Abstract
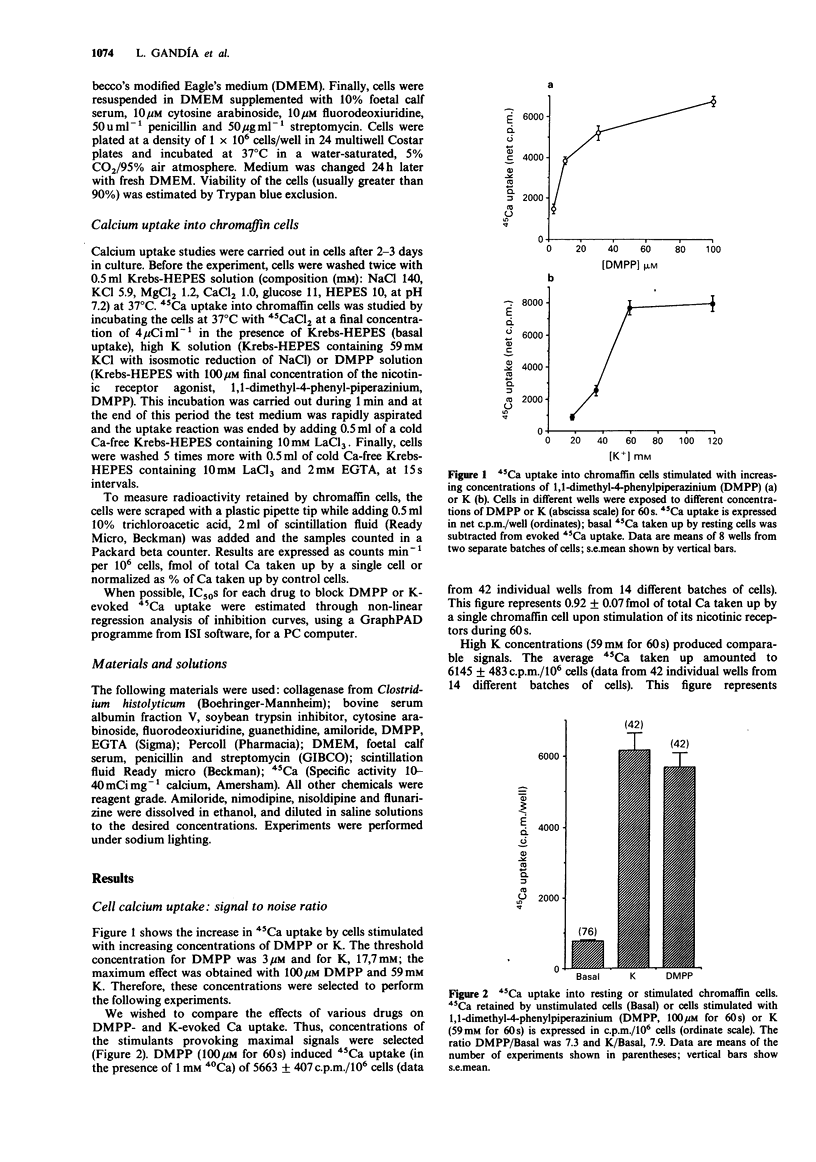
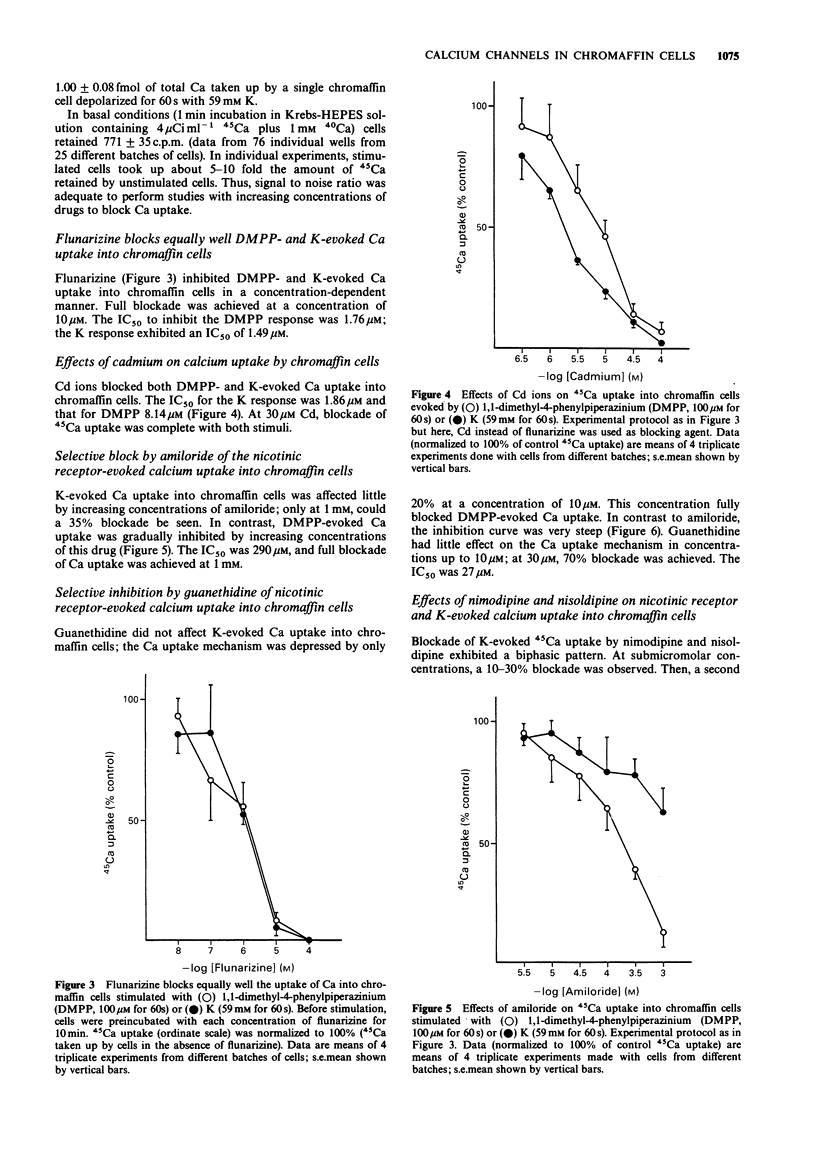
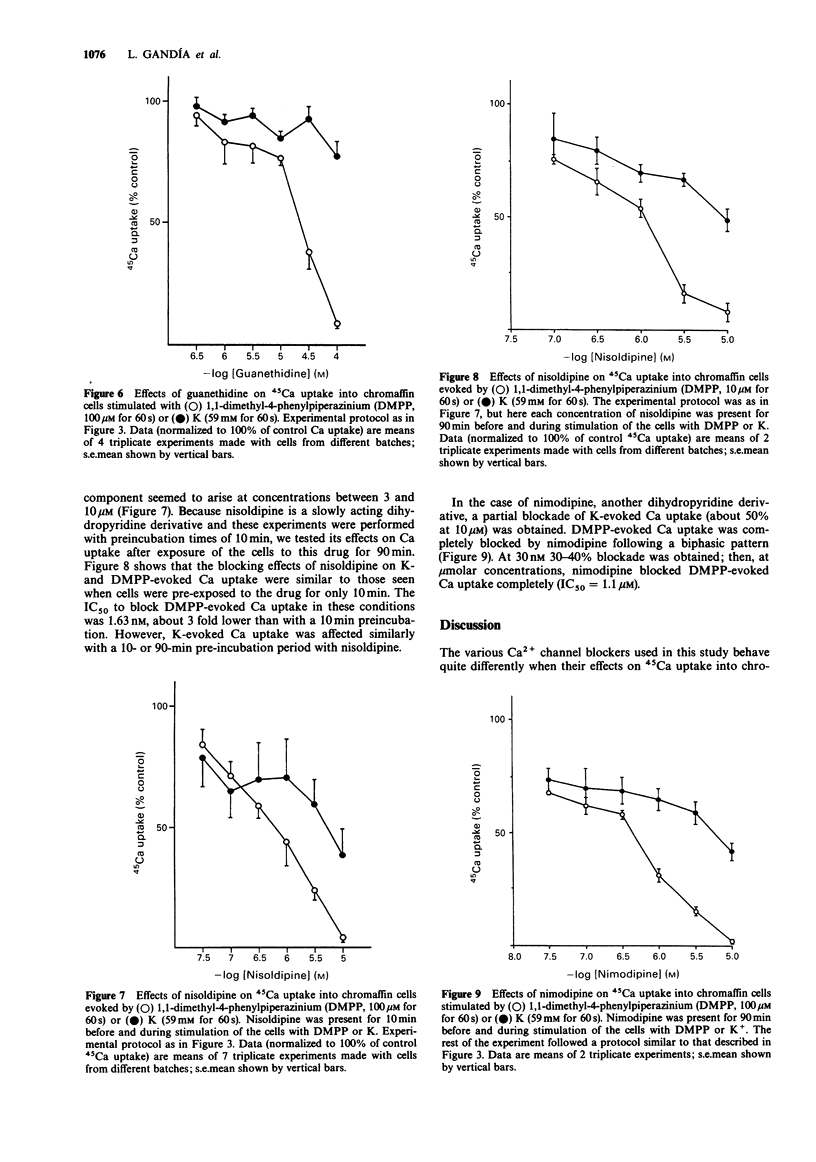
1. The effects of various drugs on 45Ca + 40Ca uptake into cultured bovine adrenal chromaffin cells evoked by 1,1-dimethyl-4-phenylpiperazinium (DMPP) or high K, were studied. In the presence of 1 mM external 40Ca, with 45Ca as a radiotracer, unstimulated cells took up an average of 0.13 fmol/cell 40Ca and 772 c.p.m./10(6) cells of 45Ca (n = 76). Upon stimulation with DMPP (100 microM for 60 s) or K (59 mM for 60 s), Ca uptake increased to 0.92 and 1 fmol/cell, respectively. 2. Flunarizine behaved as a potent blocker of both DMPP- and K-evoked Ca uptake (IC50 of 1.76 and 1.49 microM, respectively for DMPP and K). A similar picture emerged with Cd ions, though Cd exhibited an IC50 against K (1.86 microM) slightly lower than the IC50 against DMPP (8.14 microM). 3. Clear cut differences were observed with amiloride, guanethidine, nimodipine and nisoldipine which behaved as selective blockers of DMPP-mediated Ca uptake responses: IC50 values to block DMPP effects were 290, 27, 1.1 and 1.63 microM respectively for amiloride, guanethidine, nimodipine and nisoldipine. Amiloride blocked K-evoked Ca uptake by only 35% and guanethidine did not affect it. Nisoldipine inhibited K-evoked Ca uptake only partially at low concentrations (about 30%); a second blocking component was observed at the highest concentration used (10 microM). At 10 microM, nimodipine blocked K-evoked Ca uptake by 50%. 4. Thus, it seems that the nicotinic receptor mediated Ca uptake pathway can be pharmacologically separated from the K-activated pathway.(ABSTRACT TRUNCATED AT 250 WORDS)
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abajo F. J., Castro M. A., Lopo C. R., Garijo B., Sanchez-Garcia P., Garcia A. G. Sodium-dependent and sodium-independent nicotine-evoked catecholamine release from cat adrenals. Neurosci Lett. 1989 Jun 5;101(1):101–106. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(89)90448-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Amy C., Kirshner N. 22Na+ uptake and catecholamine secretion by primary cultures of adrenal medulla cells. J Neurochem. 1982 Jul;39(1):132–142. