Abstract
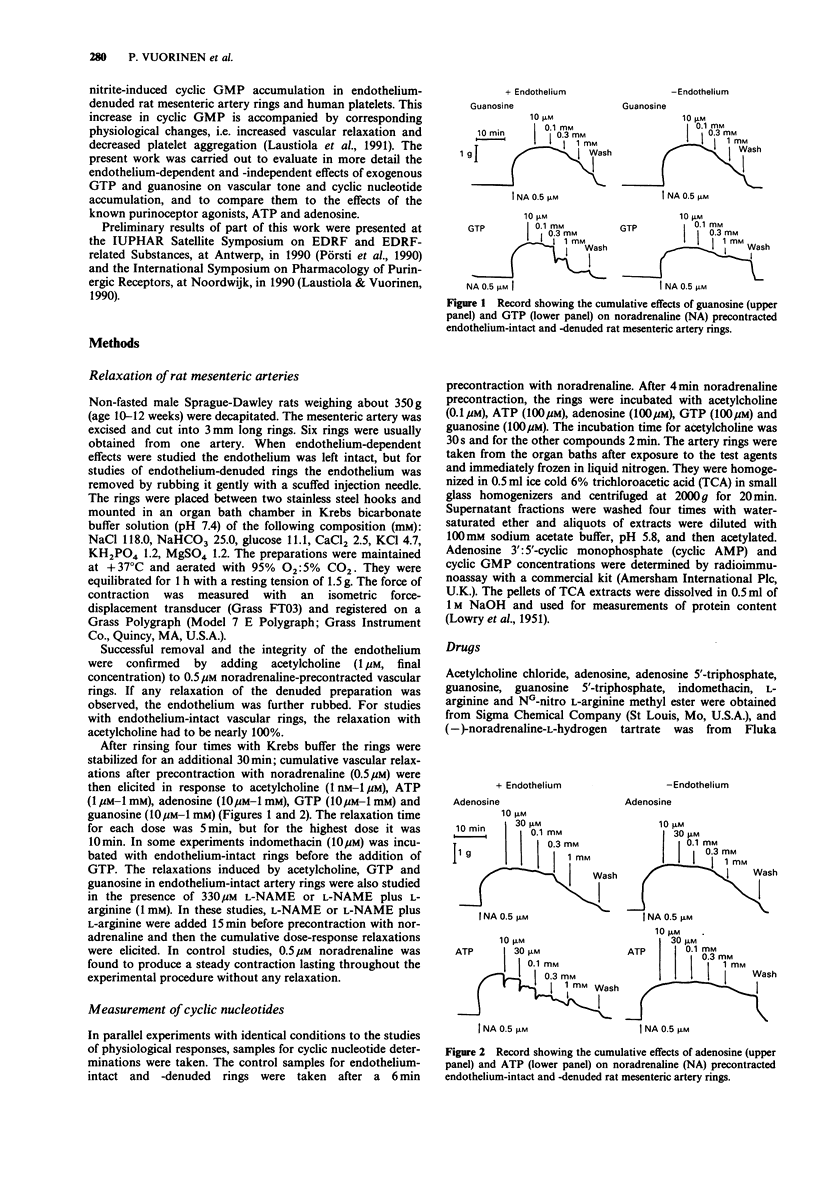
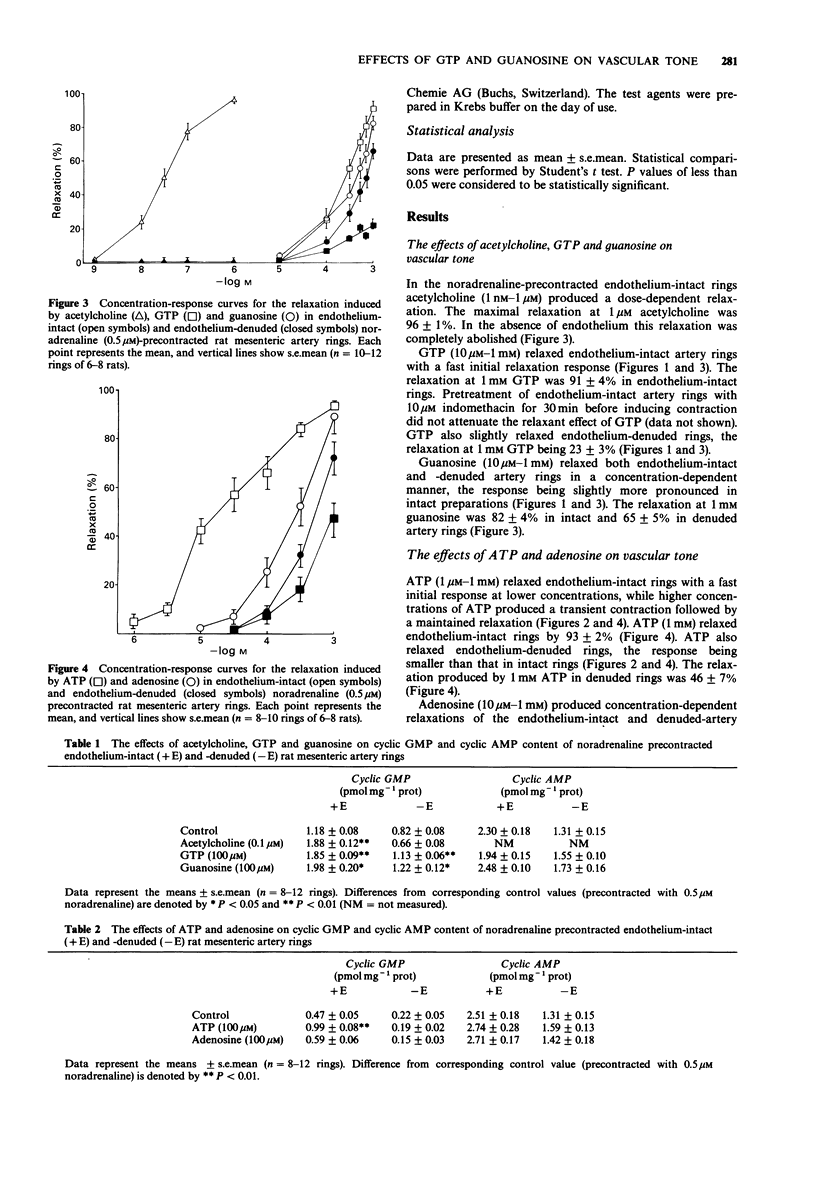
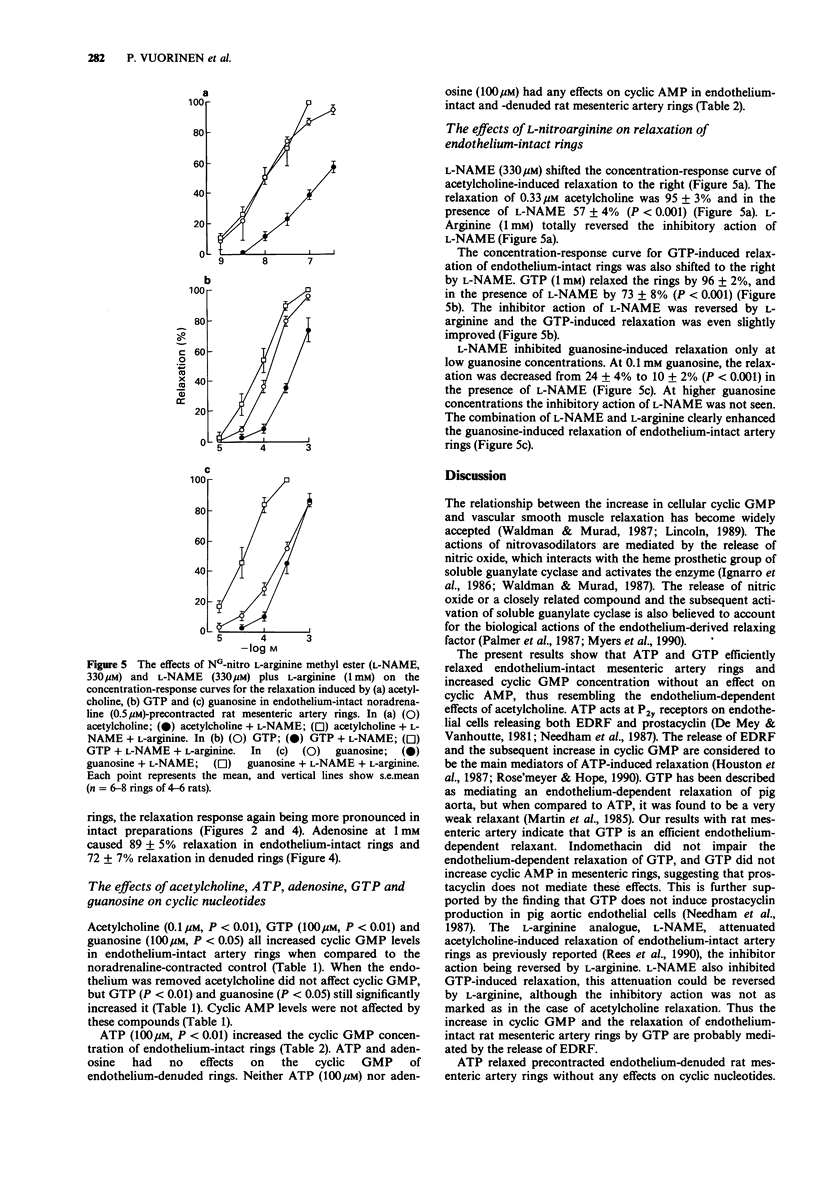
1. The effects of exogenous guanosine 5'-triphosphate (GTP) and guanosine on vascular tone and cyclic nucleotide accumulation of noradrenaline-precontracted endothelium-intact and endothelium-denuded rat mesenteric artery rings were compared with the effects of the known purinoceptor agonists adenosine 5'-triphosphate (ATP) and adenosine. 2. GTP (10 microM-1 mM) dose-dependently relaxed endothelium-intact mesenteric artery rings by producing a rapid initial response followed by sustained relaxation resembling the relaxant response to acetylcholine. GTP also slightly relaxed endothelium-denuded artery rings. The acetylcholine- and GTP-induced relaxations of endothelium-intact rings were attenuated by NG-nitro L-arginine methyl ester (L-NAME, 330 microM) which attenuation was reversed with L-arginine (1 mM). 3. Guanosine (10 microM-1 mM) relaxed both endothelium-intact and -denuded artery rings in a dose-dependent manner. The relaxations were more pronounced in endothelium-intact preparations and were only slightly attenuated by L-NAME (330 microM). 4. ATP (1 microM-1 mM) and adenosine (10 microM-1 mM) dose-dependently relaxed endothelium-intact and -denuded artery rings. The responses were more pronounced in endothelium-intact vascular preparations. 5. GTP (100 microM) and guanosine (100 microM) increased guanosine 3':5'-cyclic monophosphate (cyclic GMP) accumulation in both endothelium-intact and -denuded artery rings corresponding to the relaxations observed. The concentrations of adenosine 3':5'-cyclic monophosphate (cyclic AMP) were not affected. 6. ATP (100 microM) increased cyclic GMP concentration of endothelium-intact artery rings. The concentrations of cyclic AMP were not affected by ATP (100 microM) and adenosine (100 microM) in endothelium-intact and -denuded vascular preparations.(ABSTRACT TRUNCATED AT 250 WORDS)
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Boeynaems J. M., Pearson J. D. P2 purinoceptors on vascular endothelial cells: physiological significance and transduction mechanisms. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 1990 Jan;11(1):34–37. doi: 10.1016/0165-6147(90)90039-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burnstock G., Kennedy C. Is there a basis for distinguishing two types of P2-purinoceptor? Gen Pharmacol. 1985;16(5):433–440. doi: 10.1016/0306-3623(85)90001-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coade S. B., Pearson J. D. Metabolism of adenine nucleotides in human blood. Circ Res. 1989 Sep;65(3):531–537. doi: 10.1161/01.res.65.3.531. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collis M. G., Brown C. M. Adenosine relaxes the aorta by interacting with an A2 receptor and an intracellular site. Eur J Pharmacol. 1983 Dec 9;96(1-2):61–69. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(83)90529-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Mey J. G., Vanhoutte P. M. Role of the intima in cholinergic and purinergic relaxation of isolated canine femoral arteries. J Physiol. 1981 Jul;316:347–355. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1981.sp013792. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Furchgott R. F. The role of endothelium in the responses of vascular smooth muscle to drugs. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol. 1984;24:175–197. doi: 10.1146/annurev.pa.24.040184.001135. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Furchgott R. F., Zawadzki J. V. The obligatory role of endothelial cells in the relaxation of arterial smooth muscle by acetylcholine. Nature. 1980 Nov 27;288(5789):373–376. doi: 10.1038/288373a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gaw A. J., Aberdeen J., Humphrey P. P., Wadsworth R. M., Burnstock G. Relaxation of sheep cerebral arteries by vasoactive intestinal polypeptide and neurogenic stimulation: inhibition by L-NG-monomethyl arginine in endothelium-denuded vessels. Br J Pharmacol. 1991 Mar;102(3):567–572. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1991.tb12213.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geisbuhler T. P., Johnson D. A., Rovetto M. J. Cardiac myocyte guanosine transport and metabolism. Am J Physiol. 1987 Nov;253(5 Pt 1):C645–C651. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1987.253.5.C645. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gordon J. L. Extracellular ATP: effects, sources and fate. Biochem J. 1986 Jan 15;233(2):309–319. doi: 10.1042/bj2330309. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gordon J. L., Martin W. Endothelium-dependent relaxation of the pig aorta: relationship to stimulation of 86Rb efflux from isolated endothelial cells. Br J Pharmacol. 1983 Jun;79(2):531–541. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1983.tb11028.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Houston D. A., Burnstock G., Vanhoutte P. M. Different P2-purinergic receptor subtypes of endothelium and smooth muscle in canine blood vessels. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1987 May;241(2):501–506. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ignarro L. J., Adams J. B., Horwitz P. M., Wood K. S. Activation of soluble guanylate cyclase by NO-hemoproteins involves NO-heme exchange. Comparison of heme-containing and heme-deficient enzyme forms. J Biol Chem. 1986 Apr 15;261(11):4997–5002. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ignarro L. J. Endothelium-derived nitric oxide: actions and properties. FASEB J. 1989 Jan;3(1):31–36. doi: 10.1096/fasebj.3.1.2642868. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Janssens P. M., De Jong C. C., Vink A. A., Van Haastert P. J. Regulatory properties of magnesium-dependent guanylate cyclase in Dictyostelium discoideum membranes. J Biol Chem. 1989 Mar 15;264(8):4329–4335. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kennedy C., Delbro D., Burnstock G. P2-purinoceptors mediate both vasodilation (via the endothelium) and vasoconstriction of the isolated rat femoral artery. Eur J Pharmacol. 1985 Jan 2;107(2):161–168. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(85)90055-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krishnamurthi S., Patel Y., Kakkar V. V. Inhibition of agonist-induced platelet aggregation, Ca2+ mobilization and granule secretion by guanosine 5'-[beta-thio]diphosphate and GDP in intact platelets. Evidence for an inhibitory mechanism unrelated to the inhibition of G-protein-GTP interaction. Biochem J. 1988 Feb 15;250(1):209–214. doi: 10.1042/bj2500209. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kurose H., Ui M. Dual pathways of receptor-mediated cyclic GMP generation in NG108-15 cells as differentiated by susceptibility to islet-activating protein, pertussis toxin. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1985 May 1;238(2):424–434. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(85)90183-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kurtz A. Adenosine stimulates guanylate cyclase activity in vascular smooth muscle cells. J Biol Chem. 1987 May 5;262(13):6296–6300. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laustiola K. E., Vuorinen P., Pörsti I., Metsä-Ketelä T., Manninen V., Vapaatalo H. Exogenous GTP enhances the effects of sodium nitrite on cyclic GMP accumulation, vascular smooth muscle relaxation and platelet aggregation. Pharmacol Toxicol. 1991 Jan;68(1):60–63. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0773.1991.tb01209.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lincoln T. M. Cyclic GMP and mechanisms of vasodilation. Pharmacol Ther. 1989;41(3):479–502. doi: 10.1016/0163-7258(89)90127-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin W., Cusack N. J., Carleton J. S., Gordon J. L. Specificity of P2-purinoceptor that mediates endothelium-dependent relaxation of the pig aorta. Eur J Pharmacol. 