Abstract
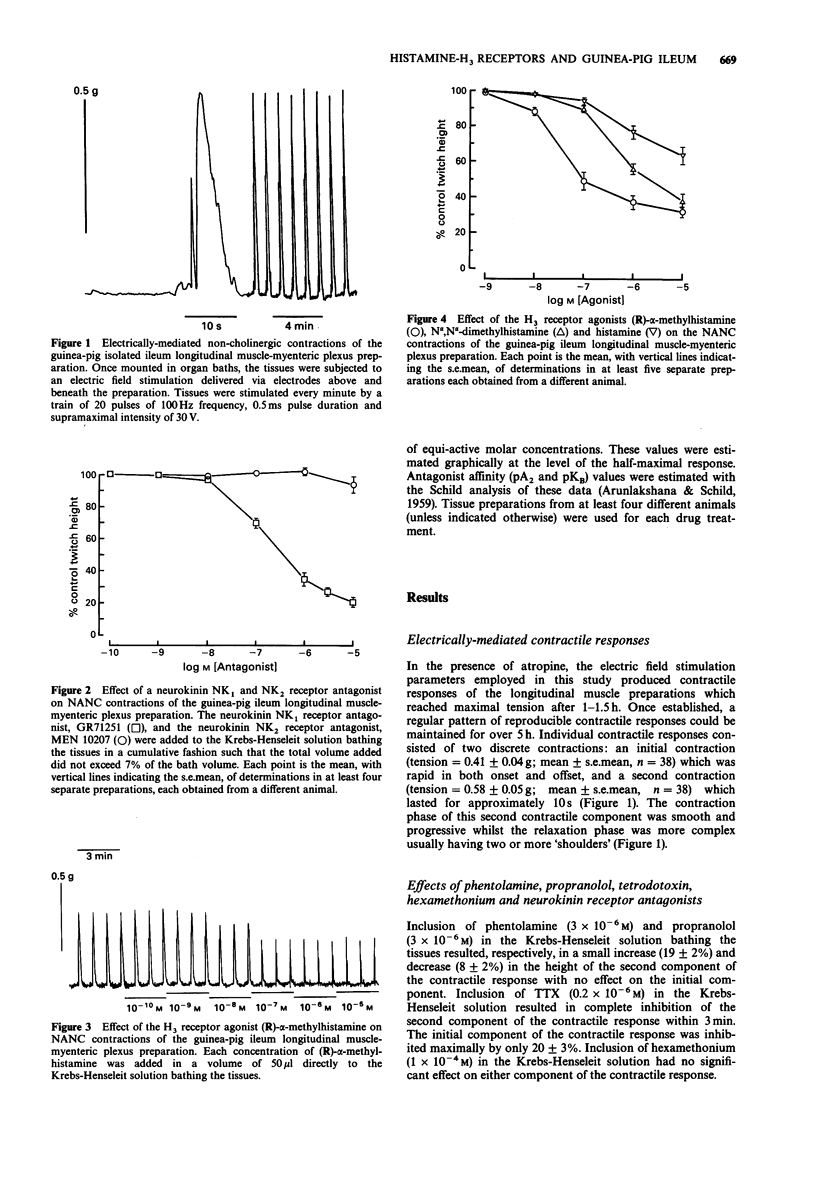
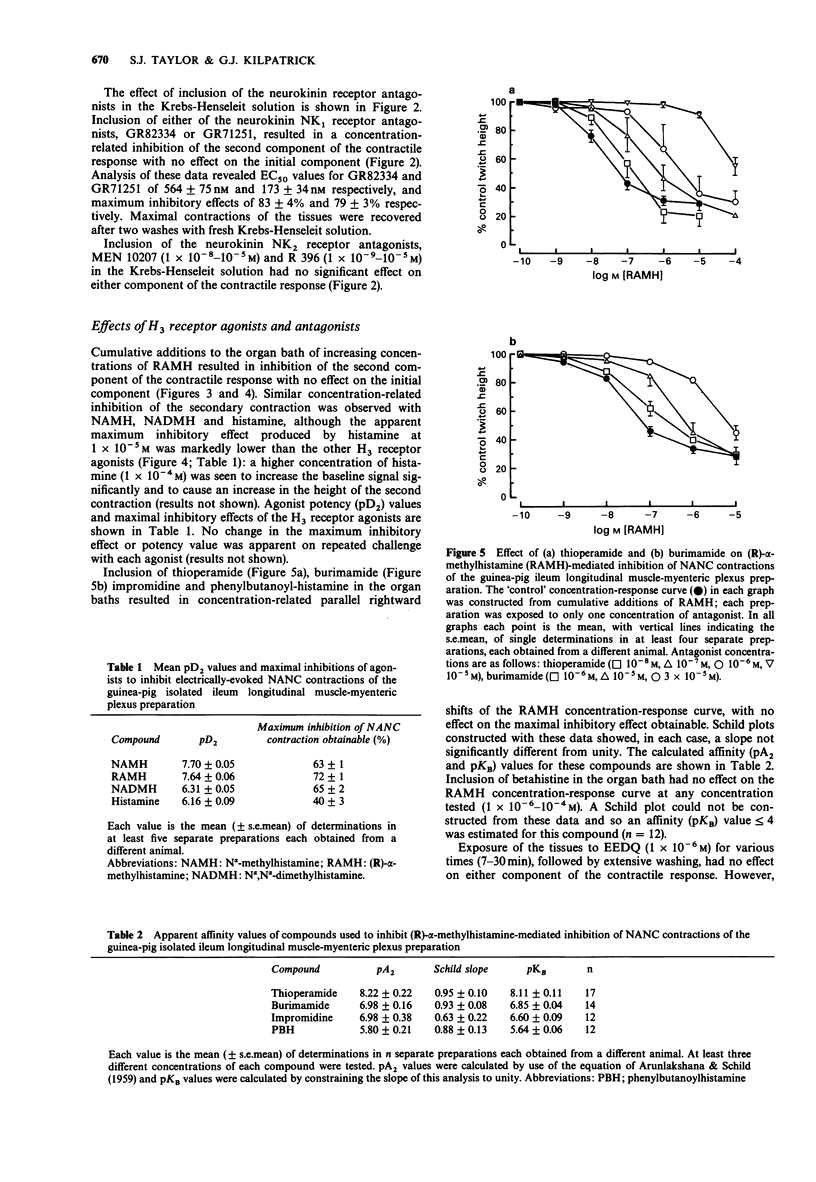
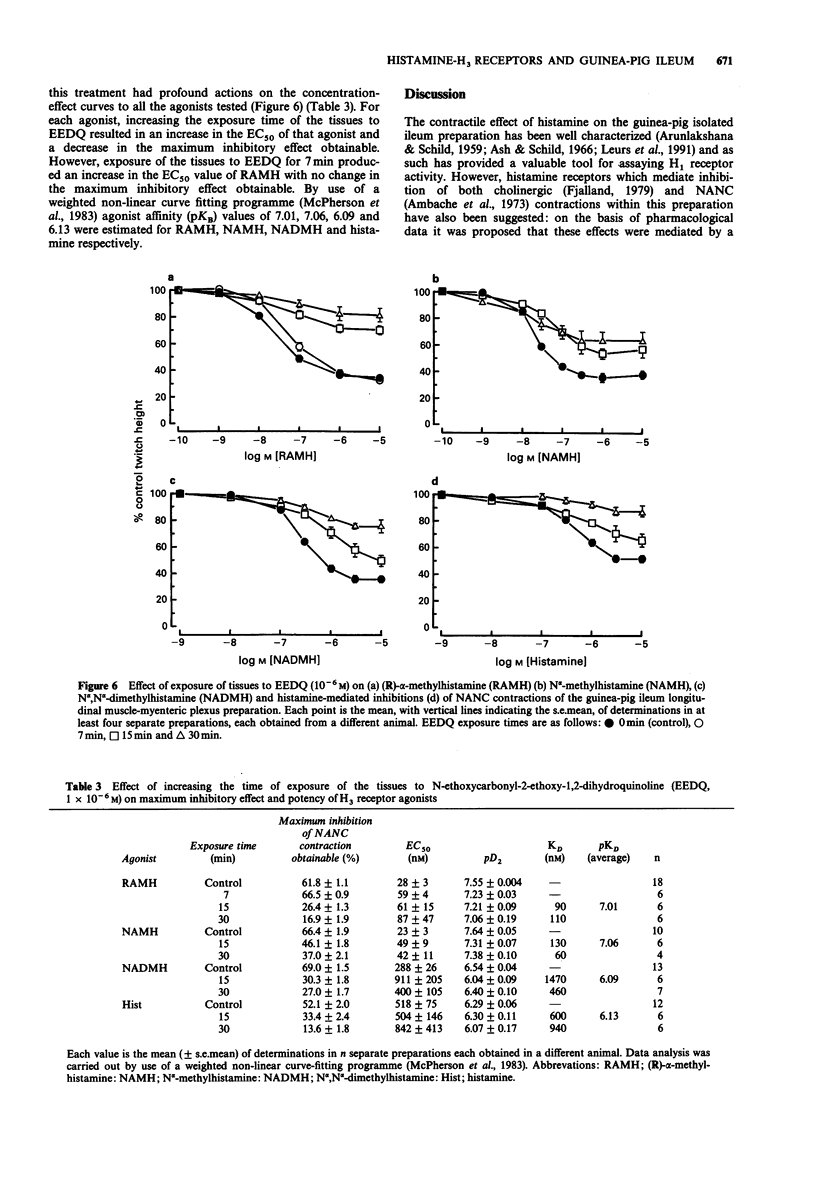
1. In the presence of atropine, mepyramine and ranitidine, electric field stimulation of the guinea-pig isolated ileum longitudinal muscle-myenteric plexus preparation resulted in a two component non-adrenergic non-cholinergic contraction. The initial contraction had a duration of approximately 1 s whereas the second contraction lasted approximately 10 s. The second contraction was completely inhibited by tetrodotoxin (0.2 x 10(-6) M) with minimal effect on the initial contraction. Phentolamine (3 x 10(-6) M), propranolol (3 x 10(-6) M) and hexamethonium (10(-4) M), did not significantly reduce either component of the contractile response. 2. The neurokinin NK1 receptor antagonists, GR82334 and GR71251, produced concentration-related (EC50 = 564 and 173 nM respectively) inhibitions of the second contraction with no effect on the initial contraction. The neurokinin NK2 receptor antagonists MEN 10207 and Ac-Leu-Asp-Gln-Trp-Phe-Gly-NH2 (R 396), 1 x 10(-9)-10(-5) M, were without effect on either component of the contractile response. 3. Concentration-related inhibitions of the second contraction, with no effect on the initial contraction, were observed after inclusion of the histamine H3 receptor agonists (R)-alpha-methylhistamine (pD2 = 7.6), N alpha-methylhistamine (pD2 = 7.7) and N alpha,N alpha-dimethylhistamine (pD2 = 6.3). Histamine also inhibited the second contraction (pD2 = 6.2) in a concentration-related manner but produced a lower maximum inhibitory effect than the other agonists tested. 4. Inclusion of the H3 receptor antagonists, thioperamide, burimamide, impromidine and phenylbutanoylhistamine, caused parallel concentration-related rightward shifts in the concentration-response curve to (R)-alpha-methylhistamine.(ABSTRACT TRUNCATED AT 250 WORDS)
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ambache N., Freeman M. A. Atropine-resistant longitudinal muscle spasms due to excitation of non-cholinergic neurones in Auerbach's plexus. J Physiol. 1968 Dec;199(3):705–727. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1968.sp008674. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ambache N., Killick S. W., Zar M. A. Antagonism by burimamide of inhibitions induced by histamine in plexus-containing longitudinal muscle preparations from guinea-pig ileum. Br J Pharmacol. 1973 Jun;48(2):362P–363P. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ambache N., Zar M. A. An inhibitory action of histamine on the guinea-pig ileum. Br J Pharmacol. 1970 Jan;38(1):229–240. