Abstract
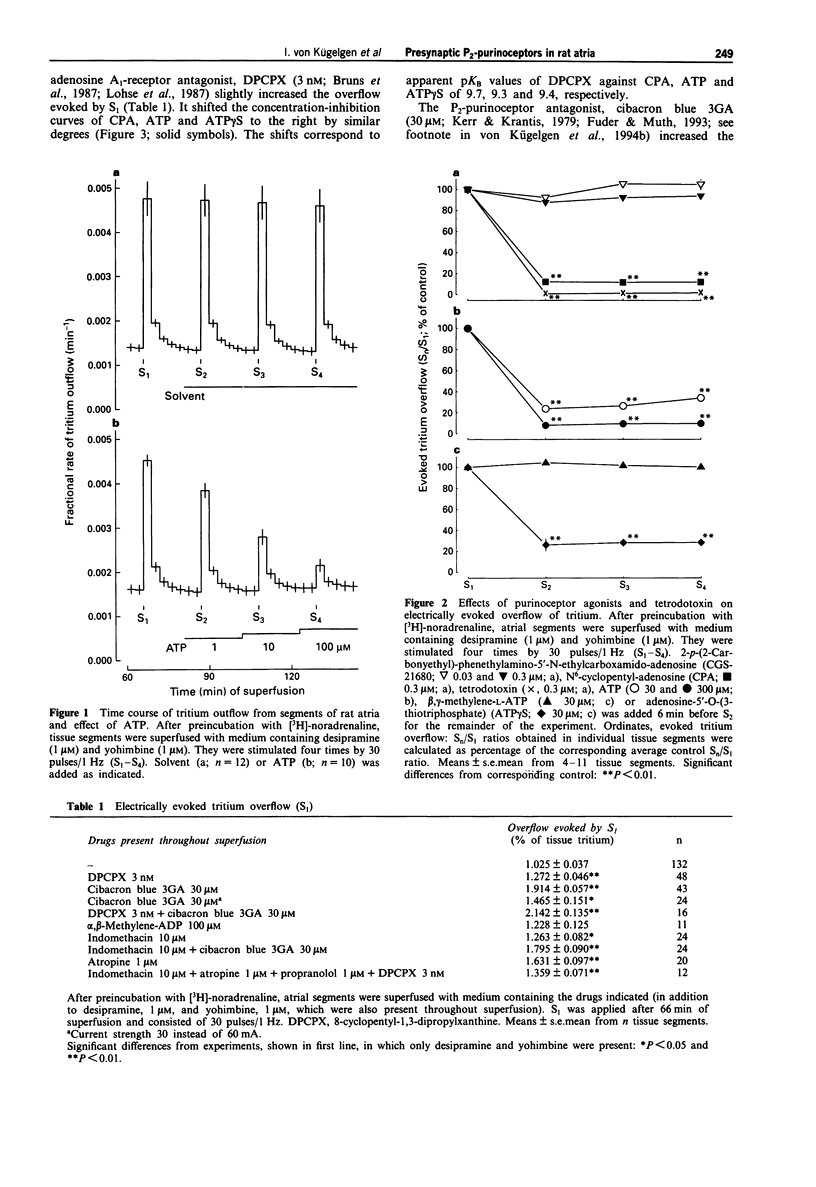
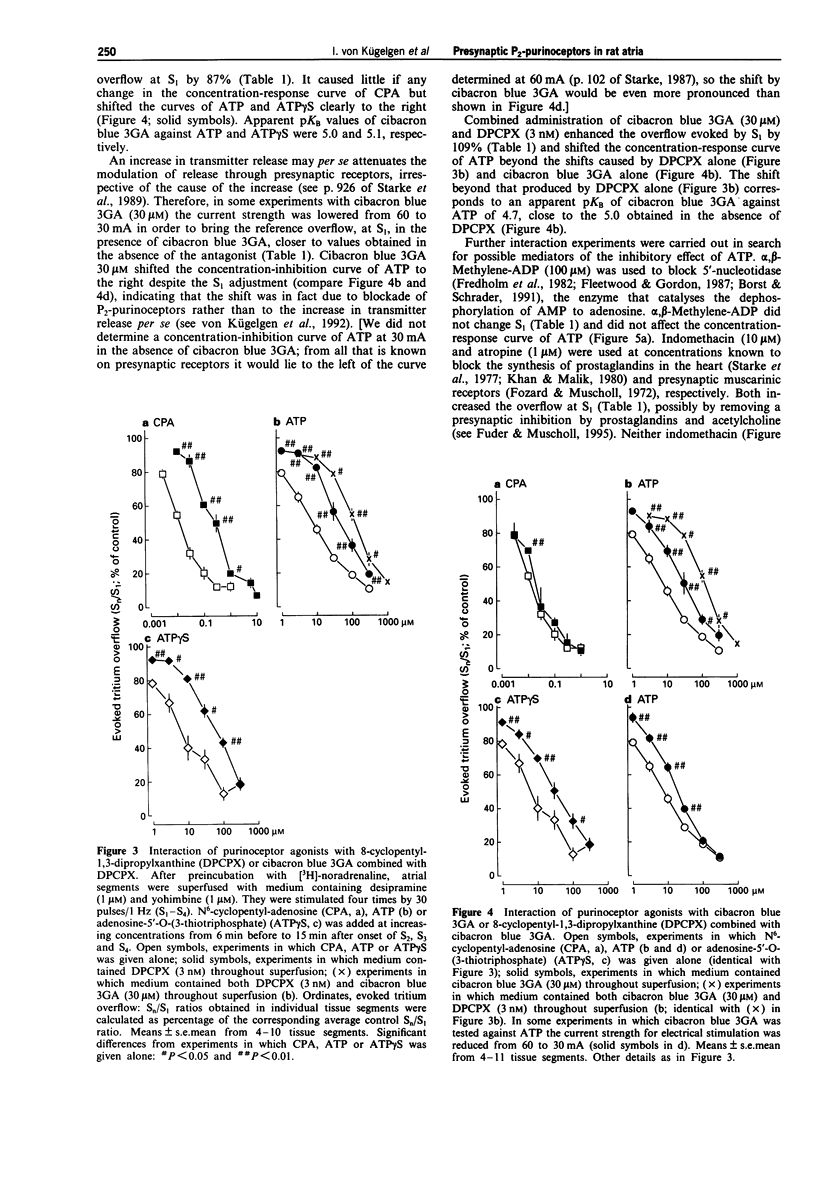
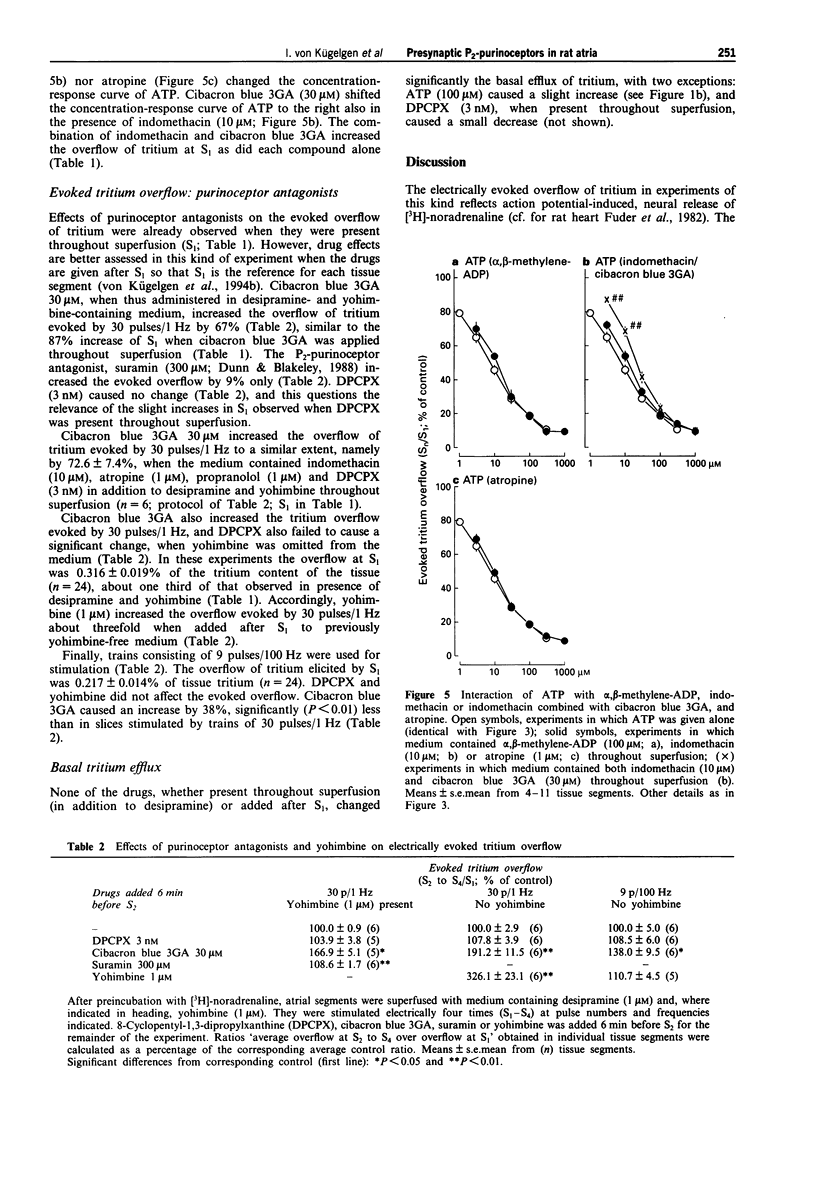
1. We looked for P2-purinoceptors modulating noradrenaline release in rat heart atria. Segments of the atria were preincubated with [3H]-noradrenaline and then superfused with medium containing desipramine (1 microM) and yohimbine (1 microM) and stimulated electrically, by 30 pulses/1 Hz unless stated otherwise. 2. The adenosine A1-receptor agonist, N6-cyclopentyl-adenosine (CPA; EC50 9.7 nM) and the nucleotides, ATP (EC50 6.6 microM) and adenosine-5'-O-(3-thiotriphosphate) (ATP gamma S; EC50 4.8 microM), decreased the evoked overflow of tritium. The adenosine A2a-agonist, 2-p-(2-carbonylethyl)-phenethylamino-5'-N-ethylcarboxamido-a denosine (CGS-21680; 0.03-0.3 microM) and the P2x-purinoceptor agonist beta, gamma-methylene-L-ATP (30 microM) caused no change. 3. The concentration-response curve of CPA was shifted to the right by the adenosine A1-receptor antagonist, 8-cyclopentyl-1,3-dipropyl-xanthine (DPCPX; 3 nM; apparent pKB value 9.7) but hardly affected by the P2-purinoceptor antagonist, cibacron blue 3GA (30 microM). In contrast, the concentration-response curves of ATP and ATP gamma S were shifted to the right by DPCPX (3 nM; apparent pKB values 9.3 and 9.4, respectively) as well as by cibacron blue 3GA (30 microM; apparent pKB values 5.0 and 5.1, respectively). Combined administration of DPCPX and cibacron blue 3GA caused a much greater shift of the concentration-response curve of ATP than either antagonist alone. The concentration-response curve of ATP was not changed by indomethacin, atropine or the 5'-nucleotidase blocker alpha, beta-methylene-ADP. 4. Cibacron blue 3GA (30 microM) increased the evoked overflow of tritium by about 70%.(ABSTRACT TRUNCATED AT 250 WORDS)
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bailey S. J., Hickman D., Hourani S. M. Characterization of the P1-purinoceptors mediating contraction of the rat colon muscularis mucosae. Br J Pharmacol. 1992 Feb;105(2):400–404. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1992.tb14265.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borst M. M., Schrader J. Adenine nucleotide release from isolated perfused guinea pig hearts and extracellular formation of adenosine. Circ Res. 1991 Mar;68(3):797–806. doi: 10.1161/01.res.68.3.797. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bruns R. F., Fergus J. H., Badger E. W., Bristol J. A., Santay L. A., Hartman J. D., Hays S. J., Huang C. C. Binding of the A1-selective adenosine antagonist 8-cyclopentyl-1,3-dipropylxanthine to rat brain membranes. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1987 Jan;335(1):59–63. doi: 10.1007/BF00165037. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burnstock G. The fifth Heymans memorial lecture-Ghent, February 17, 1990. Co-transmission. Arch Int Pharmacodyn Ther. 1990 Mar-Apr;304:7–33. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collis M. G., Pettinger S. J. Can ATP stimulate P1-receptors in guinea-pig atrium without conversion to adenosine? Eur J Pharmacol. 1982 Jul 30;81(4):521–529. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(82)90341-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunn P. M., Blakeley A. G. Suramin: a reversible P2-purinoceptor antagonist in the mouse vas deferens. Br J Pharmacol. 1988 Feb;93(2):243–245. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1988.tb11427.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fieber L. A., Adams D. J. Adenosine triphosphate-evoked currents in cultured neurones dissociated from rat parasympathetic cardiac ganglia. J Physiol. 1991 Mar;434:239–256. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1991.sp018467. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fleetwood G., Gordon J. L. Purinoceptors in the rat heart. Br J Pharmacol. 1987 Jan;90(1):219–227. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1987.tb16843.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fozard J. R., Muscholl E. Effects of several muscarinic agonists on cardiac performance and the release of noradrenaline from sympathetic nerves of the perfused rabbit heart. Br J Pharmacol. 1972 Aug;45(4):616–629. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1972.tb08119.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fredholm B. B., Hedqvist P., Lindström K., Wennmalm M. Release of nucleosides and nucleotides from the rabbit heart by sympathetic nerve stimulation. Acta Physiol Scand. 1982 Nov;116(3):285–295. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1982.tb07142.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fuder H., Brink A., Meincke M., Tauber U. Purinoceptor-mediated modulation by endogenous and exogenous agonists of stimulation-evoked [3H]noradrenaline release on rat iris. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1992 Apr;345(4):417–423. doi: 10.1007/BF00176619. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fuder H., Muscholl E. Heteroreceptor-mediated modulation of noradrenaline and acetylcholine release from peripheral nerves. Rev Physiol Biochem Pharmacol. 1995;126:265–412. doi: 10.1007/BFb0049778. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fuder H., Muth U. ATP and endogenous agonists inhibit evoked [3H]-noradrenaline release in rat iris via A1 and P2y-like purinoceptors. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1993 Oct;348(4):352–357. doi: 10.1007/BF00171333. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fuder H., Siebenborn R., Muscholl E. Nicotine receptors do not modulate the 3H-noradrenaline release from the isolated rat heart evoked by sympathetic nerve stimulation. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1982 Mar;318(4):301–307. doi: 10.1007/BF00501169. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujioka M., Cheung D. W. Autoregulation of neuromuscular transmission in the guinea-pig saphenous artery. Eur J Pharmacol. 1987 Jul 9;139(2):147–153. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(87)90246-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grimm U., Fuder H., Moser U., Bümert H. G., Mutschler E., Lambrecht G. Characterization of the prejunctional muscarinic receptors mediating inhibition of evoked release of endogenous noradrenaline in rabbit isolated vas deferens. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1994 Jan;349(1):1–10. doi: 10.1007/BF00178199. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hourani S. M., Loizou G. D., Cusack N. J. Pharmacological effects of L-AMP-PCP on ATP receptors in smooth muscle. Eur J Pharmacol. 1986 Nov 12;131(1):99–103. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(86)90521-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jarvis M. F., Schulz R., Hutchison A. J., Do U. H., Sills M. A., Williams M. [3H]CGS 21680, a selective A2 adenosine receptor agonist directly labels A2 receptors in rat brain. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1989 Dec;251(3):888–893. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Khan M. T., Malik K. U. Inhibitory effect of adenosine and adenine nucleotides on potassium-evoked efflux of [3H]-noradrenaline from the rat isolated heart: lack of relationship to prostaglandins. Br J Pharmacol. 1980 Mar;68(3):551–561. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1980.tb14571.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kurz K., von Kügelgen I., Starke K. Prejunctional modulation of noradrenaline release in mouse and rat vas deferens: contribution of P1- and P2-purinoceptors. Br J Pharmacol. 1993 Dec;110(4):1465–1472. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1993.tb13986.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Limberger N., Trendelenburg A. U., Starke K. Pharmacological characterization of presynaptic alpha 2-autoreceptors in rat submaxillary gland and heart atrium. Br J Pharmacol. 