1985 Feb 5;108(3):295–299. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(85)90452-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moncada S., Palmer R. M., Higgs E. A. Biosynthesis of nitric oxide from L-arginine. A pathway for the regulation of cell function and communication. Biochem Pharmacol. 1989 Jun 1;38(11):1709–1715. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(89)90403-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moritoki H., Matsugi T., Takase H., Ueda H., Tanioka A. Evidence for the involvement of cyclic GMP in adenosine-induced, age-dependent vasodilatation. Br J Pharmacol. 1990 Jul;100(3):569–575. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1990.tb15848.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Myers P. R., Minor R. L., Jr, Guerra R., Jr, Bates J. N., Harrison D. G. Vasorelaxant properties of the endothelium-derived relaxing factor more closely resemble S-nitrosocysteine than nitric oxide. Nature. 1990 May 10;345(6271):161–163. doi: 10.1038/345161a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Needham L., Cusack N. J., Pearson J. D., Gordon J. L. Characteristics of the P2 purinoceptor that mediates prostacyclin production by pig aortic endothelial cells. Eur J Pharmacol. 1987 Feb 10;134(2):199–209. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(87)90166-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olsson R. A., Pearson J. D. Cardiovascular purinoceptors. Physiol Rev. 1990 Jul;70(3):761–845. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1990.70.3.761. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palmer R. M., Ashton D. S., Moncada S. Vascular endothelial cells synthesize nitric oxide from L-arginine. Nature. 1988 Jun 16;333(6174):664–666. doi: 10.1038/333664a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palmer R. M., Ferrige A. G., Moncada S. Nitric oxide release accounts for the biological activity of endothelium-derived relaxing factor. Nature. 1987 Jun 11;327(6122):524–526. doi: 10.1038/327524a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pearson J. D., Gordon J. L. Nucleotide metabolism by endothelium. Annu Rev Physiol. 1985;47:617–627. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ph.47.030185.003153. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pearson J. D. Purine nucleotides as regulators of vessel tone. Biochem Soc Trans. 1988 Aug;16(4):480–482. doi: 10.1042/bst0160480. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ramagopal M. V., Chitwood R. W., Jr, Mustafa S. J. Evidence for an A2 adenosine receptor in human coronary arteries. Eur J Pharmacol. 1988 Jul 14;151(3):483–486. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(88)90548-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rapoport R. M., Murad F. Endothelium-dependent and nitrovasodilator-induced relaxation of vascular smooth muscle: role of cyclic GMP. J Cyclic Nucleotide Protein Phosphor Res. 1983;9(4-5):281–296. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rees D. D., Palmer R. M., Schulz R., Hodson H. F., Moncada S. Characterization of three inhibitors of endothelial nitric oxide synthase in vitro and in vivo. Br J Pharmacol. 1990 Nov;101(3):746–752. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1990.tb14151.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rose'Meyer R. B., Hope W. Evidence that A2 purinoceptors are involved in endothelium-dependent relaxation of the rat thoracic aorta. Br J Pharmacol. 1990 Jul;100(3):576–580. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1990.tb15849.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rubanyi G., Vanhoutte P. M. Endothelium-removal decreases relaxations of canine coronary arteries caused by beta-adrenergic agonists and adenosine. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol. 1985 Jan-Feb;7(1):139–144. doi: 10.1097/00005344-198501000-00023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schini V. B., Junquero D. C., Scott-Burden T., Vanhoutte P. M. Interleukin-1 beta induces the production of an L-arginine-derived relaxing factor from cultured smooth muscle cells from rat aorta. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1991 Apr 15;176(1):114–121. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(91)90897-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tremblay J., Gerzer R., Hamet P. Cyclic GMP in cell function. Adv Second Messenger Phosphoprotein Res. 1988;22:319–383. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waldman S. A., Murad F. Cyclic GMP synthesis and function. Pharmacol Rev. 1987 Sep;39(3):163–196. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Welford L. A., Cusack N. J., Hourani S. M. The structure-activity relationships of ectonucleotidases and of excitatory P2-purinoceptors: evidence that dephosphorylation of ATP analogues reduces pharmacological potency. Eur J Pharmacol. 1987 Sep 2;141(1):123–130. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(87)90418-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White T. D., Angus J. A. Relaxant effects of ATP and adenosine on canine large and small coronary arteries in vitro. Eur J Pharmacol. 1987 Nov 3;143(1):119–126. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(87)90741-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


