Abstract
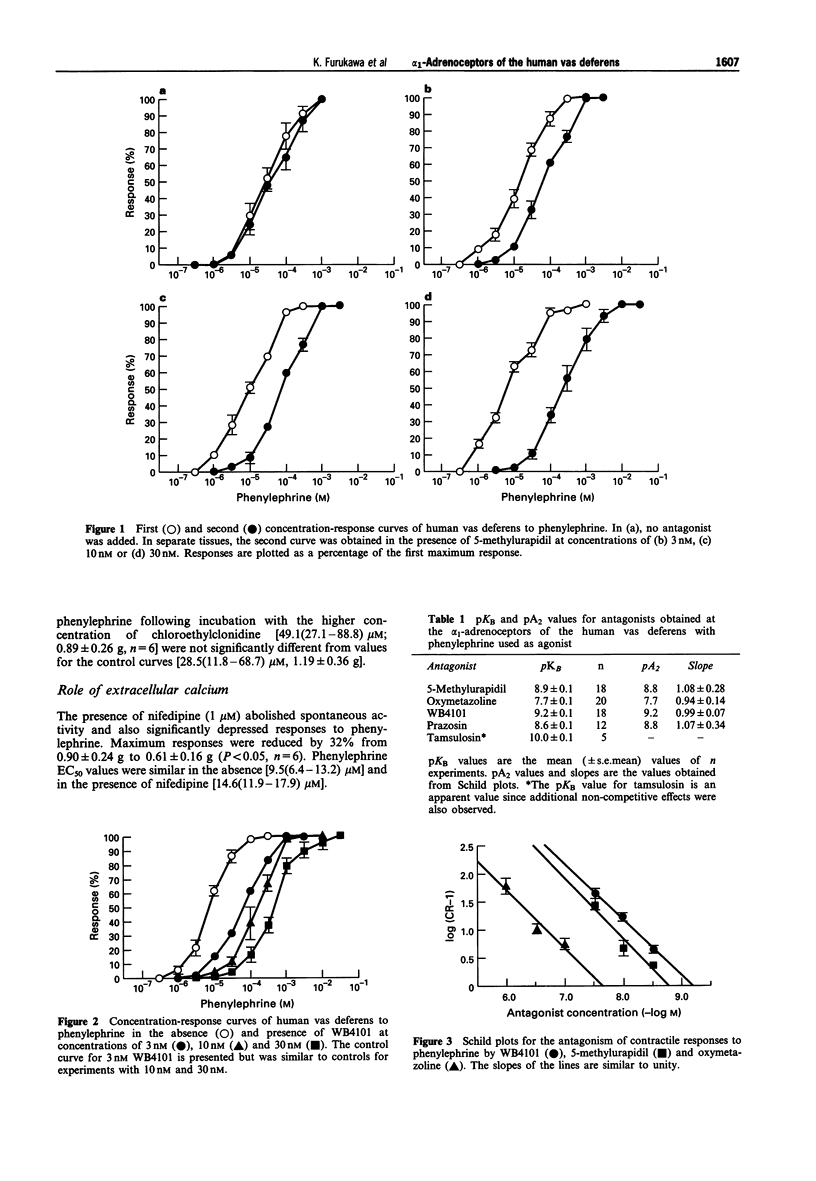
1. The predominant alpha 1-adrenoceptor mediating contractions of the human vas deferens has been characterised in vitro by use of subtype selective antagonists. 2. Responses of human epididymal vas deferens were obtained to phenylephrine in the presence of amine uptake inhibitors and propranolol. The effects of the alpha 1-adrenoceptor antagonists, 5-methylurapidil, oxymetazoline, WB4101, prazosin and chloroethylclonidine were examined and also the L-type calcium channel blocker, nifedipine. 3. 5-Methylurapidil, WB4101, oxymetazoline and prazosin acted as competitive antagonists of the responses to phenylephrine, yielding pA2 values of 8.8, 9.2, 7.7 and 8.8 respectively. All four antagonists produced Schild plots with slopes similar to unity and maximum responses to phenylephrine were not altered in the presence of any of the antagonists. 4. Tamsulosin (1 nM) caused rightward shifts of phenylephrine concentration-response curves yielding an apparent pKB value of 10.0. However, maximum responses were also reduced by 51% with this concentration of antagonist. 5. Incubation of tissues with chloroethylclonidine (100 microM for 40 min) failed to alter responses significantly but the presence of nifedipine (1 microM) reduced maximum responses to phenylephrine by 32%. 6. The high affinity of 5-methylurapidil, oxymetazoline and WB4101, together with the failure of chloroethylclonidine to antagonize responses, indicate that the predominant alpha 1-adrenoceptor mediating contraction of the human vas deferens has the characteristics previously described for the pharmacologically-defined alpha 1A-adrenoceptor. The data are also consistent with those described for the cloned alpha 1c-adrenoceptor subtype thereby supporting the hypothesis that the two receptors are identical. The human vas deferens therefore represents a readily accessible preparation for functional studies of the human alpha 1A-adrenoceptor.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ARUNLAKSHANA O., SCHILD H. O. Some quantitative uses of drug antagonists. Br J Pharmacol Chemother. 1959 Mar;14(1):48–58. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1959.tb00928.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birmingham A. T. The human isolated vas deferens: its response to electrical stimulation and to drugs. Br J Pharmacol. 1968 Nov;34(3):692P–693P. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boer R., Grassegger A., Schudt C., Glossmann H. (+)-Niguldipine binds with very high affinity to Ca2+ channels and to a subtype of alpha 1-adrenoceptors. Eur J Pharmacol. 1989 May 11;172(2):131–145. doi: 10.1016/0922-4106(89)90004-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chapple C. R., Burt R. P., Andersson P. O., Greengrass P., Wyllie M., Marshall I. Alpha 1-adrenoceptor subtypes in the human prostate. Br J Urol. 1994 Nov;74(5):585–589. doi: 10.1111/j.1464-410x.1994.tb09188.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cotecchia S., Schwinn D. A., Randall R. R., Lefkowitz R. J., Caron M. G., Kobilka B. K. Molecular cloning and expression of the cDNA for the hamster alpha 1-adrenergic receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Oct;85(19):7159–7163. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.19.7159. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Couldwell C., Jackson A., O'Brien H., Chess-Williams R. Characterization of the alpha 1-adrenoceptors of the rat prostate gland. J Pharm Pharmacol. 1993 Oct;45(10):922–924. doi: 10.1111/j.2042-7158.1993.tb05623.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Faure C., Pimoule C., Arbilla S., Langer S. Z., Graham D. Expression of alpha 1-adrenoceptor subtypes in rat tissues: implications for alpha 1-adrenoceptor classification. Eur J Pharmacol. 1994 Jul 15;268(2):141–149. doi: 10.1016/0922-4106(94)90183-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Figini M., Javdan P., Cioncolini F., Geppetti P. Involvement of tachykinins in plasma extravasation induced by bradykinin and low pH medium in the guinea-pig conjunctiva. Br J Pharmacol. 1995 May;115(1):128–132. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1995.tb16329.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ford A. P., Williams T. J., Blue D. R., Clarke D. E. Alpha 1-adrenoceptor classification: sharpening Occam's razor. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 1994 Jun;15(6):167–170. doi: 10.1016/0165-6147(94)90136-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Han C., Abel P. W., Minneman K. P. Alpha 1-adrenoceptor subtypes linked to different mechanisms for increasing intracellular Ca2+ in smooth muscle. Nature. 1987 Sep 24;329(6137):333–335. doi: 10.1038/329333a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Han C., Abel P. W., Minneman K. P. Heterogeneity of alpha 1-adrenergic receptors revealed by chlorethylclonidine. Mol Pharmacol. 1987 Oct;32(4):505–510. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanft G., Gross G. Subclassification of alpha 1-adrenoceptor recognition sites by urapidil derivatives and other selective antagonists. Br J Pharmacol. 1989 Jul;97(3):691–700. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1989.tb12005.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holmquist F., Hedlund H., Andersson K. E. Effects of the alpha 1-adrenoceptor antagonist R-(-)-YM12617 on isolated human penile erectile tissue and vas deferens. Eur J Pharmacol. 1990 Sep 4;186(1):87–93. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(90)94063-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lepor H., Tang R., Shapiro E. The alpha-adrenoceptor subtype mediating the tension of human prostatic smooth muscle. Prostate. 1993;22(4):301–307. doi: 10.1002/pros.2990220404. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li D. Y., Varma D. R., Chemtob S. Ontogenic increase in PGE2 and PGF2 alpha receptor density in brain microvessels of pigs. Br J Pharmacol. 1994 May;112(1):59–64. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1994.tb13029.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michel M. C., Hanft G., Gross G. Radioligand binding studies of alpha 1-adrenoceptor subtypes in rat heart. Br J Pharmacol. 1994 Feb;111(2):533–538. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1994.tb14770.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Minneman K. P. Alpha 1-adrenergic receptor subtypes, inositol phosphates, and sources of cell Ca2+. Pharmacol Rev. 1988 Jun;40(2):87–119. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Minneman K. P., Han C., Abel P. W. Comparison of alpha 1-adrenergic receptor subtypes distinguished by chlorethylclonidine and WB 4101. Mol Pharmacol. 1988 May;33(5):509–514. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morrow A. L., Creese I. Characterization of alpha 1-adrenergic receptor subtypes in rat brain: a reevaluation of [3H]WB4104 and [3H]prazosin binding. Mol Pharmacol. 1986 Apr;29(4):321–330. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perez D. M., Piascik M. T., Graham R. M. Solution-phase library screening for the identification of rare clones: isolation of an alpha 1D-adrenergic receptor cDNA. Mol Pharmacol. 1991 Dec;40(6):876–883. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Price D. T., Schwinn D. A., Lomasney J. W., Allen L. F., Caron M. G., Lefkowitz R. J. Identification, quantification, and localization of mRNA for three distinct alpha 1 adrenergic receptor subtypes in human prostate. J Urol. 1993 Aug;150(2 Pt 1):546–551. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5347(17)35544-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rokosh D. G., Bailey B. A., Stewart A. F., Karns L. R., Long C. S., Simpson P. C. Distribution of alpha 1C-adrenergic receptor mRNA in adult rat tissues by RNase protection assay and comparison with alpha 1B and alpha 1D. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1994 May 16;200(3):1177–1184. doi: 10.1006/bbrc.1994.1575. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwinn D. A., Lomasney J. W., Lorenz W., Szklut P. J., Fremeau R. T., Jr, Yang-Feng T. L., Caron M. G., Lefkowitz R. J., Cotecchia S. Molecular cloning and expression of the cDNA for a novel alpha 1-adrenergic receptor subtype. J Biol Chem. 1990 May 15;265(14):8183–8189. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Testa R., Guarneri L., Ibba M., Strada G., Poggesi E., Taddei C., Simonazzi I., Leonardi A. Characterization of alpha 1-adrenoceptor subtypes in prostate and prostatic urethra of rat, rabbit, dog and man. Eur J Pharmacol. 1993 Nov 16;249(3):307–315. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(93)90527-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


