Abstract
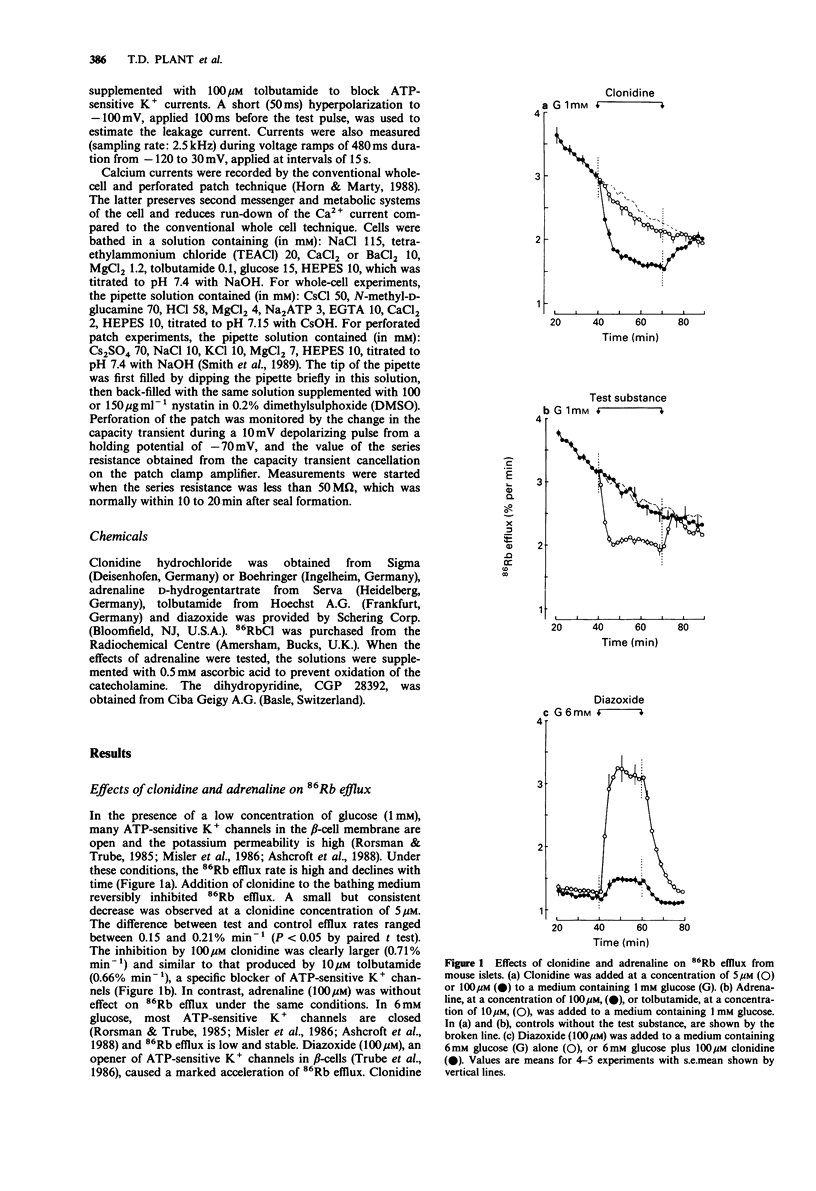
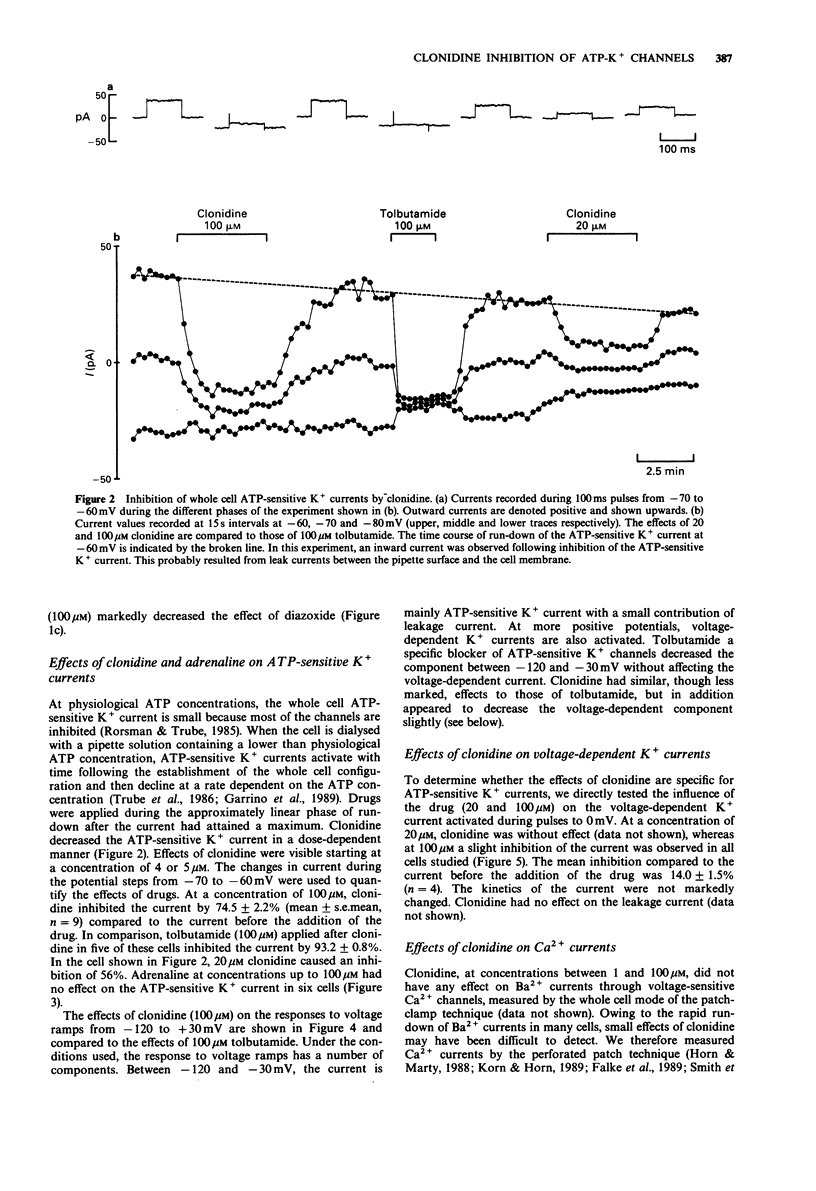
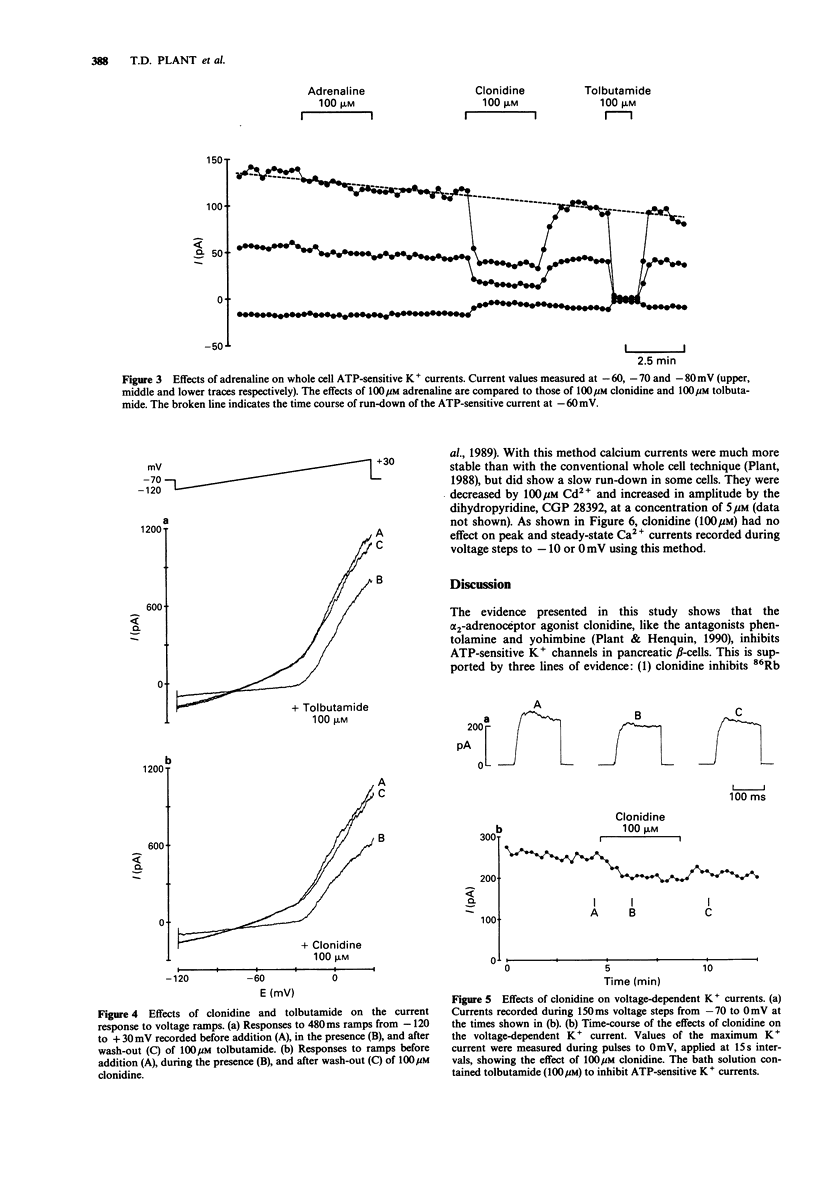
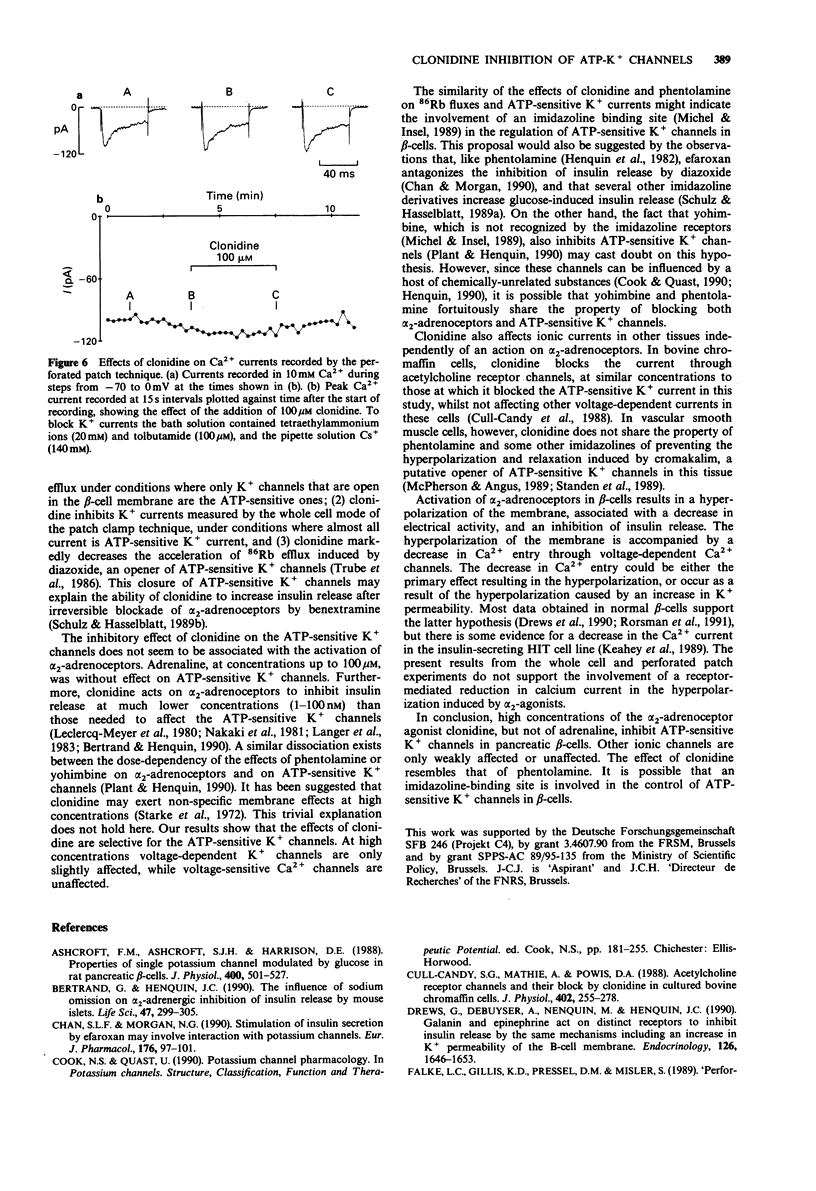
1. The effects of clonidine and adrenaline on adenosine 5'-triphosphate (ATP)-sensitive K+ channels were studied in pancreatic beta-cells from normal mice. 2. When perifused with a medium containing 1 mM glucose, many of the ATP-sensitive K+ channels in the beta-cell membrane are open. Under these conditions, clonidine (5-100 microM) reversibly decreased 86Rb efflux from the islets, whereas adrenaline was ineffective at concentrations up to 100 microM. 3. In 6 mM glucose, most of the ATP-sensitive K+ channels in the beta-cell membrane are closed. Opening these channels by diazoxide (100 microM) caused a marked acceleration of 86Rb efflux from the islets, which was attenuated by 100 microM clonidine. 4. ATP-sensitive K+ currents were measured in single beta-cells by the whole cell mode of the patch-clamp technique. At concentrations above 4 microM, clonidine reversibly inhibited the ATP-sensitive K+ current in a dose-dependent manner. 5. Voltage-sensitive K+ currents were unaffected by 20 microM but decreased slightly by 100 microM clonidine. 6. Calcium currents, measured by the whole cell or perforated patch technique, were unaffected by clonidine at concentrations up to 100 microM. 7. It is concluded that high concentrations of the alpha 2-adrenoceptor agonist clonidine, but not of adrenaline, can inhibit ATP-sensitive K+ channels in pancreatic beta-cells. Other ionic channels are only slightly affected or unaffected.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ashcroft F. M., Ashcroft S. J., Harrison D. E. Properties of single potassium channels modulated by glucose in rat pancreatic beta-cells. J Physiol. 1988 Jun;400:501–527. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1988.sp017134. