Abstract
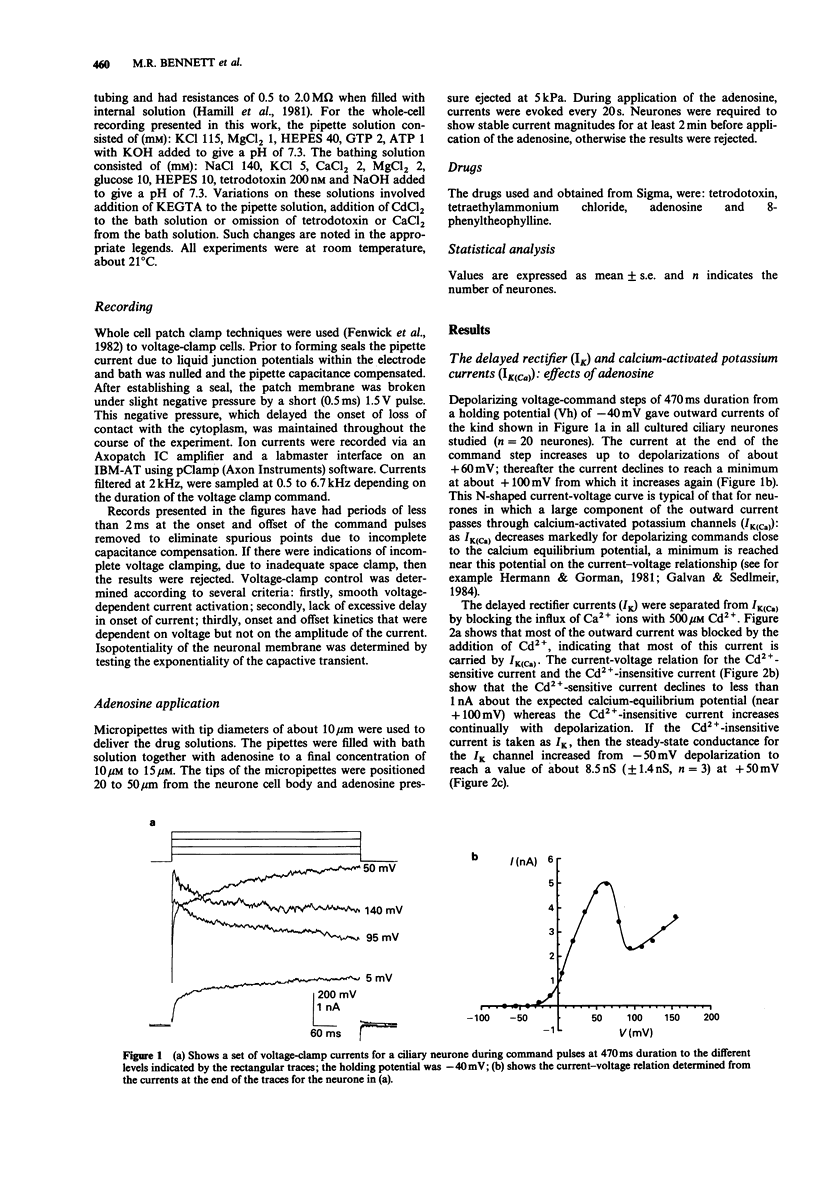
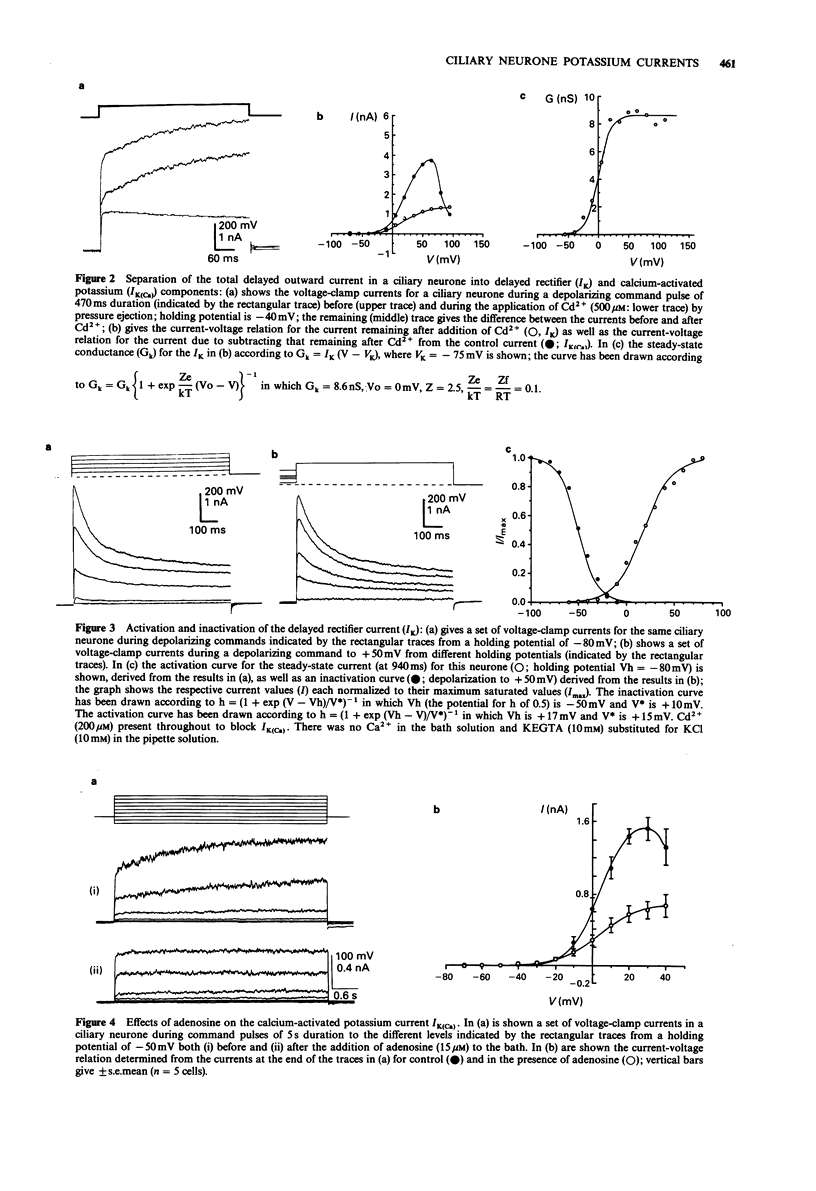
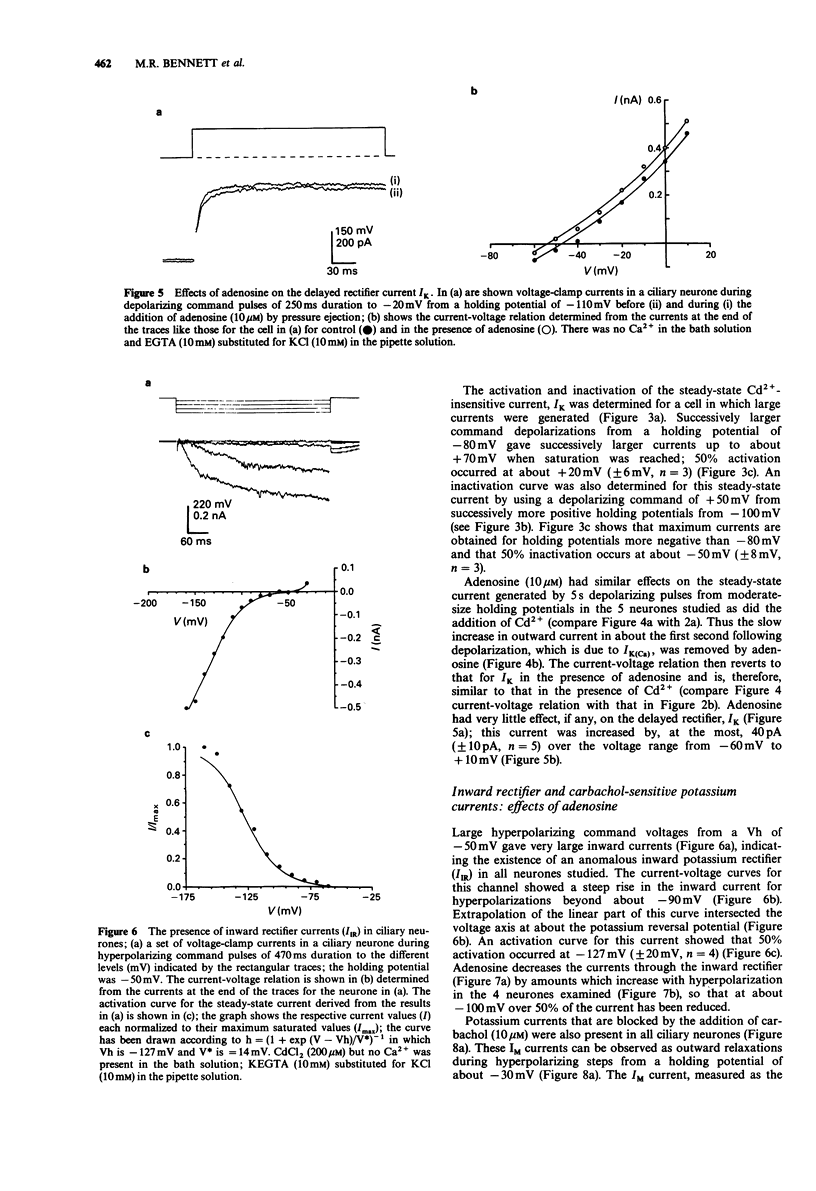
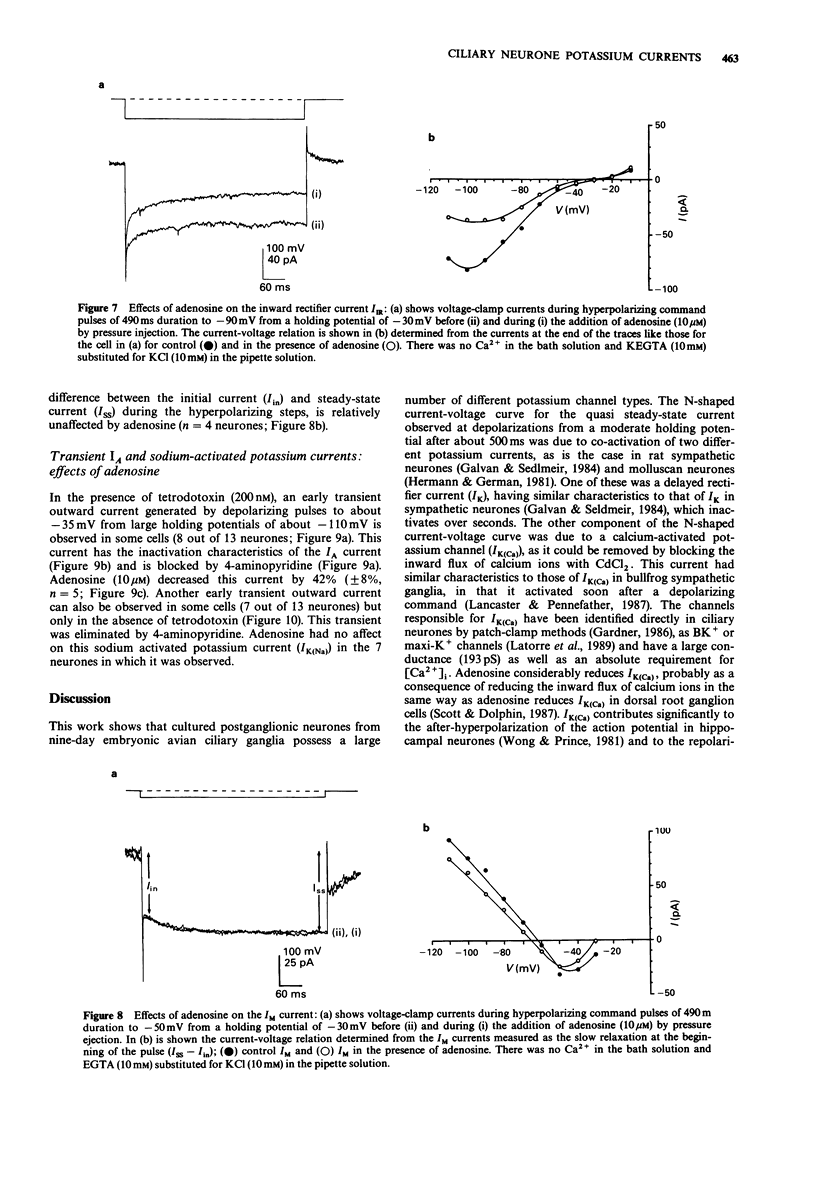
1. Potassium currents in cultured postganglionic neurones of avian ciliary ganglia were analysed under whole-cell voltage clamp and their modulation by adenosine determined. 2. In the presence of tetrodotoxin (200 nM), and with moderate holding potentials (Vh = -40 mV), the steady-state current-voltage (I/V) curve was N-shaped over the range from -70 mV to +155 mV. CsCl (1 M) blocked the current, indicating that it was carried by K+. If Ca2+ influx was blocked by CdCl2 (500 microM) then the outward current was reduced and the N-shaped I-V curve lost, indicating the presence of a calcium-activated potassium current (IK(Ca)); the remaining current, due to the delayed rectifier (IK), increased with depolarization up to about a conductance of 10 nS near + 50 mV. This IK was 50% activated at about +20 mV and 50% inactivated at about -50 mV. Adenosine (10 microM) had similar affects on the N-shaped I/V curve as did CdCl2, indicating that it blocked IK(Ca). However, adenosine had little affect on the steady-state current in the presence of CdCl, indicating that it did not much affect IK. 3. In the presence of tetrodotoxin (200 nM), a large inward current occurred for large hyperpolarizations from a Vh = -50 mV. This inward rectifying current (IIR) had a reversal potential near EK and showed 50% activation at about -130 mV. Adenosine (10 microM) reduced IIR, by as much as 50% at large hyperpolarizations beyond -80 mV.(ABSTRACT TRUNCATED AT 250 WORDS)
