Abstract
1. In the present study, the ability of the 5-hydroxytryptamine, receptor (5-HT4 receptor) to modulate the release of 5-HT in the hippocampus of freely-moving rats was investigated by the in vivo microdialysis technique. 2. The 5-HT4 receptor agonist, renzapride (1.0-100 microM, administered via the microdialysis probe) increased extracellular hippocampal levels of 5-HT in concentration-dependent manner (approximately 200% maximal increase). The ability of renzapride (100 microM, administered via the microdialysis probe) to elevate extracellular levels of 5-HT remained in the presence of the selective 5-HT reuptake blocker, paroxetine (1.0 microM, administered via the microdialysis probe). Furthermore, another 5-HT4 receptor agonist 5-methoxytryptamine (5-MeOT; 10 microM, administered via the microdialysis probe, in the presence of the non-5-HT4 5-HT receptor antagonists pindolol (10 microM) and methysergide (10 microM)) maximally elevated extracellular levels of 5-HT by approximately 450% in the rat hippocampus. The elevation of extracellular 5-HT levels induced by either renzapride (100 microM) or 5-MeOT (10 microM) was completely prevented by combined administration of the selective 5-HT4 receptor antagonist, GR113808 (100 nM, administered via the microdialysis probe). GR113808 (100 nM, administered via the microdialysis probe) administered alone, however, reduced extracellular hippocampal 5-HT levels by some 60%. 3. Systemic administration of the 5-HT1A receptor agonist, 8-OH-DPAT (0.1 mg kg-1, s.c.) reduced extracellular levels of 5-HT in the rat hippocampus by approximately 40%. Prior administration of 8-OH-DPAT (0.1 mg kg-1, s.c.), with an associated reduction of extracellular hippocampal 5-HT levels by approximately 40-50%, however, failed to prevent a subsequent elevation of extracellular levels of 5-HT induced by renzapride (100 microM, administered via the microdialysis probe). 4. Systemic administration of the 5-HT4 receptor agonist, renzapride (0.25 and 1.0 mg kg-1, i.p.) increased extracellular levels of 5-HT in the hippocampus in a dose-dependent manner. The higher dose of renzapride increasing extracellular 5-HT levels by some 200%. The selective 5-HT4 receptor antagonist, GR125487D (1.0-100 micrograms kg-1, i.p.) caused a dose-dependent reduction in extracellular levels of 5-HT in the hippocampus (maximally approximately 80% reduction). Prior administration of GR125487D (10 micrograms kg-1, i.p.) prevented the elevation of extracellular levels of 5-HT induced by renzapride (1.0 mg kg-1, i.p.). 5. In conclusion, the present study provides evidence that activation of the 5-HT4 receptor facilitates 5-HT release in the rat hippocampus in vivo.
