Abstract
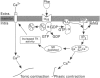
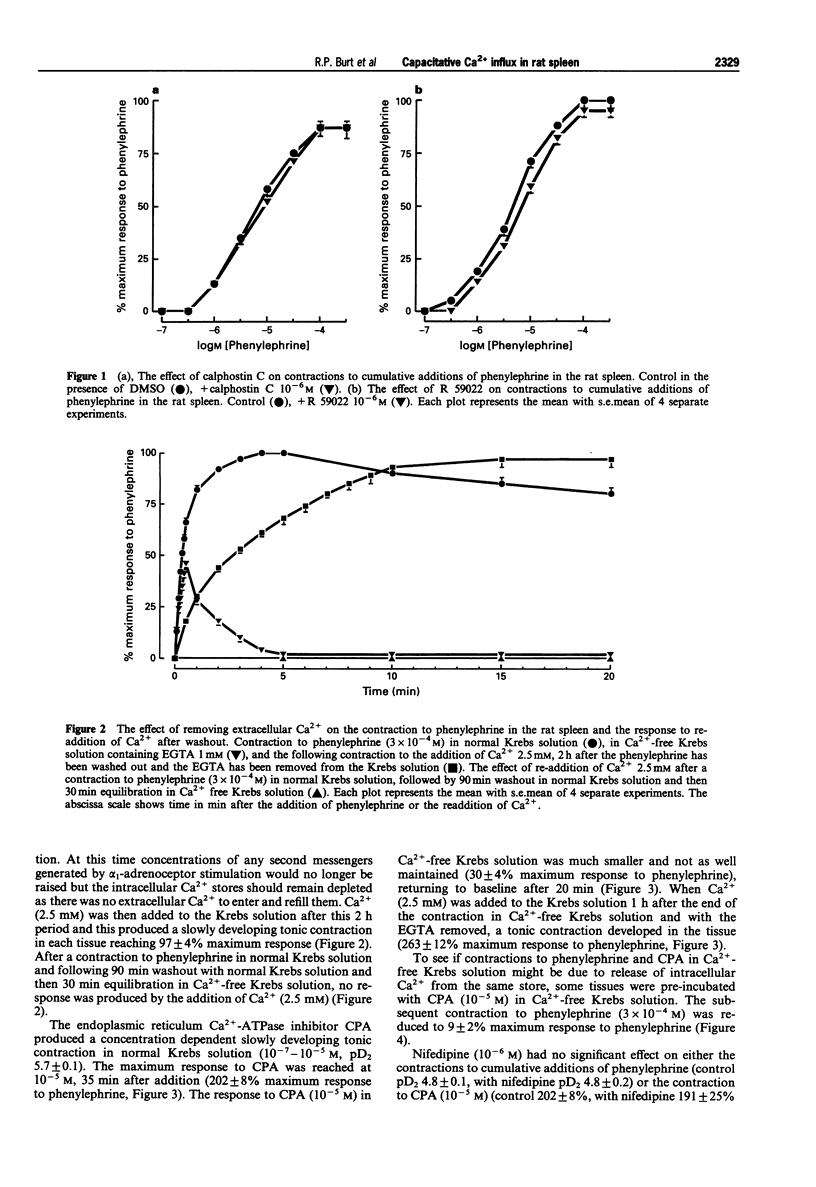
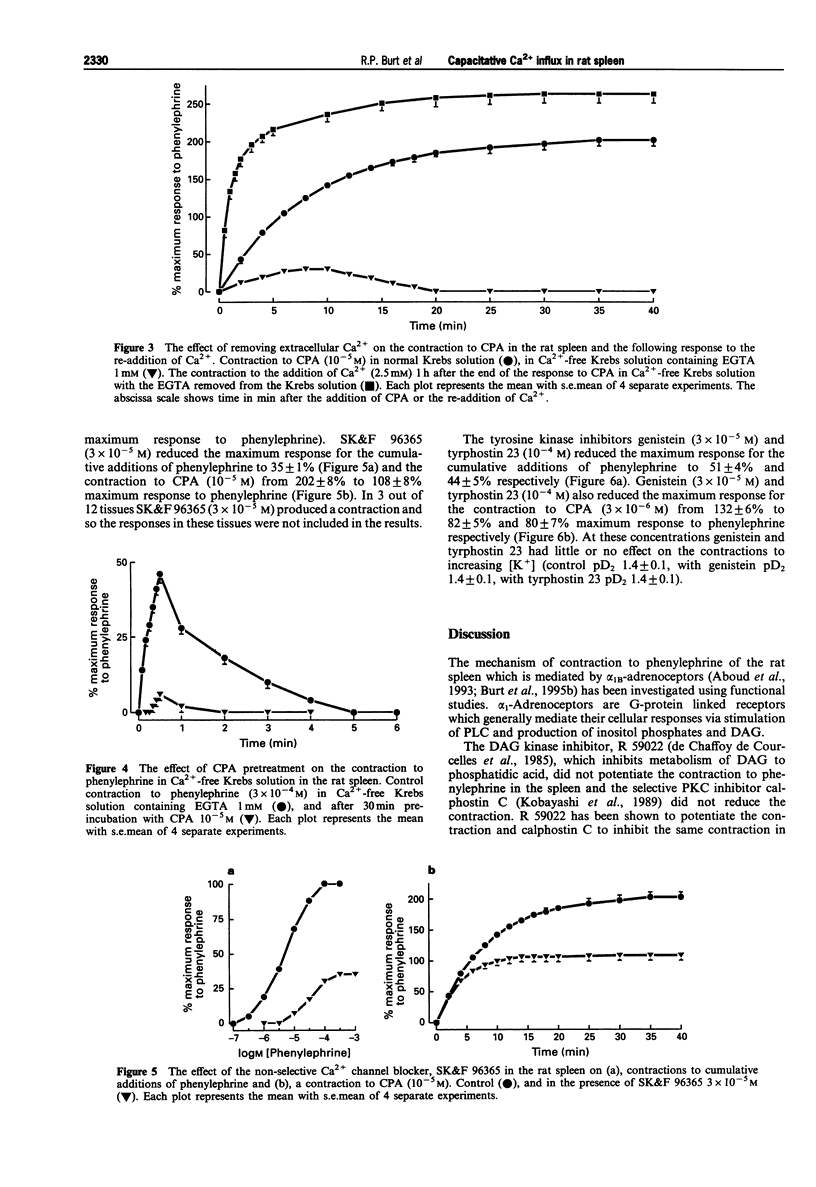
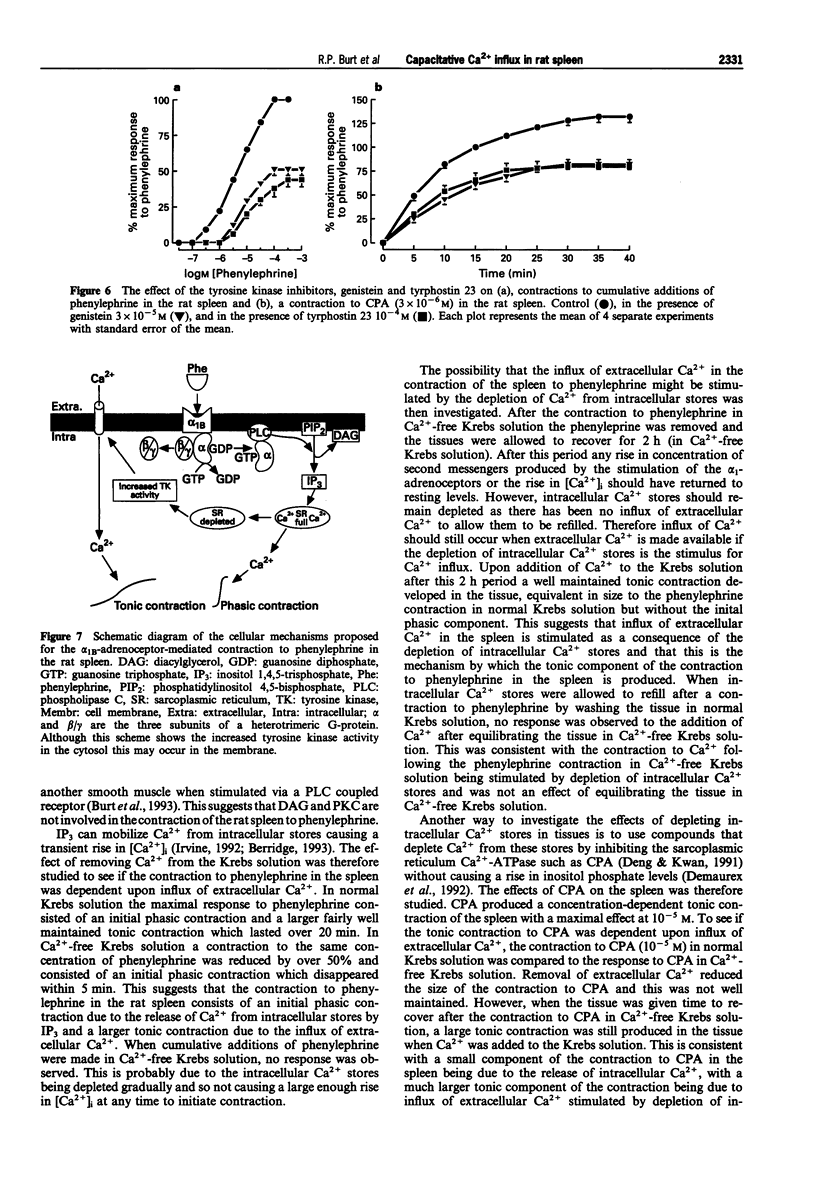
1. The mechanism of contraction to phenylephrine in the rat spleen (mediated via alpha 1B-adrenoceptors) has been studied in functional experiments. 2. The concentration-dependent contraction of the rat spleen to cumulative additions of phenylephrine (pD2 4.8 +/- 0.1) was not significantly reduced by the selective protein kinase C (PKC) inhibitor, calphostin C (10(-6)M) or potentiated by the DAG kinase inhibitor, R59022 (10(-6) M). 3. Contraction of the rat spleen in normal Krebs solution containing Ca2+ (2.5 mM) to a single concentration of phenylephrine (3 x 10(-4) M) produced a maximal response consisting of an initial phasic component and a more slowly developing tonic component. However in Ca(2+)-free Krebs solution (containing EGTA), phenylephrine (3 x 10(-4)M) produced only a phasic contraction which was reduced to 46 +/- 3% maximum response to phenylephrine in normal Krebs solution. 4. In some tissues after the contraction to phenylephrine (3 x 10(-4) M) in Ca(2+)-free Krebs solution (containing EGTA), the phenylephrine was washed out and the tissue was allowed to recover. After 2 h, upon addition of Ca2+ (2.5 mM) to the Krebs solution (EGTA now removed) a tonic contraction developed in the tissue (97 +/- 4% maximum response to phenylephrine). 5. Cyclopiazonic acid produced a tonic contraction of the rat spleen with a maximum effect at 10(-5) M (202 +/- 8% maximum response compared with that to phenylephrine). The contraction to CPA (10(-5) M) was reduced in Ca(2+)-free Krebs solution containing EGTA (30 +/- 4% of the maximum response to phenylephrine). One hour after the end of the contraction in Ca(2+)-free Krebs solution (EGTA now removed), upon addition of Ca2+ (2.5 mM) to the Krebs solution a tonic contraction developed in the tissue (263 +/- 12% maximum response to phenylephrine).(ABSTRACT TRUNCATED AT 250 WORDS)