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adams P. R., Brown D. A., Constanti A. Pharmacological inhibition of the M-current. J Physiol. 1982 Nov;332:223–262. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1982.sp014411. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bennett M. R., Ho S. Probabilistic secretion of quanta from nerve terminals in avian ciliary ganglia modulated by adenosine. J Physiol. 1991;440:513–527. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1991.sp018722. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bennett M. R., Karunanithi S., Lavidis N. A. Probabilistic secretion of quanta from nerve terminals in toad (Bufo marinus) muscle modulated by adenosine. J Physiol. 1991 Feb;433:421–434. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1991.sp018435. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown D. A., Adams P. R., Constanti A. Voltage-sensitive K-currents in sympathetic neurons and their modulation by neurotransmitters. J Auton Nerv Syst. 1982 Jul;6(1):23–35. doi: 10.1016/0165-1838(82)90019-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cassell J. F., Clark A. L., McLachlan E. M. Characteristics of phasic and tonic sympathetic ganglion cells of the guinea-pig. J Physiol. 1986 Mar;372:457–483. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1986.sp016020. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Constanti A., Galvan M. Fast inward-rectifying current accounts for anomalous rectification in olfactory cortex neurones. J Physiol. 1983 Feb;335:153–178. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1983.sp014526. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dryer S. E., Fujii J. T., Martin A. R. A Na+-activated K+ current in cultured brain stem neurones from chicks. J Physiol. 