Full text
PDF
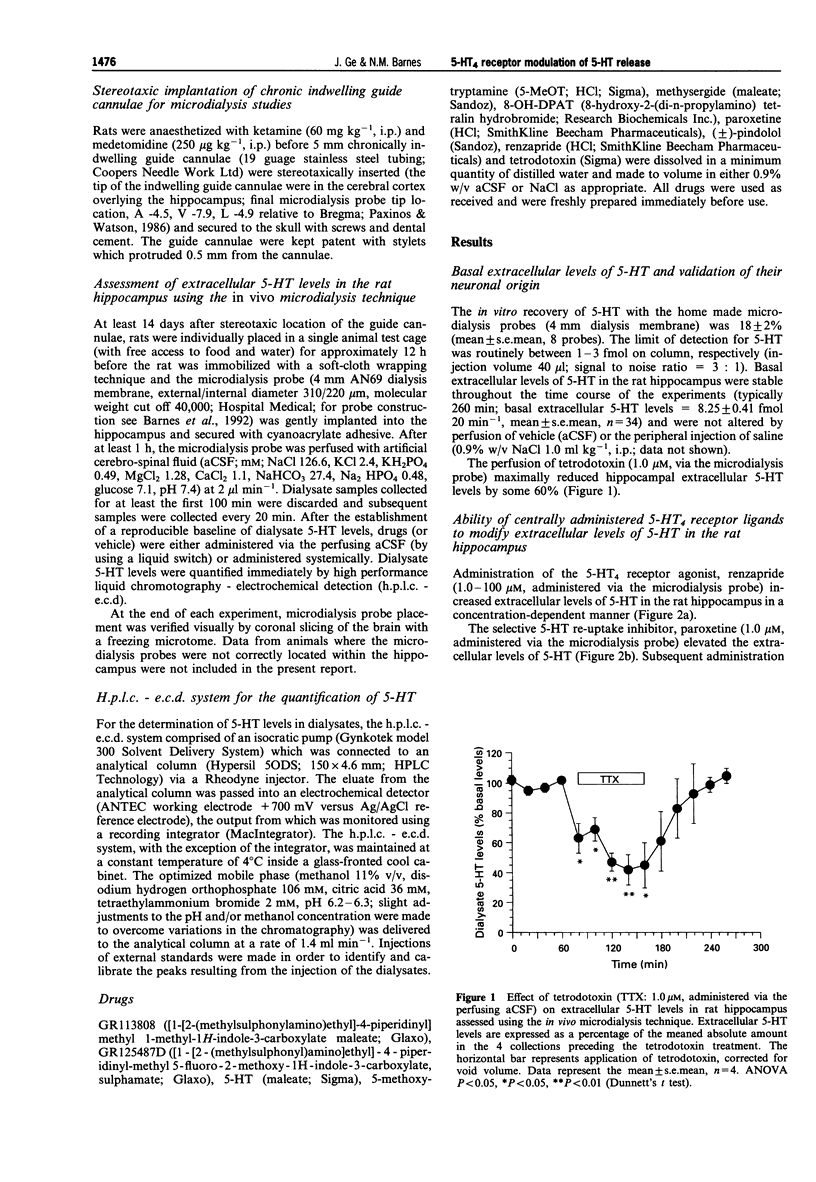
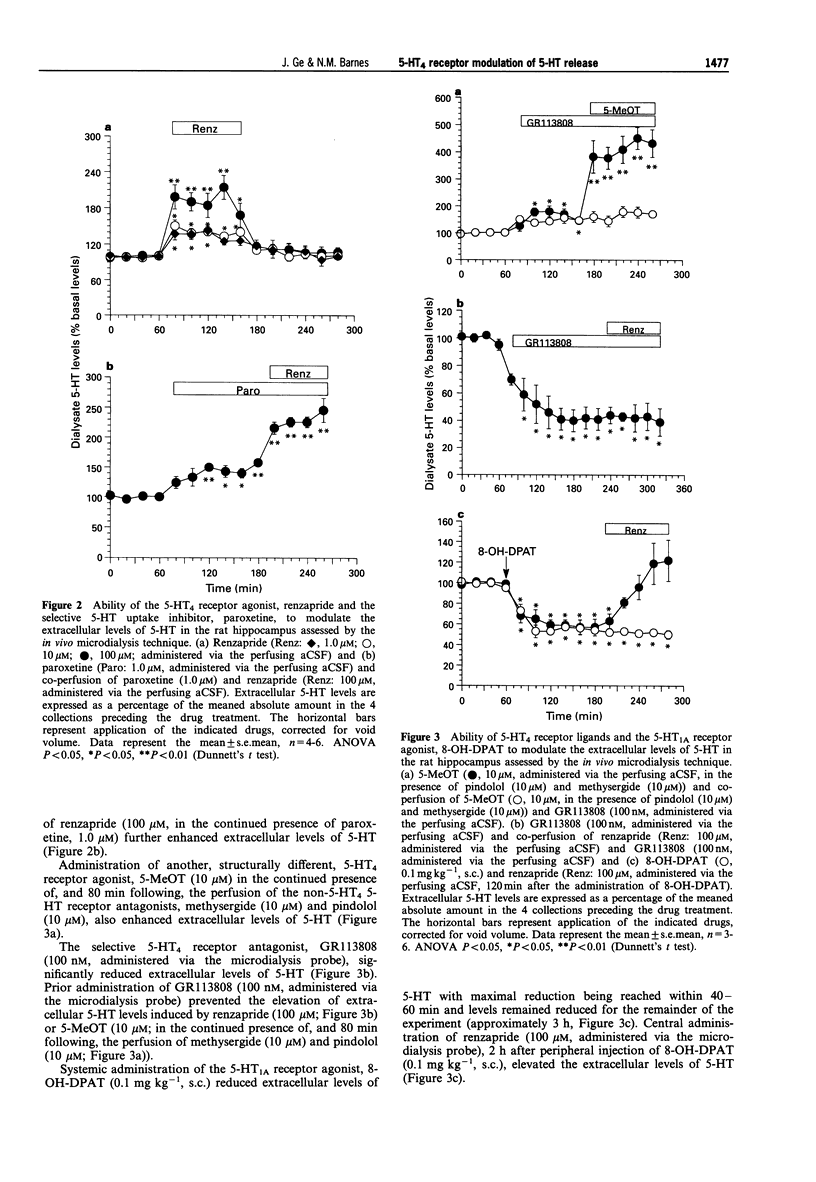
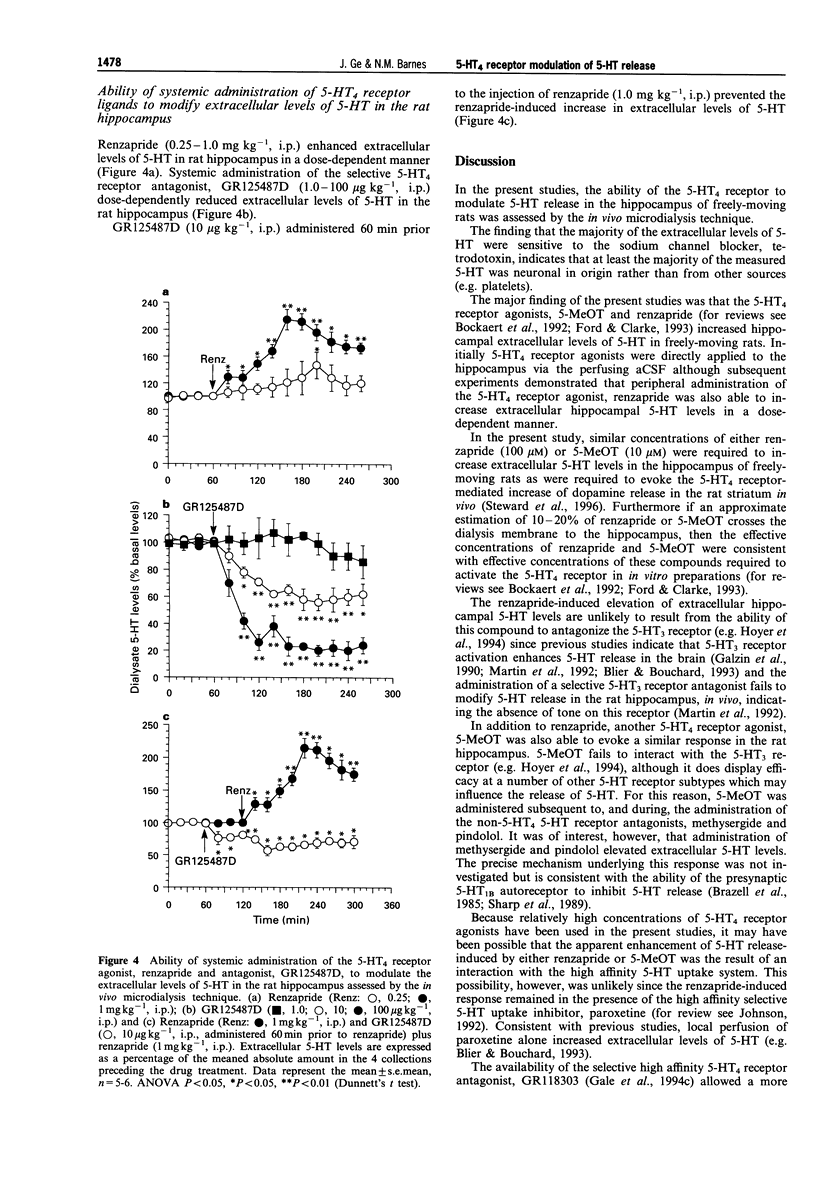


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Andrade R., Chaput Y. 5-Hydroxytryptamine4-like receptors mediate the slow excitatory response to serotonin in the rat hippocampus. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1991 Jun;257(3):930–937. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Auerbach S. B., Minzenberg M. J., Wilkinson L. O. Extracellular serotonin and 5-hydroxyindoleacetic acid in hypothalamus of the unanesthetized rat measured by in vivo dialysis coupled to high-performance liquid chromatography with electrochemical detection: dialysate serotonin reflects neuronal release. Brain Res. 1989 Oct 16;499(2):281–290. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(89)90776-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barnes N. M., Cheng C. H., Costall B., Ge J., Naylor R. J. Differential modulation of extracellular levels of 5-hydroxytryptamine in the rat frontal cortex by (R)- and (S)-zacopride. Br J Pharmacol. 1992 Sep;107(1):233–239. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1992.tb14492.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baxter G. S., Craig D. A., Clarke D. E. 5-Hydroxytryptamine4 receptors mediate relaxation of the rat oesophageal tunica muscularis mucosae. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1991 May;343(5):439–446. doi: 10.1007/BF00169544. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blier P., Bouchard C. Functional characterization of a 5-HT3 receptor which modulates the release of 5-HT in the guinea-pig brain. Br J Pharmacol. 1993 Jan;108(1):13–22. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1993.tb13433.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bockaert J., Fozard J. R., Dumuis A., Clarke D. E. The 5-HT4 receptor: a place in the sun. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 1992 Apr;13(4):141–145. doi: 10.1016/0165-6147(92)90051-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bockaert J., Sebben M., Dumuis A. Pharmacological characterization of 5-hydroxytryptamine4(5-HT4) receptors positively coupled to adenylate cyclase in adult guinea pig hippocampal membranes: effect of substituted benzamide derivatives. Mol Pharmacol. 1990 Mar;37(3):408–411. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brazell M. P., Marsden C. A., Nisbet A. P., Routledge C. The 5-HT1 receptor agonist RU-24969 decreases 5-hydroxytryptamine (5-HT) release and metabolism in the rat frontal cortex in vitro and in vivo. Br J Pharmacol. 