Abstract
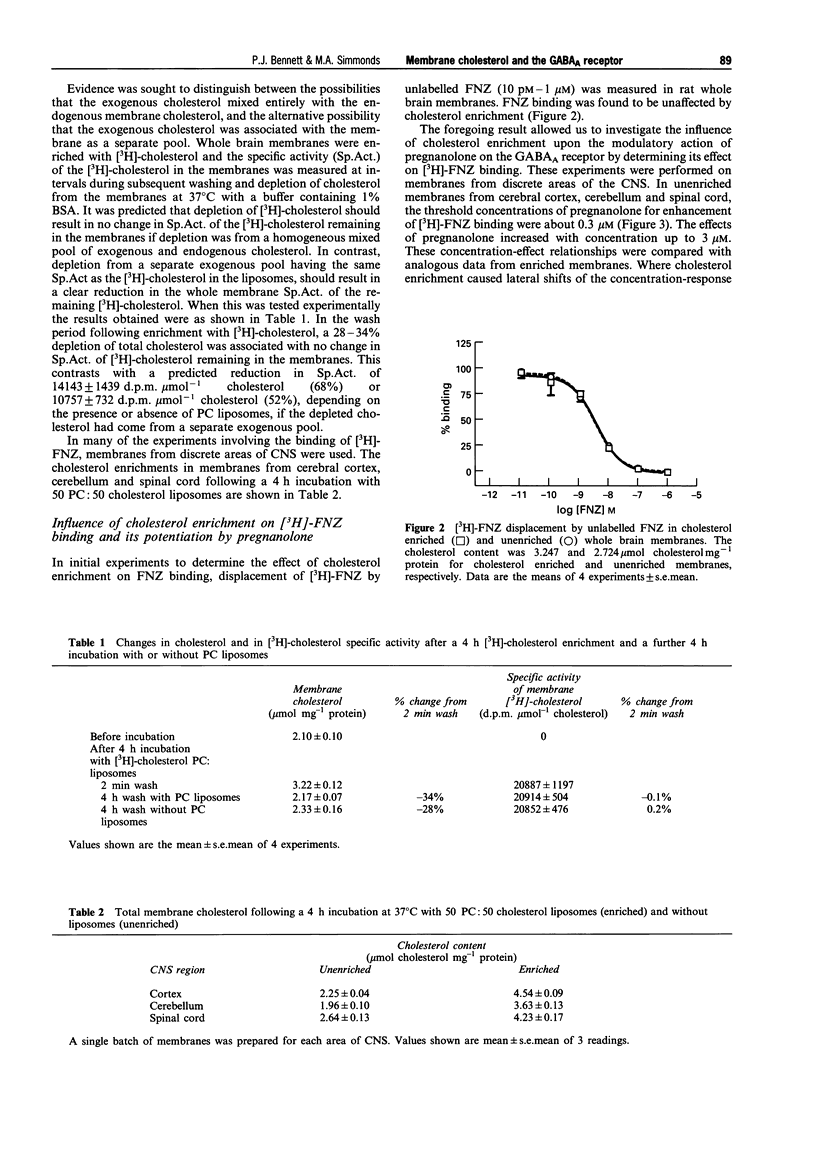
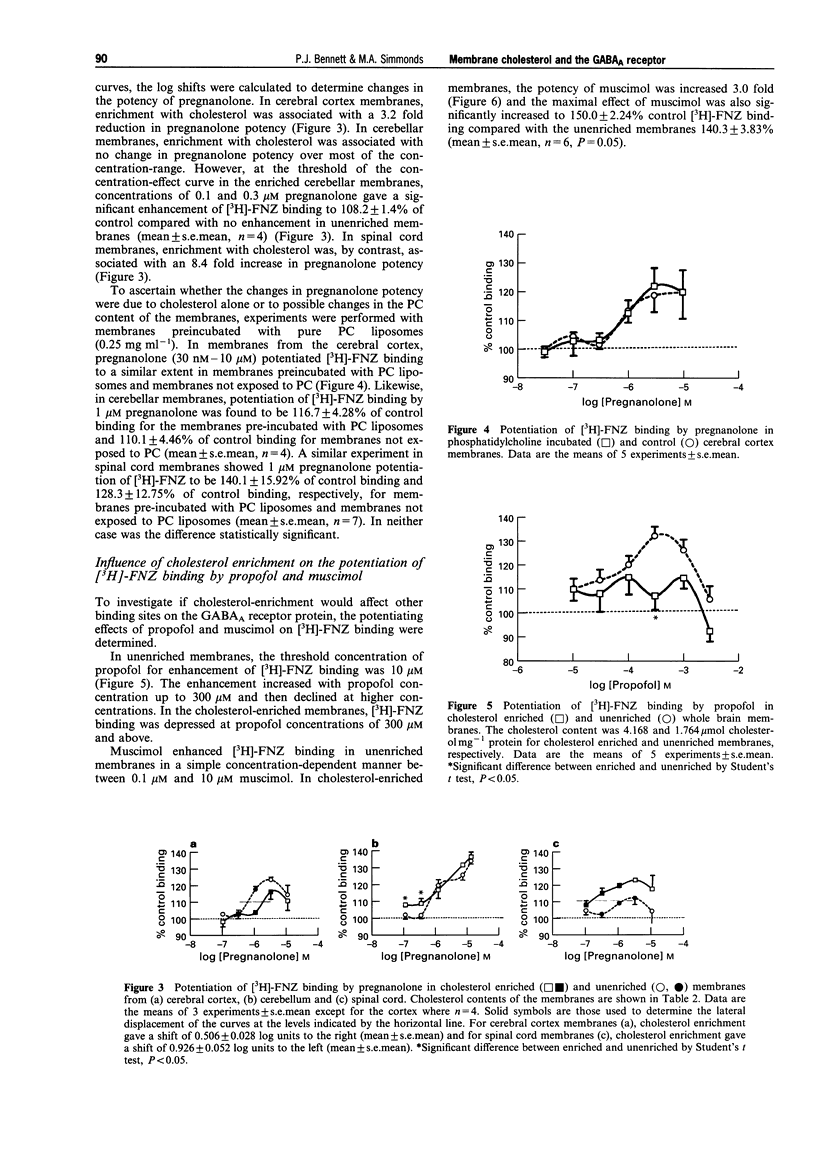
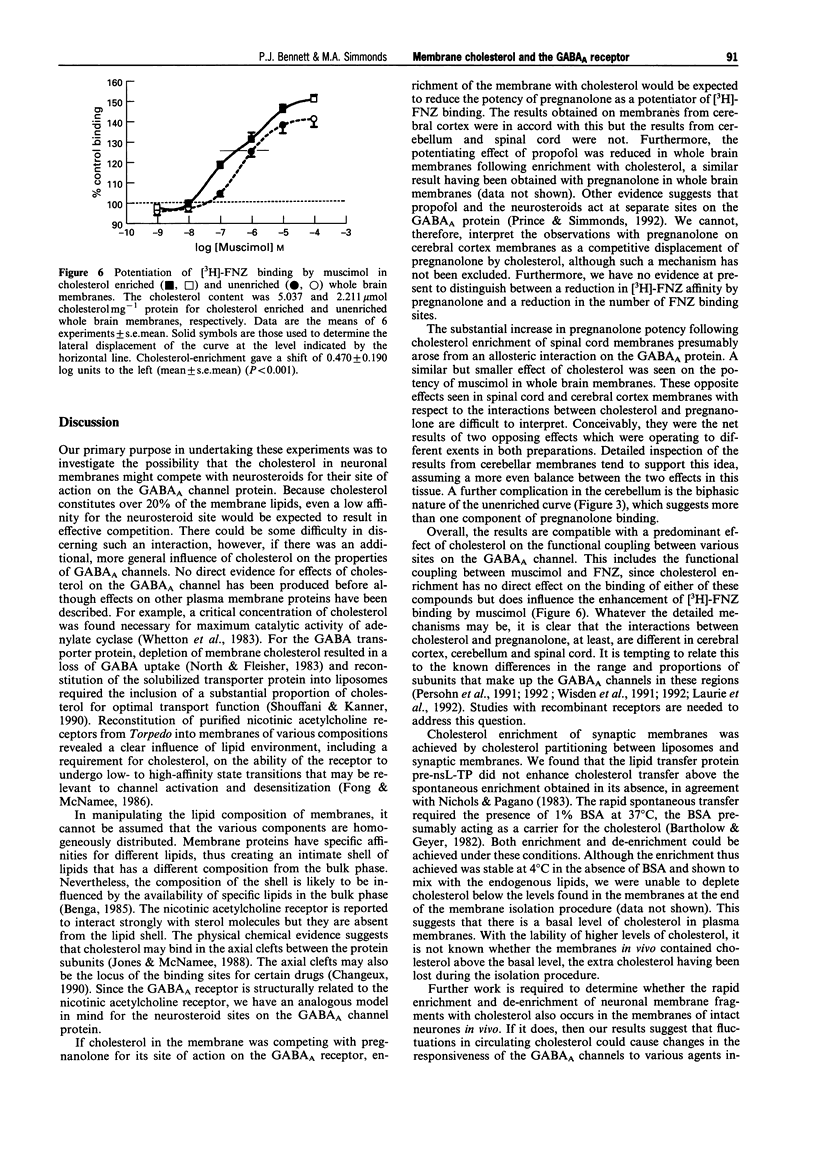
1. Neurosteroids such as pregnanolone have been established as potent modulators of the GABAA receptor in both electrophysiological and binding studies. Since cholesterol is present in substantial amounts in the neuronal membranes, we have sought evidence for possible interactions of cholesterol with the neurosteroid site and more generally, with the GABAA channel. 2. Synaptosomal membranes were prepared from rat whole brain, cerebral cortex, cerebellum and spinal cord. These membranes were enriched with cholesterol to about double the original level by incubation with liposomes comprised of 50 phosphatidylcholine: 50 cholesterol in the presence of 1% BSA. The additional cholesterol formed a homogeneous mixture with the endogenous cholesterol. 3. The effects of cholesterol and modulatory drugs on the GABAA channel were assessed from the changes induced in [3H]-flunitrazepam (FNZ) binding. Cholesterol enrichment did not affect FNZ binding itself; however, the enhancement of [3H]-FNZ binding by pregnanolone was affected. In membranes from cerebral cortex, the potency of pregnanolone was reduced by a factor of 3.2 following cholesterol enrichment. By contrast, in membranes from spinal cord, the potency of pregnanolone was increased by a factor of 8.4 following cholesterol enrichment. In membranes from cerebellum, there was little overall change in pregnanolone potency although the effects of threshold concentrations were increased. 4. The enhancement of [3H]-FNZ binding by propofol in whole brain membranes was reduced in cholesterol-enriched membranes, similar to the effects of pregnanolone. Experiments with muscimol resulted in an increase in its potency as a potentiator of [3H]-FNZ binding, following cholesterol enrichment. 5. These results provide little evidence for a selective competition between cholesterol and pregnanolone at its binding site. Rather, they suggest an influence of membrane cholesterol on the functional coupling between the benzodiazepine site and the other specific drug sites on the GABAA channel. The detailed pattern of influence depended upon the region of CNS and may be related to the subunit composition of the GABAA channels present.