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1982.tb04711.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Artalejo C. R., Bader M. F., Aunis D., García A. G. Inactivation of the early calcium uptake and noradrenaline release evoked by potassium in cultured chromaffin cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1986 Jan 14;134(1):1–7. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(86)90518-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ballesta J. J., Garcia A. G., Gutierrez L. M., Hidalgo M. J., Palmero M., Reig J. A., Viniegra S. Separate [3H]-nitrendipine binding sites in mitochondria and plasma membranes of bovine adrenal medulla. Br J Pharmacol. 1990 Sep;101(1):21–26. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1990.tb12082.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ballesta J. J., Palmero M., Hidalgo M. J., Gutierrez L. M., Reig J. A., Viniegra S., Garcia A. G. Separate binding and functional sites for omega-conotoxin and nitrendipine suggest two types of calcium channels in bovine chromaffin cells. J Neurochem. 1989 Oct;53(4):1050–1056. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1989.tb07394.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Castillo C. J., Fonteríz R. I., López M. G., Rosenheck K., García A. G. (+)-PN200-110 and ouabain binding sites in purified bovine adrenomedullary plasma membranes and chromaffin cells. J Neurochem. 1989 Nov;53(5):1442–1449. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1989.tb08536.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ceña V., Nicolas G. P., Sanchez-Garcia P., Kirpekar S. M., Garcia A. G. Pharmacological dissection of receptor-associated and voltage-sensitive ionic channels involved in catecholamine release. Neuroscience. 1983 Dec;10(4):1455–1462. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(83)90126-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ceña V., Stutzin A., Rojas E. Effects of calcium and Bay K-8644 on calcium currents in adrenal medullary chromaffin cells. J Membr Biol. 1989 Dec;112(3):255–265. doi: 10.1007/BF01870956. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cárdenas A. M., Montiel C., Artalejo A. R., Sánchez-García P., García A. G. Sodium-dependent inhibition by PN200-110 enantiomers of nicotinic adrenal catecholamine release. Br J Pharmacol. 