Abstract
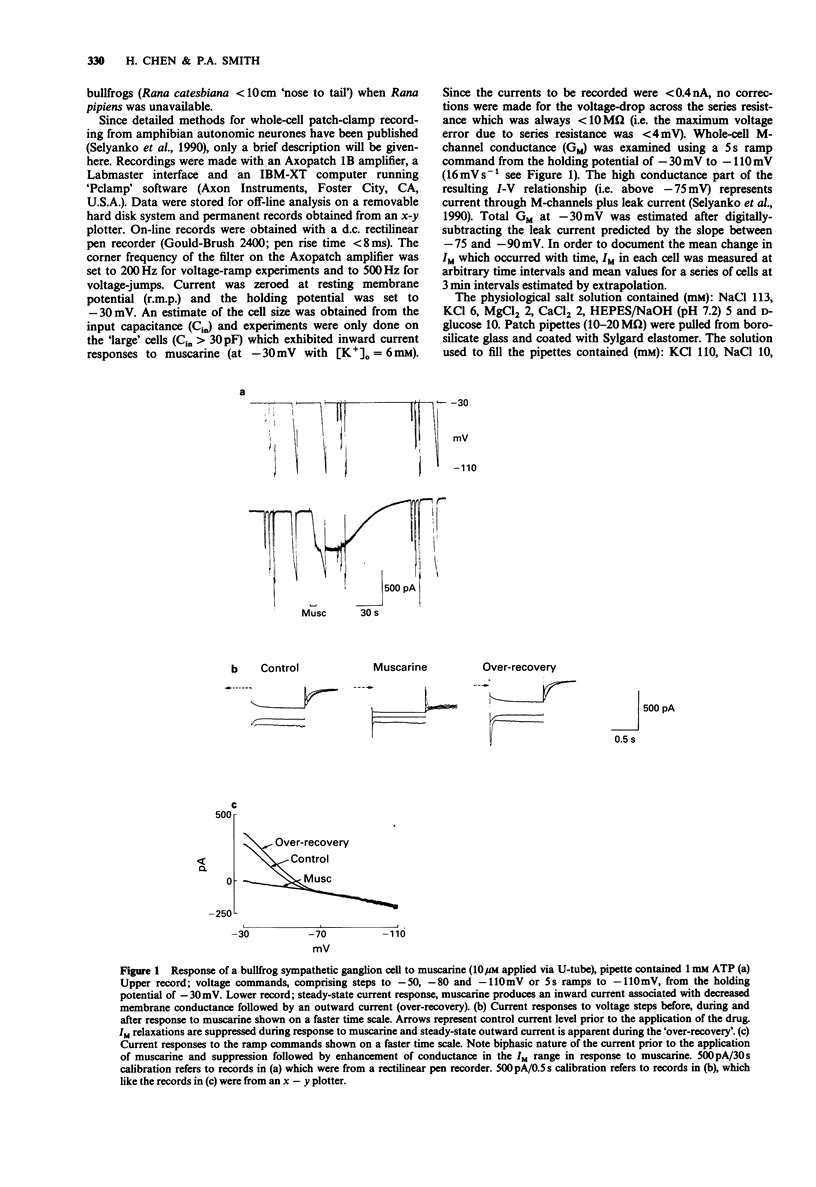
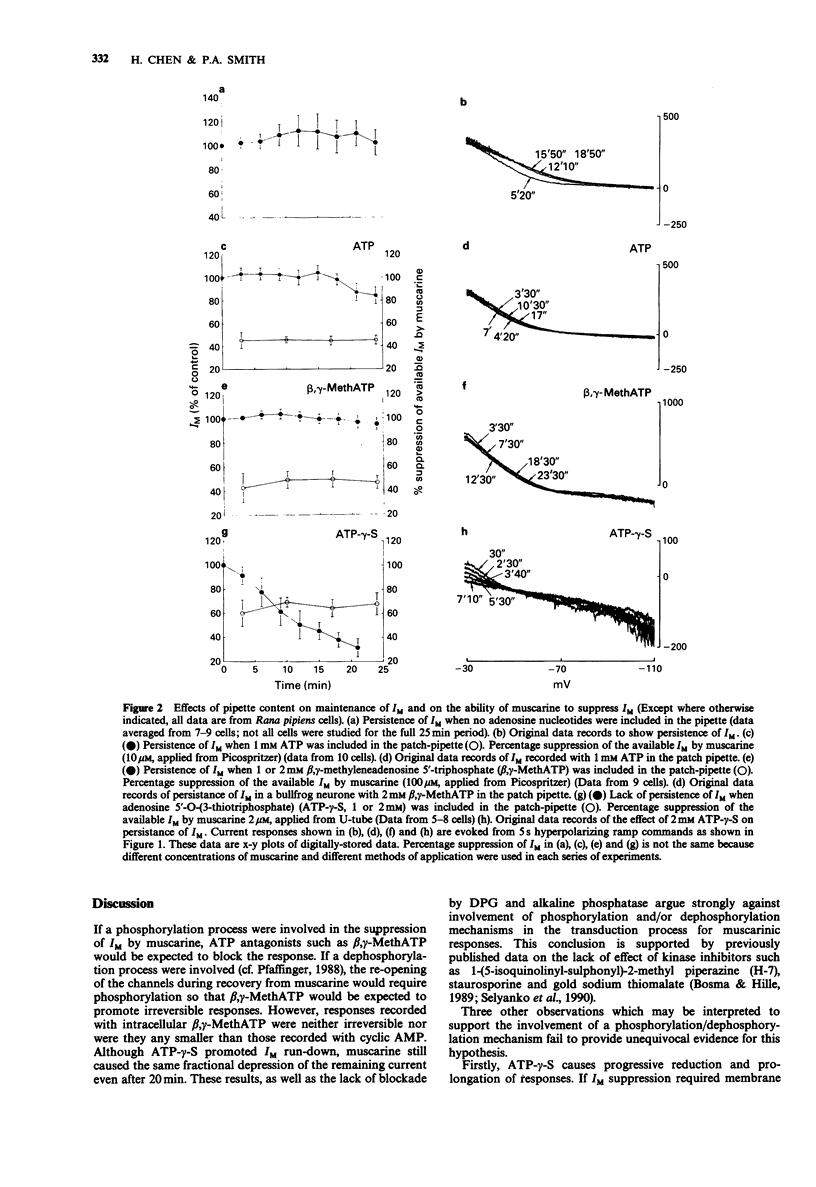
1. The inward current and the M-current (IM) suppression produced when muscarine is applied to frog sympathetic ganglion cells was recorded by means of the whole-cell patch-clamp technique. The holding potential was -30 mV and [K+]o was 6 mM. 2. The steady-state IM was maintained for at least 20 min when the patch pipette contained neither adenosine 5'-triphosphate (ATP) nor adenosine 3':5'-cyclic monophosphate (cyclic AMP). Inclusion of these substances or the ATP antagonist, beta,gamma-methyleneadenosine 5'-triphosphate (beta,gamma-MethATP; 1 or 2 nM) (failed to alter the rate of IM 'run down'. By contrast, inclusion of adenosine-5'-O-(3-thiotriphosphate) (ATP-gamma-S, 1 or 2 mM) resulted in a 60% reduction of the current within 18 min. 3. Despite the inability of ATP-gamma-S to maintain steady-state IM, it had no effect on the ability of muscarine (2-100 microM) to suppress a constant fraction of the available current. ATP-gamma-S and beta,gamma-MethATP increased the rise time and duration of the response to muscarine. 4. Inclusion of a phosphatase inhibitor, diphosphoglyceric acid (DPG, 1-2.5 mM) or alkaline phosphatase (100 micrograms ml-1) failed to affect the amplitude of muscarinic responses. 5. These results question the role of the phosphorylation and/or dephosphorylation reactions in the transduction mechanism for muscarine-induced IM suppression but are consistent with the possibility that M-channels are 'directly coupled' via G-protein to the muscarinic receptor.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adams P. R., Brown D. A., Constanti A. M-currents and other potassium currents in bullfrog sympathetic neurones. J Physiol. 1982 Sep;330:537–572. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1982.sp014357. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Adams P. R., Brown D. A., Constanti A. Pharmacological inhibition of the M-current. J Physiol. 1982 Nov;332:223–262. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1982.sp014411. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Adams P. R., Jones S. W., Pennefather P., Brown D. A., Koch C., Lancaster B. Slow synaptic transmission in frog sympathetic ganglia. J Exp Biol. 1986 Sep;124:259–285. doi: 10.1242/jeb.124.1.259. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ahmad Z., Green F. J., Subuhi H. S., Watanabe A. M. Autonomic regulation of type 1 protein phosphatase in cardiac muscle. J Biol Chem. 1989 Mar 5;264(7):3859–3863. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Akasu T., Gallagher J. P., Koketsu K., Shinnick-Gallagher P. Slow excitatory post-synaptic currents in bull-frog sympathetic neurones. J Physiol. 1984 Jun;351:583–593. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1984.sp015264. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beech D. J., Bernheim L., Mathie A., Hille B. Intracellular Ca2+ buffers disrupt muscarinic suppression of Ca2+ current and M current in rat sympathetic neurons. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Jan 15;88(2):652–656. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.2.652. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bosma M. M., Hille B. Protein kinase C is not necessary for peptide-induced suppression of M current or for desensitization of the peptide receptors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Apr;86(8):2943–2947. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.8.2943. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown D. A., Adams P. R. Effects of phorbol dibutyrate on M currents and M current inhibition in bullfrog sympathetic neurons. Cell Mol Neurobiol. 1987 Sep;7(3):255–269. doi: 10.1007/BF00711303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown D. A., Adams P. R. Muscarinic suppression of a novel voltage-sensitive K+ current in a vertebrate neurone. Nature. 1980 Feb 14;283(5748):673–676. doi: 10.1038/283673a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown D. A., Marrion N. V., Smart T. G. On the transduction mechanism for muscarine-induced inhibition of M-current in cultured rat sympathetic neurones. J Physiol. 1989 Jun;413:469–488. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1989.sp017664. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Busis N. A., Weight F. F., Smith P. A. Synaptic potentials in sympathetic ganglia: are they mediated by cyclic nucleotides? Science. 1978 Jun 2;200(4345):1079–1081. doi: 10.1126/science.206964. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DiFrancesco D., Tortora P. Direct activation of cardiac pacemaker channels by intracellular cyclic AMP. Nature. 1991 May 9;351(6322):145–147. doi: 10.1038/351145a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Downes C. P., Mussat M. C., Michell R. H. The inositol trisphosphate phosphomonoesterase of the human erythrocyte membrane. Biochem J. 1982 Apr 1;203(1):169–177. doi: 10.1042/bj2030169. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eckstein F. Nucleoside phosphorothioates. Annu Rev Biochem. 1985;54:367–402. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.54.070185.002055. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elmslie K. S., Zhou W., Jones S. W. LHRH and GTP-gamma-S modify calcium current activation in bullfrog sympathetic neurons. Neuron. 1990 Jul;5(1):75–80. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(90)90035-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gross R. A., Uhler M. D., Macdonald R. L. The reduction of neuronal calcium currents by ATP-gamma-S is mediated by a G protein and occurs independently of cyclic AMP-dependent protein kinase. Brain Res. 1990 Dec 10;535(2):214–220. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(90)91603-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hille B. The Sharpey-Schafer Lecture. Ionic channels: evolutionary origins and modern roles. Q J Exp Physiol. 1989 Nov;74(6):785–804. doi: 10.1113/expphysiol.1989.sp003349. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kirkwood A., Simmons M. A., Mather R. J., Lisman J. Muscarinic suppression of the M-current is mediated by a rise in internal Ca2+ concentration. Neuron. 1991 Jun;6(6):1009–1014. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(91)90240-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krishtal O. A., Pidoplichko V. I. A receptor for protons in the nerve cell membrane. Neuroscience. 1980;5(12):2325–2327. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(80)90149-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levitan I. B. Phosphorylation of ion channels. J Membr Biol. 1985;87(3):177–190. doi: 10.1007/BF01871217. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marrion N. V., Zucker R. S., Marsh S. J., Adams P. R. Modulation of M-current by intracellular Ca2+. Neuron. 1991 Apr;6(4):533–545. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(91)90056-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- North R. A. Twelfth Gaddum memorial lecture. Drug receptors and the inhibition of nerve cells. Br J Pharmacol. 1989 Sep;98(1):13–28. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1989.tb16855.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Otero A. S., Breitwieser G. E., Szabo G. Activation of muscarinic potassium currents by ATP gamma S in atrial cells. Science. 1988 Oct 21;242(4877):443–445. doi: 10.1126/science.3051383. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Owen D. G., Marsh S. J., Brown D. A. M-current noise and putative M-channels in cultured rat sympathetic ganglion cells. J Physiol. 1990 Dec;431:269–290. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1990.sp018330. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pfaffinger P. J., Leibowitz M. D., Subers E. M., Nathanson N. M., Almers W., Hille B. Agonists that suppress M-current elicit phosphoinositide turnover and Ca2+ transients, but these events do not explain M-current suppression. Neuron. 1988 Aug;1(6):477–484. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(88)90178-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pfaffinger P. J., Martin J. M., Hunter D. D., Nathanson N. M., Hille B. GTP-binding proteins couple cardiac muscarinic receptors to a K channel. Nature. 1985 Oct 10;317(6037):536–538. doi: 10.1038/317536a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pfaffinger P. Muscarine and t-LHRH suppress M-current by activating an IAP-insensitive G-protein. J Neurosci. 1988 Sep;8(9):3343–3353. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.08-09-03343.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Selyanko A. A., Smith P. A., Zidichouski J. A. Effects of muscarine and adrenaline on neurones from Rana pipiens sympathetic ganglia. J Physiol. 1990 Jun;425:471–500. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1990.sp018114. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simmons M. A., Becker J. B., Mather R. J. Desensitization of the inhibition of the M-current in sympathetic neurons: effects of ATP analogs, polyanions, and multiple agonist applications. Neuron. 1990 Apr;4(4):557–562. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(90)90113-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yatani A., Codina J., Imoto Y., Reeves J. P., Birnbaumer L., Brown A. M. A G protein directly regulates mammalian cardiac calcium channels. Science. 1987 Nov 27;238(4831):1288–1292. doi: 10.1126/science.2446390. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yatani A., Okabe K., Codina J., Birnbaumer L., Brown A. M. Heart rate regulation by G proteins acting on the cardiac pacemaker channel. Science. 1990 Sep 7;249(4973):1163–1166. doi: 10.1126/science.1697697. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


