Abstract
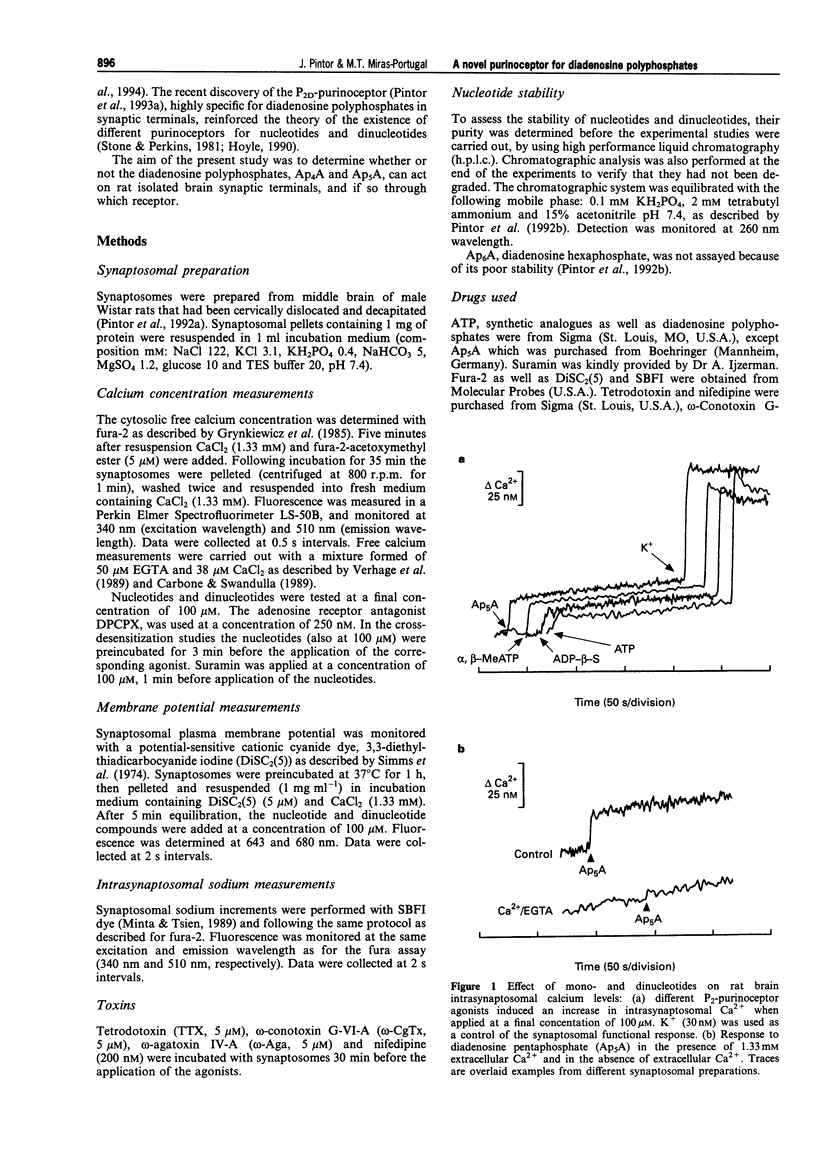
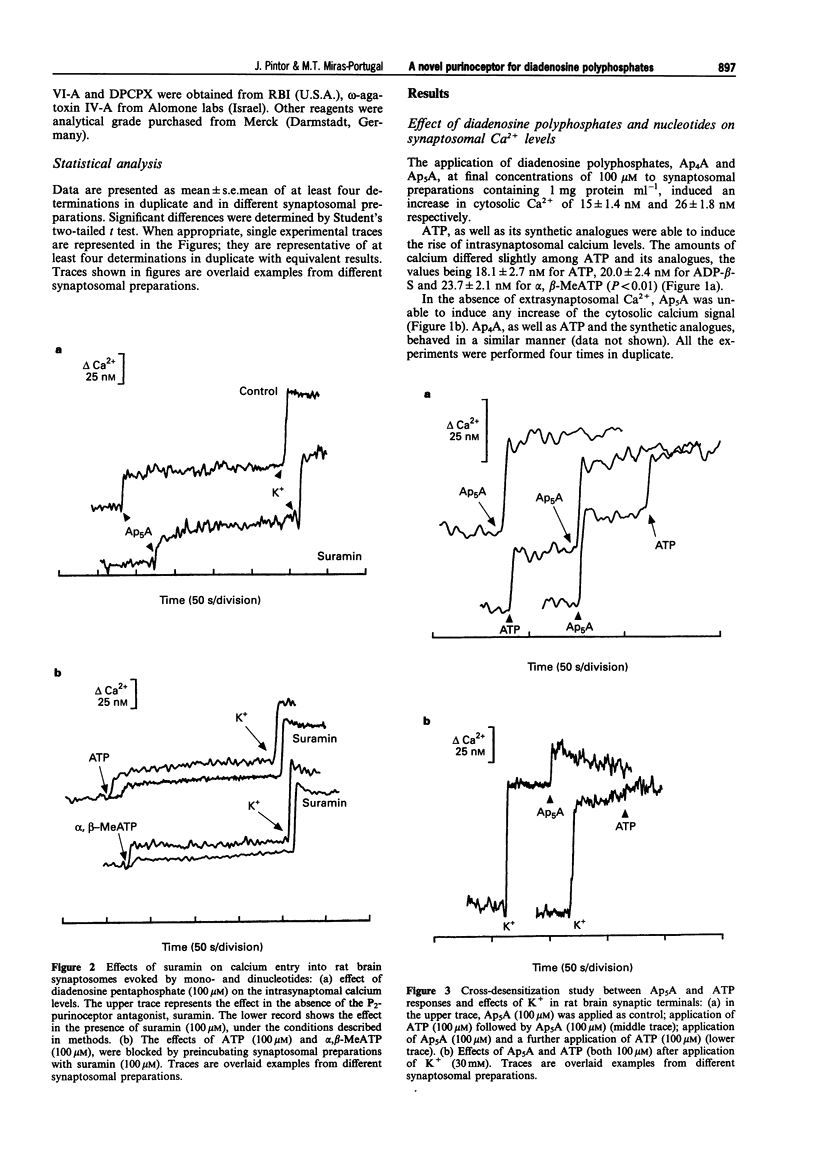
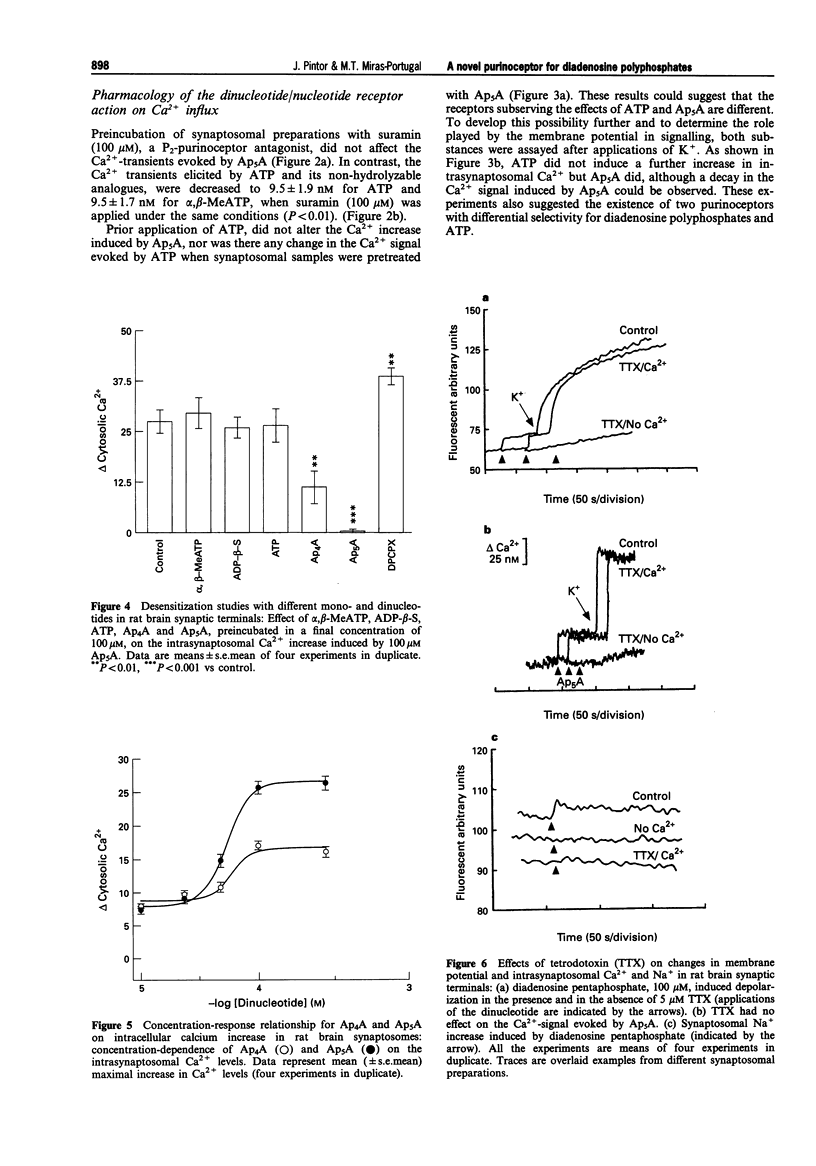
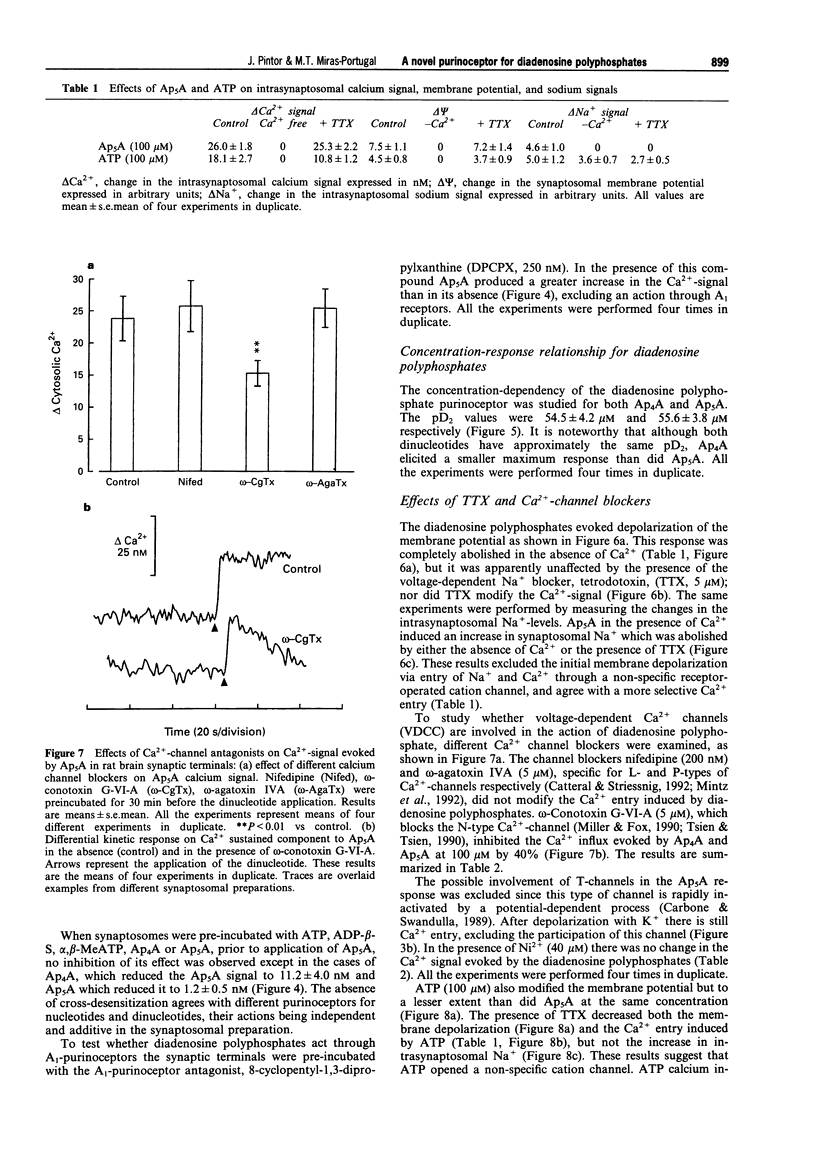
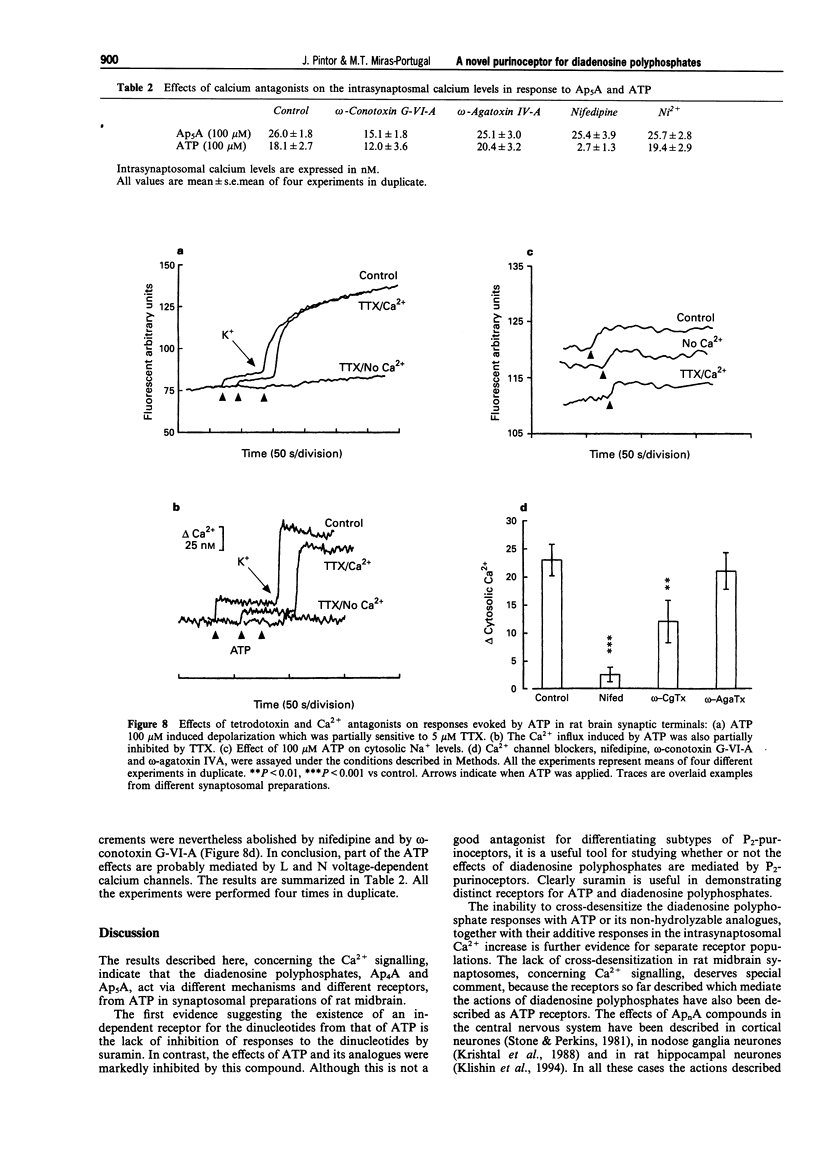
1. Diadenosine polyphosphates, Ap4A and Ap5A, as well as ATP, alpha,beta-MeATP and ADP-beta-S, were able to elicit variable intrasynaptosomal Ca2+ increases in rat midbrain synaptic terminals. The origin of the Ca2+ increment was the extrasynaptosomal space since the elimination of extracellular Ca2+ abolished the effect of all the agonists. 2. The P2-purinoceptor antagonist, suramin, did not affect the Ca(2+)-increase evoked by diadenosine polyphosphates but dramatically blocked the Ca2+ entry induced by ATP and its synthetic analogues. 3. The actions of Ap5A and ATP on the intrasynaptosomal Ca2+ increase did not cross-desensitize. 4. Concentration-response studies for diadenosine polyphosphates showed pD2 values of 54.5 +/- 4.2 microM and 55.6 +/- 3.8 microM for Ap4A and Ap5A, respectively. 5. The entry of calcium induced by diadenosine polyphosphates could be separated into two components. The first represented a selective voltage-independent Ca2+ entry; the second, a sustained phase which was voltage-dependent. 6. Studies on the voltage-dependent Ca(2+)-channels involved in the effects of the diadenosine polyphosphates, demonstrated that omega-conotoxin G-VI-A inhibited the sustained Ca(2+)-entry, suggesting the participation of an N-type Ca(2+)-channel. This toxin was unable to abolish the initial cation entry induced by Ap4A or Ap5A. omega-Agatoxin IV-A, tetrodotoxin, or nifedipine did not inhibit the effects of the diadenosine polyphosphates. 7. The effect of ATP on Ca(2+)-entry was abolished by nifedipine and omega-conotoxin G-VI-A, suggesting the participation of L- and N-type Ca(2+)-channels in the response to ATP.(ABSTRACT TRUNCATED AT 250 WORDS)
