Abstract
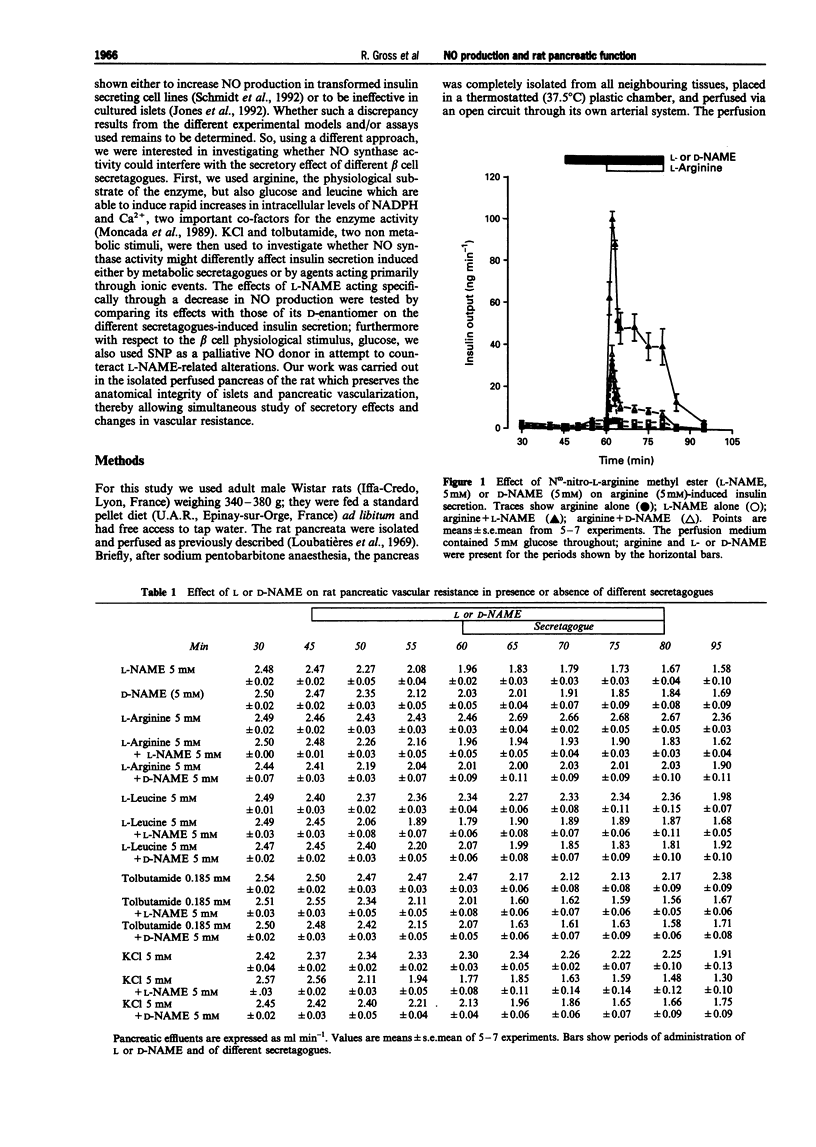
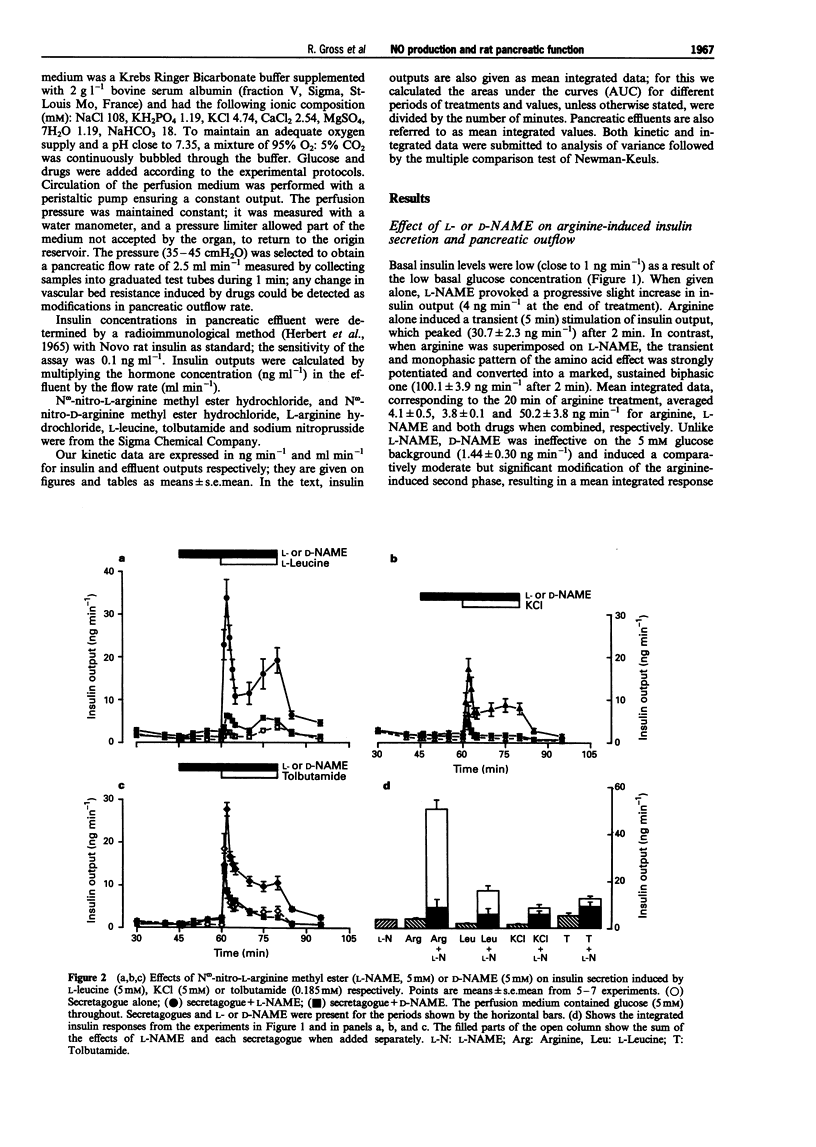
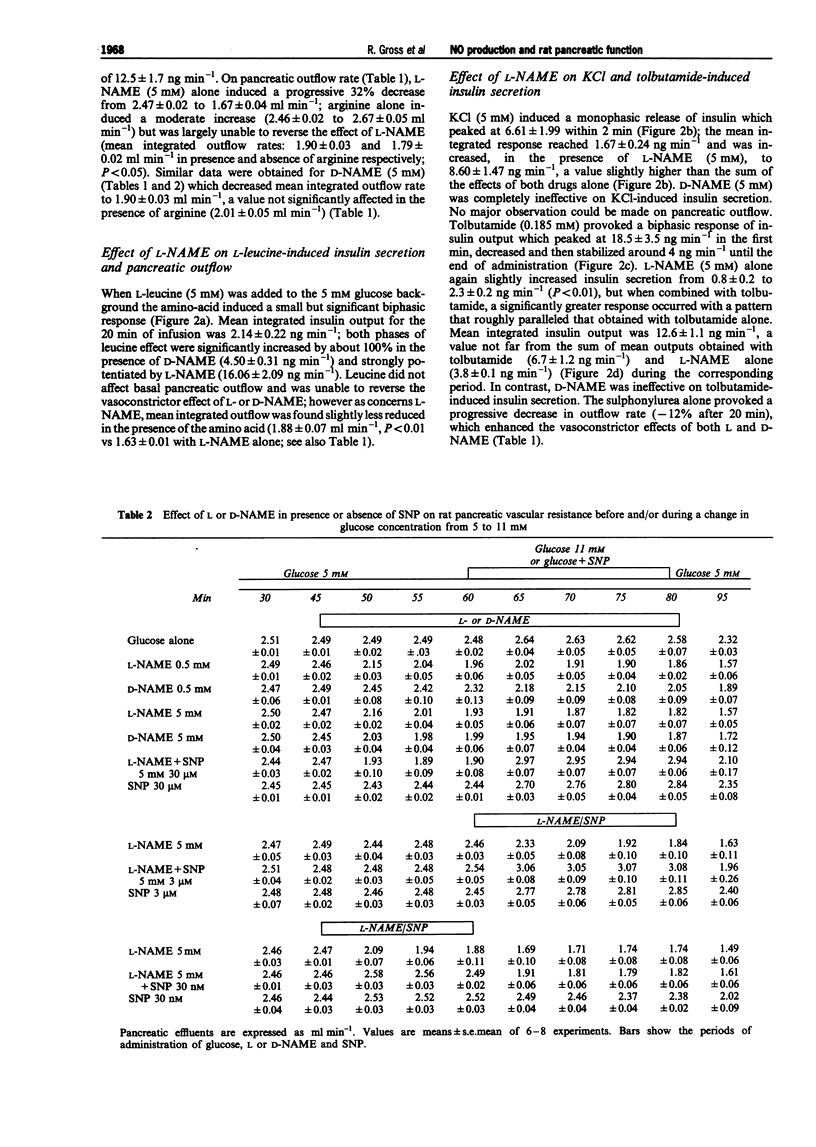
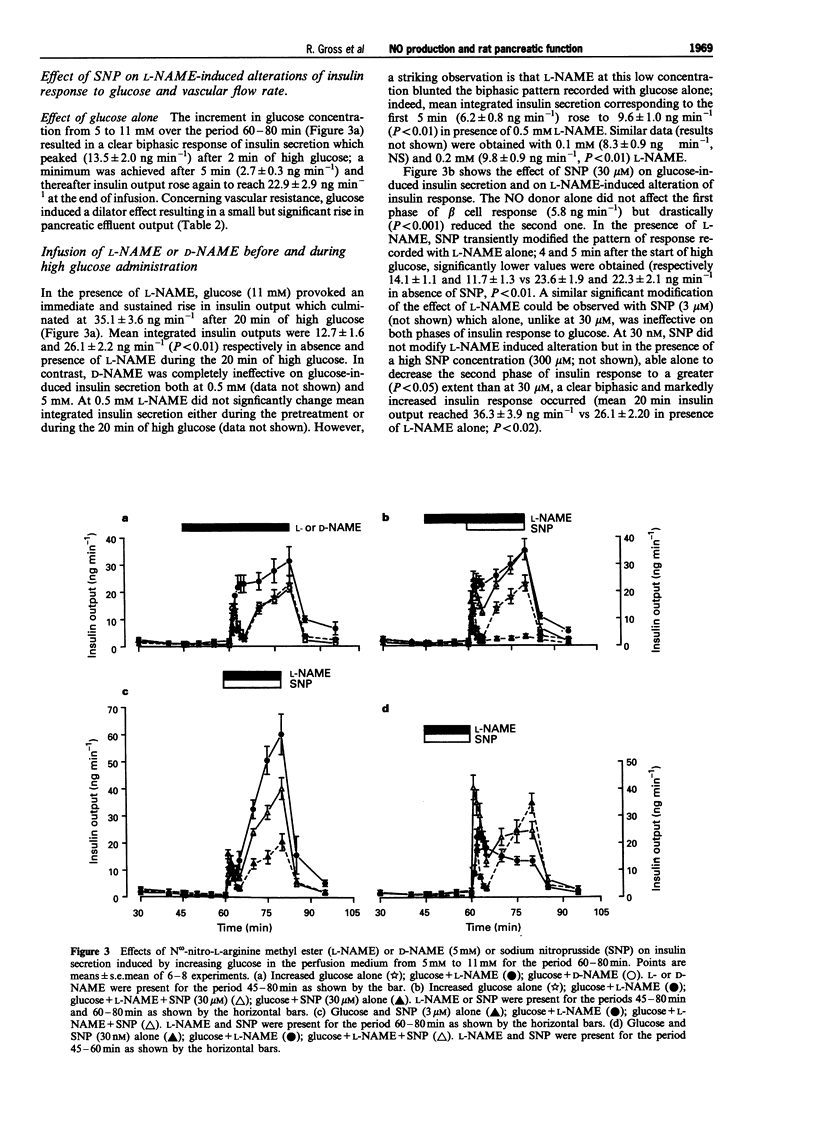
1. We studied a possible interplay of pancreatic NO synthase activity on insulin secretion induced by different beta cell secretagogues and also on pancreatic vascular bed resistance. 2. This study was performed in the isolated perfused pancreas of the rat. Blockage of NO synthase was achieved with Nw-nitro-L-arginine methyl ester (L-NAME); The specificity of the antagonist was checked by using its D-enantiomer as well as by substitutive treatments with sodium nitroprusside (SNP) as a NO donor in studies of glucose-induced insulin secretion. 3. Arginine (5 mM) induced a monophasic response which was, in the presence of L-NAME at equimolar concentration, very strongly potentiated and converted into a 13 times higher biphasic one. D-NAME (5 mM) was only able to induce a 3 times higher response, but provoked a similar vasoconstrictor effect. 4. The small biphasic insulin secretion induced by L-leucine (5 mM) was also strongly enhanced, by 8 times, in the presence of L-NAME (5 mM) vs 2 times in the presence of D-NAME (5 mM). 5. beta cell responses to KCl (5 mM) and tolbutamide (0.185 mM) were only slight increased by L-NAME (5 mM) to values not far from the sum of the effects of L-NAME and of the two drugs alone. D-NAME (5 mM) was totally ineffective on the actions of both secretagogues. 6. L-NAME, infused 15 min before and during a rise in glucose concentration from 5 to 11 mM, was able in the low millimolar range (0.1-0.5 mM) to blunt the classical biphasic pattern of beta cell response to glucose and, at 5 mM, to convert it into a significantly greater monophasic one. In contrast, D-NAME (5 mM) was unable to induce similar effects. 7. SNP alone at 3 microM was ineffective but at 30 microM substantially reduced to second phase of insulin response to glucose; however, at both concentrations the NO donor partly reversed alterations in insulin secretion caused by L-NAME (5 mM) and restored a biphasic response.