Abstract
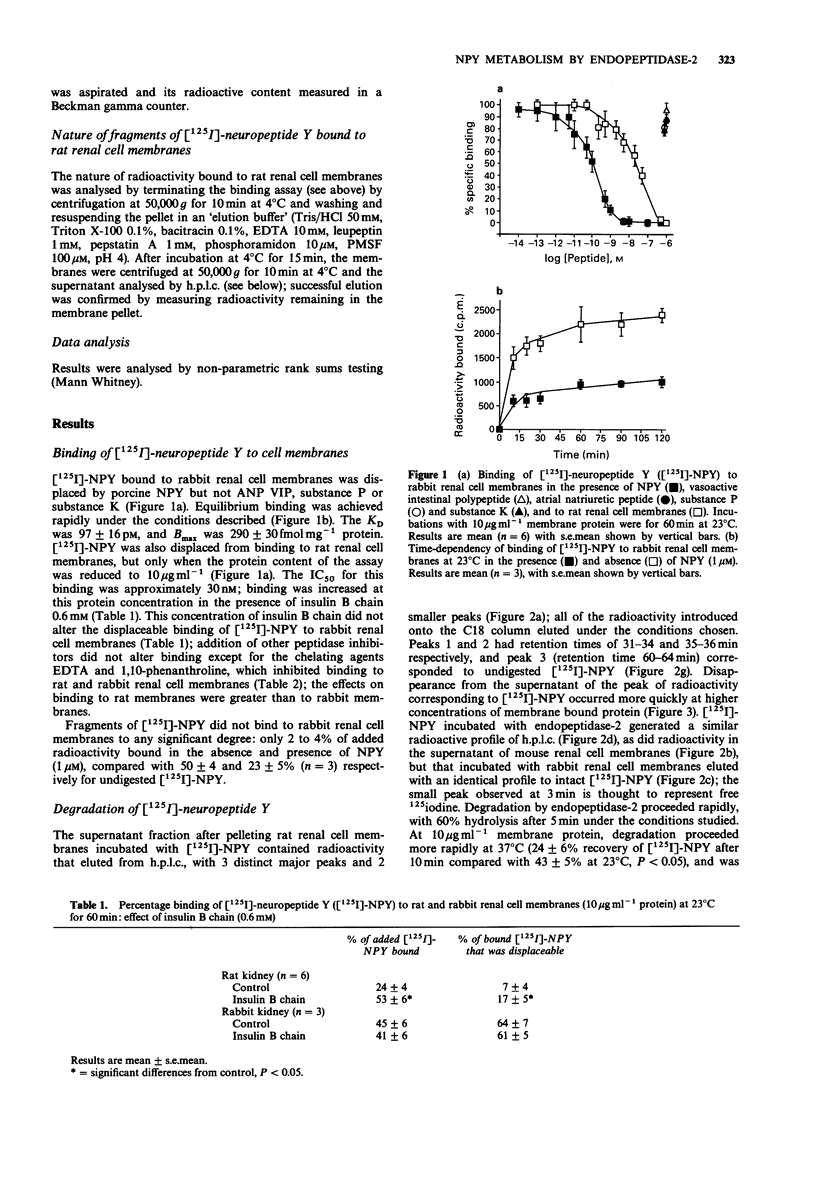
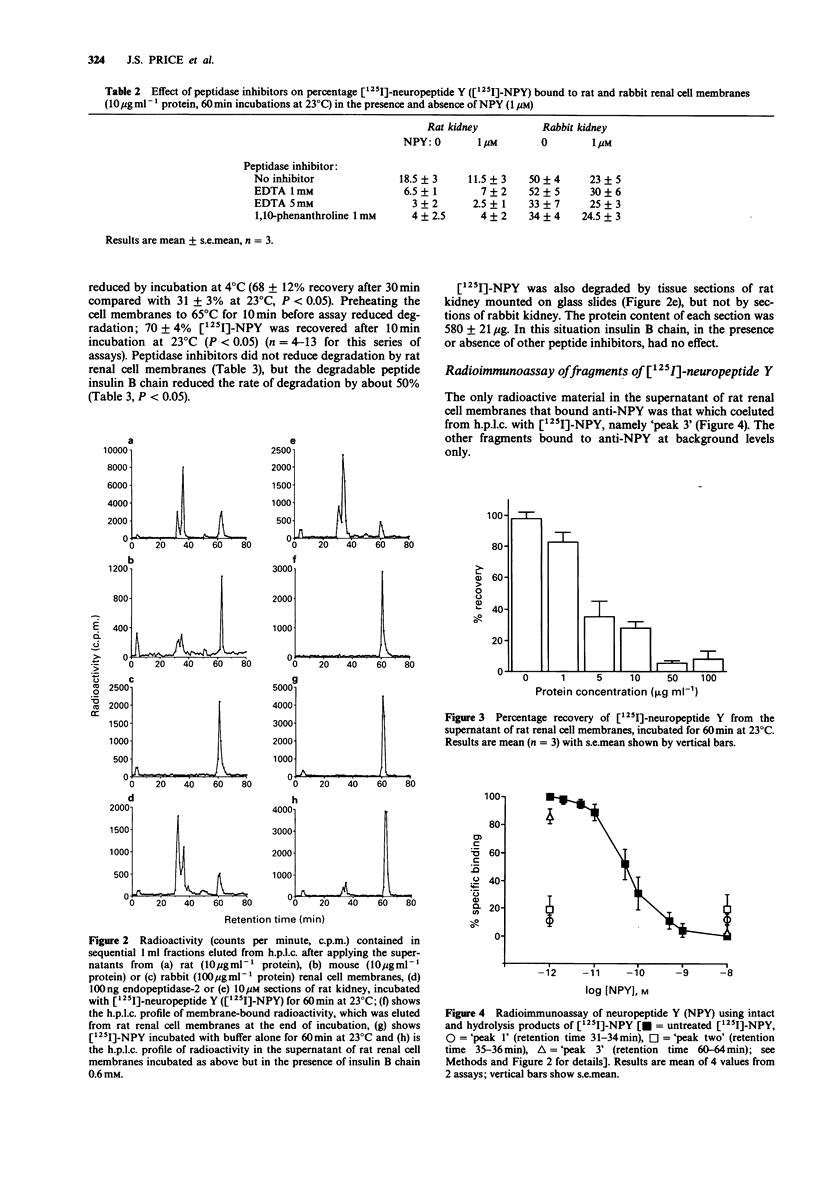
1. Despite the observation of pharmacological responses to neuropeptide Y (NPY) in mammalian kidneys, there are species differences in the ease with which specific NPY binding sites can be demonstrated; we have investigated whether this can be explained by differential metabolism of NPY by a membrane-bound peptidase. 2. NPY receptors were identified on cell membranes isolated from the rabbit kidney (KD = 97 +/- 16 pM, Bmax = 290 +/- 30 fmol mg-1 protein), and this preparation did not degrade [125I]-NPY. However, a similar preparation of cell membranes from the rat kidney exhibited a much lower apparent receptor affinity (IC50 approximately 30 nM); these membranes rapidly degraded [125I]-NPY to fragments which did not bind NPY receptors in either tissue. 3. [125I]-NPY binding sites were revealed in the rat kidney when degradation was inhibited by insulin B chain. Chelating agents also inhibited degradation, but interfered with receptor binding. Binding sites could not be demonstrated in sections of rat kidney, even in the presence of insulin B chain. 4. The difference in degradative activity between rat and rabbit renal cell membranes, inhibition of degradation by chelating agents and insulin B chain, and insensitivity to phosphoramidon suggest that the enzyme responsible was endopeptidase-2, and this was confirmed by comparing the hydrolysis of [125I]-NPY by purified enzyme with rat renal tissue. Activity of this enzyme explains the difficulties encountered demonstrating receptors in the rat kidney. 5. Renal cell membranes from the mouse digested [125I]-NPY in a similar manner and this may be due to the closely related enzyme, meprin.(ABSTRACT TRUNCATED AT 250 WORDS)
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Allen J. M., Raine A. E., Ledingham J. G., Bloom S. R. Neuropeptide Y: a novel renal peptide with vasoconstrictor and natriuretic activity. Clin Sci (Lond) 1985 Apr;68(4):373–377. doi: 10.1042/cs0680373. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ballesta J., Polak J. M., Allen J. M., Bloom S. R. The nerves of the juxtaglomerular apparatus of man and other mammals contain the potent peptide NPY. Histochemistry. 1984;80(5):483–485. doi: 10.1007/BF00495438. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barnes K., Ingram J., Kenny A. J. Proteins of the kidney microvillar membrane. Structural and immunochemical properties of rat endopeptidase-2 and its immunohistochemical localization in tissues of rat and mouse. Biochem J. 1989 Dec 1;264(2):335–346. doi: 10.1042/bj2640335. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beynon R. J., Shannon J. D., Bond J. S. Purification and characterization of a metallo-endoproteinase from mouse kidney. Biochem J. 1981 Dec 1;199(3):591–598. doi: 10.1042/bj1990591. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeBlasi A., O'Reilly K., Motulsky H. J. Calculating receptor number from binding experiments using same compound as radioligand and competitor. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 1989 Jun;10(6):227–229. doi: 10.1016/0165-6147(89)90266-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edvinsson L., Ekblad E., Håkanson R., Wahlestedt C. Neuropeptide Y potentiates the effect of various vasoconstrictor agents on rabbit blood vessels. Br J Pharmacol. 1984 Oct;83(2):519–525. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1984.tb16516.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ekblad E., Edvinsson L., Wahlestedt C., Uddman R., Håkanson R., Sundler F. Neuropeptide Y co-exists and co-operates with noradrenaline in perivascular nerve fibers. Regul Pept. 1984 Apr;8(3):225–235. doi: 10.1016/0167-0115(84)90064-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evéquoz D., Waeber B., Corder R., Nussberger J., Gaillard R., Brunner H. R. Markedly reduced blood pressure responsiveness in endotoxemic rats; reversal by neuropeptide Y. Life Sci. 1987 Dec 7;41(23):2573–2580. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(87)90442-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kassis S., Olasmaa M., Terenius L., Fishman P. H. Neuropeptide Y inhibits cardiac adenylate cyclase through a pertussis toxin-sensitive G protein. J Biol Chem. 1987 Mar 15;262(8):3429–3431. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kenny A. J., Fulcher I. S., Ridgwell K., Ingram J. Microvillar membrane neutral endopeptidases. Acta Biol Med Ger. 1981;40(10-11):1465–1471. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kenny A. J., Ingram J. Proteins of the kidney microvillar membrane. Purification and properties of the phosphoramidon-insensitive endopeptidase ('endopeptidase-2') from rat kidney. Biochem J. 1987 Jul 15;245(2):515–524. doi: 10.1042/bj2450515. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leys K., Schachter M., Sever P. Autoradiographic localisation of NPY receptors in rabbit kidney: comparison with rat, guinea-pig and human. Eur J Pharmacol. 1987 Feb 10;134(2):233–237. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(87)90171-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lundberg J. M., Hemsén A., Larsson O., Rudehill A., Saria A., Fredholm B. B. Neuropeptide Y receptor in pig spleen: binding characteristics, reduction of cyclic AMP formation and calcium antagonist inhibition of vasoconstriction. Eur J Pharmacol. 1988 Jan 5;145(1):21–29. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(88)90344-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lundberg J. M., Stjarne L. Neuropeptide Y (NPY) depresses the secretion of 3H-noradrenaline and the contractile response evoked by field stimulation, in rat vas deferens. Acta Physiol Scand. 1984 Mar;120(3):477–479. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1984.tb07410.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lundberg J. M., Terenius L., Hökfelt T., Martling C. R., Tatemoto K., Mutt V., Polak J., Bloom S., Goldstein M. Neuropeptide Y (NPY)-like immunoreactivity in peripheral noradrenergic neurons and effects of NPY on sympathetic function. Acta Physiol Scand. 1982 Dec;116(4):477–480. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1982.tb07171.