Abstract
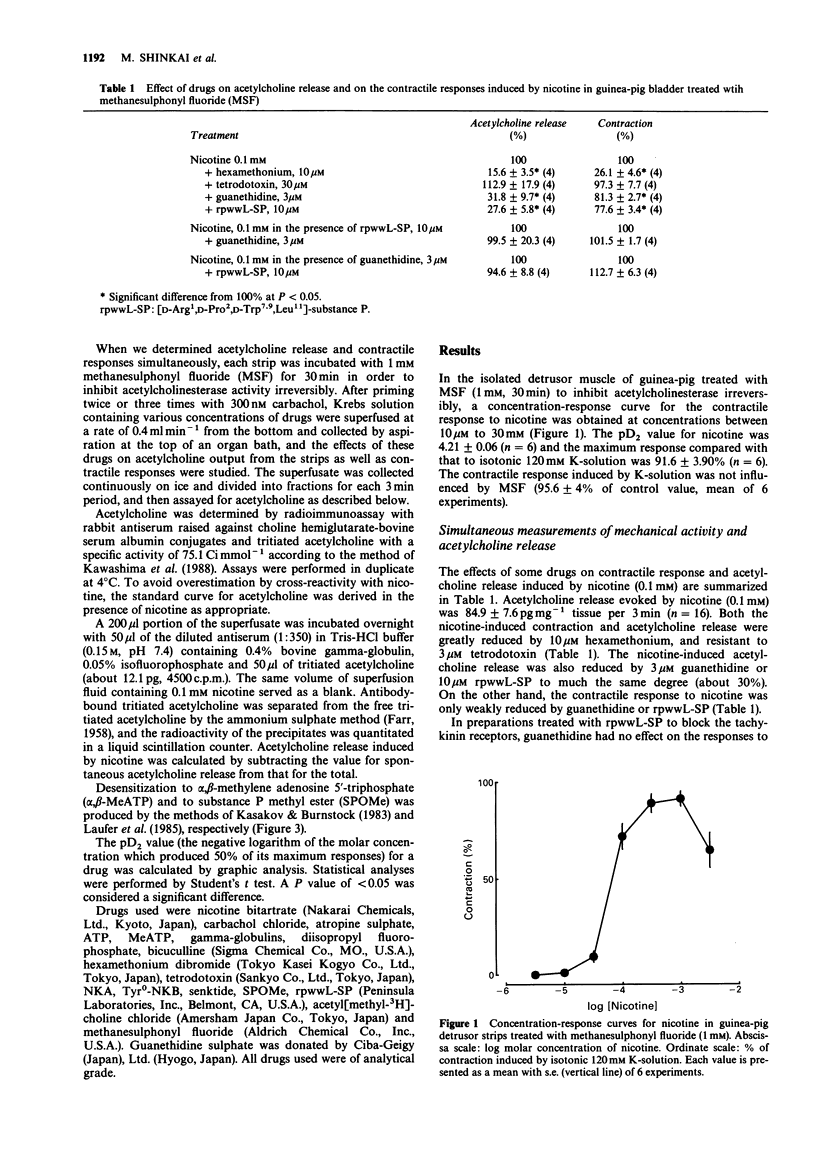
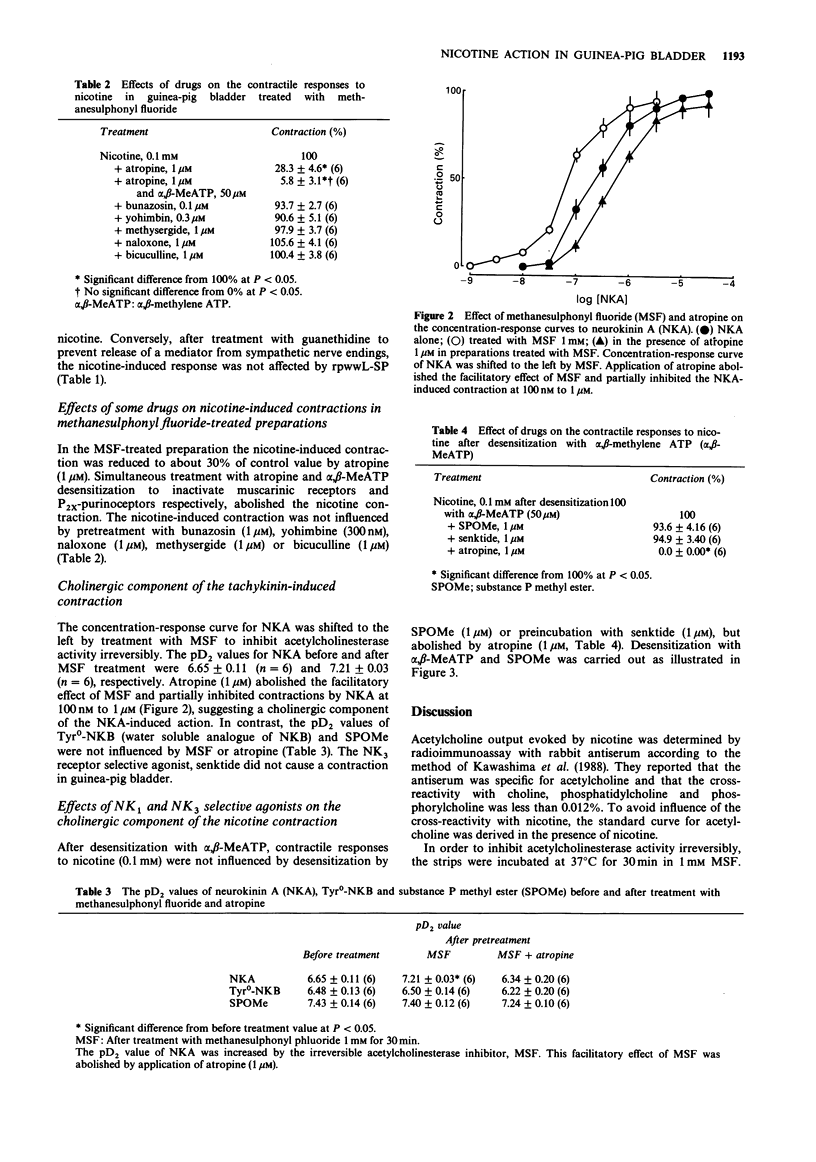
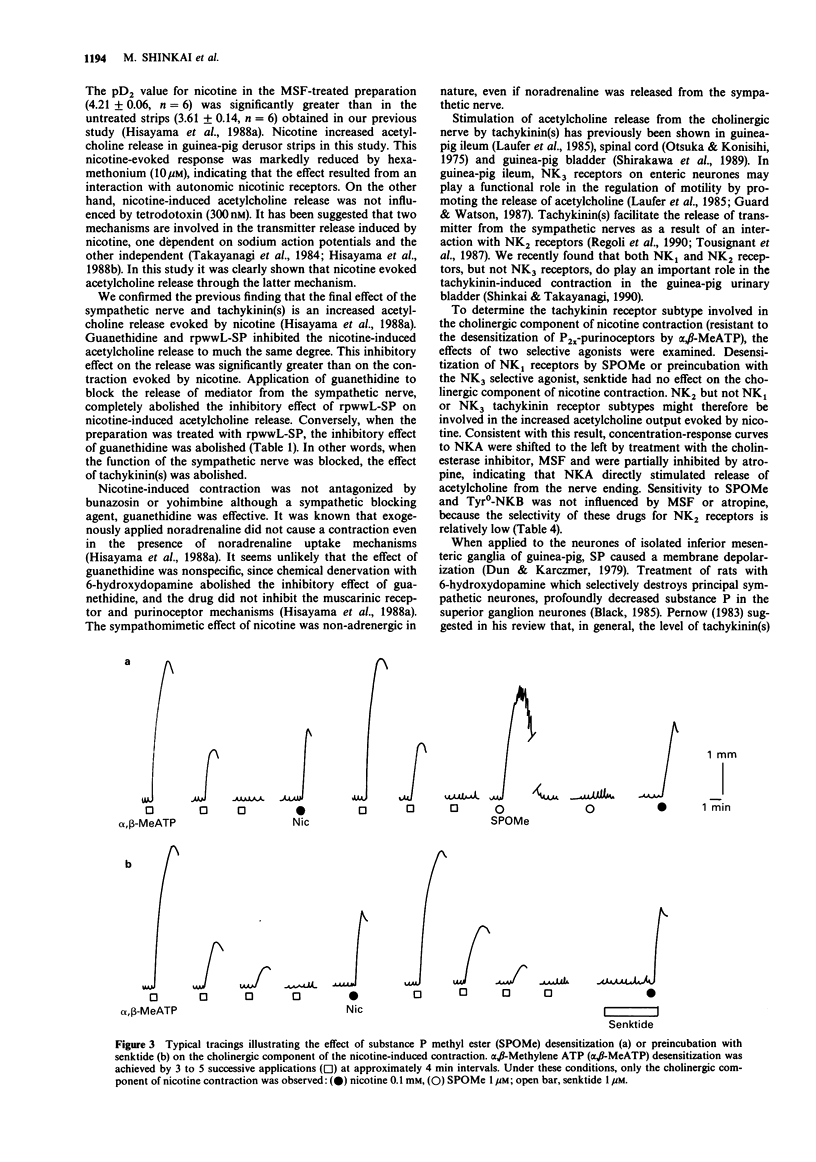
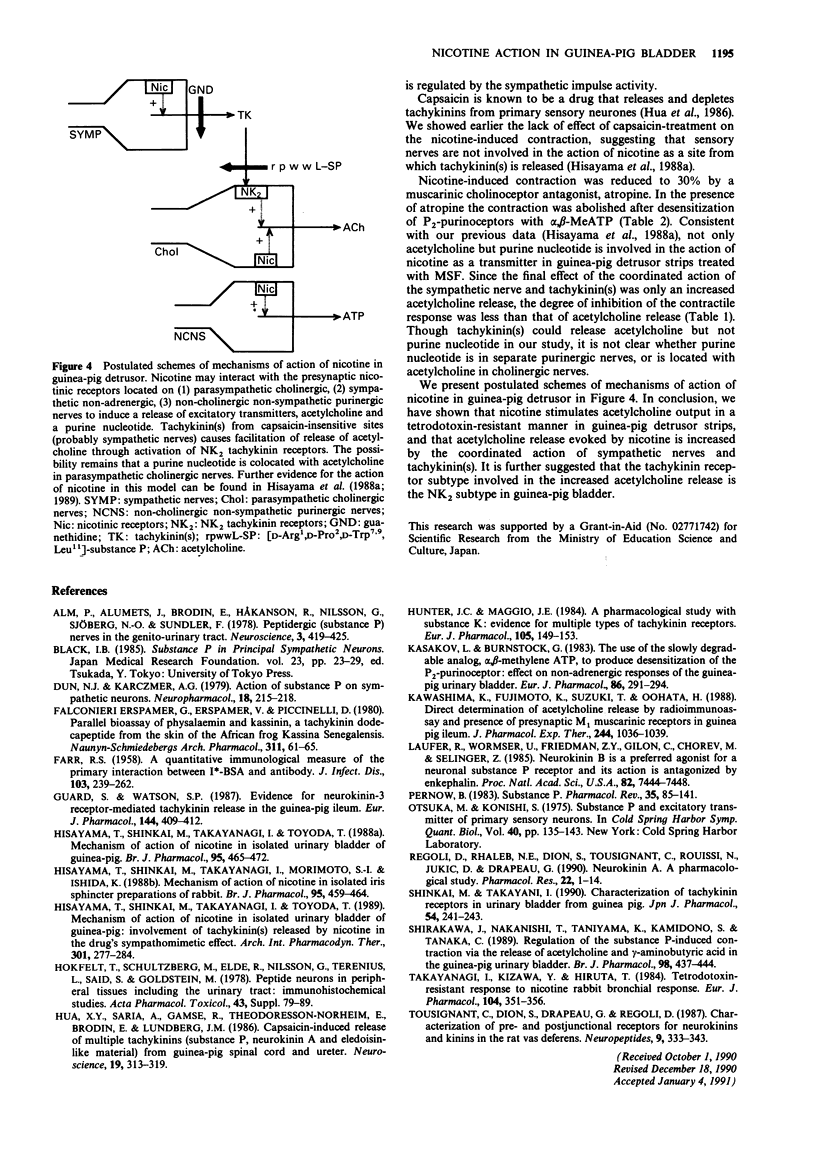
1. Contractile responses and acetylcholine release evoked by nicotine in guinea-pig detrusor strips were determined by isotonic transducer and radioimmunoassay, respectively. Nicotine stimulated acetylcholine release and a contractile response in guinea-pig detrusor strips treated with the cholinesterase inhibitor, methanesulphonyl fluoride (MSF). Both actions evoked by nicotine were antagonized by the nicotinic receptor antagonist, hexamethonium but were insensitive to tetrodotoxin. 2. A sympathetic nerve blocker, guanethidine and a tachykinin antagonist, [D-Arg1, D-Pro2, D-Trp7,9, Leu11]-substance P (rpwwL-SP) partially inhibited the acetylcholine release evoked by nicotine to much the same degree. The inhibitory effects of guanethidine and rpwwL-SP on acetylcholine release were significantly greater than corresponding effects on the contraction evoked by nicotine. 3. In preparations treated with rpwwL-SP to block the tachykinin receptors, guanethidine had no effect on the response to nicotine. Conversely, after treatment with guanethidine to block release of a mediator from sympathetic nerve endings, nicotine-induced responses were not affected by rpwwL-SP. 4. Nicotine-induced contraction was reduced to 30% by the muscarinic cholinoceptor antagonist, atropine and completely abolished after desensitization of P2-purinoceptors with alpha,beta-methylene ATP in the presence of atropine. 