1985 Sep;86(1):209–216. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1985.tb09451.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Butler A., Hill J. M., Ireland S. J., Jordan C. C., Tyers M. B. Pharmacological properties of GR38032F, a novel antagonist at 5-HT3 receptors. Br J Pharmacol. 1988 Jun;94(2):397–412. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1988.tb11542.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chaput Y., Araneda R. C., Andrade R. Pharmacological and functional analysis of a novel serotonin receptor in the rat hippocampus. Eur J Pharmacol. 1990 Jul 17;182(3):441–456. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(90)90041-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Consolo S., Arnaboldi S., Giorgi S., Russi G., Ladinsky H. 5-HT4 receptor stimulation facilitates acetylcholine release in rat frontal cortex. Neuroreport. 1994 Jun 2;5(10):1230–1232. doi: 10.1097/00001756-199406020-00018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Craig D. A., Clarke D. E. Pharmacological characterization of a neuronal receptor for 5-hydroxytryptamine in guinea pig ileum with properties similar to the 5-hydroxytryptamine receptor. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1990 Mar;252(3):1378–1386. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dumuis A., Bouhelal R., Sebben M., Cory R., Bockaert J. A nonclassical 5-hydroxytryptamine receptor positively coupled with adenylate cyclase in the central nervous system. Mol Pharmacol. 1988 Dec;34(6):880–887. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dumuis A., Sebben M., Bockaert J. The gastrointestinal prokinetic benzamide derivatives are agonists at the non-classical 5-HT receptor (5-HT4) positively coupled to adenylate cyclase in neurons. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1989 Oct;340(4):403–410. doi: 10.1007/BF00167041. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eglen R. M., Swank S. R., Walsh L. K., Whiting R. L. Characterization of 5-HT3 and 'atypical' 5-HT receptors mediating guinea-pig ileal contractions in vitro. Br J Pharmacol. 1990 Nov;101(3):513–520. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1990.tb14113.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elswood C. J., Bunce K. T., Humphrey P. P. Identification of putative 5-HT4 receptors in guinea-pig ascending colon. Eur J Pharmacol. 1991 Apr 17;196(2):149–155. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(91)90421-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fagni L., Dumuis A., Sebben M., Bockaert J. The 5-HT4 receptor subtype inhibits K+ current in colliculi neurones via activation of a cyclic AMP-dependent protein kinase. Br J Pharmacol. 