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barrie A. P., Nicholls D. G. Adenosine A1 receptor inhibition of glutamate exocytosis and protein kinase C-mediated decoupling. J Neurochem. 1993 Mar;60(3):1081–1086. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1993.tb03257.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benham C. D., Tsien R. W. A novel receptor-operated Ca2+-permeable channel activated by ATP in smooth muscle. Nature. 1987 Jul 16;328(6127):275–278. doi: 10.1038/328275a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burnstock G., Kennedy C. Is there a basis for distinguishing two types of P2-purinoceptor? Gen Pharmacol. 1985;16(5):433–440. doi: 10.1016/0306-3623(85)90001-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carbone E., Swandulla D. Neuronal calcium channels: kinetics, blockade and modulation. Prog Biophys Mol Biol. 1989;54(1):31–58. doi: 10.1016/0079-6107(89)90008-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Castro E., Tomé A. R., Miras-Portugal M. T., Rosário L. M. Single-cell fura-2 microfluorometry reveals different purinoceptor subtypes coupled to Ca2+ influx and intracellular Ca2+ release in bovine adrenal chromaffin and endothelial cells. Pflugers Arch. 1994 Apr;426(6):524–533. doi: 10.1007/BF00378530. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Catterall W. A., Striessnig J. Receptor sites for Ca2+ channel antagonists. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 1992 Jun;13(6):256–262. doi: 10.1016/0165-6147(92)90079-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cockcroft S., Gomperts B. D. ATP induces nucleotide permeability in rat mast cells. Nature. 1979 Jun 7;279(5713):541–542. doi: 10.1038/279541a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colman R. W. ADP receptors in platelets. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1990;603:198–210. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1990.tb37673.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edwards F. A., Gibb A. J., Colquhoun D. ATP receptor-mediated synaptic currents in the central nervous system. Nature. 1992 Sep 10;359(6391):144–147. doi: 10.1038/359144a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gordon J. L. Extracellular ATP: effects, sources and fate. Biochem J. 1986 Jan 15;233(2):309–319. doi: 10.1042/bj2330309. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grynkiewicz G., Poenie M., Tsien R. Y. A new generation of Ca2+ indicators with greatly improved fluorescence properties. J Biol Chem. 1985 Mar 25;260(6):3440–3450. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harden T. K., Boyer J. L., Brown H. A., Cooper C. L., Jeffs R. A., Martin M. W. Biochemical properties of a P2Y-purinergic receptor. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1990;603:256–266. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1990.tb37677.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoyle C. H., Chapple C., Burnstock G. Isolated human bladder: evidence for an adenine dinucleotide acting on P2X-purinoceptors and for purinergic transmission. Eur J Pharmacol. 1989 Dec 12;174(1):115–118. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(89)90881-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoyle C. H., Knight G. E., Burnstock G. Suramin antagonizes responses to P2-purinoceptor agonists and purinergic nerve stimulation in the guinea-pig urinary bladder and taenia coli. Br J Pharmacol. 1990 Mar;99(3):617–621. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1990.tb12979.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoyle C. H. Pharmacological activity of adenine dinucleotides in the periphery: possible receptor classes and transmitter function. Gen Pharmacol. 1990;21(6):827–831. doi: 10.1016/0306-3623(90)90440-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Illes P., Nörenberg W. Neuronal ATP receptors and their mechanism of action. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 1993 Feb;14(2):50–54. doi: 10.1016/0165-6147(93)90030-n. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klishin A., Lozovaya N., Pintor J., Miras-Portugal M. T., Krishtal O. Possible functional role of diadenosine polyphosphates: negative feedback for excitation in hippocampus. Neuroscience. 1994 Jan;58(2):235–236. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(94)90030-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krishtal O. A., Marchenko S. M., Obukhov A. G., Volkova T. M. Receptors for ATP in rat sensory neurones: the structure-function relationship for ligands. Br J Pharmacol. 1988 Dec;95(4):1057–1062. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1988.tb11739.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacKenzie I., Kirkpatrick K. A., Burnstock G. Comparative study of the actions of AP5A and alpha,beta-methylene ATP on nonadrenergic, noncholinergic neurogenic excitation in the guinea-pig vas deferens. Br J Pharmacol. 1988 Jul;94(3):699–706. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1988.tb11578.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Minta A., Tsien R. Y. Fluorescent indicators for cytosolic sodium. J Biol Chem. 1989 Nov 15;264(32):19449–19457. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mintz I. M., Venema V. J., Swiderek K. M., Lee T. D., Bean B. P., Adams M. E. P-type calcium channels blocked by the spider toxin omega-Aga-IVA. Nature. 1992 Feb 27;355(6363):827–829. doi: 10.1038/355827a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Connor S. E., Dainty I. A., Leff P. Further subclassification of ATP receptors based on agonist studies. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 1991 Apr;12(4):137–141. doi: 10.1016/0165-6147(91)90530-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Connor S. E. Recent developments in the classification and functional significance of receptors for ATP and UTP, evidence for nucleotide receptors. Life Sci. 1992;50(22):1657–1664. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(92)90420-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pintor J., Díaz-Rey M. A., Miras-Portugal M. T. Ap4A and ADP-beta-S binding to P2 purinoceptors present on rat brain synaptic terminals. Br J Pharmacol. 1993 Apr;108(4):1094–1099. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1993.tb13510.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pintor J., Díaz-Rey M. A., Torres M., Miras-Portugal M. T. Presence of diadenosine polyphosphates--Ap4A and Ap5A--in rat brain synaptic terminals. Ca2+ dependent release evoked by 4-aminopyridine and veratridine. Neurosci Lett. 1992 Mar 2;136(2):141–144. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(92)90034-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pintor J., Miras-Portugal M. T. P2 purinergic receptors for diadenosine polyphosphates in the nervous system. Gen Pharmacol. 1995 Mar;26(2):229–235. doi: 10.1016/0306-3623(94)00182-m. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pintor J., Porras A., Mora F., Miras-Portugal M. T. Amphetamine-induced release of diadenosine polyphosphates--Ap4A and Ap5A--from caudate putamen of conscious rat. Neurosci Lett. 1993 Feb 5;150(1):13–16. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(93)90096-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pintor J., Porras A., Mora F., Miras-Portugal M. T. Dopamine receptor blockade inhibits the amphetamine-induced release of diadenosine polyphosphates, diadenosine tetraphosphate and diadenosine pentaphosphate, from neostriatum of the conscious rat. J Neurochem. 1995 Feb;64(2):670–676. doi: 10.1046/j.1471-4159.1995.64020670.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pintor J., Rotllán P., Torres M., Miras-Portugal M. T. Characterization and quantification of diadenosine hexaphosphate in chromaffin cells: granular storage and secretagogue-induced release. Anal Biochem. 1992 Feb 1;200(2):296–300. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(92)90469-n. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pintor J., Torres M., Castro E., Miras-Portugal M. T. Characterization of diadenosine tetraphosphate (Ap4A) binding sites in cultured chromaffin cells: evidence for a P2y site. Br J Pharmacol. 1991 Aug;103(4):1980–1984. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1991.tb12363.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Potter P., White T. D. Release of adenosine 5'-triphosphate from synaptosomes from different regions of rat brain. Neuroscience. 1980;5(7):1351–1356. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(80)90207-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ralevic V., Hoyle C. H., Burnstock G. Pivotal role of phosphate chain length in vasoconstrictor versus vasodilator actions of adenine dinucleotides in rat mesenteric arteries. J Physiol. 1995 Mar 15;483(Pt 3):703–713. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1995.sp020615. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shen K. Z., North R. A. Excitation of rat locus coeruleus neurons by adenosine 5'-triphosphate: ionic mechanism and receptor characterization. J Neurosci. 1993 Mar;13(3):894–899. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.13-03-00894.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sims P. J., Waggoner A. S., Wang C. H., Hoffman J. F. Studies on the mechanism by which cyanine dyes measure membrane potential in red blood cells and phosphatidylcholine vesicles. Biochemistry. 1974 Jul 30;13(16):3315–3330. doi: 10.1021/bi00713a022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stone T. W., Perkins M. N. Adenine dinucleotide effects on rat cortical neurones. Brain Res. 1981 Dec 14;229(1):241–245. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(81)90764-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsien R. W., Tsien R. Y. Calcium channels, stores, and oscillations. Annu Rev Cell Biol. 1990;6:715–760. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cb.06.110190.003435. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ueno S., Harata N., Inoue K., Akaike N. ATP-gated current in dissociated rat nucleus solitarii neurons. J Neurophysiol. 1992 Sep;68(3):778–785. doi: 10.1152/jn.1992.68.3.778. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Verhage M., Besselsen E., Lopes da Silva F. H., Ghijsen W. E. Ca2+-dependent regulation of presynaptic stimulus-secretion coupling. J Neurochem. 1989 Oct;53(4):1188–1194. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1989.tb07413.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White T. D. Direct detection of depolarisation-induced release of ATP from a synaptosomal preparation. Nature. 1977 May 5;267(5606):67–68. doi: 10.1038/267067a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