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bartholow L. C., Geyer R. P. Influence of phospholipid structure on sterol efflux induced by albumin-phospholipid complexes. Biochemistry. 1982 Mar 16;21(6):1271–1273. doi: 10.1021/bi00535a025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Changeux J. P. The TiPS lecture. The nicotinic acetylcholine receptor: an allosteric protein prototype of ligand-gated ion channels. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 1990 Dec;11(12):485–492. doi: 10.1016/0165-6147(90)90049-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fong T. M., McNamee M. G. Correlation between acetylcholine receptor function and structural properties of membranes. Biochemistry. 1986 Feb 25;25(4):830–840. doi: 10.1021/bi00352a015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Franks N. P., Lieb W. R. Molecular and cellular mechanisms of general anaesthesia. Nature. 1994 Feb 17;367(6464):607–614. doi: 10.1038/367607a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones O. T., McNamee M. G. Annular and nonannular binding sites for cholesterol associated with the nicotinic acetylcholine receptor. Biochemistry. 1988 Apr 5;27(7):2364–2374. doi: 10.1021/bi00407a018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Langley M. S., Heel R. C. Propofol. A review of its pharmacodynamic and pharmacokinetic properties and use as an intravenous anaesthetic. Drugs. 1988 Apr;35(4):334–372. doi: 10.2165/00003495-198835040-00002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laurie D. J., Seeburg P. H., Wisden W. The distribution of 13 GABAA receptor subunit mRNAs in the rat brain. II. Olfactory bulb and cerebellum. J Neurosci. 1992 Mar;12(3):1063–1076. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.12-03-01063.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nayeem N., Green T. P., Martin I. L., Barnard E. A. Quaternary structure of the native GABAA receptor determined by electron microscopic image analysis. J Neurochem. 1994 Feb;62(2):815–818. doi: 10.1046/j.1471-4159.1994.62020815.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nichols J. W., Pagano R. E. Resonance energy transfer assay of protein-mediated lipid transfer between vesicles. J Biol Chem. 1983 May 10;258(9):5368–5371. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- North P., Fleischer S. Alteration of synaptic membrane cholesterol/phospholipid ratio using a lipid transfer protein. Effect on gamma-aminobutyric acid uptake. J Biol Chem. 1983 Jan 25;258(2):1242–1253. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ossendorp B. C., Geijtenbeek T. B., Wirtz K. W. The precursor form of the rat liver non-specific lipid-transfer protein, expressed in Escherichia coli, has lipid transfer activity. FEBS Lett. 1992 Jan 20;296(2):179–183. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(92)80374-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paul S. M., Purdy R. H. Neuroactive steroids. FASEB J. 1992 Mar;6(6):2311–2322. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Persohn E., Malherbe P., Richards J. G. Comparative molecular neuroanatomy of cloned GABAA receptor subunits in the rat CNS. J Comp Neurol. 1992 Dec 8;326(2):193–216. doi: 10.1002/cne.903260204. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Persohn E., Malherbe P., Richards J. G. In situ hybridization histochemistry reveals a diversity of GABAA receptor subunit mRNAs in neurons of the rat spinal cord and dorsal root ganglia. Neuroscience. 1991;42(2):497–507. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(91)90392-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prince R. J., Simmonds M. A. Propofol potentiates the binding of [3H]flunitrazepam to the GABAA receptor complex. Brain Res. 1992 Nov 20;596(1-2):238–242. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(92)91553-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Puia G., Santi M. R., Vicini S., Pritchett D. B., Purdy R. H., Paul S. M., Seeburg P. H., Costa E. Neurosteroids act on recombinant human GABAA receptors. Neuron. 1990 May;4(5):759–765. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(90)90202-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schofield P. R., Darlison M. G., Fujita N., Burt D. R., Stephenson F. A., Rodriguez H., Rhee L. M., Ramachandran J., Reale V., Glencorse T. A. Sequence and functional expression of the GABA A receptor shows a ligand-gated receptor super-family. Nature. 