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bertrand G., Henquin J. C. The influence of sodium omission on alpha 2-adrenergic inhibition of insulin release by mouse islets. Life Sci. 1990;47(4):299–305. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(90)90587-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chan S. L., Morgan N. G. Stimulation of insulin secretion by efaroxan may involve interaction with potassium channels. Eur J Pharmacol. 1990 Jan 25;176(1):97–101. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(90)90137-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cull-Candy S. G., Mathie A., Powis D. A. Acetylcholine receptor channels and their block by clonidine in cultured bovine chromaffin cells. J Physiol. 1988 Aug;402:255–278. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1988.sp017203. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drews G., Debuyser A., Nenquin M., Henquin J. C. Galanin and epinephrine act on distinct receptors to inhibit insulin release by the same mechanisms including an increase in K+ permeability of the B-cell membrane. Endocrinology. 1990 Mar;126(3):1646–1653. doi: 10.1210/endo-126-3-1646. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Falke L. C., Gillis K. D., Pressel D. M., Misler S. 'Perforated patch recording' allows long-term monitoring of metabolite-induced electrical activity and voltage-dependent Ca2+ currents in pancreatic islet B cells. FEBS Lett. 1989 Jul 17;251(1-2):167–172. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(89)81448-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garrino M. G., Henquin J. C. Highly potent and stereoselective effects of the benzoic acid derivative AZ-DF 265 on pancreatic beta-cells. Br J Pharmacol. 1988 Jan;93(1):61–68. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1988.tb11405.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garrino M. G., Plant T. D., Henquin J. C. Effects of putative activators of K+ channels in mouse pancreatic beta-cells. Br J Pharmacol. 1989 Nov;98(3):957–965. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1989.tb14626.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henquin J. C., Charles S., Nenquin M., Mathot F., Tamagawa T. Diazoxide and D600 inhibition of insulin release. Distinct mechanisms explain the specificity for different stimuli. Diabetes. 1982 Sep;31(9):776–783. doi: 10.2337/diab.31.9.776. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henquin J. C. D-glucose inhibits potassium efflux from pancreatic islet cells. Nature. 1978 Jan 19;271(5642):271–273. doi: 10.1038/271271a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horn R., Marty A. Muscarinic activation of ionic currents measured by a new whole-cell recording method. J Gen Physiol. 1988 Aug;92(2):145–159. doi: 10.1085/jgp.92.2.145. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keahey H. H., Boyd A. E., 3rd, Kunze D. L. Catecholamine modulation of calcium currents in clonal pancreatic beta-cells. Am J Physiol. 1989 Dec;257(6 Pt 1):C1171–C1176. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1989.257.6.C1171. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Korn S. J., Horn R. Influence of sodium-calcium exchange on calcium current rundown and the duration of calcium-dependent chloride currents in pituitary cells, studied with whole cell and perforated patch recording. J Gen Physiol. 1989 Nov;94(5):789–812. doi: 10.1085/jgp.94.5.789. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Langer J., Panten U., Zielmann S. Effects of alpha-adrenoceptor antagonists on clonidine-induced inhibition of insulin secretion by isolated pancreatic islets. Br J Pharmacol. 1983 Jun;79(2):415–420. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1983.tb11014.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leclercq-Meyer V., Herchuelz A., Valverde I., Couturier E., Marchand J., Malaisse W. J. Mode of action of clonidine upon islet function: dissociated effects upon the time course and magnitude of insulin release. Diabetes. 