Abstract
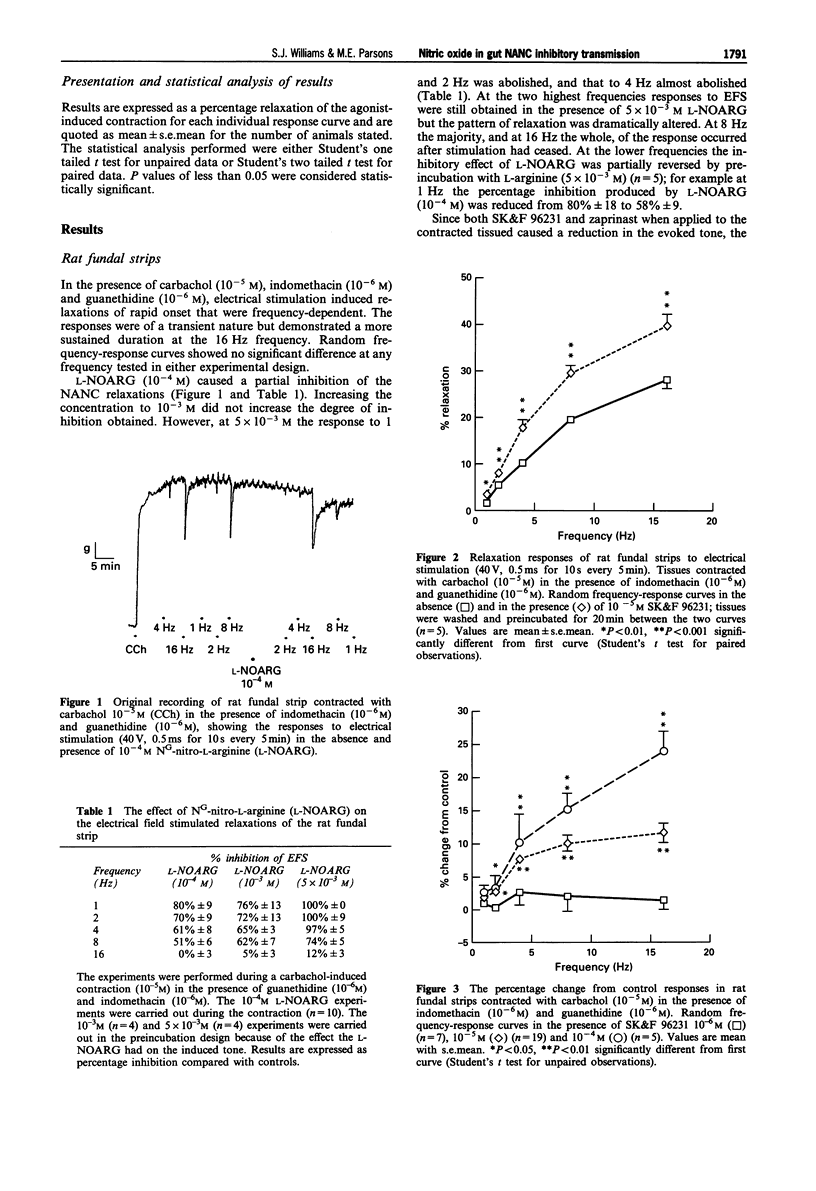
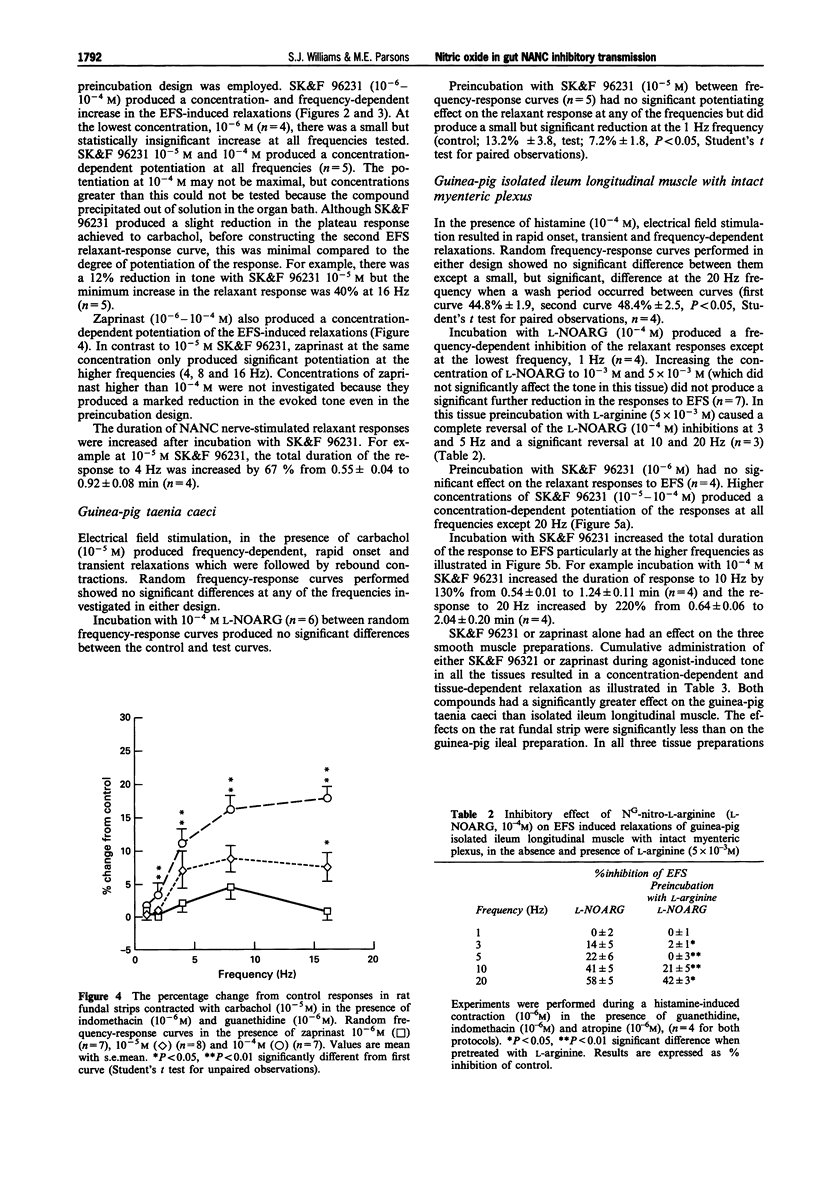
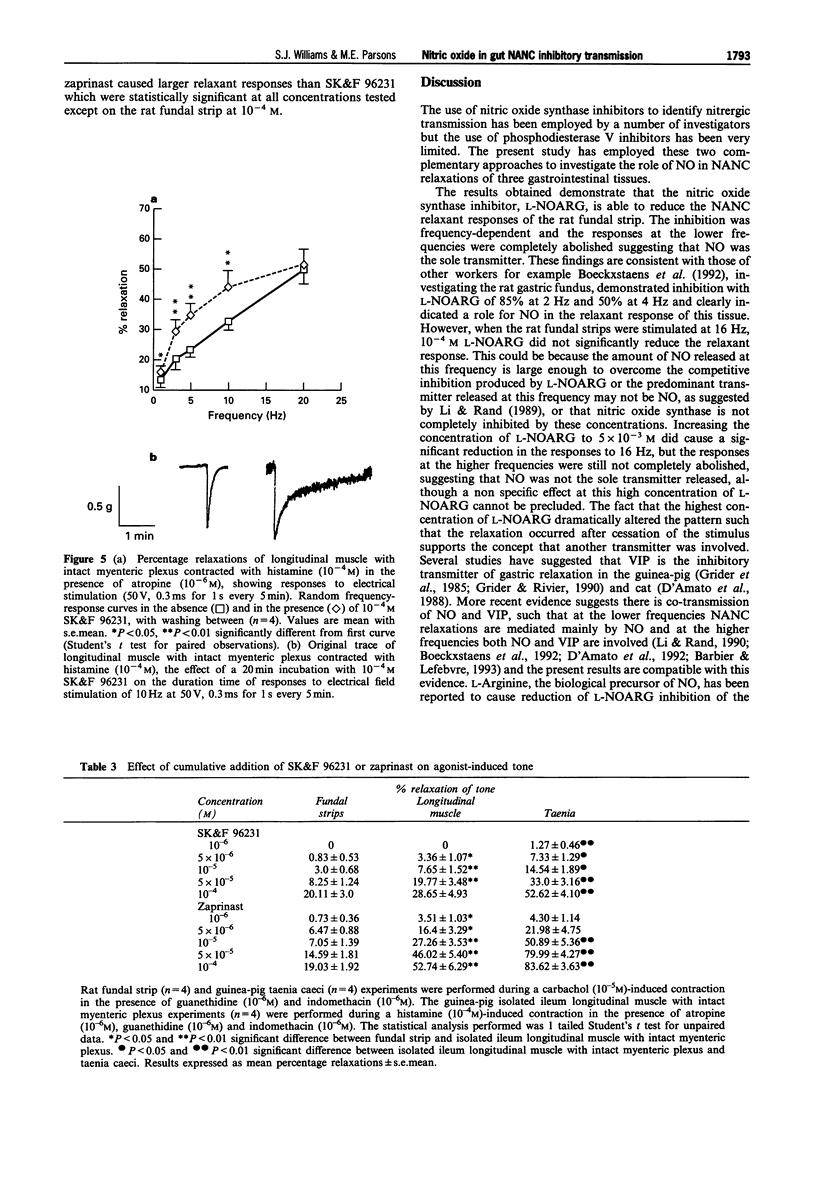
1. The effects of NG-nitro-L-arginine (L-NOARG), a nitric oxide synthase inhibitor, and SK&F 96231, a phosphodiesterase type V inhibitor, on electrical field stimulated (EFS) nonadrenergic noncholinergic (NANC) relaxations of rat fundal strips, guinea-pig isolated ileum longitudinal muscle with intact myenteric plexus, and guinea-pig taenia caeci were investigated. 2. Reproducible repeated control random EFS frequency-response curves were obtained for all three tissues. 3. Depending on the frequency of stimulation, L-NOARG (10(-4)-5 x 10(-3) M) caused either a complete or partial inhibition of the NANC-induced relaxations of the rat fundal strips and the guinea-pig isolated ileum longitudinal muscle with intact myenteric plexus, but not of the guinea-pig taenia caeci. The inhibitory action of L-NOARG was partially or totally reversed, depending on the tissue, by L-arginine (5 x 10(-3) M). 4. SK&F 96231 (10(-6)-10(-4) M) caused a concentration- and frequency-dependent potentiation of both the size and duration of the EFS-induced NANC relaxant response of rat fundal strips and guinea-pig isolated ileum longitudinal muscle with intact myenteric plexus, but not of the guinea-pig taenia caeci. 5. Zaprinast, another phosphodiesterase type V inhibitor (10(-6)-10(-4) M) caused a concentration- and frequency-dependent potentiation of the NANC relaxant responses to EFS of rat fundal strips. 6. SK&F 96231 and zaprinast alone (10(-6)-10(-4) M) caused a concentration-dependent relaxation of the agonist-induced tone of all three tissues with the maximum degree of relaxation found to be in the order stomach < ileum < caecum. This is the reverse order for ability of SK&F 96231 to potentiate relaxant responses to EFS.(ABSTRACT TRUNCATED AT 250 WORDS)
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arnold W. P., Mittal C. K., Katsuki S., Murad F. Nitric oxide activates guanylate cyclase and increases guanosine 3':5'-cyclic monophosphate levels in various tissue preparations. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Aug;74(8):3203–3207. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.8.3203. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barbier A. J., Lefebvre R. A. Effect of 3-isobutyl-1-methylxanthine and zaprinast on non-adrenergic non-cholinergic relaxation in the rat gastric fundus. Eur J Pharmacol. 1992 Jan 21;210(3):315–323. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(92)90421-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barbier A. J., Lefebvre R. A. Involvement of the L-arginine: nitric oxide pathway in nonadrenergic noncholinergic relaxation of the cat gastric fundus. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1993 Jul;266(1):172–178. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barnette M. S., Barone F. C., Fowler P. J., Grous M., Price W. J., Ormsbee H. S. Human lower oesophageal sphincter relaxation is associated with raised cyclic nucleotide content. Gut. 1991 Jan;32(1):4–9. doi: 10.1136/gut.32.1.4. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barnette M. S., Manning C. D., Price W. J., Barone F. C. Initial biochemical and functional characterization of cyclic nucleotide phosphodiesterase isozymes in canine colonic smooth muscle. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1993 Feb;264(2):801–812. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barnette M., Torphy T. J., Grous M., Fine C., Ormsbee H. S., 3rd Cyclic GMP: a potential mediator of neurally- and drug-induced relaxation of opossum lower esophageal sphincter. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1989 May;249(2):524–528. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boeckxstaens G. E., Pelckmans P. A., Bogers J. J., Bult H., De Man J. G., Oosterbosch L., Herman A. G., Van Maercke Y. M. Release of nitric oxide upon stimulation of nonadrenergic noncholinergic nerves in the rat gastric fundus. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1991 Feb;256(2):441–447. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boeckxstaens G. E., Pelckmans P. A., Bult H., De Man J. G., Herman A. G., Van Maercke Y. M. Non-adrenergic non-cholinergic relaxation mediated by nitric oxide in the canine ileocolonic junction. Eur J Pharmacol. 1990 Nov 6;190(1-2):239–246. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(90)94132-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boeckxstaens G. E., Pelckmans P. A., Bult H., De Man J. G., Herman A. G., van Maercke Y. M. Evidence for nitric oxide as mediator of non-adrenergic non-cholinergic relaxations induced by ATP and GABA in the canine gut. Br J Pharmacol. 1991 Feb;102(2):434–438. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1991.tb12191.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boeckxstaens G. E., Pelckmans P. A., De Man J. G., Bult H., Herman A. G., Van Maercke Y. M. Evidence for a differential release of nitric oxide and vasoactive intestinal polypeptide by nonadrenergic noncholinergic nerves in the rat gastric fundus. Arch Int Pharmacodyn Ther. 1992 Jul-Aug;318:107–115. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bowman A., Drummond A. H. Cyclic GMP mediates neurogenic relaxation in the bovine retractor penis muscle. Br J Pharmacol. 