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aboud R., Shafii M., Docherty J. R. Investigation of the subtypes of alpha 1-adrenoceptor mediating contractions of rat aorta, vas deferens and spleen. Br J Pharmacol. 1993 May;109(1):80–87. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1993.tb13534.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Akiyama T., Ishida J., Nakagawa S., Ogawara H., Watanabe S., Itoh N., Shibuya M., Fukami Y. Genistein, a specific inhibitor of tyrosine-specific protein kinases. J Biol Chem. 1987 Apr 25;262(12):5592–5595. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berridge M. J. Inositol trisphosphate and calcium signalling. Nature. 1993 Jan 28;361(6410):315–325. doi: 10.1038/361315a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bruns R. F., Miller F. D., Merriman R. L., Howbert J. J., Heath W. F., Kobayashi E., Takahashi I., Tamaoki T., Nakano H. Inhibition of protein kinase C by calphostin C is light-dependent. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1991 Apr 15;176(1):288–293. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(91)90922-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burt R. P., Chapple C. R., Marshall I. Evidence for a functional alpha 1A- (alpha 1C-) adrenoceptor mediating contraction of the rat epididymal vas deferens and an alpha 1B-adrenoceptor mediating contraction of the rat spleen. Br J Pharmacol. 1995 Jun;115(3):467–475. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1995.tb16356.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Demaurex N., Lew D. P., Krause K. H. Cyclopiazonic acid depletes intracellular Ca2+ stores and activates an influx pathway for divalent cations in HL-60 cells. J Biol Chem. 1992 Feb 5;267(4):2318–2324. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ehrlich B. E., Kaftan E., Bezprozvannaya S., Bezprozvanny I. The pharmacology of intracellular Ca(2+)-release channels. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 1994 May;15(5):145–149. doi: 10.1016/0165-6147(94)90074-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fasolato C., Innocenti B., Pozzan T. Receptor-activated Ca2+ influx: how many mechanisms for how many channels? Trends Pharmacol Sci. 1994 Mar;15(3):77–83. doi: 10.1016/0165-6147(94)90282-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gazit A., Yaish P., Gilon C., Levitzki A. Tyrphostins I: synthesis and biological activity of protein tyrosine kinase inhibitors. J Med Chem. 1989 Oct;32(10):2344–2352. doi: 10.1021/jm00130a020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoth M., Penner R. Depletion of intracellular calcium stores activates a calcium current in mast cells. Nature. 