Abstract
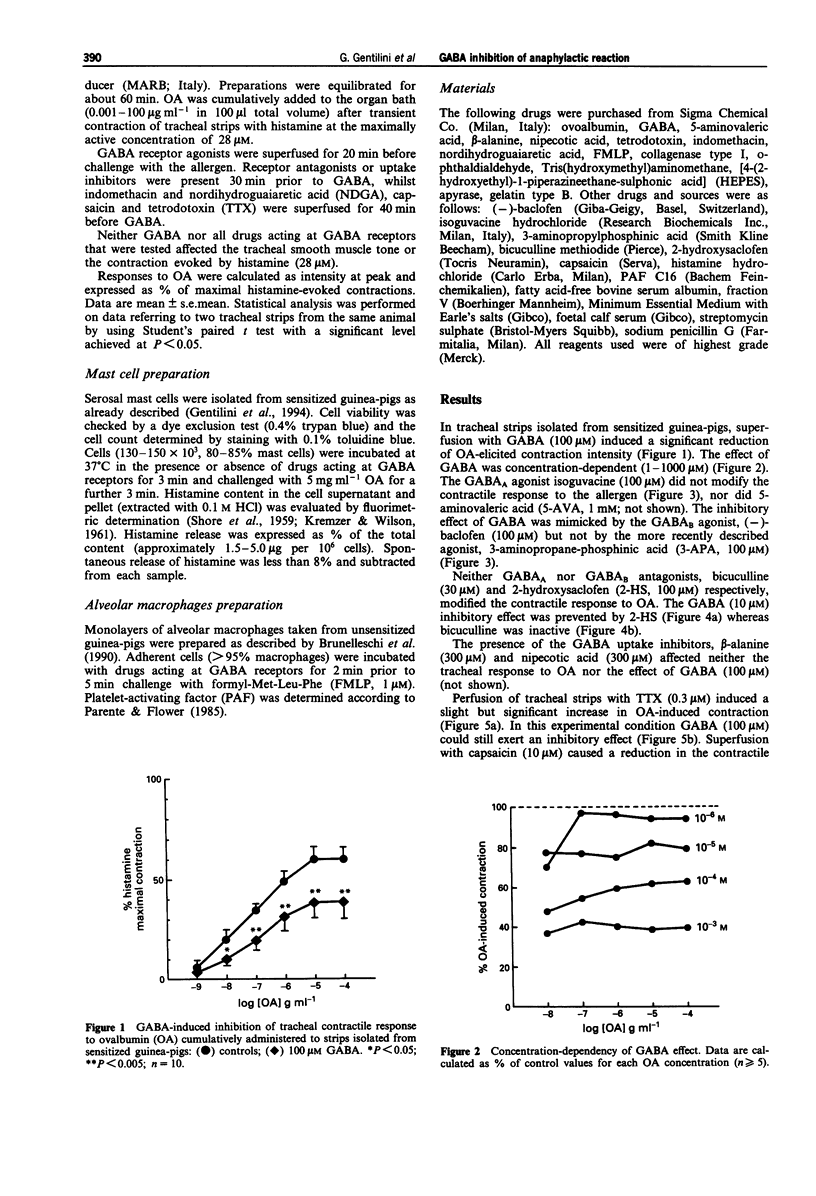
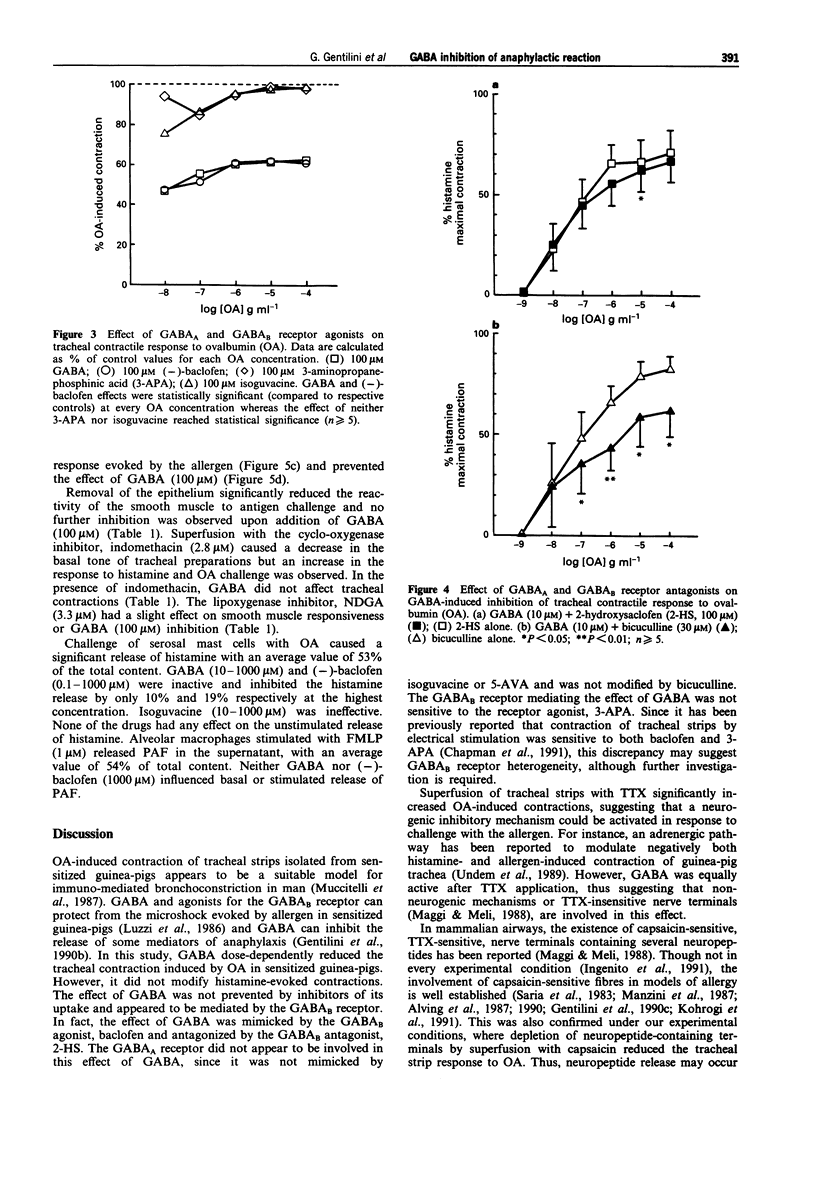
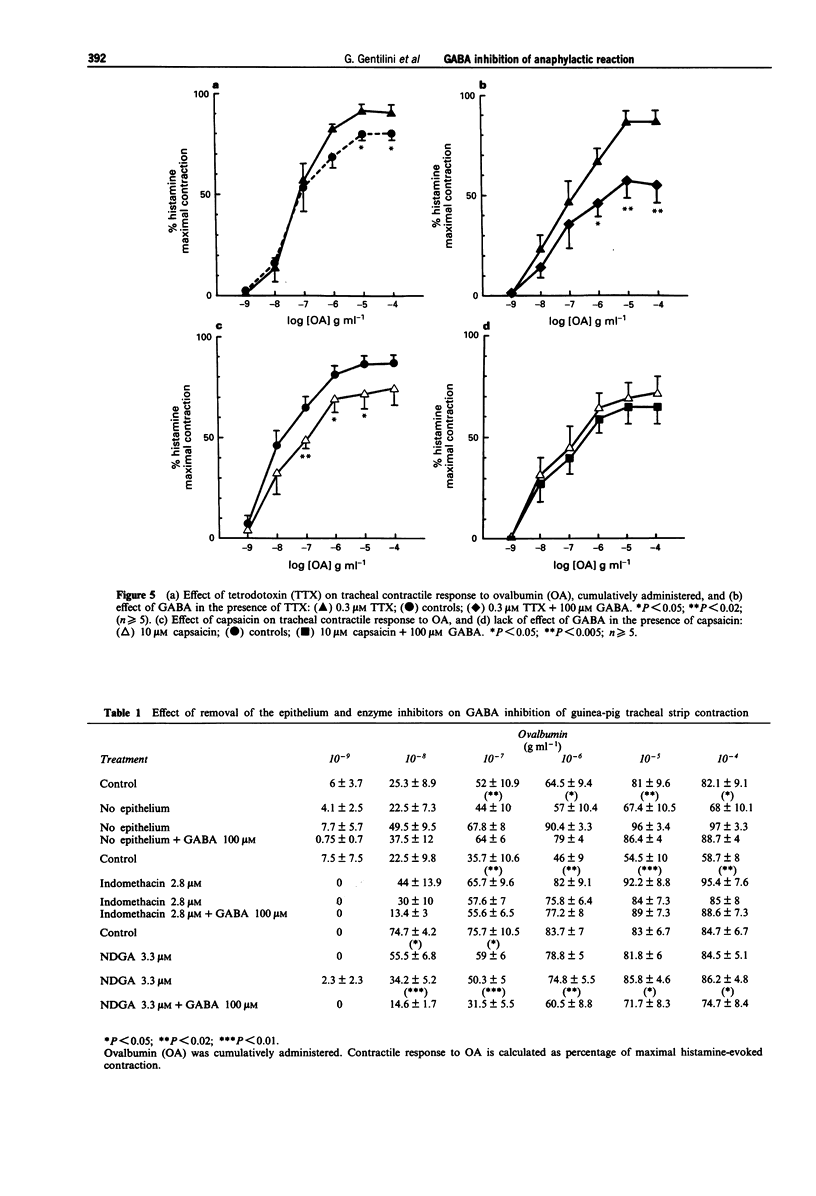
1. In sensitized guinea-pigs, the effects of gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) and GABAmimetic drugs have been investigated on tracheal segments contracted by cumulative application of an allergen (ovoalbumin, OA) and on serosal mast cells. The same drugs have also been tested on activation of alveolar macrophages isolated from unsensitized guinea-pigs. 2. Superfusion with GABA (1-1000 microM) reduced the contraction intensity of tracheal strips. The effect of GABA (100 microM) was not affected by the carrier blockers, nipecotic acid and beta-alanine (300 microM each). It was mimicked by the GABAB agonist (-)-baclofen (100 microM) but not 3-aminopropanephosphinic acid (100 microM, 3-APA). The GABAA agonist, isoguvacine (100 microM) did not exert any effect. GABA (10 microM)-induced inhibition of tracheal contractions was reduced by the GABAB antagonist, 2-hydroxysaclofen (100 microM, 2-HS), but not by the GABAA antagonist, bicuculline (30 microM). 3. The reduction in contraction intensity induced by GABA (100 microM) was prevented by a 40 min preincubation of tracheal strips with capsaicin (10 microM), but not tetrodotoxin (TTX, 0.3 microM). The effect of GABA (1000 microM) was absent after preincubation with indomethacin (2.8 microM) but unmodified when nordihydroguaiaretic acid (NDGA, 3.3 microM) was used. Finally, removal of the epithelium prevented the GABA effect. 4. Anaphylactic histamine release from serosal mast cells isolated from sensitized animals was not affected either by GABA (10-1000 microM) or the selective receptor agonists (-)-baclofen (0.1-1000 microM) and isoguvacine (10-1000 microM).(ABSTRACT TRUNCATED AT 250 WORDS)
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alving K., Matran R., Lacroix J. S., Lundberg J. M. Capsaicin and histamine antagonist-sensitive mechanisms in the immediate allergic reaction of pig airways. Acta Physiol Scand. 1990 Jan;138(1):49–60. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1990.tb08811.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alving K., Ulfgren A. K., Lundberg J. M., Ahlstedt S. Effect of capsaicin on bronchial reactivity and inflammation in sensitized adult rats. Int Arch Allergy Appl Immunol. 1987;82(3-4):377–379. doi: 10.1159/000234231. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Belvisi M. G., Ichinose M., Barnes P. J. Modulation of non-adrenergic, non-cholinergic neural bronchoconstriction in guinea-pig airways via GABAB-receptors. Br J Pharmacol. 