Abstract
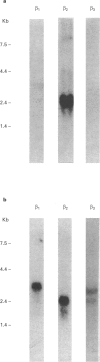
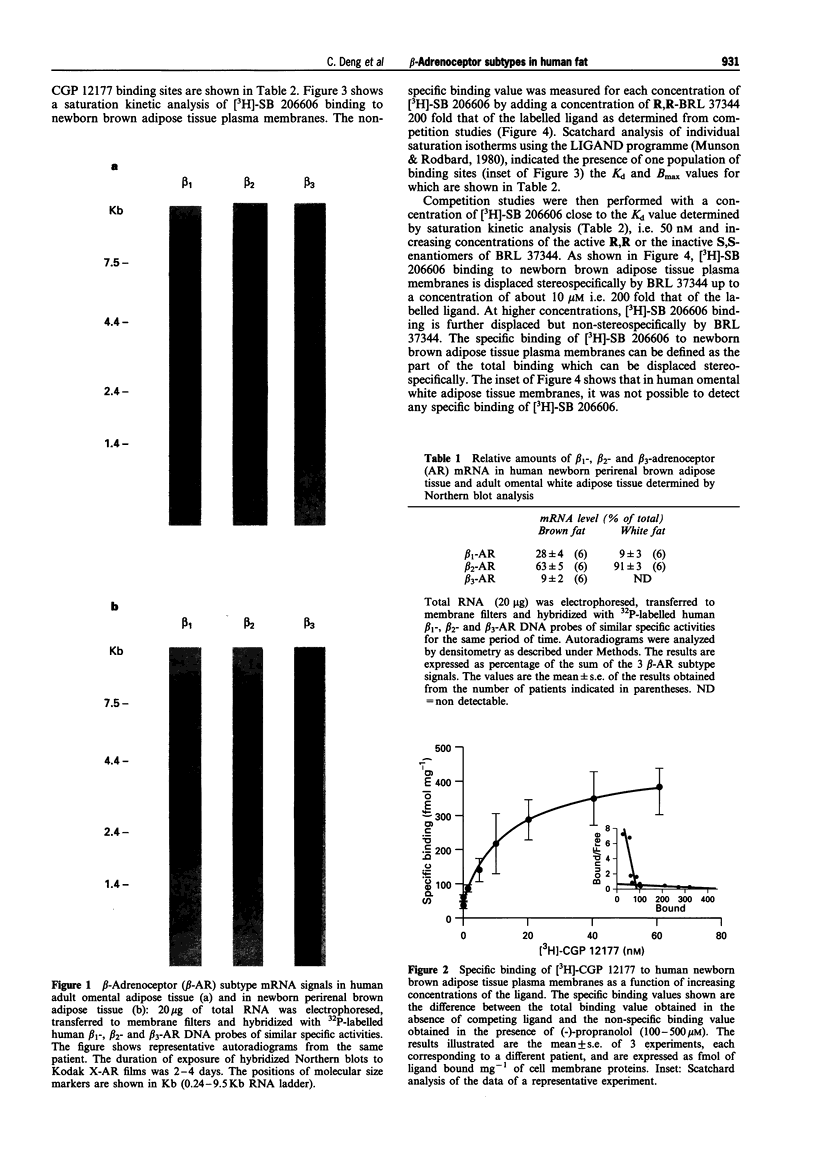
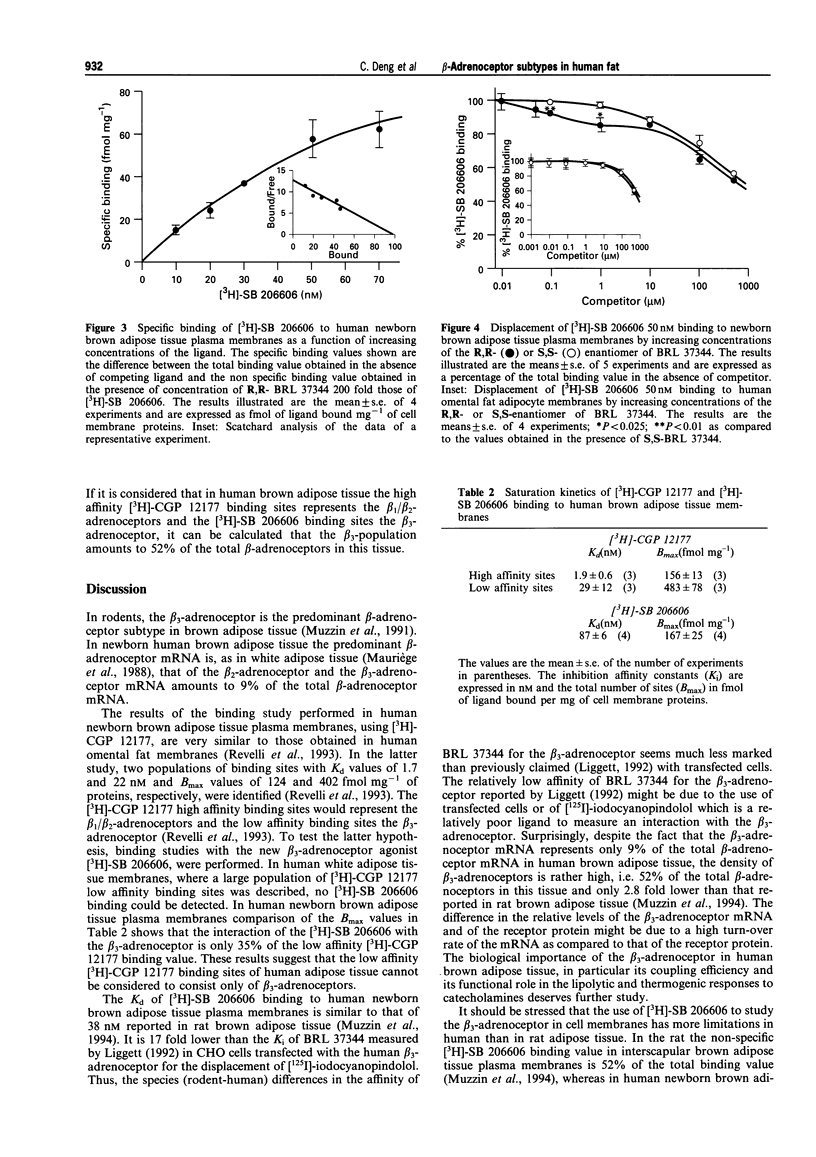
1. The possible existence of a beta 3-adrenoceptor in human brown and white adipose tissues was investigated by mRNA expression and binding studies. 2. The relative amounts of beta 1-, beta 2- and beta 3-adrenoceptor mRNA, as determined by total RNA Northern blot analysis in newborn brown adipose tissue, were 28, 63 and 9% respectively of the total beta-adrenoceptor mRNA. 3. The beta 1/beta 2-adrenoceptors of human brown adipose tissue plasma membranes were characterized using [3H]-CGP 12177 as a ligand. Their Kd and Bmax values were 1.9 nM and 156 fmol mg-1 of membrane proteins, respectively. The beta 3-adrenoceptor was characterized by use of the new specific radioligand [3H]-SB 206606. The binding of this ligand was stereospecifically displaced by the active R,R- or the inactive S,S-enantiomer of BRL 37344 up to a concentration of about 10 microM. The Kd and Bmax values of the brown adipose tissue membrane beta 3-adrenoceptors were 87 nM and 167 fmol mg-1 of proteins, respectively. A low affinity [3H]-CGP 12177 binding site population was also detected in these membranes. 4. In human omental white adipose tissue, no beta 3-adrenoceptor mRNA could be detected in total RNA Northern blots and the beta 1-and beta 2-adrenoceptor mRNAs represented 9 and 91%, respectively of the total beta-adrenoceptor mRNA, and no specific binding of [3H]-SB 206606 could be measured.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arch J. R., Kaumann A. J. Beta 3 and atypical beta-adrenoceptors. Med Res Rev. 1993 Nov;13(6):663–729. doi: 10.1002/med.2610130604. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bensaid M., Kaghad M., Rodriguez M., Le Fur G., Caput D. The rat beta 3-adrenergic receptor gene contains an intron. FEBS Lett. 1993 Mar 8;318(3):223–226. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(93)80516-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Casteilla L., Muzzin P., Revelli J. P., Ricquier D., Giacobino J. P. Expression of beta 1- and beta 3-adrenergic-receptor messages and adenylate cyclase beta-adrenergic response in bovine perirenal adipose tissue during its transformation from brown into white fat. Biochem J. 1994 Jan 1;297(Pt 1):93–97. doi: 10.1042/bj2970093. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chung F. Z., Lentes K. U., Gocayne J., Fitzgerald M., Robinson D., Kerlavage A. R., Fraser C. M., Venter J. C. Cloning and sequence analysis of the human brain beta-adrenergic receptor. Evolutionary relationship to rodent and avian beta-receptors and porcine muscarinic receptors. FEBS Lett. 1987 Jan 26;211(2):200–206. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(87)81436-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Emorine L. J., Marullo S., Briend-Sutren M. M., Patey G., Tate K., Delavier-Klutchko C., Strosberg A. D. Molecular characterization of the human beta 3-adrenergic receptor. Science. 1989 Sep 8;245(4922):1118–1121. doi: 10.1126/science.2570461. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Enocksson S., Shimizu M., Lönnqvist F., Nordenström J., Arner P. Demonstration of an in vivo functional beta 3-adrenoceptor in man. J Clin Invest. 1995 May;95(5):2239–2245. doi: 10.1172/JCI117914. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fève B., Emorine L. J., Lasnier F., Blin N., Baude B., Nahmias C., Strosberg A. D., Pairault J. Atypical beta-adrenergic receptor in 3T3-F442A adipocytes. Pharmacological and molecular relationship with the human beta 3-adrenergic receptor. J Biol Chem. 1991 Oct 25;266(30):20329–20336. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giacobino J. P. Beta 3-adrenoceptor: an update. Eur J Endocrinol. 1995 Apr;132(4):377–385. doi: 10.1530/eje.0.1320377. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giacobino J. P. Subcellular fractionation of brown adipose tissue. J Supramol Struct. 1979;11(4):445–449. doi: 10.1002/jss.400110403. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Granneman J. G., Lahners K. N., Chaudhry A. Characterization of the human beta 3-adrenergic receptor gene. Mol Pharmacol. 1993 Aug;44(2):264–270. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Granneman J. G., Lahners K. N., Chaudhry A. Molecular cloning and expression of the rat beta 3-adrenergic receptor. Mol Pharmacol. 1991 Dec;40(6):895–899. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Granneman J. G., Lahners K. N. Differential adrenergic regulation of beta 1- and beta 3-adrenoreceptor messenger ribonucleic acids in adipose tissues. Endocrinology. 1992 Jan;130(1):109–114. doi: 10.1210/endo.130.1.1309320. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Granneman J. G. Why do adipocytes make the beta 3 adrenergic receptor? Cell Signal. 1995 Jan;7(1):9–15. doi: 10.1016/0898-6568(94)00066-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hollenga C., Brouwer F., Zaagsma J. Relationship between lipolysis and cyclic AMP generation mediated by atypical beta-adrenoceptors in rat adipocytes. Br J Pharmacol. 1991 Mar;102(3):577–580. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1991.tb12215.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krief S., Lönnqvist F., Raimbault S., Baude B., Van Spronsen A., Arner P., Strosberg A. D., Ricquier D., Emorine L. J. Tissue distribution of beta 3-adrenergic receptor mRNA in man. J Clin Invest. 