Abstract
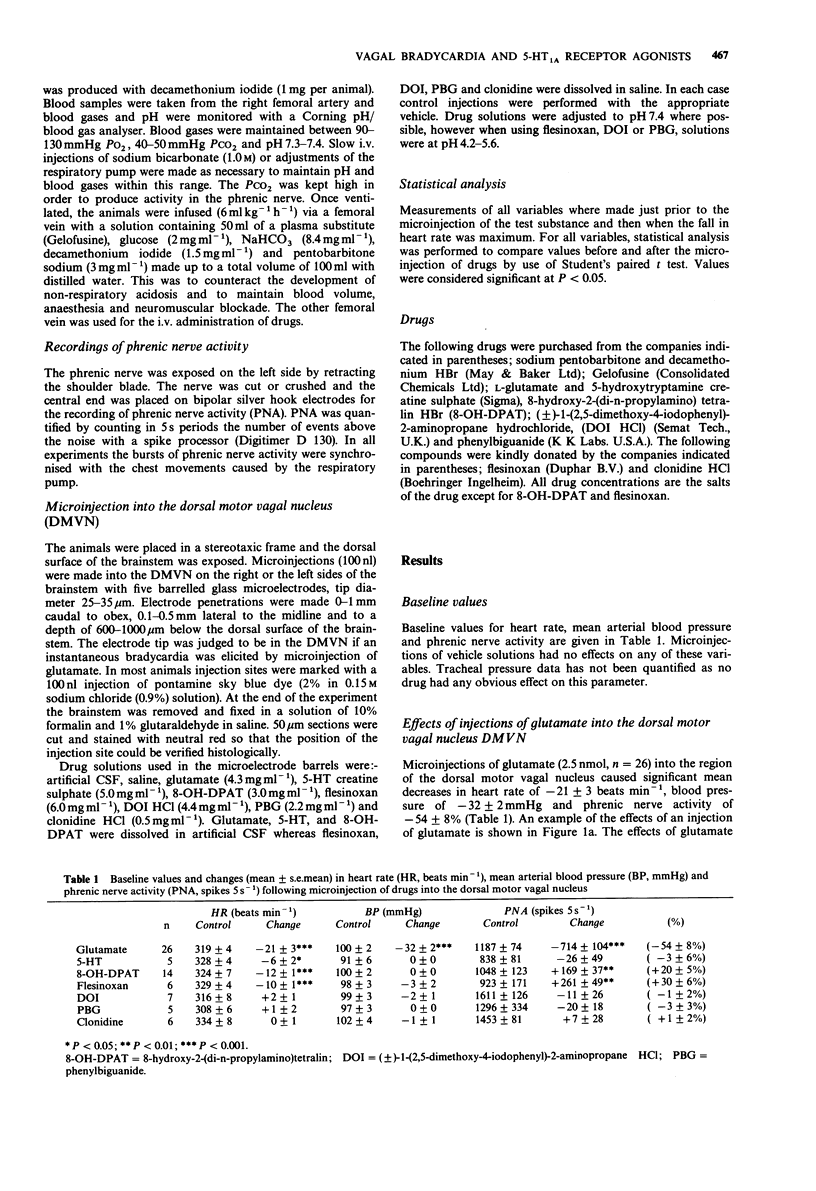
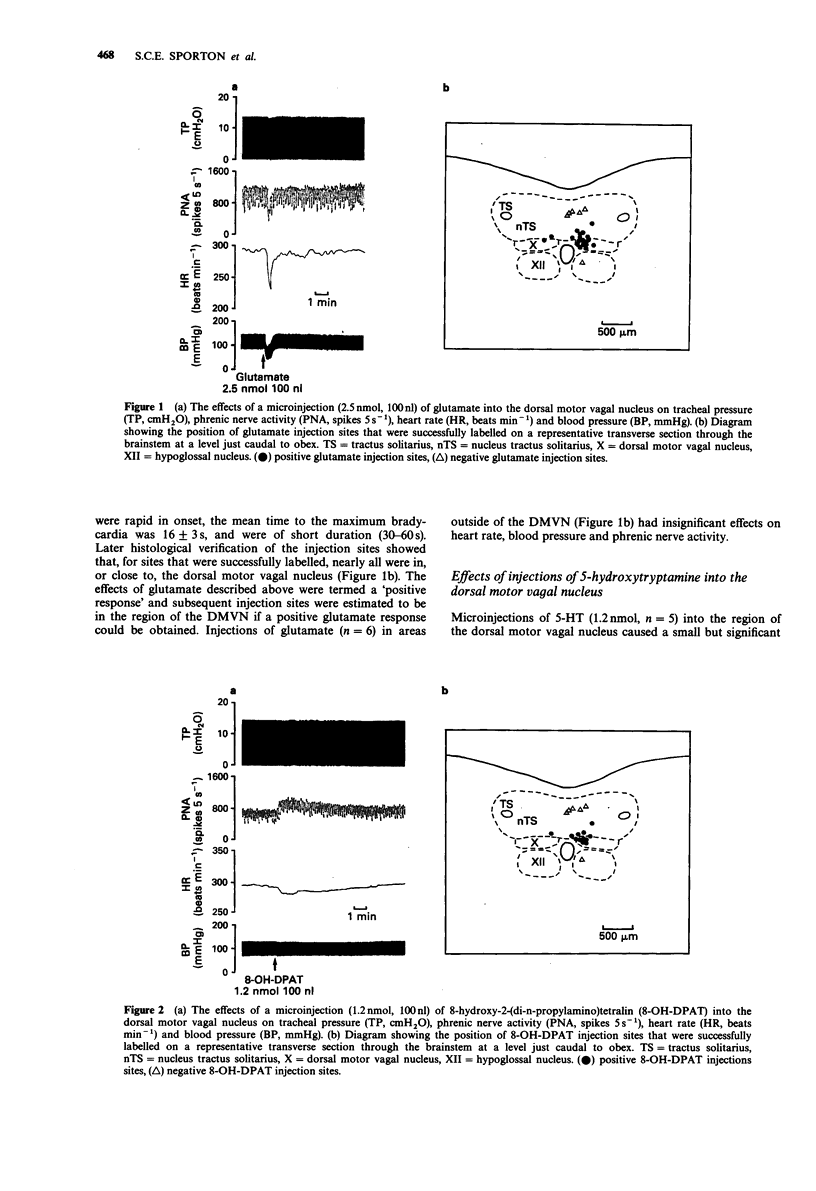
1. The effects of microinjections (100 nl) into the dorsal motor vagal nucleus of the 5-HT1A receptor agonists 8-hydroxy-2-(di-n-propylamino)tetralin (8-OH-DPAT) and flesinoxan, the 5-HT2 receptor agonist (+-)-1-(2,5-dimethoxy-4-iodophenyl)-2-aminopropane hydrochloride (DOI), the 5-HT3 receptor agonist phenylbiguanide (PBG), the alpha 2-adrenoceptor agonist clonidine and the excitatory amino acid glutamate on heart rate, blood pressure, tracheal pressure and phrenic nerve activity were investigated in atenolol-pretreated rats anaesthetized with sodium pentobarbitone. 2. Microinjections of glutamate (2.5 nmol) caused decreases in blood pressure, heart rate and phrenic nerve activity. In contrast, microinjections of 5-HT (1.2 nmol), 8-OH-DPAT (1.2 nmol) and flesinoxan (1.3 nmol) all caused a bradycardia but had no effect on blood pressure. In addition, 8-OH-DPAT and flesinoxan caused an increase in phrenic nerve activity. 3. Microinjections of DOI, PBG and clonidine had no significant effect on any of the variables recorded. None of the drugs used had any significant effect on tracheal pressure. 4. These results support the hypothesis that activation of 5-HT1A receptors causes excitation of cardiac vagal motoneurones and suggest that these receptors are also important in the control of central respiratory drive.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barraco R. A., el-Ridi M. R. Cardiorespiratory responses following electrical stimulation of caudal sites in the rat medulla. Brain Res Bull. 1989 Oct-Nov;23(4-5):299–310. doi: 10.1016/0361-9230(89)90213-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bogle R. G., Pires J. G., Ramage A. G. Evidence that central 5-HT1A-receptors play a role in the von Bezold-Jarisch reflex in the rat. Br J Pharmacol. 1990 Aug;100(4):757–760. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1990.tb14088.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cherqui C., Dabiré H., Fournier B., Schmitt H. Participation of sympathetic and vagal tones in the hypotensive and bradycardic effects of some 5-HT1-like receptor agonists in the rat. Arch Int Pharmacodyn Ther. 1988 Nov-Dec;296:18–28. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collis M. G., Keddie J. R., Rouse W. The cardiovascular pharmacology of ICI 170777 ((6RS)-6-methyl-5-(pyrid-4-yl)-3H,6H-1,3,4- thiadiazin-2-one) a novel compound with positive inotropic and vasodilator effects. Br J Pharmacol. 1989 Jun;97(2):409–418. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1989.tb11968.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dalton D. W. The cardiovascular effects of centrally administered 5-hydroxytryptamine in the conscious normotensive and hypertensive rat. J Auton Pharmacol. 1986 Mar;6(1):67–75. doi: 10.1111/j.1474-8673.1986.tb00632.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Direct evidence for an interaction of beta-adrenergic blockers with the 5-HT receptor. Nature. 