1980 Mar;29(3):193–200. doi: 10.2337/diab.29.3.193. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McPherson G. A., Angus J. A. Phentolamine and structurally related compounds selectively antagonize the vascular actions of the K+ channel opener, cromromakalim. Br J Pharmacol. 1989 Jul;97(3):941–949. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1989.tb12035.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michel M. C., Insel P. A. Are there multiple imidazoline binding sites? Trends Pharmacol Sci. 1989 Sep;10(9):342–344. doi: 10.1016/0165-6147(89)90002-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Misler S., Falke L. C., Gillis K., McDaniel M. L. A metabolite-regulated potassium channel in rat pancreatic B cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Sep;83(18):7119–7123. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.18.7119. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakaki T., Nakadate T., Ishii K., Kato R. Postsynaptic alpha-2 adrenergic receptors in isolated rat islets of Langerhans: inhibition of insulin release and cyclic 3':5'-adenosine monophosphate accumulation. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1981 Mar;216(3):607–612. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plant T. D., Henquin J. C. Phentolamine and yohimbine inhibit ATP-sensitive K+ channels in mouse pancreatic beta-cells. Br J Pharmacol. 1990 Sep;101(1):115–120. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1990.tb12099.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plant T. D. Properties and calcium-dependent inactivation of calcium currents in cultured mouse pancreatic B-cells. J Physiol. 1988 Oct;404:731–747. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1988.sp017316. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rorsman P., Bokvist K., Ammälä C., Arkhammar P., Berggren P. O., Larsson O., Wåhlander K. Activation by adrenaline of a low-conductance G protein-dependent K+ channel in mouse pancreatic B cells. Nature. 