1989 Aug;97(4):1225–1231. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1989.tb12582.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bertrand C., Tschirhart E., Landry Y. Nedocromil sodium inhibits IgE- and IgG-related antigen-induced contraction in guinea-pig trachea. Int Arch Allergy Appl Immunol. 1989;88(4):439–446. doi: 10.1159/000234730. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Braunstein G., Labat C., Brunelleschi S., Benveniste J., Marsac J., Brink C. Evidence that the histamine sensitivity and responsiveness of guinea-pig isolated trachea are modulated by epithelial prostaglandin E2 production. Br J Pharmacol. 1988 Sep;95(1):300–308. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1988.tb16577.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brink C., Duncan P. G., Douglas J. S. The response and sensitivity to histamine of respiratory tissues from normal and ovalbumin-sensitized guinea pigs: effects of cyclooxygenase and lipoxygenase inhibition. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1981 Jun;217(3):592–601. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brunelleschi S., Vanni L., Ledda F., Giotti A., Maggi C. A., Fantozzi R. Tachykinins activate guinea-pig alveolar macrophages: involvement of NK2 and NK1 receptors. Br J Pharmacol. 1990 Jul;100(3):417–420. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1990.tb15821.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burka J. F. Studies on the role of arachidonic acid metabolites in airways contraction induced in vitro by antigen and calcium ionophore A23187. Agents Actions. 1983 Jun;13(4):318–326. doi: 10.1007/BF01971483. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chapman R. W., Danko G., Rizzo C., Egan R. W., Mauser P. J., Kreutner W. Prejunctional GABA-B inhibition of cholinergic, neurally-mediated airway contractions in guinea-pigs. Pulm Pharmacol. 1991;4(4):218–224. doi: 10.1016/0952-0600(91)90014-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chapman R. W., Hey J. A., Rizzo C. A., Bolser D. C. GABAB receptors in the lung. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 1993 Jan;14(1):26–29. doi: 10.1016/0165-6147(93)90110-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coleridge J. C., Coleridge H. M. Afferent vagal C fibre innervation of the lungs and airways and its functional significance. Rev Physiol Biochem Pharmacol. 1984;99:1–110. doi: 10.1007/BFb0027715. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Franchi-Micheli S., Luzzi S., Ciuffi M., Zilletti L. The effect of lipoxygenase inhibitors and leukotriene antagonists on anaphylaxis. Agents Actions. 1986 Apr;18(1-2):242–244. doi: 10.1007/BF01988031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frossard N., Muller F. Epithelial modulation of tracheal smooth muscle response to antigenic stimulation. J Appl Physiol (1985) 1986 Oct;61(4):1449–1456. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1986.61.4.1449. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gentilini G., Franchi-Micheli S., Ciuffi M., Bindi D., Zilletti L. Capsaicin and anaphylactic reactions in the guinea-pig airways. Agents Actions. 1990 Apr;30(1-2):92–94. doi: 10.1007/BF01969007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gentilini G., Franchi-Micheli S., Ciuffi M., Bindi D., Zilletti L. GABA and neuropeptides affect anaphylaxis in guinea-pig airways. Pharmacol Res. 1990 Sep-Oct;22 (Suppl 1):23–24. doi: 10.1016/1043-6618(90)90789-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gentilini G., Grazia di Bello M., Raspanti S., Bindi D., Mugnai S., Zilletti L. Salmeterol inhibits anaphylactic histamine release from guinea-pig isolated mast cells. J Pharm Pharmacol. 1994 Jan;46(1):76–77. doi: 10.1111/j.2042-7158.1994.tb03725.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldie R. G., Fernandes L. B., Farmer S. G., Hay D. W. Airway epithelium-derived inhibitory factor. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 1990 Feb;11(2):67–70. doi: 10.1016/0165-6147(90)90320-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hay D. W., Raeburn D., Farmer S. G., Fleming W. W., Fedan J. S. Epithelium modulates the reactivity of ovalbumin-sensitized guinea-pig airway smooth muscle. Life Sci. 1986 Jun 30;38(26):2461–2468. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(86)90617-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holgate S. T., Kay A. B. Mast cells, mediators and asthma. Clin Allergy. 1985 May;15(3):221–234. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holroyde M. C. The influence of epithelium on the responsiveness of guinea-pig isolated trachea. Br J Pharmacol. 1986 Mar;87(3):501–507. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1986.tb10192.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ingenito E. P., Pliss L. B., Martins M. A., Ingram R. H., Jr Effects of capsaicin on mechanical, cellular, and mediator responses to antigen in sensitized guinea pigs. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1991 Mar;143(3):572–577. doi: 10.1164/ajrccm/143.3.572. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones T. R., Charette L., Denis D. Antigen-induced contraction of guinea-pig isolated trachea: studies with novel inhibitors and antagonists of arachidonic acid metabolites. Br J Pharmacol. 1988 Sep;95(1):309–321. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1988.tb16578.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kohrogi H., Yamaguchi T., Kawano O., Honda I., Ando M., Araki S. Inhibition of neutral endopeptidase potentiates bronchial contraction induced by immune response in guinea pigs in vitro. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1991 Sep;144(3 Pt 1):636–641. doi: 10.1164/ajrccm/144.3_Pt_1.636. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lundberg J. M., Saria A. Polypeptide-containing neurons in airway smooth muscle. Annu Rev Physiol. 1987;49:557–572. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ph.49.030187.003013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luzzi S., Franchi-Micheli S., Ciuffi M., Zilletti L. Effects of GABA agonists on Herxheimer microshock in guinea pigs. Agents Actions. 1986 Apr;18(1-2):245–247. doi: 10.1007/BF01988032. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luzzi S., Franchi-Micheli S., Folco G., Rossoni G., Ciuffi M., Zilletti L. Effect of baclofen on different models of bronchial hyperreactivity in the guinea-pig. Agents Actions. 1987 Apr;20(3-4):307–309. doi: 10.1007/BF02074698. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maggi C. A., Meli A. The sensory-efferent function of capsaicin-sensitive sensory neurons. Gen Pharmacol. 1988;19(1):1–43. doi: 10.1016/0306-3623(88)90002-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manzini S., Maggi C. A., Geppetti P., Bacciarelli C. Capsaicin desensitization protects from antigen-induced bronchospasm in conscious guinea-pigs. Eur J Pharmacol. 1987 Jun 19;138(2):307–308. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(87)90451-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muccitelli R. M., Tucker S. S., Hay D. W., Torphy T. J., Wasserman M. A. Is the guinea pig trachea a good in vitro model of human large and central airways? Comparison on leukotriene-, methacholine-, histamine- and antigen-induced contractions. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1987 Nov;243(2):467–473. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parente L., Flower R. J. Hydrocortisone and 'macrocortin' inhibit the zymosan-induced release of lyso-PAF from rat peritoneal leucocytes. Life Sci. 1985 Apr 1;36(13):1225–1231. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(85)90266-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ray N. J., Jones A. J., Keen P. GABAB receptor modulation of the release of substance P from capsaicin-sensitive neurones in the rat trachea in vitro. Br J Pharmacol. 1991 Apr;102(4):801–804. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1991.tb12255.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SHORE P. A., BURKHALTER A., COHN V. H., Jr A method for the fluorometric assay of histamine in tissues. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1959 Nov;127:182–186. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saria A., Lundberg J. M., Skofitsch G., Lembeck F. Vascular protein linkage in various tissue induced by substance P, capsaicin, bradykinin, serotonin, histamine and by antigen challenge. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1983 Nov;324(3):212–218. doi: 10.1007/BF00503897. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shirakawa J., Taniyama K., Tanaka C. gamma-Aminobutyric acid-induced modulation of acetylcholine release from the guinea pig lung. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1987 Oct;243(1):364–369. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tamaoki J., Graf P. D., Nadel J. A. Effect of gamma-aminobutyric acid on neurally mediated contraction of guinea pig trachealis smooth muscle. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1987 Oct;243(1):86–90. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tschirhart E., Frossard N., Bertrand C., Landry Y. Arachidonic acid metabolites and airway epithelium-dependent relaxant factor. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1987 Oct;243(1):310–316. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Undem B. J., Adams G. K., 3rd, Buckner C. K. Influence of electrical field stimulation on antigen-induced contraction and mediator release in the guinea pig isolated superfused trachea and bronchus. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1989 Apr;249(1):23–30. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Undem B. J., Raible D. G., Adkinson N. F., Jr, Adams G. K., 3rd Effect of removal of epithelium on antigen-induced smooth muscle contraction and mediator release from guinea pig isolated trachea. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1988 Feb;244(2):659–665. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