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1970.tb10352.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arrang J. M., Garbarg M., Lancelot J. C., Lecomte J. M., Pollard H., Robba M., Schunack W., Schwartz J. C. Highly potent and selective ligands for histamine H3-receptors. Nature. 1987 May 14;327(6118):117–123. doi: 10.1038/327117a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arrang J. M., Garbarg M., Quach T. T., Dam Trung TuongM, Yeramian E., Schwartz J. C. Actions of betahistine at histamine receptors in the brain. Eur J Pharmacol. 1985 Apr 23;111(1):73–84. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(85)90115-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arrang J. M., Garbarg M., Schwartz J. C. Auto-inhibition of brain histamine release mediated by a novel class (H3) of histamine receptor. Nature. 1983 Apr 28;302(5911):832–837. doi: 10.1038/302832a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ash A. S., Schild H. O. Receptors mediating some actions of histamine. Br J Pharmacol Chemother. 1966 Aug;27(2):427–439. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1966.tb01674.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Battaglia G., Norman A. B., Newton P. L., Creese I. In vitro and in vivo irreversible blockade of cortical S2 serotonin receptors by N-ethoxycarbonyl-2-ethoxy-1,2-dihydroquinoline: a technique for investigating S2 serotonin receptor recovery. J Neurochem. 1986 Feb;46(2):589–593. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1986.tb13008.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Belleau B., DiTullio V., Godin D. The mechanism of irreversible adrenergic blockade by N-carbethoxydihydroquinolines--model studies with typical serine hydrolases. Biochem Pharmacol. 1969 May;18(5):1039–1044. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(69)90107-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Belleau B., Martel R., Lacasse G., Ménard M., Weinberg N. L., Perron Y. G. N-carboxylic acid esters of 1,2- and 1,4-dihydroquinolines. A new class of irreversible inactivators of the catecholamine alpha receptors and potent central nervous system depressants. J Am Chem Soc. 1968 Jan 31;90(3):823–824. doi: 10.1021/ja01005a067. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeLean A., Munson P. J., Rodbard D. Simultaneous analysis of families of sigmoidal curves: application to bioassay, radioligand assay, and physiological dose-response curves. Am J Physiol. 1978 Aug;235(2):E97–102. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.1978.235.2.E97. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Demolle D., Boeynaems J. M. Cholera and pertussis toxins amplify prostacyclin synthesis in aortic smooth muscle cells. Br J Pharmacol. 