1993 Jan;91(1):344–349. doi: 10.1172/JCI116191. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lai E., Rosen O. M., Rubin C. S. Dexamethasone regulates the beta-adrenergic receptor subtype expressed by 3T3 L1 preadipocytes and adipocytes. J Biol Chem. 1982 Jun 25;257(12):6691–6696. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Langin D., Portillo M. P., Saulnier-Blache J. S., Lafontan M. Coexistence of three beta-adrenoceptor subtypes in white fat cells of various mammalian species. Eur J Pharmacol. 1991 Jul 9;199(3):291–301. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(91)90492-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lehrach H., Diamond D., Wozney J. M., Boedtker H. RNA molecular weight determinations by gel electrophoresis under denaturing conditions, a critical reexamination. Biochemistry. 1977 Oct 18;16(21):4743–4751. doi: 10.1021/bi00640a033. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levin B. E., Sullivan A. C. Beta-1 receptor is the predominant beta-adrenoreceptor on rat brown adipose tissue. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1986 Mar;236(3):681–688. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liggett S. B. Functional properties of the rat and human beta 3-adrenergic receptors: differential agonist activation of recombinant receptors in Chinese hamster ovary cells. Mol Pharmacol. 1992 Oct;42(4):634–637. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lönnqvist F., Krief S., Strosberg A. D., Nyberg S., Emorine L. J., Arner P. Evidence for a functional beta 3-adrenoceptor in man. Br J Pharmacol. 1993 Nov;110(3):929–936. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1993.tb13902.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lönnqvist F., Thöme A., Nilsell K., Hoffstedt J., Arner P. A pathogenic role of visceral fat beta 3-adrenoceptors in obesity. J Clin Invest. 1995 Mar;95(3):1109–1116. doi: 10.1172/JCI117758. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mauriège P., De Pergola G., Berlan M., Lafontan M. Human fat cell beta-adrenergic receptors: beta-agonist-dependent lipolytic responses and characterization of beta-adrenergic binding sites on human fat cell membranes with highly selective beta 1-antagonists. J Lipid Res. 1988 May;29(5):587–601. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Munson P. J., Rodbard D. Ligand: a versatile computerized approach for characterization of ligand-binding systems. Anal Biochem. 1980 Sep 1;107(1):220–239. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(80)90515-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muzzin P., Boss O., Mathis N., Revelli J. P., Giacobino J. P., Willcocks K., Badman G. T., Cantello B. C., Hindley R. M., Cawthorne M. A. Characterization of a new, highly specific, beta 3-adrenergic receptor radioligand, [3H]SB 206606. Mol Pharmacol. 1994 Aug;46(2):357–363. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muzzin P., Colomb C., Giacobino J. P., Venter J. C., Fraser C. M. Biochemical characterization of brown adipose tissue beta-adrenergic receptor. J Recept Res. 1988;8(5):713–729. doi: 10.3109/10799898809049021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muzzin P., Revelli J. P., Fraser C. M., Giacobino J. P. Radioligand binding studies of the atypical beta 3-adrenergic receptor in rat brown adipose tissue using [3H]CGP 12177. FEBS Lett. 1992 Feb 24;298(2-3):162–164. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(92)80046-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muzzin P., Revelli J. P., Kuhne F., Gocayne J. D., McCombie W. R., Venter J. C., Giacobino J. P., Fraser C. M. An adipose tissue-specific beta-adrenergic receptor. Molecular cloning and down-regulation in obesity. J Biol Chem. 1991 Dec 15;266(35):24053–24058. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nahmias C., Blin N., Elalouf J. M., Mattei M. G., Strosberg A. D., Emorine L. J. Molecular characterization of the mouse beta 3-adrenergic receptor: relationship with the atypical receptor of adipocytes. EMBO J. 1991 Dec;10(12):3721–3727. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb04940.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okayama H., Kawaichi M., Brownstein M., Lee F., Yokota T., Arai K. High-efficiency cloning of full-length cDNA; construction and screening of cDNA expression libraries for mammalian cells. Methods Enzymol. 1987;154:3–28. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(87)54067-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RODBELL M. METABOLISM OF ISOLATED FAT CELLS. I. EFFECTS OF HORMONES ON GLUCOSE METABOLISM AND LIPOLYSIS. J Biol Chem. 1964 Feb;239:375–380. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Revelli J. P., Muzzin P., Paoloni A., Moinat M., Giacobino J. P. Expression of the beta 3-adrenergic receptor in human white adipose tissue. J Mol Endocrinol. 1993 Apr;10(2):193–197. doi: 10.1677/jme.0.0100193. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rothwell N. J., Stock M. J., Sudera D. K. Beta-adrenoreceptors in rat brown adipose tissue: proportions of beta 1- and beta 2-subtypes. Am J Physiol. 1985 Apr;248(4 Pt 1):E397–E402. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.1985.248.4.E397. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]