5. A concentration-contractile response curve to neurokinin A (NKA) was shifted to the left after cholinesterase inhibition with MSF. Atropine abolished the facilitatory effect of MSF and partially inhibited contractions induced by NKA at 100 nM to 1 microM. The contractile responses to substance P methyl ester (SPOMe) and Tyr0-neurokinin B (Tyr0-NKB) were not influenced by MSF or atropine.(ABSTRACT TRUNCATED AT 250 WORDS)
Full text
PDF
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alm P., Alumets J., Brodin E., Håkanson R., Nilsson G., Sjöberg N. O., Sundler F. Peptidergic (substance P) nerves in the genito-urinary tract. Neuroscience. 1978;3(4-5):419–425. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(78)90044-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dun N. J., Karczmar A. G. Actions of substance P on sympathetic neurons. Neuropharmacology. 1979 Feb;18(2):215–218. doi: 10.1016/0028-3908(79)90064-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Erspamer G. F., Erspamer V., Piccinelli D. Parallel bioassay of physalaemin and kassinin, a tachykinin dodecapeptide from the skin of the African frog Kassina senegalensis. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1980 Feb;311(1):61–65. doi: 10.1007/BF00500303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FARR R. S. A quantitative immunochemical measure of the primary interaction between I BSA and antibody. J Infect Dis. 1958 Nov-Dec;103(3):239–262. doi: 10.1093/infdis/103.3.239. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guard S., Watson S. P. Evidence for neurokinin-3 receptor-mediated tachykinin release in the guinea-pig ileum. Eur J Pharmacol. 1987 Dec 15;144(3):409–412. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(87)90398-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hisayama T., Shinkai M., Takayanagi I., Morimoto S., Ishida K. Mechanism of action of nicotine in isolated iris sphincter preparations of rabbit. Br J Pharmacol. 1988 Oct;95(2):459–464. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1988.tb11666.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hisayama T., Shinkai M., Takayanagi I., Toyoda T. Mechanism of action of nicotine in isolated urinary bladder of guinea-pig. Br J Pharmacol. 1988 Oct;95(2):465–472. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1988.tb11667.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hisayama T., Shinkai M., Takayanagi I., Toyoda T. Mechanism of action of nicotine in isolated urinary bladder of guinea-pig: involvement of tachykinin(s) released by nicotine in the drug's sympathomimetic effect. Arch Int Pharmacodyn Ther. 1989 Sep-Oct;301:277–284. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hua X. Y., Saria A., Gamse R., Theodorsson-Norheim E., Brodin E., Lundberg J. M. Capsaicin induced release of multiple tachykinins (substance P, neurokinin A and eledoisin-like material) from guinea-pig spinal cord and ureter. Neuroscience. 1986 Sep;19(1):313–319. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(86)90024-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunter J. C., Maggio J. E. A pharmacological study with substance K: evidence for multiple types of tachykinin receptors. Eur J Pharmacol. 1984 Oct 1;105(1-2):149–153. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(84)90659-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hökfelt T., Schultzberg M., Elde R., Nilsson G., Terenius L., Said S., Goldstein M. Peptide neurons in peripheral tissues including the urinary tract: immunohistochemical studies. Acta Pharmacol Toxicol (Copenh) 1978;43 (Suppl 2):79–89. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0773.1978.tb03224.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kasakov L., Burnstock G. The use of the slowly degradable analog, alpha, beta-methylene ATP, to produce desensitisation of the P2-purinoceptor: effect on non-adrenergic, non-cholinergic responses of the guinea-pig urinary bladder. Eur J Pharmacol. 1982 Dec 24;86(2):291–294. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(82)90330-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kawashima K., Fujimoto K., Suzuki T., Oohata H. Direct determination of acetylcholine release by radioimmunoassay and presence of presynaptic M1 muscarinic receptors in guinea pig ileum. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1988 Mar;244(3):1036–1039. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laufer R., Wormser U., Friedman Z. Y., Gilon C., Chorev M., Selinger Z. Neurokinin B is a preferred agonist for a neuronal substance P receptor and its action is antagonized by enkephalin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Nov;82(21):7444–7448. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.21.7444. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Otsuka M., Konishi S. Substance P and excitatory transmitter of primary sensory neurons. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1976;40:135–143. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1976.040.01.015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pernow B. Substance P. Pharmacol Rev. 1983 Jun;35(2):85–141. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Regoli D., Rhaleb N. E., Dion S., Tousignant C., Rouissi N., Jukic D., Drapeau G. Neurokinin A. A pharmacological study. Pharmacol Res. 1990 Jan-Feb;22(1):1–14. doi: 10.1016/1043-6618(90)90738-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shinkai M., Takayanagi I. Characterization of tachykinin receptors in urinary bladder from guinea pig. Jpn J Pharmacol. 1990 Oct;54(2):241–243. doi: 10.1254/jjp.54.241. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shirakawa J., Nakanishi T., Taniyama K., Kamidono S., Tanaka C. Regulation of the substance P-induced contraction via the release of acetylcholine and gamma-aminobutyric acid in the guinea-pig urinary bladder. Br J Pharmacol. 1989 Oct;98(2):437–444. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1989.tb12615.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takayanagi I., Kizawa Y., Hiruta T. Tetrodotoxin-resistant response to nicotine in rabbit bronchial preparation. Eur J Pharmacol. 1984 Sep 17;104(3-4):351–356. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(84)90412-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tousignant C., Dion S., Drapeau G., Regoli D. Characterization of pre- and postjunctional receptors for neurokinins and kinins in the rat vas deferens. Neuropeptides. 1987 May-Jun;9(4):333–343. doi: 10.1016/0143-4179(87)90007-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