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bogle R. G., Moncada S., Pearson J. D., Mann G. E. Identification of inhibitors of nitric oxide synthase that do not interact with the endothelial cell L-arginine transporter. Br J Pharmacol. 1992 Apr;105(4):768–770. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1992.tb09053.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bult H., Boeckxstaens G. E., Pelckmans P. A., Jordaens F. H., Van Maercke Y. M., Herman A. G. Nitric oxide as an inhibitory non-adrenergic non-cholinergic neurotransmitter. Nature. 1990 May 24;345(6273):346–347. doi: 10.1038/345346a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corbett J. A., Sweetland M. A., Wang J. L., Lancaster J. R., Jr, McDaniel M. L. Nitric oxide mediates cytokine-induced inhibition of insulin secretion by human islets of Langerhans. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Mar 1;90(5):1731–1735. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.5.1731. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eizirik D. L., Leijerstam F. The inducible form of nitric oxide synthase (iNOS) in insulin-producing cells. Diabete Metab. 1994 Mar-Apr;20(2):116–122. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gepts W. Pathologic anatomy of the pancreas in juvenile diabetes mellitus. Diabetes. 1965 Oct;14(10):619–633. doi: 10.2337/diab.14.10.619. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herbert V., Lau K. S., Gottlieb C. W., Bleicher S. J. Coated charcoal immunoassay of insulin. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1965 Oct;25(10):1375–1384. doi: 10.1210/jcem-25-10-1375. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hibbs J. B., Jr, Taintor R. R., Vavrin Z., Rachlin E. M. Nitric oxide: a cytotoxic activated macrophage effector molecule. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1988 Nov 30;157(1):87–94. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(88)80015-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jansson L., Sandler S. The nitric oxide synthase II inhibitor NG-nitro-L-arginine stimulates pancreatic islet insulin release in vitro, but not in the perfused pancreas. Endocrinology. 1991 Jun;128(6):3081–3085. doi: 10.1210/endo-128-6-3081. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones P. M., Persaud S. J., Bjaaland T., Pearson J. D., Howell S. L. Nitric oxide is not involved in the initiation of insulin secretion from rat islets of Langerhans. Diabetologia. 1992 Nov;35(11):1020–1027. doi: 10.1007/BF02221676. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klatt P., Schmidt K., Brunner F., Mayer B. Inhibitors of brain nitric oxide synthase. Binding kinetics, metabolism, and enzyme inactivation. J Biol Chem. 1994 Jan 21;269(3):1674–1680. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knowles R. G., Moncada S. Nitric oxide synthases in mammals. Biochem J. 1994 Mar 1;298(Pt 2):249–258. doi: 10.1042/bj2980249. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knowles R. G., Palacios M., Palmer R. M., Moncada S. Kinetic characteristics of nitric oxide synthase from rat brain. Biochem J. 1990 Jul 1;269(1):207–210. doi: 10.1042/bj2690207. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lancaster J. R., Jr, Hibbs J. B., Jr EPR demonstration of iron-nitrosyl complex formation by cytotoxic activated macrophages. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Feb;87(3):1223–1227. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.3.1223. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laychock S. G., Modica M. E., Cavanaugh C. T. L-arginine stimulates cyclic guanosine 3',5'-monophosphate formation in rat islets of Langerhans and RINm5F insulinoma cells: evidence for L-arginine:nitric oxide synthase. Endocrinology. 1991 Dec;129(6):3043–3052. doi: 10.1210/endo-129-6-3043. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lenzen S., Brand F. H., Panten U. Structural requirements of alloxan and ninhydrin for glucokinase inhibition and of glucose for protection against inhibition. Br J Pharmacol. 1988 Nov;95(3):851–859. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1988.tb11714.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loubatières A., Mariani M. M., Ribes G., de Malbosc H., Chapal J. Etude expérimentale d'un nouveau sulfamide hypoglycémiant particulièrement actif, le HB 419 ou glibenclamide. Diabetologia. 1969 Feb;5(1):1–10. doi: 10.1007/BF01212212. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marletta M. A., Yoon P. S., Iyengar R., Leaf C. D., Wishnok J. S. Macrophage oxidation of L-arginine to nitrite and nitrate: nitric oxide is an intermediate. Biochemistry. 1988 Nov 29;27(24):8706–8711. doi: 10.1021/bi00424a003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Milner R. D., Hales C. N. The role of calcium and magnesium in insulin secretion from rabbit pancreas studied in vitro. Diabetologia. 1967 Mar;3(1):47–49. doi: 10.1007/BF01269910. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moncada S., Palmer R. M., Higgs E. A. Biosynthesis of nitric oxide from L-arginine. A pathway for the regulation of cell function and communication. Biochem Pharmacol. 1989 Jun 1;38(11):1709–1715. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(89)90403-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moncada S., Palmer R. M., Higgs E. A. Nitric oxide: physiology, pathophysiology, and pharmacology. Pharmacol Rev. 1991 Jun;43(2):109–142. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moncada S., Rees D. D., Schulz R., Palmer R. M. Development and mechanism of a specific supersensitivity to nitrovasodilators after inhibition of vascular nitric oxide synthesis in vivo. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Mar 15;88(6):2166–2170. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.6.2166. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palacios M., Knowles R. G., Palmer R. M., Moncada S. Nitric oxide from L-arginine stimulates the soluble guanylate cyclase in adrenal glands. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1989 Dec 15;165(2):802–809. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(89)80037-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palmer R. M., Rees D. D., Ashton D. S., Moncada S. L-arginine is the physiological precursor for the formation of nitric oxide in endothelium-dependent relaxation. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1988 Jun 30;153(3):1251–1256. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(88)81362-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Panten U., Kriegstein E. v., Poser W., Schönborn J., Hasselblatt A. Effects of L-leucine and alpha-ketoisocaproic acid upon insulin secretion and metabolism of isolated pancreatic islets. FEBS Lett. 1972 Feb 1;20(2):225–228. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(72)80801-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pralong W. F., Bartley C., Wollheim C. B. Single islet beta-cell stimulation by nutrients: relationship between pyridine nucleotides, cytosolic Ca2+ and secretion. EMBO J. 1990 Jan;9(1):53–60. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb08079.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Radomski M. W., Palmer R. M., Moncada S. An L-arginine/nitric oxide pathway present in human platelets regulates aggregation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Jul;87(13):5193–5197. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.13.5193. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rees D. D., Palmer R. M., Schulz R., Hodson H. F., Moncada S. Characterization of three inhibitors of endothelial nitric oxide synthase in vitro and in vivo. Br J Pharmacol. 1990 Nov;101(3):746–752. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1990.tb14151.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt H. H., Warner T. D., Ishii K., Sheng H., Murad F. Insulin secretion from pancreatic B cells caused by L-arginine-derived nitrogen oxides. Science. 1992 Feb 7;255(5045):721–723. doi: 10.1126/science.1371193. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern C., Schulster D., Green I. C. Inhibition of insulin secretion by interleukin-1 beta and tumour necrosis factor-alpha via an L-arginine-dependent nitric oxide generating mechanism. FEBS Lett. 1990 Dec 10;276(1-2):42–44. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(90)80502-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stamler J. S., Simon D. I., Osborne J. A., Mullins M. E., Jaraki O., Michel T., Singel D. J., Loscalzo J. S-nitrosylation of proteins with nitric oxide: synthesis and characterization of biologically active compounds. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Jan 1;89(1):444–448. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.1.444. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


