Abstract
1. Livers of 10 New Zealand White rabbits were perfused in vitro with Krebs-Bülbring buffer via the hepatic artery (HA) and portal vein (PV) at constant flows of 23 +/- 1 and 77 +/- 1 ml min-1 100 g-1 respectively. The tone of the preparation was raised with noradrenaline (concentration: 10 microM). 2. Dose-response curves for the vasodilatation produced by adenosine 5'-triphosphate (ATP), acetylcholine (ACh), adenosine, and sodium nitroprusside (SNP) were obtained following injection into the HA supply. Injections were then repeated in the presence of the L-arginine to nitric oxide pathway inhibitors N-monomethyl-L-arginine (L-NMMA, n = 6) and N-nitro-L-arginine methyl ester (L-NAME, n = 4) at concentrations of 30 microM and 100 microM for each inhibitor. 3. Both L-NMMA and L-NAME antagonized the responses to ATP and ACh; L-NAME was 2-3 times more potent than L-NMMA as an inhibitor of these endothelium-dependent vasodilatations. Neither L-NMMA nor L-NAME attenuated responses of the endothelium-independent vasodilators, adenosine and SNP. 4. These results indicate that nitric oxide is the mediator of ATP-induced vasodilatation in the HA vascular bed of the rabbit and that the receptor responsible for the release of nitric oxide, the P2y-purinoceptor, is located predominantly on the endothelium.
Full text
PDF
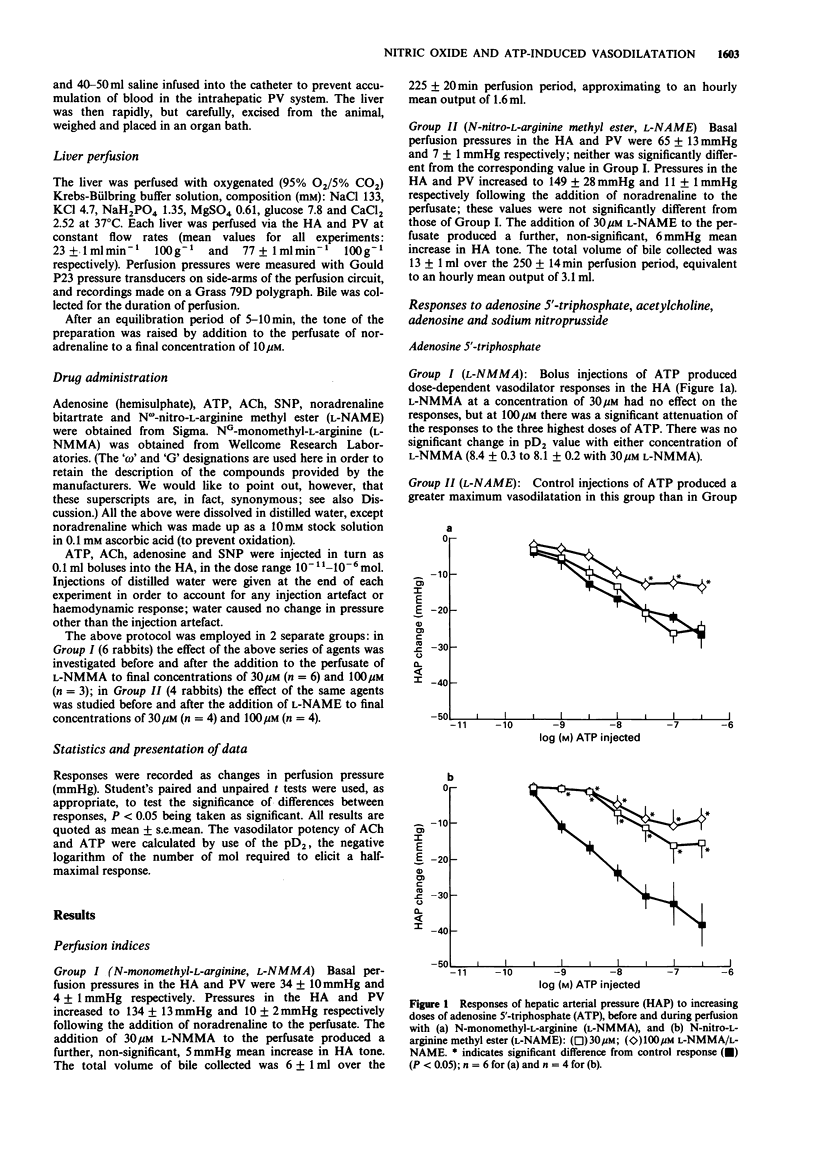
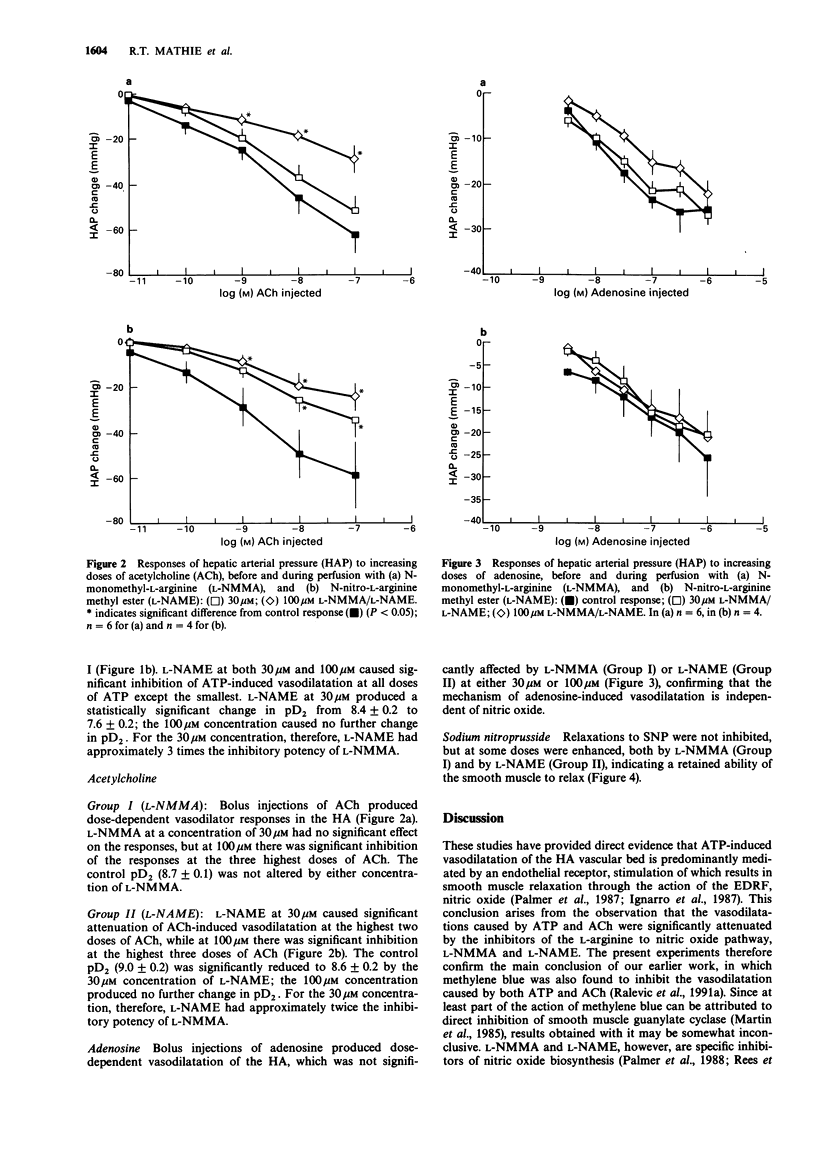


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ezzat W. R., Lautt W. W. Hepatic arterial pressure-flow autoregulation is adenosine mediated. Am J Physiol. 1987 Apr;252(4 Pt 2):H836–H845. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.1987.252.4.H836. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ignarro L. J. Biological actions and properties of endothelium-derived nitric oxide formed and released from artery and vein. Circ Res. 1989 Jul;65(1):1–21. doi: 10.1161/01.res.65.1.1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ignarro L. J., Buga G. M., Wood K. S., Byrns R. E., Chaudhuri G. Endothelium-derived relaxing factor produced and released from artery and vein is nitric oxide. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Dec;84(24):9265–9269. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.24.9265. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lautt W. W., Legare D. J. The use of 8-phenyltheophylline as a competitive antagonist of adenosine and an inhibitor of the intrinsic regulatory mechanism of the hepatic artery. Can J Physiol Pharmacol. 1985 Jun;63(6):717–722. doi: 10.1139/y85-117. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lautt W. W., Legare D. J., d'Almeida M. S. Adenosine as putative regulator of hepatic arterial flow (the buffer response). Am J Physiol. 1985 Mar;248(3 Pt 2):H331–H338. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.1985.248.3.H331. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin W., Villani G. M., Jothianandan D., Furchgott R. F. Selective blockade of endothelium-dependent and glyceryl trinitrate-induced relaxation by hemoglobin and by methylene blue in the rabbit aorta. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1985 Mar;232(3):708–716. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mathie R. T., Alexander B., Ralevic V., Burnstock G. Adenosine-induced dilatation of the rabbit hepatic arterial bed is mediated by A2-purinoceptors. Br J Pharmacol. 1991 May;103(1):1103–1107. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1991.tb12307.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mathie R. T., Alexander B. The role of adenosine in the hyperaemic response of the hepatic artery to portal vein occlusion (the 'buffer response'). Br J Pharmacol. 1990 Jul;100(3):626–630. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1990.tb15857.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moncada S., Palmer R. M., Higgs E. A. Biosynthesis of nitric oxide from L-arginine. A pathway for the regulation of cell function and communication. Biochem Pharmacol. 1989 Jun 1;38(11):1709–1715. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(89)90403-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore P. K., al-Swayeh O. A., Chong N. W., Evans R. A., Gibson A. L-NG-nitro arginine (L-NOARG), a novel, L-arginine-reversible inhibitor of endothelium-dependent vasodilatation in vitro. Br J Pharmacol. 