1992 Jan 23;355(6358):353–356. doi: 10.1038/355353a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hughes A. D., Schachter M. Multiple pathways for entry of calcium and other divalent cations in a vascular smooth muscle cell line (A7r5). Cell Calcium. 1994 Apr;15(4):317–330. doi: 10.1016/0143-4160(94)90071-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Irvine R. F. Inositol phosphates and Ca2+ entry: toward a proliferation or a simplification? FASEB J. 1992 Sep;6(12):3085–3091. doi: 10.1096/fasebj.6.12.1325932. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacob R. Agonist-stimulated divalent cation entry into single cultured human umbilical vein endothelial cells. J Physiol. 1990 Feb;421:55–77. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1990.sp017933. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kobayashi E., Nakano H., Morimoto M., Tamaoki T. Calphostin C (UCN-1028C), a novel microbial compound, is a highly potent and specific inhibitor of protein kinase C. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1989 Mar 15;159(2):548–553. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(89)90028-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marshall I., Burt R. P., Chapple C. R. Noradrenaline contractions of human prostate mediated by alpha 1A-(alpha 1c-) adrenoceptor subtype. Br J Pharmacol. 1995 Jul;115(5):781–786. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1995.tb15001.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merritt J. E., Armstrong W. P., Benham C. D., Hallam T. J., Jacob R., Jaxa-Chamiec A., Leigh B. K., McCarthy S. A., Moores K. E., Rink T. J. SK&F 96365, a novel inhibitor of receptor-mediated calcium entry. Biochem J. 1990 Oct 15;271(2):515–522. doi: 10.1042/bj2710515. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Minneman K. P., Esbenshade T. A. Alpha 1-adrenergic receptor subtypes. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol. 1994;34:117–133. doi: 10.1146/annurev.pa.34.040194.001001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morris A. P., Gallacher D. V., Irvine R. F., Petersen O. H. Synergism of inositol trisphosphate and tetrakisphosphate in activating Ca2+-dependent K+ channels. Nature. 