1992 Sep;107(1):246–255. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1992.tb14494.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lohse M. J., Klotz K. N., Lindenborn-Fotinos J., Reddington M., Schwabe U., Olsson R. A. 8-Cyclopentyl-1,3-dipropylxanthine (DPCPX)--a selective high affinity antagonist radioligand for A1 adenosine receptors. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1987 Aug;336(2):204–210. doi: 10.1007/BF00165806. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miyahara H., Suzuki H. Pre- and post-junctional effects of adenosine triphosphate on noradrenergic transmission in the rabbit ear artery. J Physiol. 1987 Aug;389:423–440. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1987.sp016664. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moody C. J., Meghji P., Burnstock G. Stimulation of P1-purinoceptors by ATP depends partly on its conversion to AMP and adenosine and partly on direct action. Eur J Pharmacol. 1984 Jan 13;97(1-2):47–54. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(84)90511-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paddle B. M., Burnstock G. Release of ATP from perfused heart during coronary vasodilatation. Blood Vessels. 1974;11(3):110–119. doi: 10.1159/000158005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ralevic V., Burnstock G. Roles of P2-purinoceptors in the cardiovascular system. Circulation. 1991 Jul;84(1):1–14. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.84.1.1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richardt G., Waas W., Kranzhöfer R., Mayer E., Schömig A. Adenosine inhibits exocytotic release of endogenous noradrenaline in rat heart: a protective mechanism in early myocardial ischemia. Circ Res. 1987 Jul;61(1):117–123. doi: 10.1161/01.res.61.1.117. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rubino A., Amerini S., Ledda F., Mantelli L. ATP modulates the efferent function of capsaicin-sensitive neurones in guinea-pig isolated atria. Br J Pharmacol. 1992 Mar;105(3):516–520. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1992.tb09011.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schütz W., Ströher M., Freissmuth M., Valenta B., Singer E. A. Adenosine receptors mediate a pertussis toxin-insensitive prejunctional inhibition of noradrenaline release on a papillary muscle model. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1991 Mar;343(3):311–316. doi: 10.1007/BF00251132. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sebastião A. M., Stone T. W., Ribeiro J. A. The inhibitory adenosine receptor at the neuromuscular junction and hippocampus of the rat: antagonism by 1,3,8-substituted xanthines. Br J Pharmacol. 1990 Oct;101(2):453–459. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1990.tb12729.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shinozuka K., Bjur R. A., Westfall D. P. Characterization of prejunctional purinoceptors on adrenergic nerves of the rat caudal artery. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1988 Sep;338(3):221–227. doi: 10.1007/BF00173391. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sperlagh B., Vizi E. S. Effect of presynaptic P2 receptor stimulation on transmitter release. J Neurochem. 1991 May;56(5):1466–1470. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1991.tb02039.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Starke K., Göthert M., Kilbinger H. Modulation of neurotransmitter release by presynaptic autoreceptors. Physiol Rev. 1989 Jul;69(3):864–989. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1989.69.3.864. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Starke K., Peskar B. A., Schumacher K. A., Taube H. D. Bradykinin and postganglionic sympathetic transmission. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1977 Aug;299(1):23–32. doi: 10.1007/BF00508633. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Starke K. Presynaptic alpha-autoreceptors. Rev Physiol Biochem Pharmacol. 1987;107:73–146. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Todorov L. D., Bjur R. A., Westfall D. P. Inhibitory and facilitatory effects of purines on transmitter release from sympathetic nerves. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1994 Feb;268(2):985–989. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wakade A. R., Wakade T. D. Inhibition of noradrenaline release by adenosine. J Physiol. 1978 Sep;282:35–49. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1978.sp012446. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Welford L. A., Cusack N. J., Hourani S. M. ATP analogues and the guinea-pig taenia coli: a comparison of the structure-activity relationships of ectonucleotidases with those of the P2-purinoceptor. Eur J Pharmacol. 1986 Oct 7;129(3):217–224. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(86)90431-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiklund N. P., Gustafsson L. E., Lundin J. Pre- and postjunctional modulation of cholinergic neuroeffector transmission by adenine nucleotides. Experiments with agonist and antagonist. Acta Physiol Scand. 1985 Dec;125(4):681–691. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1985.tb07771.