig D. A., Clarke D. E. Pharmacological characterization of a neuronal receptor for 5-hydroxytryptamine in guinea pig ileum with properties similar to the 5-hydroxytryptamine receptor. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1990 Mar;252(3):1378–1386. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dumuis A., Bouhelal R., Sebben M., Cory R., Bockaert J. A nonclassical 5-hydroxytryptamine receptor positively coupled with adenylate cyclase in the central nervous system. Mol Pharmacol. 1988 Dec;34(6):880–887. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dumuis A., Sebben M., Bockaert J. The gastrointestinal prokinetic benzamide derivatives are agonists at the non-classical 5-HT receptor (5-HT4) positively coupled to adenylate cyclase in neurons. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1989 Oct;340(4):403–410. doi: 10.1007/BF00167041. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feniuk W., Humphrey P. P., Perren M. J., Watts A. D. A comparison of 5-hydroxytryptamine receptors mediating contraction in rabbit aorta and dog saphenous vein: evidence for different receptor types obtained by use of selective agonists and antagonists. Br J Pharmacol. 1985 Nov;86(3):697–704. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1985.tb08948.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fozard J. R. MDL 72222: a potent and highly selective antagonist at neuronal 5-hydroxytryptamine receptors. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1984 May;326(1):36–44. doi: 10.1007/BF00518776. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoyer D., Engel G., Kalkman H. O. Molecular pharmacology of 5-HT1 and 5-HT2 recognition sites in rat and pig brain membranes: radioligand binding studies with [3H]5-HT, [3H]8-OH-DPAT, (-)[125I]iodocyanopindolol, [3H]mesulergine and [3H]ketanserin. Eur J Pharmacol. 1985 Nov 26;118(1-2):13–23. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(85)90658-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Humphrey P. P. Peripheral 5-hydroxytryptamine receptors and their classification. Neuropharmacology. 1984 Dec;23(12B):1503–1510. doi: 10.1016/0028-3908(84)90094-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Narahashi T. Mechanism of action of tetrodotoxin and saxitoxin on excitable membranes. Fed Proc. 1972 May-Jun;31(3):1124–1132. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reeves J. J., Bunce K. T., Humphrey P. P., Gunning S. J. Further characterisation of the 5-HT receptor mediating smooth muscle relaxation in rat oesophagus. Br J Pharmacol. 1989 Dec;98 (Suppl):800P–800P. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richardson B. P., Engel G., Donatsch P., Stadler P. A. Identification of serotonin M-receptor subtypes and their specific blockade by a new class of drugs. Nature. 1985 Jul 11;316(6024):126–131. doi: 10.1038/316126a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger G. J., Nelson D. R. Selective and functional 5-hydroxytryptamine3 receptor antagonism by BRL 43694 (granisetron). Eur J Pharmacol. 1989 Jan 10;159(2):113–124. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(89)90695-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