1991 Jan 3;349(6304):77–79. doi: 10.1038/349077a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rorsman P., Trube G. Glucose dependent K+-channels in pancreatic beta-cells are regulated by intracellular ATP. Pflugers Arch. 1985 Dec;405(4):305–309. doi: 10.1007/BF00595682. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schulz A., Hasselblatt A. An insulin-releasing property of imidazoline derivatives is not limited to compounds that block alpha-adrenoceptors. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1989 Sep;340(3):321–327. doi: 10.1007/BF00168517. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schulz A., Hasselblatt A. Dual action of clonidine on insulin release: suppression, but stimulation when alpha 2-adrenoceptors are blocked. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1989 Dec;340(6):712–714. doi: 10.1007/BF00717749. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith P. A., Rorsman P., Ashcroft F. M. Modulation of dihydropyridine-sensitive Ca2+ channels by glucose metabolism in mouse pancreatic beta-cells. Nature. 1989 Nov 30;342(6249):550–553. doi: 10.1038/342550a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Standen N. B., Quayle J. M., Davies N. W., Brayden J. E., Huang Y., Nelson M. T. Hyperpolarizing vasodilators activate ATP-sensitive K+ channels in arterial smooth muscle. Science. 1989 Jul 14;245(4914):177–180. doi: 10.1126/science.2501869. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Starke K., Wagner J., Schümann H. J. Adrenergic neuron blockade by clonidine: comparison with guanethidine and local anesthetics. Arch Int Pharmacodyn Ther. 1972 Feb;195(2):291–308. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trube G., Rorsman P., Ohno-Shosaku T. Opposite effects of tolbutamide and diazoxide on the ATP-dependent K+ channel in mouse pancreatic beta-cells. Pflugers Arch. 1986 Nov;407(5):493–499. doi: 10.1007/BF00657506. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