1989 Mar;410:283–296. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1989.sp017533. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fenwick E. M., Marty A., Neher E. A patch-clamp study of bovine chromaffin cells and of their sensitivity to acetylcholine. J Physiol. 1982 Oct;331:577–597. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1982.sp014393. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galvan M., Sedlmeir C. Outward currents in voltage-clamped rat sympathetic neurones. J Physiol. 1984 Nov;356:115–133. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1984.sp015456. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gardner P. I. Single-channel recordings of three K+-selective currents in cultured chick ciliary ganglion neurons. J Neurosci. 1986 Jul;6(7):2106–2116. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.06-07-02106.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerber U., Greene R. W., Haas H. L., Stevens D. R. Characterization of inhibition mediated by adenosine in the hippocampus of the rat in vitro. J Physiol. 1989 Oct;417:567–578. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1989.sp017819. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamill O. P., Marty A., Neher E., Sakmann B., Sigworth F. J. Improved patch-clamp techniques for high-resolution current recording from cells and cell-free membrane patches. Pflugers Arch. 1981 Aug;391(2):85–100. doi: 10.1007/BF00656997. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartung K. Potentiation of a transient outward current by Na+ influx in crayfish neurones. Pflugers Arch. 1985 May;404(1):41–44. doi: 10.1007/BF00581488. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hermann A., Gorman A. L. Effects of tetraethylammonium on potassium currents in a molluscan neurons. J Gen Physiol. 1981 Jul;78(1):87–110. doi: 10.1085/jgp.78.1.87. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kurachi Y., Nakajima T., Sugimoto T. On the mechanism of activation of muscarinic K+ channels by adenosine in isolated atrial cells: involvement of GTP-binding proteins. Pflugers Arch. 1986 Sep;407(3):264–274. doi: 10.1007/BF00585301. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lancaster B., Adams P. R. Calcium-dependent current generating the afterhyperpolarization of hippocampal neurons. J Neurophysiol. 1986 Jun;55(6):1268–1282. doi: 10.1152/jn.1986.55.6.1268. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lancaster B., Pennefather P. Potassium currents evoked by brief depolarizations in bull-frog sympathetic ganglion cells. J Physiol. 1987 Jun;387:519–548. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1987.sp016587. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Latorre R., Oberhauser A., Labarca P., Alvarez O. Varieties of calcium-activated potassium channels. Annu Rev Physiol. 1989;51:385–399. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ph.51.030189.002125. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loose M. D., Kelly M. J. Opioids act at mu-receptors to hyperpolarize arcuate neurons via an inwardly rectifying potassium conductance. Brain Res. 1990 Apr 9;513(1):15–23. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(90)91084-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MARTIN A. R., PILAR G. TRANSMISSION THROUGH THE CILIARY GANGLION OF THE CHICK. J Physiol. 