1987 Jul 16;328(6127):221–227. doi: 10.1038/328221a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shouffani A., Kanner B. I. Cholesterol is required for the reconstruction of the sodium- and chloride-coupled, gamma-aminobutyric acid transporter from rat brain. J Biol Chem. 1990 Apr 15;265(11):6002–6008. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sieghart W. GABAA receptors: ligand-gated Cl- ion channels modulated by multiple drug-binding sites. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 1992 Dec;13(12):446–450. doi: 10.1016/0165-6147(92)90142-s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sieghart W. Multiplicity of GABAA--benzodiazepine receptors. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 1989 Oct;10(10):407–411. doi: 10.1016/0165-6147(89)90189-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turner J. P., Simmonds M. A. Modulation of the GABAA receptor complex by steroids in slices of rat cuneate nucleus. Br J Pharmacol. 1989 Feb;96(2):409–417. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1989.tb11832.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whetton A. D., Gordon L. M., Houslay M. D. Adenylate cyclase is inhibited upon depletion of plasma-membrane cholesterol. Biochem J. 1983 May 15;212(2):331–338. doi: 10.1042/bj2120331. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wisden W., Gundlach A. L., Barnard E. A., Seeburg P. H., Hunt S. P. Distribution of GABAA receptor subunit mRNAs in rat lumbar spinal cord. Brain Res Mol Brain Res. 1991 May;10(2):179–183. doi: 10.1016/0169-328x(91)90109-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wisden W., Laurie D. J., Monyer H., Seeburg P. H. The distribution of 13 GABAA receptor subunit mRNAs in the rat brain. I. Telencephalon, diencephalon, mesencephalon. J Neurosci. 1992 Mar;12(3):1040–1062. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.12-03-01040.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zukin S. R., Young A. B., Snyder S. H. Gamma-aminobutyric acid binding to receptor sites in the rat central nervous system. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Dec;71(12):4802–4807. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.12.4802. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