1992 Apr;105(4):973–979. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1992.tb09087.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ford A. P., Clarke D. E. The 5-HT4 receptor. Med Res Rev. 1993 Nov;13(6):633–662. doi: 10.1002/med.2610130603. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gale J. D., Grossman C. J., Whitehead J. W., Oxford A. W., Bunce K. T., Humphrey P. P. GR113808: a novel, selective antagonist with high affinity at the 5-HT4 receptor. Br J Pharmacol. 1994 Jan;111(1):332–338. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1994.tb14064.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerald C., Adham N., Kao H. T., Olsen M. A., Laz T. M., Schechter L. E., Bard J. A., Vaysse P. J., Hartig P. R., Branchek T. A. The 5-HT4 receptor: molecular cloning and pharmacological characterization of two splice variants. EMBO J. 1995 Jun 15;14(12):2806–2815. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1995.tb07280.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grossman C. J., Kilpatrick G. J., Bunce K. T. Development of a radioligand binding assay for 5-HT4 receptors in guinea-pig and rat brain. Br J Pharmacol. 1993 Jul;109(3):618–624. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1993.tb13617.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoyer D., Clarke D. E., Fozard J. R., Hartig P. R., Martin G. R., Mylecharane E. J., Saxena P. R., Humphrey P. P. International Union of Pharmacology classification of receptors for 5-hydroxytryptamine (Serotonin). Pharmacol Rev. 1994 Jun;46(2):157–203. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hutson P. H., Sarna G. S., O'Connell M. T., Curzon G. Hippocampal 5-HT synthesis and release in vivo is decreased by infusion of 8-OHDPAT into the nucleus raphe dorsalis. Neurosci Lett. 1989 May 22;100(1-3):276–280. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(89)90698-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jakeman L. B., To Z. P., Eglen R. M., Wong E. H., Bonhaus D. W. Quantitative autoradiography of 5-HT4 receptors in brains of three species using two structurally distinct radioligands, [3H]GR113808 and [3H]BIMU-1. Neuropharmacology. 1994 Aug;33(8):1027–1038. doi: 10.1016/0028-3908(94)90162-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson A. M. Paroxetine: a pharmacological review. Int Clin Psychopharmacol. 1992 Jun;6 (Suppl 4):15–24. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lefebvre H., Contesse V., Delarue C., Feuilloley M., Hery F., Grise P., Raynaud G., Verhofstad A. A., Wolf L. M., Vaudry H. Serotonin-induced stimulation of cortisol secretion from human adrenocortical tissue is mediated through activation of a serotonin4 receptor subtype. Neuroscience. 1992;47(4):999–1007. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(92)90047-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin K. F., Hannon S., Phillips I., Heal D. J. Opposing roles for 5-HT1B and 5-HT3 receptors in the control of 5-HT release in rat hippocampus in vivo. Br J Pharmacol. 1992 May;106(1):139–142. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1992.tb14306.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sakurada T., Manome Y., Tan-No K., Sakurada S., Kisara K. The effects of substance P analogues on the scratching, biting and licking response induced by intrathecal injection of N-methyl-D-aspartate in mice. Br J Pharmacol. 1990 Oct;101(2):307–310. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1990.tb12706.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharp T., Bramwell S. R., Grahame-Smith D. G. 5-HT1 agonists reduce 5-hydroxytryptamine release in rat hippocampus in vivo as determined by brain microdialysis. Br J Pharmacol. 1989 Feb;96(2):283–290. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1989.tb11815.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steward L. J., Ge J., Stowe R. L., Brown D. C., Bruton R. K., Stokes P. R., Barnes N. M. Ability of 5-HT4 receptor ligands to modulate rat striatal dopamine release in vitro and in vivo. Br J Pharmacol. 1996 Jan;117(1):55–62. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1996.tb15154.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Torres G. E., Chaput Y., Andrade R. Cyclic AMP and protein kinase A mediate 5-hydroxytryptamine type 4 receptor regulation of calcium-activated potassium current in adult hippocampal neurons. Mol Pharmacol. 1995 Jan;47(1):191–197. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Villalón C. M., den Boer M. O., Heiligers J. P., Saxena P. R. Further characterization, by use of tryptamine and benzamide derivatives, of the putative 5-HT4 receptor mediating tachycardia in the pig. Br J Pharmacol. 1991 Jan;102(1):107–112. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1991.tb12140.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waeber C., Sebben M., Grossman C., Javoy-Agid F., Bockaert J., Dumuis A. [3H]-GR113808 labels 5-HT4 receptors in the human and guinea-pig brain. Neuroreport. 1993 Sep 10;4(11):1239–1242. doi: 10.1097/00001756-199309000-00007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