1987 Dec 17;330(6149):653–655. doi: 10.1038/330653a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Putney J. W., Jr A model for receptor-regulated calcium entry. Cell Calcium. 1986 Feb;7(1):1–12. doi: 10.1016/0143-4160(86)90026-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Putney J. W., Jr Capacitative calcium entry revisited. Cell Calcium. 1990 Nov-Dec;11(10):611–624. doi: 10.1016/0143-4160(90)90016-n. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sargeant P., Farndale R. W., Sage S. O. Calcium store depletion in dimethyl BAPTA-loaded human platelets increases protein tyrosine phosphorylation in the absence of a rise in cytosolic calcium. Exp Physiol. 1994 Mar;79(2):269–272. doi: 10.1113/expphysiol.1994.sp003762. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seidler N. W., Jona I., Vegh M., Martonosi A. Cyclopiazonic acid is a specific inhibitor of the Ca2+-ATPase of sarcoplasmic reticulum. J Biol Chem. 1989 Oct 25;264(30):17816–17823. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sorrentino V., Volpe P. Ryanodine receptors: how many, where and why? Trends Pharmacol Sci. 1993 Mar;14(3):98–103. doi: 10.1016/0165-6147(93)90072-r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tepel M., Kühnapfel S., Theilmeier G., Teupe C., Schlotmann R., Zidek W. Filling state of intracellular Ca2+ pools triggers trans plasma membrane Na+ and Ca2+ influx by a tyrosine kinase-dependent pathway. J Biol Chem. 1994 Oct 21;269(42):26239–26242. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yule D. I., Kim E. T., Williams J. A. Tyrosine kinase inhibitors attenuate "capacitative" Ca2+ influx in rat pancreatic acinar cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1994 Aug 15;202(3):1697–1704. doi: 10.1006/bbrc.1994.2130. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Chaffoy de Courcelles D. C., Roevens P., Van Belle H. R 59 022, a diacylglycerol kinase inhibitor. Its effect on diacylglycerol and thrombin-induced C kinase activation in the intact platelet. J Biol Chem. 1985 Dec 15;260(29):15762–15770. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]