Abstract
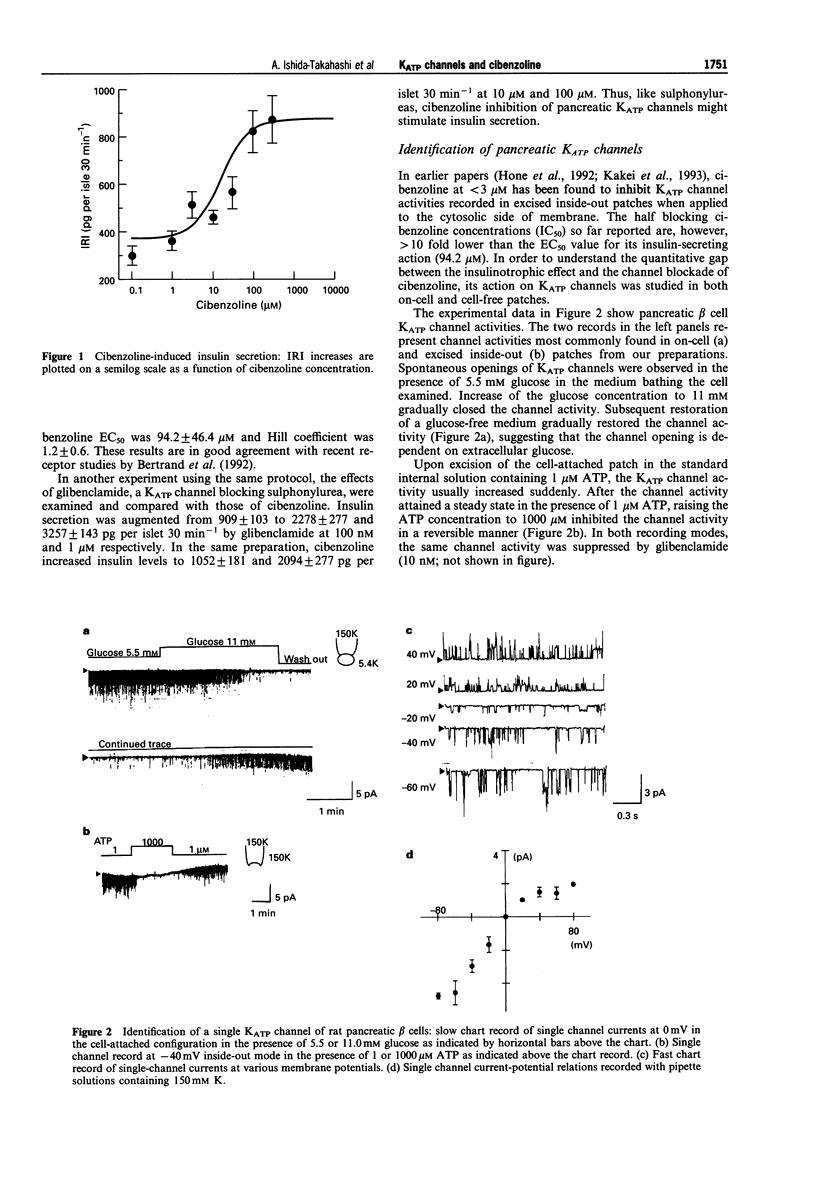
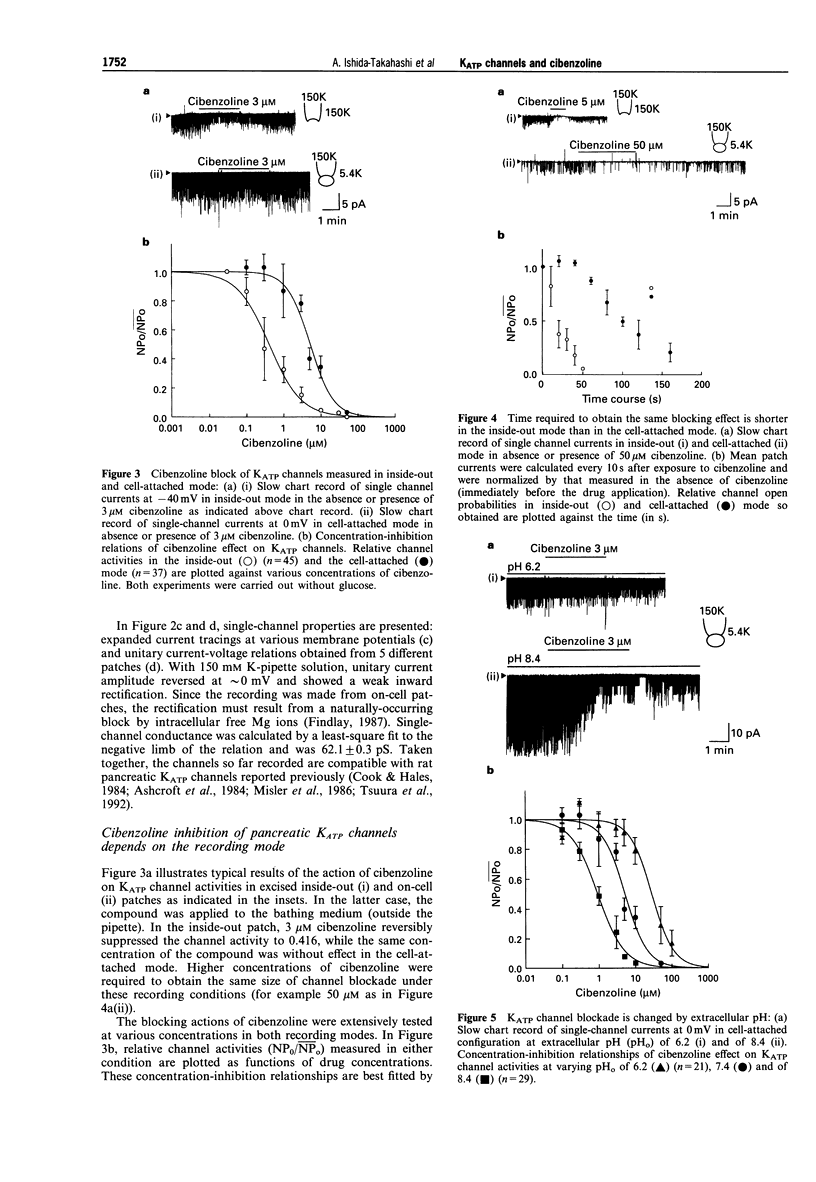
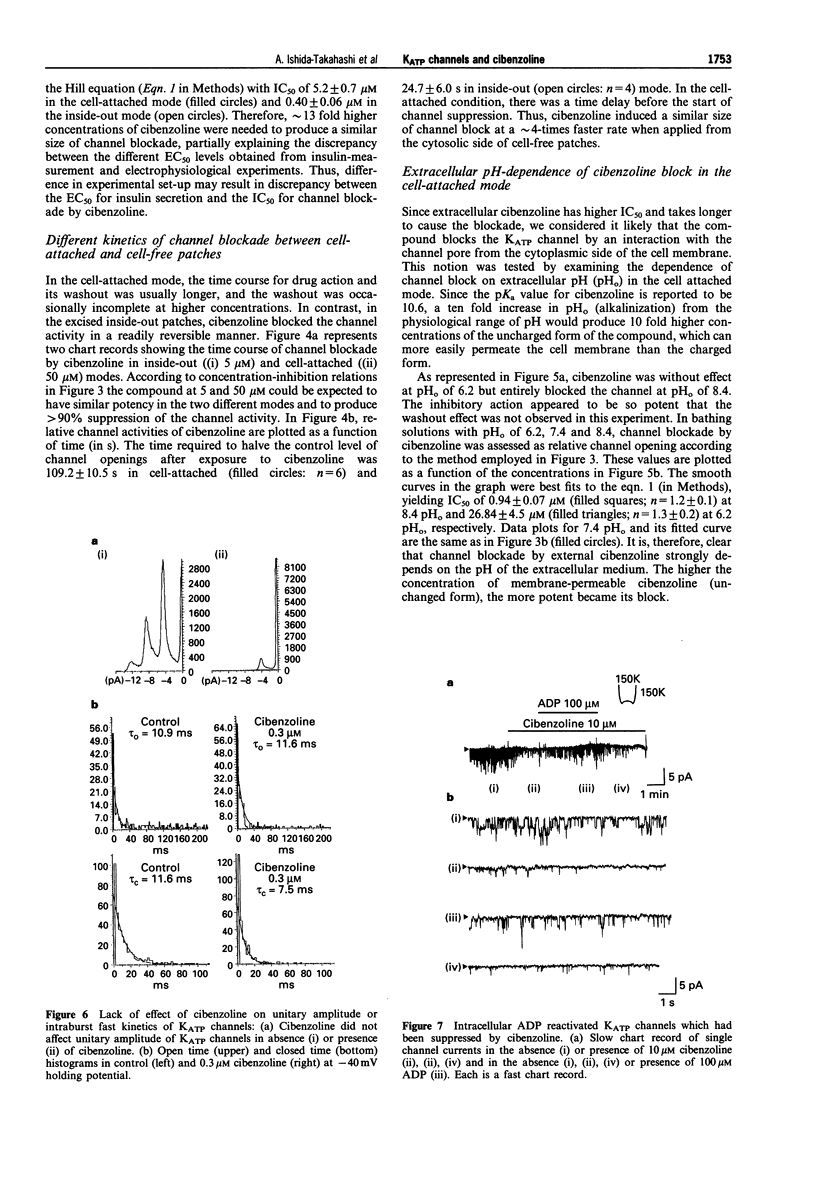
1. We investigated the effect of cibenzoline (a class Ia antiarrhythmic drug) on basal insulin secretory activity of rat pancreatic islets and ATP-sensitive K+ channels (KATP) in single pancreatic beta cells of the same species, using radioimmunoassay and patch clamp techniques. 2. Micromolar cibenzoline had a dose-dependent insulinotrophic action with an EC50 of 94.2 +/- 46.4 microM. The compound inhibited the activity of the KATP channel recorded from a single beta-cell in a concentration-dependent manner. The IC50 was 0.4 microM in the inside-out mode and 5.2 microM in the cell-attached mode, at pH 7.4. 3. In the cell-attached mode, alkalinization of extracellular solution increased the inhibitory action of cibenzoline and the IC50 was reduced from 26.8 microM at pH 6.2 to 0.9 microM at pH 8.4. On the other hand, the action of cibenzoline in the excised inside-out mode was acute in onset with a small IC50, indicating that the drug attains its binding site from the cytoplasmic side of the cell membrane. 4. In the inside-out mode, micromolar ADP reactivated the cibenzoline-blocked KATP channels in a manner similar to that by which ADP restored ATP-dependent block of the channel. 5. The binding of [3H]-glibenclamide to pancreatic islets was inhibited by glibenclamide but not by cibenzoline. In contrast, the [3H]-cibenzoline binding was displaced by unlabelled cibenzoline but not by glibenclamide. It is concluded that cibenzoline blocks pancreatic KATP channels via a binding site distinct from the sulphonylurea receptor.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ashcroft F. M. Adenosine 5'-triphosphate-sensitive potassium channels. Annu Rev Neurosci. 1988;11:97–118. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ne.11.030188.000525. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ashcroft F. M., Harrison D. E., Ashcroft S. J. Glucose induces closure of single potassium channels in isolated rat pancreatic beta-cells. 