1977 May 19;267(5608):289–290. doi: 10.1038/267289a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dreteler G. H., Wouters W., Saxena P. R., Ramage A. G. Pressor effects following microinjection of 5-HT1A receptor agonists into the raphe obscurus of the anaesthetized rat. Br J Pharmacol. 1991 Feb;102(2):317–322. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1991.tb12172.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gradin K., Pettersson A., Hedner T., Persson B. Acute administration of 8-hydroxy-2-(di-n-propylamino)tetralin (8-OH-DPAT), a selective 5-HT-receptor agonist, causes a biphasic blood pressure response and a bradycardia in the normotensive Sprague-Dawley rat and in the spontaneously hypertensive rat. J Neural Transm. 1985;62(3-4):305–319. doi: 10.1007/BF01252244. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holtman J. R., Jr, Anastasi N. C., Norman W. P., Dretchen K. L. Effect of electrical and chemical stimulation of the raphe obscurus on phrenic nerve activity in the cat. Brain Res. 1986 Jan 8;362(2):214–220. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(86)90446-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holtman J. R., Jr, Marion L. J., Speck D. F. Origin of serotonin-containing projections to the ventral respiratory group in the rat. Neuroscience. 1990;37(2):541–552. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(90)90422-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manaker S., Verderame H. M. Organization of serotonin 1A and 1B receptors in the nucleus of the solitary tract. J Comp Neurol. 1990 Nov 22;301(4):535–553. doi: 10.1002/cne.903010405. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Middlemiss D. N., Fozard J. R. 8-Hydroxy-2-(di-n-propylamino)-tetralin discriminates between subtypes of the 5-HT1 recognition site. Eur J Pharmacol. 1983 May 20;90(1):151–153. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(83)90230-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pazos A., Cortés R., Palacios J. M. Quantitative autoradiographic mapping of serotonin receptors in the rat brain. II. Serotonin-2 receptors. Brain Res. 1985 Nov 4;346(2):231–249. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(85)90857-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pazos A., Palacios J. M. Quantitative autoradiographic mapping of serotonin receptors in the rat brain. I. Serotonin-1 receptors. Brain Res. 1985 Nov 4;346(2):205–230. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(85)90856-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pratt G. D., Bowery N. G., Kilpatrick G. J., Leslie R. A., Barnes N. M., Naylor R. J., Jones B. J., Nelson D. R., Palacids J. M., Slater P. Consensus meeting agrees distribution of 5-HT3 receptors in mammalian hindbrain. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 1990 Apr;11(4):135–137. doi: 10.1016/0165-6147(90)90058-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ramage A. G., Fozard J. R. Evidence that the putative 5-HT1A receptor agonists, 8-OH-DPAT and ipsapirone, have a central hypotensive action that differs from that of clonidine in anaesthetised cats. Eur J Pharmacol. 1987 Jun 19;138(2):179–191. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(87)90431-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ramage A. G., Wouters W., Bevan P. Evidence that the novel antihypertensive agent, flesinoxan, causes differential sympathoinhibition and also increases vagal tone by a central action. Eur J Pharmacol. 1988 Jul 14;151(3):373–379. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(88)90533-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schaffar N., Kessler J. P., Bosler O., Jean A. Central serotonergic projections to the nucleus tractus solitarii: evidence from a double labeling study in the rat. Neuroscience. 1988 Sep;26(3):951–958. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(88)90111-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shapiro R. E., Miselis R. R. The central organization of the vagus nerve innervating the stomach of the rat. J Comp Neurol. 1985 Aug 22;238(4):473–488. doi: 10.1002/cne.902380411. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steinbusch H. W. Distribution of serotonin-immunoreactivity in the central nervous system of the rat-cell bodies and terminals. Neuroscience. 1981;6(4):557–618. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(81)90146-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Street J. A., Hemsworth B. A., Roach A. G., Day M. D. Tissue levels of several radiolabelled beta-adrenoceptor antagonists after intravenous administration in rats. Arch Int Pharmacodyn Ther. 1979 Feb;237(2):180–190. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Unnerstall J. R., Kopajtic T. A., Kuhar M. J. Distribution of alpha 2 agonist binding sites in the rat and human central nervous system: analysis of some functional, anatomic correlates of the pharmacologic effects of clonidine and related adrenergic agents. Brain Res. 1984 Mar;319(1):69–101. doi: 10.1016/0165-0173(84)90030-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolf W. A., Kuhn D. M., Lovenberg W. Blood pressure responses to local application of serotonergic agents in the nucleus tractus solitarii. Eur J Pharmacol. 1981 Jan 29;69(3):291–299. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(81)90475-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wouters W., Tulp M. T., Bevan P. Flesinoxan lowers blood pressure and heart rate in cats via 5-HT1A receptors. Eur J Pharmacol. 1988 May 10;149(3):213–223. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(88)90651-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Wijngaarden I., Tulp M. T., Soudijn W. The concept of selectivity in 5-HT receptor research. Eur J Pharmacol. 1990 Jun 12;188(6):301–312. doi: 10.1016/0922-4106(90)90190-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