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pernow J., Lundberg J. M., Kaijser L. Vasoconstrictor effects in vivo and plasma disappearance rate of neuropeptide Y in man. Life Sci. 1987 Jan 5;40(1):47–54. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(87)90251-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pernow J., Svenberg T., Lundberg J. M. Actions of calcium antagonists on pre- and postjunctional effects of neuropeptide Y on human peripheral blood vessels in vitro. Eur J Pharmacol. 1987 Apr 14;136(2):207–218. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(87)90712-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reynolds E. E., Yokota S. Neuropeptide Y receptor-effector coupling mechanisms in cultured vascular smooth muscle cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1988 Mar 15;151(2):919–925. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(88)80369-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sheikh S. P., Håkanson R., Schwartz T. W. Y1 and Y2 receptors for neuropeptide Y. FEBS Lett. 1989 Mar 13;245(1-2):209–214. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(89)80223-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stephenson S. L., Kenny A. J. Metabolism of neuropeptides. Hydrolysis of the angiotensins, bradykinin, substance P and oxytocin by pig kidney microvillar membranes. Biochem J. 1987 Jan 1;241(1):237–247. doi: 10.1042/bj2410237. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stephenson S. L., Kenny A. J. The metabolism of neuropeptides. Hydrolysis of peptides by the phosphoramidon-insensitive rat kidney enzyme 'endopeptidase-2' and by rat microvillar membranes. Biochem J. 1988 Oct 1;255(1):45–51. doi: 10.1042/bj2550045. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sterchi E. E., Green J. R., Lentze M. J. Non-pancreatic hydrolysis of N-benzoyl-l-tyrosyl-p-aminobenzoic acid (PABA-peptide) in the human small intestine. Clin Sci (Lond) 1982 May;62(5):557–560. doi: 10.1042/cs0620557. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stjärne L., Lundberg J. M., Astrand P. Neuropeptide Y--a cotransmitter with noradrenaline and adenosine 5'-triphosphate in the sympathetic nerves of the mouse vas deferens? A biochemical, physiological and electropharmacological study. Neuroscience. 1986 May;18(1):151–166. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(86)90184-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tatemoto K. Neuropeptide Y: complete amino acid sequence of the brain peptide. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Sep;79(18):5485–5489. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.18.5485. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Undén A., Tatemoto K., Mutt V., Bartfai T. Neuropeptide Y receptor in the rat brain. Eur J Biochem. 1984 Dec 17;145(3):525–530. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1984.tb08588.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wahlestedt C., Yanaihara N., Håkanson R. Evidence for different pre-and post-junctional receptors for neuropeptide Y and related peptides. Regul Pept. 1986 Feb;13(3-4):307–318. doi: 10.1016/0167-0115(86)90048-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


