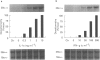Abstract
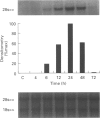
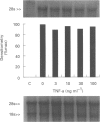
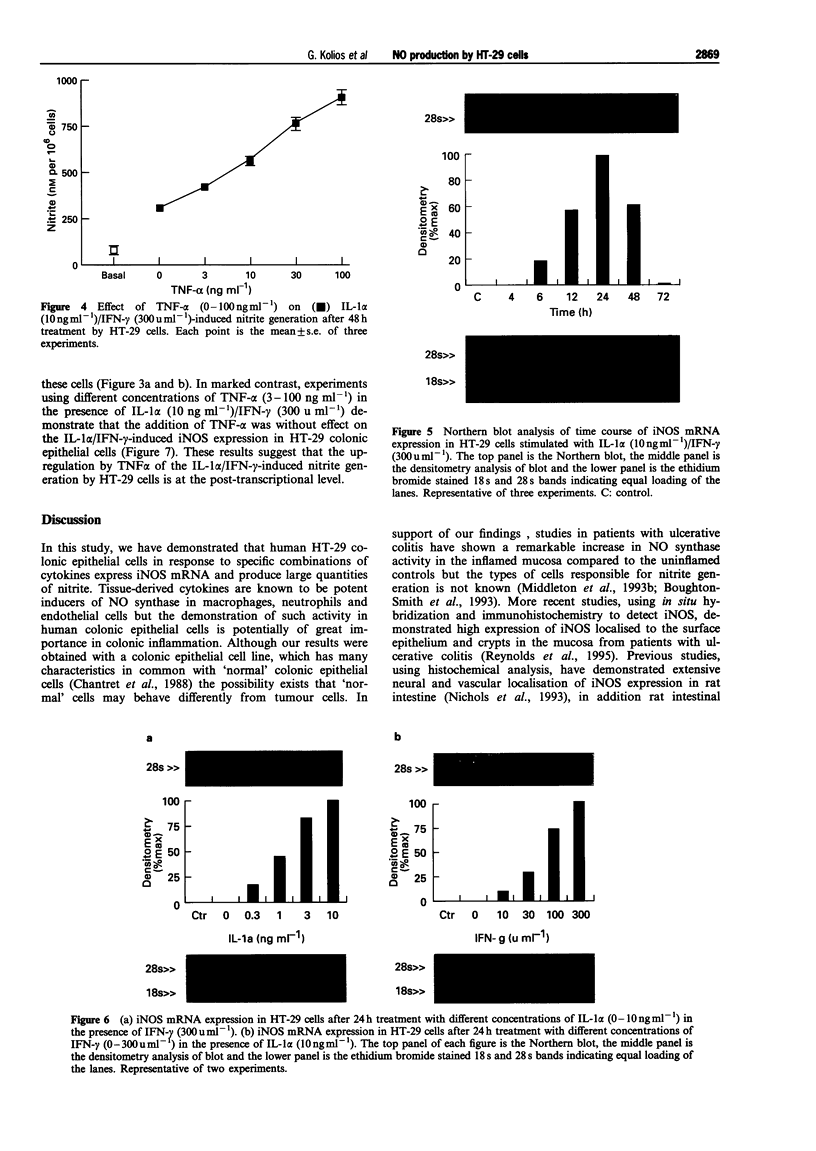
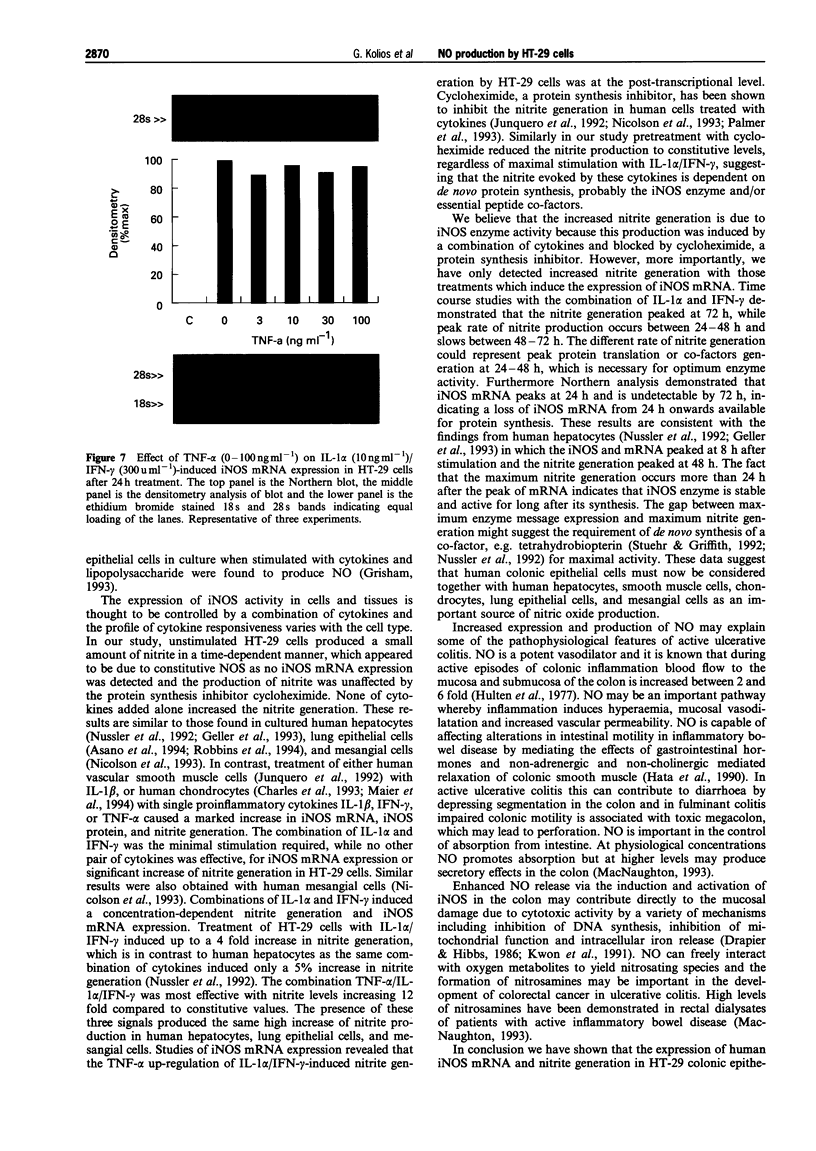
1 We have determined which cytokines regulate the expression of human inducible nitric oxide synthase (iNOS) mRNA and nitrite generation in the human colonic-epithelial cell line HT-29. 2 Growth arrested cell cultures were stimulated with the human recombinant cytokines interleukin-1 alpha (IL-1 alpha), tumour necrosisfactor-alpha (TNF-alpha), interferon gamma (IFN-gamma) or vehicle added alone or in combination. Human iNOS mRNA was determined by Northern blot analysis and nitrite generation by the use of a fluorometric assay. 3 Unstimulated cells produced a small time-dependent increase in nitrite generation of 50 +/- 4, 75 +/- 8, and 103 +/- 8 nM per 10(6) cells at 24 h, 48 h, and 72 h respectively. This nitrite generation was unaffected by cycloheximide (5 micrograms ml-1) pretreatment and iNOS mRNA was not detected. 4 None of cytokines alone induced either iNOS mRNA expression or an increase in nitrite generation. The combination of IL-1 alpha/IFN-gamma produced a highly significant (P < 0.001) 4 fold increase in nitrite production at 48 h, compared to basal values, while no other pair of cytokines was effective. 5 Time course studies with IL-1 alpha/IFN-gamma combination revealed significant (P < 0.001) increases in nitrite at 24 h (153 +/- 7), 48 h (306 +/- 24), and 72 h (384 +/- 15) compared to basal values of 50 +/- 4, 75 +/- 8, and 103 +/- 8 nM per 10(6) cells respectively. 6 Studies with IL-1 alpha/IFN-gamma combination demonstrated a time dependent expression of iNOS mRNA, first observed at 6 h, peaked at 24 h and was undetectable by 72 h. IL-1 alpha (0.3-10 ng ml-1) and IFN-gamma (10-300 u ml-1) in combination induced a concentration-dependent expression of iNOS mRNA at 24 h. 7 Pretreatment with cycloheximide before IL-1 alpha/IFN-gamma stimulation reduced nitrite levels to basal values. These data suggest that the IL-1 alpha/IFN-gamma-induced nitrite production by HT-29 cells is dependent on de novo protein synthesis, probably the iNOS enzyme. 8 The addition of TNF-alpha produced a significant (P < 0.001) 3 fold increase of IL-1 alpha/IFN-gamma-induced nitrite generation. In marked contrast the presence of TNF-alpha had no effect on IL-1 alpha/IFN-gamma-induced iNOS mRNA expression by HT-29 cells. These findings suggest that the up-regulation by TNF-alpha of IL-1 alpha/IFN-gamma-induced nitrite generation is at the post-transcriptional level. 9 These data suggest that pro-inflammatory cytokines induce NO production in colonic epithelial cells probably due to the induction of iNOS and these cells may be a major source of NO generation in inflammatory bowel disease.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Andoh A., Fujiyama Y., Bamba T., Hosoda S. Differential cytokine regulation of complement C3, C4, and factor B synthesis in human intestinal epithelial cell line, Caco-2. J Immunol. 