1990 Feb;99(2):408–412. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1990.tb14717.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murad F. Cyclic guanosine monophosphate as a mediator of vasodilation. J Clin Invest. 1986 Jul;78(1):1–5. doi: 10.1172/JCI112536. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palmer R. M., Ferrige A. G., Moncada S. Nitric oxide release accounts for the biological activity of endothelium-derived relaxing factor. Nature. 1987 Jun 11;327(6122):524–526. doi: 10.1038/327524a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palmer R. M., Rees D. D., Ashton D. S., Moncada S. L-arginine is the physiological precursor for the formation of nitric oxide in endothelium-dependent relaxation. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1988 Jun 30;153(3):1251–1256. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(88)81362-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ralevic V., Mathie R. T., Alexander B., Burnstock G. Characterization of P2X- and P2Y-purinoceptors in the rabbit hepatic arterial vasculature. Br J Pharmacol. 1991 May;103(1):1108–1113. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1991.tb12308.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rees D. D., Palmer R. M., Hodson H. F., Moncada S. A specific inhibitor of nitric oxide formation from L-arginine attenuates endothelium-dependent relaxation. Br J Pharmacol. 1989 Feb;96(2):418–424. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1989.tb11833.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rees D. D., Palmer R. M., Moncada S. Role of endothelium-derived nitric oxide in the regulation of blood pressure. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 May;86(9):3375–3378. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.9.3375. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watanabe M., Rosenblum W. I., Nelson G. H. In vivo effect of methylene blue on endothelium-dependent and endothelium-independent dilations of brain microvessels in mice. Circ Res. 1988 Jan;62(1):86–90. doi: 10.1161/01.res.62.1.86. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