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams M., Braunwalder A., Erickson T. J. Evaluation of the binding of the A-1 selective adenosine radioligand, cyclopentyladenosine (CPA), to rat brain tissue. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1986 Feb;332(2):179–183. doi: 10.1007/BF00511410. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zimmermann H. Signalling via ATP in the nervous system. Trends Neurosci. 1994 Oct;17(10):420–426. doi: 10.1016/0166-2236(94)90016-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- von Kügelgen I., Kurz K., Bültmann R., Driessen B., Starke K. Presynaptic modulation of the release of the co-transmitters noradrenaline and ATP. Fundam Clin Pharmacol. 1994;8(3):207–213. doi: 10.1111/j.1472-8206.1994.tb00800.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- von Kügelgen I., Kurz K., Starke K. Axon terminal P2-purinoceptors in feedback control of sympathetic transmitter release. Neuroscience. 1993 Sep;56(2):263–267. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(93)90330-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- von Kügelgen I., Kurz K., Starke K. P2-purinoceptor-mediated autoinhibition of sympathetic transmitter release in mouse and rat vas deferens. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1994 Feb;349(2):125–132. doi: 10.1007/BF00169828. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- von Kügelgen I., Schöffel E., Starke K. Inhibition by nucleotides acting at presynaptic P2-receptors of sympathetic neuro-effector transmission in the mouse isolated vas deferens. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1989 Nov;340(5):522–532. doi: 10.1007/BF00260607. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- von Kügelgen I., Späth L., Starke K. Evidence for P2-purinoceptor-mediated inhibition of noradrenaline release in rat brain cortex. Br J Pharmacol. 1994 Nov;113(3):815–822. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1994.tb17066.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- von Kügelgen I., Späth L., Starke K. Stable adenine nucleotides inhibit [3H]-noradrenaline release in rabbit brain cortex slices by direct action at presynaptic adenosine A1-receptors. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1992 Aug;346(2):187–196. doi: 10.1007/BF00165300. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- von Kügelgen I., Starke K. Noradrenaline-ATP co-transmission in the sympathetic nervous system. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 1991 Sep;12(9):319–324. doi: 10.1016/0165-6147(91)90587-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