1993 Oct 15;151(8):4239–4247. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Asano K., Chee C. B., Gaston B., Lilly C. M., Gerard C., Drazen J. M., Stamler J. S. Constitutive and inducible nitric oxide synthase gene expression, regulation, and activity in human lung epithelial cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Oct 11;91(21):10089–10093. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.21.10089. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boughton-Smith N. K., Evans S. M., Hawkey C. J., Cole A. T., Balsitis M., Whittle B. J., Moncada S. Nitric oxide synthase activity in ulcerative colitis and Crohn's disease. Lancet. 1993 Aug 7;342(8867):338–340. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(93)91476-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boughton-Smith N. K. Pathological and therapeutic implications for nitric oxide in inflammatory bowel disease. J R Soc Med. 1994 Jun;87(6):312–314. doi: 10.1177/014107689408700602. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chantret I., Barbat A., Dussaulx E., Brattain M. G., Zweibaum A. Epithelial polarity, villin expression, and enterocytic differentiation of cultured human colon carcinoma cells: a survey of twenty cell lines. Cancer Res. 1988 Apr 1;48(7):1936–1942. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Charles I. G., Palmer R. M., Hickery M. S., Bayliss M. T., Chubb A. P., Hall V. S., Moss D. W., Moncada S. Cloning, characterization, and expression of a cDNA encoding an inducible nitric oxide synthase from the human chondrocyte. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Dec 1;90(23):11419–11423. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.23.11419. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drapier J. C., Hibbs J. B., Jr Murine cytotoxic activated macrophages inhibit aconitase in tumor cells. Inhibition involves the iron-sulfur prosthetic group and is reversible. J Clin Invest. 1986 Sep;78(3):790–797. doi: 10.1172/JCI112642. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eckmann L., Jung H. C., Schürer-Maly C., Panja A., Morzycka-Wroblewska E., Kagnoff M. F. Differential cytokine expression by human intestinal epithelial cell lines: regulated expression of interleukin 8. Gastroenterology. 1993 Dec;105(6):1689–1697. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(93)91064-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geller D. A., Lowenstein C. J., Shapiro R. A., Nussler A. K., Di Silvio M., Wang S. C., Nakayama D. K., Simmons R. L., Snyder S. H., Billiar T. R. Molecular cloning and expression of inducible nitric oxide synthase from human hepatocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Apr 15;90(8):3491–3495. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.8.3491. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hata F., Ishii T., Kanada A., Yamano N., Kataoka T., Takeuchi T., Yagasaki O. Essential role of nitric oxide in descending inhibition in the rat proximal colon. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1990 Nov 15;172(3):1400–1406. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(90)91605-r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hultén L., Lindhagen J., Lundgren O., Fasth S., Ahrén C. Regional intestinal blood flow in ulcerative colitis and Crohn's disease. Gastroenterology. 1977 Mar;72(3):388–396. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Junquero D. C., Scott-Burden T., Schini V. B., Vanhoutte P. M. Inhibition of cytokine-induced nitric oxide production by transforming growth factor-beta 1 in human smooth muscle cells. J Physiol. 1992 Aug;454:451–465. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1992.sp019273. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karanjia N. D., Widdison A. L., Lutrin F. J., Reber H. A. Dopamine in models of alcoholic acute pancreatitis. Gut. 1994 Apr;35(4):547–551. doi: 10.1136/gut.35.4.547. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kwon N. S., Stuehr D. J., Nathan C. F. Inhibition of tumor cell ribonucleotide reductase by macrophage-derived nitric oxide. J Exp Med. 1991 Oct 1;174(4):761–767. doi: 10.1084/jem.174.4.761. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee S. C., Dickson D. W., Liu W., Brosnan C. F. Induction of nitric oxide synthase activity in human astrocytes by interleukin-1 beta and interferon-gamma. J Neuroimmunol. 1993 Jul;46(1-2):19–24. doi: 10.1016/0165-5728(93)90229-r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lichtman S. N., Sartor R. B. Examining the role of inflammatory cytokines in chronic inflammatory bowel disease. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 1993 Apr;16(3):239–240. doi: 10.1097/00005176-199304000-00002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacNaughton W. K. Nitric oxide-donating compounds stimulate electrolyte transport in the guinea pig intestine in vitro. Life Sci. 1993;53(7):585–593. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(93)90716-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maier R., Bilbe G., Rediske J., Lotz M. Inducible nitric oxide synthase from human articular chondrocytes: cDNA cloning and analysis of mRNA expression. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1994 Sep 21;1208(1):145–150. doi: 10.1016/0167-4838(94)90171-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mayer L., Eisenhardt D., Salomon P., Bauer W., Plous R., Piccinini L. Expression of class II molecules on intestinal epithelial cells in humans. Differences between normal and inflammatory bowel disease. Gastroenterology. 1991 Jan;100(1):3–12. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(91)90575-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKay D. M., Perdue M. H. Intestinal epithelial function: the case for immunophysiological regulation. Cells and mediators (1). Dig Dis Sci. 1993 Aug;38(8):1377–1387. doi: 10.1007/BF01308592. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKay D. M., Perdue M. H. Intestinal epithelial function: the case for immunophysiological regulation. Implications for disease (2). Dig Dis Sci. 1993 Sep;38(9):1735–1745. doi: 10.1007/BF01303185. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michel T., Li G. K., Busconi L. Phosphorylation and subcellular translocation of endothelial nitric oxide synthase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Jul 1;90(13):6252–6256. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.13.6252. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Middleton S. J., Shorthouse M., Hunter J. O. Increased nitric oxide synthesis in ulcerative colitis. Lancet. 1993 Feb 20;341(8843):465–466. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(93)90211-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Middleton S. J., Shorthouse M., Hunter J. O. Relaxation of distal colonic circular smooth muscle by nitric oxide derived from human leucocytes. Gut. 1993 Jun;34(6):814–817. doi: 10.1136/gut.34.6.814. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Misko T. P., Schilling R. J., Salvemini D., Moore W. M., Currie M. G. A fluorometric assay for the measurement of nitrite in biological samples. Anal Biochem. 1993 Oct;214(1):11–16. doi: 10.1006/abio.1993.1449. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moncada S., Higgs A. The L-arginine-nitric oxide pathway. N Engl J Med. 1993 Dec 30;329(27):2002–2012. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199312303292706. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moncada S., Palmer R. M., Higgs E. A. Nitric oxide: physiology, pathophysiology, and pharmacology. Pharmacol Rev. 1991 Jun;43(2):109–142. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakane M., Schmidt H. H., Pollock J. S., Förstermann U., Murad F. Cloned human brain nitric oxide synthase is highly expressed in skeletal muscle. FEBS Lett. 1993 Jan 25;316(2):175–180. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(93)81210-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakayama I., Kawahara Y., Tsuda T., Okuda M., Yokoyama M. Angiotensin II inhibits cytokine-stimulated inducible nitric oxide synthase expression in vascular smooth muscle cells. J Biol Chem. 1994 Apr 15;269(15):11628–11633. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nathan C. Nitric oxide as a secretory product of mammalian cells. FASEB J. 1992 Sep;6(12):3051–3064. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nichols K., Staines W., Krantis A. Nitric oxide synthase distribution in the rat intestine: a histochemical analysis. Gastroenterology. 1993 Dec;105(6):1651–1661. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(93)91060-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicolson A. G., Haites N. E., McKay N. G., Wilson H. M., MacLeod A. M., Benjamin N. Induction of nitric oxide synthase in human mesangial cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1993 Jun 30;193(3):1269–1274. doi: 10.1006/bbrc.1993.1762. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nussler A. K., Billiar T. R. Inflammation, immunoregulation, and inducible nitric oxide synthase. J Leukoc Biol. 1993 Aug;54(2):171–178. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nussler A. K., Di Silvio M., Billiar T. R., Hoffman R. A., Geller D. A., Selby R., Madariaga J., Simmons R. L. Stimulation of the nitric oxide synthase pathway in human hepatocytes by cytokines and endotoxin. J Exp Med. 1992 Jul 1;176(1):261–264. doi: 10.1084/jem.176.1.261. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palmer R. M., Hickery M. S., Charles I. G., Moncada S., Bayliss M. T. Induction of nitric oxide synthase in human chondrocytes. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1993 May 28;193(1):398–405. doi: 10.1006/bbrc.1993.1637. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reiling N., Ulmer A. J., Duchrow M., Ernst M., Flad H. D., Hauschildt S. Nitric oxide synthase: mRNA expression of different isoforms in human monocytes/macrophages. Eur J Immunol. 1994 Aug;24(8):1941–1944. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830240836. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robbins R. A., Barnes P. J., Springall D. R., Warren J. B., Kwon O. J., Buttery L. D., Wilson A. J., Geller D. A., Polak J. M. Expression of inducible nitric oxide in human lung epithelial cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1994 Aug 30;203(1):209–218. doi: 10.1006/bbrc.1994.2169. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sartor R. B. Cytokines in intestinal inflammation: pathophysiological and clinical considerations. Gastroenterology. 1994 Feb;106(2):533–539. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(94)90614-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schuerer-Maly C. C., Eckmann L., Kagnoff M. F., Falco M. T., Maly F. E. Colonic epithelial cell lines as a source of interleukin-8: stimulation by inflammatory cytokines and bacterial lipopolysaccharide. Immunology. 1994 Jan;81(1):85–91. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strieter R. M., Kunkel S. L., Showell H. J., Remick D. G., Phan S. H., Ward P. A., Marks R. M. Endothelial cell gene expression of a neutrophil chemotactic factor by TNF-alpha, LPS, and IL-1 beta. Science. 1989 Mar 17;243(4897):1467–1469. doi: 10.1126/science.2648570. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stuehr D. J., Griffith O. W. Mammalian nitric oxide synthases. Adv Enzymol Relat Areas Mol Biol. 1992;65:287–346. doi: 10.1002/9780470123119.ch8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vallance P., Leone A., Calver A., Collier J., Moncada S. Accumulation of an endogenous inhibitor of nitric oxide synthesis in chronic renal failure. Lancet. 1992 Mar 7;339(8793):572–575. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(92)90865-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]