1988 Sep;95(1):9–14. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1988.tb16542.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DOUGLAS W. W., POISNER A. M. On the mode of action of acetylcholine in evoking adrenal medullary secretion: increased uptake of calcium during the secretory response. J Physiol. 1962 Aug;162:385–392. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1962.sp006940. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DOUGLAS W. W., RUBIN R. P. The role of calcium in the secretory response of the adrenal medulla to acetylcholine. J Physiol. 1961 Nov;159:40–57. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1961.sp006791. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fenwick E. M., Marty A., Neher E. Sodium and calcium channels in bovine chromaffin cells. J Physiol. 1982 Oct;331:599–635. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1982.sp014394. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holz R. W., Senter R. A., Frye R. A. Relationship between Ca2+ uptake and catecholamine secretion in primary dissociated cultures of adrenal medulla. J Neurochem. 1982 Sep;39(3):635–646. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1982.tb07940.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoshi T., Rothlein J., Smith S. J. Facilitation of Ca2+-channel currents in bovine adrenal chromaffin cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Sep;81(18):5871–5875. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.18.5871. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kilpatrick D. L., Slepetis R. J., Corcoran J. J., Kirshner N. Calcium uptake and catecholamine secretion by cultured bovine adrenal medulla cells. J Neurochem. 1982 Feb;38(2):427–435. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1982.tb08647.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kostyuk P. G. Diversity of calcium ion channels in cellular membranes. Neuroscience. 1989;28(2):253–261. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(89)90177-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lipscombe D., Kongsamut S., Tsien R. W. Alpha-adrenergic inhibition of sympathetic neurotransmitter release mediated by modulation of N-type calcium-channel gating. Nature. 