1984 Apr;81(4):665–674. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1984.tb16133.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burnstock G., Costa M. Inhibitory innervation of the gut. Gastroenterology. 1973 Jan;64(1):141–144. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- D'Amato M., Currò D., Montuschi P., Ciabattoni G., Ragazzoni E., Lefebvre R. A. Release of vasoactive intestinal polypeptide from the rat gastric fundus. Br J Pharmacol. 1992 Mar;105(3):691–695. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1992.tb09040.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- D'Amato M., De Beurme F. A., Lefebvre R. A. Comparison of the effect of vasoactive intestinal polypeptide and non-adrenergic non-cholinergic neurone stimulation in the cat gastric fundus. Eur J Pharmacol. 1988 Jul 26;152(1-2):71–82. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(88)90837-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gibson A., Mirzazadeh S. N-methylhydroxylamine inhibits and M&B 22948 potentiates relaxations of the mouse anococcygeus to non-adrenergic, non-cholinergic field stimulation and to nitrovasodilator drugs. Br J Pharmacol. 1989 Mar;96(3):637–644. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1989.tb11863.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goyal R. K., Rattan S., Said S. I. VIP as a possible neurotransmitter of non-cholinergic non-adrenergic inhibitory neurones. Nature. 1980 Nov 27;288(5789):378–380. doi: 10.1038/288378a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grider J. R., Cable M. B., Bitar K. N., Said S. I., Makhlouf G. M. Vasoactive intestinal peptide. Relaxant neurotransmitter in tenia coli of the guinea pig. Gastroenterology. 1985 Jul;89(1):36–42. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grider J. R., Rivier J. R. Vasoactive intestinal peptide (VIP) as transmitter of inhibitory motor neurons of the gut: evidence from the use of selective VIP antagonists and VIP antiserum. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1990 May;253(2):738–742. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gustafsson B. I., Delbro D. S. Tonic inhibition of small intestinal motility by nitric oxide. J Auton Nerv Syst. 1993 Aug-Sep;44(2-3):179–187. doi: 10.1016/0165-1838(93)90030-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lefebvre R. A., Baert E., Barbier A. J. Influence of NG-nitro-L-arginine on non-adrenergic non-cholinergic relaxation in the guinea-pig gastric fundus. Br J Pharmacol. 1992 May;106(1):173–179. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1992.tb14311.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li C. G., Rand M. J. Evidence for a role of nitric oxide in the neurotransmitter system mediating relaxation of the rat anococcygeus muscle. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol. 1989 Dec;16(12):933–938. doi: 10.1111/j.1440-1681.1989.tb02404.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li C. G., Rand M. J. Nitric oxide and vasoactive intestinal polypeptide mediate non-adrenergic, non-cholinergic inhibitory transmission to smooth muscle of the rat gastric fundus. Eur J Pharmacol. 1990 Dec 4;191(3):303–309. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(90)94162-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murray J., Du C., Ledlow A., Bates J. N., Conklin J. L. Nitric oxide: mediator of nonadrenergic noncholinergic responses of opossum esophageal muscle. Am J Physiol. 1991 Sep;261(3 Pt 1):G401–G406. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.1991.261.3.G401. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murray K. J., Eden R. J., England P. J., Dolan J., Grimsditch D. C., Stutchbury C. A., Patel B., Reeves M. L., Worby A., Torphy T. J. Potential use of selective phosphodiesterase inhibitors in the treatment of asthma. Agents Actions Suppl. 1991;34:27–46. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mülsch A., Busse R. NG-nitro-L-arginine (N5-[imino(nitroamino)methyl]-L-ornithine) impairs endothelium-dependent dilations by inhibiting cytosolic nitric oxide synthesis from L-arginine. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1990 Jan-Feb;341(1-2):143–147. doi: 10.1007/BF00195071. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Osthaus L. E., Galligan J. J. Antagonists of nitric oxide synthesis inhibit nerve-mediated relaxations of longitudinal muscle in guinea pig ileum. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1992 Jan;260(1):140–145. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palmer R. M., Rees D. D., Ashton D. S., Moncada S. L-arginine is the physiological precursor for the formation of nitric oxide in endothelium-dependent relaxation. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1988 Jun 30;153(3):1251–1256. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(88)81362-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patel M., Spraggs C. F. Functional comparisons of gastrin/cholecystokinin receptors in isolated preparations of gastric mucosa and ileum. Br J Pharmacol. 1992 Jun;106(2):275–282. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1992.tb14328.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rajfer J., Aronson W. J., Bush P. A., Dorey F. J., Ignarro L. J. Nitric oxide as a mediator of relaxation of the corpus cavernosum in response to nonadrenergic, noncholinergic neurotransmission. N Engl J Med. 1992 Jan 9;326(2):90–94. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199201093260203. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rattan S., Moummi C. Influence of stimulators and inhibitors of cyclic nucleotides on lower esophageal sphincter. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1989 Feb;248(2):703–709. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Satchell D. G. Nucleotide pyrophosphatase antagonizes responses to adenosine 5'-triphosphate and non-adrenergic, non-cholinergic inhibitory nerve stimulation in the guinea-pig isolated taenia coli. Br J Pharmacol. 1981 Oct;74(2):319–321. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1981.tb09973.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sonnenburg W. K., Beavo J. A. Cyclic GMP and regulation of cyclic nucleotide hydrolysis. Adv Pharmacol. 1994;26:87–114. doi: 10.1016/s1054-3589(08)60052-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Torphy T. J., Fine C. F., Burman M., Barnette M. S., Ormsbee H. S., 3rd Lower esophageal sphincter relaxation is associated with increased cyclic nucleotide content. Am J Physiol. 1986 Dec;251(6 Pt 1):G786–G793. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.1986.251.6.G786. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tøttrup A., Svane D., Forman A. Nitric oxide mediating NANC inhibition in opossum lower esophageal sphincter. Am J Physiol. 1991 Mar;260(3 Pt 1):G385–G389. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.1991.260.3.G385. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vanderwinden J. M., De Laet M. H., Schiffmann S. N., Mailleux P., Lowenstein C. J., Snyder S. H., Vanderhaeghen J. J. Nitric oxide synthase distribution in the enteric nervous system of Hirschsprung's disease. Gastroenterology. 1993 Oct;105(4):969–973. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(93)90938-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wong R. K., Maydonovitch C., Garcia J. E., Johnson L. F., Castell D. O. The effect of terbutaline sulfate, nitroglycerin, and aminophylline on lower esophageal sphincter pressure and radionuclide esophageal emptying in patients with achalasia. J Clin Gastroenterol. 1987 Aug;9(4):386–389. doi: 10.1097/00004836-198708000-00006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yagasaki O., Nabata H., Yanagiya I. Effects of desensitization to adenosine 5'-triphosphate and vasoactive intestinal polypeptide on non-adrenergic inhibitory responses of longitudinal and circular muscles in the rat ileum. J Pharm Pharmacol. 1983 Dec;35(12):818–820. doi: 10.1111/j.2042-7158.1983.tb02904.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