1989 Nov;98(3):717–720. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1989.tb14597.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fjalland B. Evidence for the existence of another type of histamine H2-receptor in guinea-pig ileum. J Pharm Pharmacol. 1979 Jan;31(1):50–51. doi: 10.1111/j.2042-7158.1979.tb13423.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamblin M. W., Creese I. Behavioral and radioligand binding evidence for irreversible dopamine receptor blockade by N-ethoxycarbonyl-2-ethoxy-1,2-dihydroquinoline. Life Sci. 1983 May 9;32(19):2247–2255. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(83)90423-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hew R. W., Hodgkinson C. R., Hill S. J. Characterization of histamine H3-receptors in guinea-pig ileum with H3-selective ligands. Br J Pharmacol. 1990 Nov;101(3):621–624. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1990.tb14130.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ichinose M., Barnes P. J. Histamine H3-receptors modulate nonadrenergic noncholinergic neural bronchoconstriction in guinea-pig in vivo. Eur J Pharmacol. 1989 Dec 12;174(1):49–55. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(89)90872-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ichinose M., Stretton C. D., Schwartz J. C., Barnes P. J. Histamine H3-receptors inhibit cholinergic neurotransmission in guinea-pig airways. Br J Pharmacol. 1989 May;97(1):13–15. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1989.tb11917.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kilpatrick G. J., Michel A. D. Characterisation of the binding of the histamine H3 receptor agonist [3H] (R)-alpha methyl histamine to homogenates of rat and guinea-pig cortex. Agents Actions Suppl. 1991;33:69–75. doi: 10.1007/978-3-0348-7309-3_4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leff P. Analysis of agonist action using the operational model. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 1988 Nov;9(11):395–398. doi: 10.1016/0165-6147(88)90065-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leff P., Dougall I. G., Harper D. H., Dainty I. A. Errors in agonist affinity estimation: do they and should they occur in isolated tissue experiments? Trends Pharmacol Sci. 1990 Feb;11(2):64–67. doi: 10.1016/0165-6147(90)90319-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leurs R., Brozius M. M., Smit M. J., Bast A., Timmerman H. Effects of histamine H1-, H2- and H3-receptor selective drugs on the mechanical activity of guinea-pig small and large intestine. Br J Pharmacol. 1991 Jan;102(1):179–185. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1991.tb12150.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maggi C. A., Patacchini R., Giuliani S., Rovero P., Dion S., Regoli D., Giachetti A., Meli A. Competitive antagonists discriminate between NK2 tachykinin receptor subtypes. Br J Pharmacol. 1990 Jul;100(3):589–592. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1990.tb15851.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McPherson G. A., Molenaar P., Raper C., Malta E. Analysis of dose-response curves and calculation of agonist dissociation constants using a weighted nonlinear curve fitting program. J Pharmacol Methods. 1983 Dec;10(4):231–241. doi: 10.1016/0160-5402(83)90017-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Menkveld G. J., Timmerman H. Inhibition of electrically evoked contractions of guinea-pig ileum preparations mediated by the histamine H3 receptor. Eur J Pharmacol. 1990 Sep 21;186(2-3):343–347. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(90)90458-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RANG H. P. STIMULANT ACTIONS OF VOLATILE ANAESTHETICS ON SMOOTH MUSCLE. Br J Pharmacol Chemother. 1964 Apr;22:356–365. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1964.tb02040.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schlicker E., Betz R., Göthert M. Histamine H3 receptor-mediated inhibition of serotonin release in the rat brain cortex. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1988 May;337(5):588–590. doi: 10.1007/BF00182737. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schlicker E., Fink K., Hinterthaner M., Göthert M. Inhibition of noradrenaline release in the rat brain cortex via presynaptic H3 receptors. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1989 Dec;340(6):633–638. doi: 10.1007/BF00717738. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Timmerman H. Histamine H3 ligands: just pharmacological tools or potential therapeutic agents? J Med Chem. 1990 Jan;33(1):4–11. doi: 10.1021/jm00163a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trzeciakowski J. P. Inhibition of guinea pig ileum contractions mediated by a class of histamine receptor resembling the H3 subtype. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1987 Dec;243(3):874–880. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- West R. E., Jr, Zweig A., Granzow R. T., Siegel M. I., Egan R. W. Biexponential kinetics of (R)-alpha-[3H]methylhistamine binding to the rat brain H3 histamine receptor. J Neurochem. 1990 Nov;55(5):1612–1616. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1990.tb04946.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