1989 Aug 24;340(6235):639–642. doi: 10.1038/340639a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Livett B. G. Adrenal medullary chromaffin cells in vitro. Physiol Rev. 1984 Oct;64(4):1103–1161. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1984.64.4.1103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moro M. A., López M. G., Gandía L., Michelena P., García A. G. Separation and culture of living adrenaline- and noradrenaline-containing cells from bovine adrenal medullae. Anal Biochem. 1990 Mar;185(2):243–248. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(90)90287-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosario L. M., Soria B., Feuerstein G., Pollard H. B. Voltage-sensitive calcium flux into bovine chromaffin cells occurs through dihydropyridine-sensitive and dihydropyridine- and omega-conotoxin-insensitive pathways. Neuroscience. 1989;29(3):735–747. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(89)90145-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tang C. M., Presser F., Morad M. Amiloride selectively blocks the low threshold (T) calcium channel. Science. 1988 Apr 8;240(4849):213–215. doi: 10.1126/science.2451291. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsien R. W., Lipscombe D., Madison D. V., Bley K. R., Fox A. P. Multiple types of neuronal calcium channels and their selective modulation. Trends Neurosci. 1988 Oct;11(10):431–438. doi: 10.1016/0166-2236(88)90194-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tytgat J., Vereecke J., Carmeliet E. Differential effects of verapamil and flunarizine on cardiac L-type and T-type Ca channels. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1988 Jun;337(6):690–692. doi: 10.1007/BF00175798. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wada A., Takara H., Izumi F., Kobayashi H., Yanagihara N. Influx of 22Na through acetylcholine receptor-associated Na channels: relationship between 22Na influx, 45Ca influx and secretion of catecholamines in cultured bovine adrenal medulla cells. Neuroscience. 1985 May;15(1):283–292. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(85)90135-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