1963 Sep;168:464–475. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1963.sp007203. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Madison D. V., Nicoll R. A. Actions of noradrenaline recorded intracellularly in rat hippocampal CA1 pyramidal neurones, in vitro. J Physiol. 1986 Mar;372:221–244. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1986.sp016006. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phillis J. W., Wu P. H. The role of adenosine and its nucleotides in central synaptic transmission. Prog Neurobiol. 1981;16(3-4):187–239. doi: 10.1016/0301-0082(81)90014-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Segal M., Rogawski M. A., Barker J. L. A transient potassium conductance regulates the excitability of cultured hippocampal and spinal neurons. J Neurosci. 1984 Feb;4(2):604–609. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.04-02-00604.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trussell L. O., Jackson M. B. Dependence of an adenosine-activated potassium current on a GTP-binding protein in mammalian central neurons. J Neurosci. 1987 Oct;7(10):3306–3316. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.07-10-03306.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wong R. K., Prince D. A. Afterpotential generation in hippocampal pyramidal cells. J Neurophysiol. 1981 Jan;45(1):86–97. doi: 10.1152/jn.1981.45.1.86. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zbicz K. L., Weight F. F. Transient voltage and calcium-dependent outward currents in hippocampal CA3 pyramidal neurons. J Neurophysiol. 1985 Apr;53(4):1038–1058. doi: 10.1152/jn.1985.53.4.1038. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