1984 Nov 29-Dec 5Nature. 312(5993):446–448. doi: 10.1038/312446a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bertrand G., Gross R., Petit P., Loubatières-Mariani M. M., Ribes G. Evidence for a direct stimulatory effect of cibenzoline on insulin secretion in rats. Eur J Pharmacol. 1992 Apr 22;214(2-3):159–163. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(92)90113-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cook D. L., Hales C. N. Intracellular ATP directly blocks K+ channels in pancreatic B-cells. Nature. 1984 Sep 20;311(5983):271–273. doi: 10.1038/311271a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunne M. J., Petersen O. H. Intracellular ADP activates K+ channels that are inhibited by ATP in an insulin-secreting cell line. FEBS Lett. 1986 Nov 10;208(1):59–62. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(86)81532-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edwards G., Weston A. H. The pharmacology of ATP-sensitive potassium channels. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol. 1993;33:597–637. doi: 10.1146/annurev.pa.33.040193.003121. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Findlay I. Inhibition of ATP-sensitive K+ channels in cardiac muscle by the sulphonylurea drug glibenclamide. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1992 May;261(2):540–545. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Findlay I. The effects of magnesium upon adenosine triphosphate-sensitive potassium channels in a rat insulin-secreting cell line. J Physiol. 1987 Oct;391:611–629. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1987.sp016759. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gachot B. A., Bezier M., Cherrier J. F., Daubeze J. Cibenzoline and hypoglycaemia. Lancet. 1988 Jul 30;2(8605):280–280. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(88)92570-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamill O. P., Marty A., Neher E., Sakmann B., Sigworth F. J. Improved patch-clamp techniques for high-resolution current recording from cells and cell-free membrane patches. Pflugers Arch. 1981 Aug;391(2):85–100. doi: 10.1007/BF00656997. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harron D. W., Brogden R. N., Faulds D., Fitton A. Cibenzoline. A review of its pharmacological properties and therapeutic potential in arrhythmias. Drugs. 1992 May;43(5):734–759. doi: 10.2165/00003495-199243050-00008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hilleman D. E., Mohiuddin S. M., Ahmed I. S., Dahl J. M. Cibenzoline-induced hypoglycemia. Drug Intell Clin Pharm. 1987 Jan;21(1 Pt 1):38–40. doi: 10.1177/10600280870211p104. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horie M., Hayashi S., Yuzuki Y., Sasayama S. Comparative studies of ATP sensitive potassium channels in heart and pancreatic beta cells using Vaughan-Williams class Ia antiarrhythmics. Cardiovasc Res. 1992 Nov;26(11):1087–1094. doi: 10.1093/cvr/26.11.1087. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Houdent C., Noblet C., Vandoren C., Levesque H., Morin C., Moore N., Courtois H., Wolf L. M. Hypoglycémie induite par la cibenzoline chez le sujet âgé. Rev Med Interne. 1991 Mar-Apr;12(2):143–145. doi: 10.1016/s0248-8663(05)81379-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ibbotson T., Edwards G., Weston A. H. Antagonism of levcromakalim by imidazoline- and guanidine-derivatives in rat portal vein: involvement of the delayed rectifier. Br J Pharmacol. 1993 Dec;110(4):1556–1564. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1993.tb14001.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jeandel C., Preiss M. A., Pierson H., Penin F., Cuny G., Bannwarth B., Netter P. Hypoglycaemia induced by cibenzoline. Lancet. 1988 May 28;1(8596):1232–1233. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(88)92058-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kakei M., Kelly R. P., Ashcroft S. J., Ashcroft F. M. The ATP-sensitivity of K+ channels in rat pancreatic B-cells is modulated by ADP. FEBS Lett. 1986 Nov 10;208(1):63–66. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(86)81533-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kakei M., Nakazaki M., Kamisaki T., Nagayama I., Fukamachi Y., Tanaka H. Inhibition of the ATP-sensitive potassium channel by class I antiarrhythmic agent, cibenzoline, in rat pancreatic beta-cells. Br J Pharmacol. 1993 Aug;109(4):1226–1231. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1993.tb13753.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lefort G., Haissaguerre M., Floro J., Beauffigeau P., Warin J. F., Latapie J. L. Hypoglycémies au cours de surdosages par un nouvel antiarythmique: la cibenzoline. Trois observations. Presse Med. 1988 Apr 16;17(14):687–691. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Massarella J. W., Khoo K. C., Szuna A. J., Sandor D. A., Morganroth J., Aogaichi K. Pharmacokinetics of cibenzoline after single and repetitive dosing in healthy volunteers. J Clin Pharmacol. 1986 Feb;26(2):125–130. doi: 10.1002/j.1552-4604.1986.tb02920.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Misler S., Falke L. C., Gillis K., McDaniel M. L. A metabolite-regulated potassium channel in rat pancreatic B cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Sep;83(18):7119–7123. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.18.7119. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noack T., Edwards G., Deitmer P., Greengrass P., Morita T., Andersson P. O., Criddle D., Wyllie M. G., Weston A. H. The involvement of potassium channels in the action of ciclazindol in rat portal vein. Br J Pharmacol. 1992 May;106(1):17–24. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1992.tb14286.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rorsman P., Trube G. Glucose dependent K+-channels in pancreatic beta-cells are regulated by intracellular ATP. Pflugers Arch. 1985 Dec;405(4):305–309. doi: 10.1007/BF00595682. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmid-Antomarchi H., De Weille J., Fosset M., Lazdunski M. The receptor for antidiabetic sulfonylureas controls the activity of the ATP-modulated K+ channel in insulin-secreting cells. J Biol Chem. 1987 Nov 25;262(33):15840–15844. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sutton R., Peters M., McShane P., Gray D. W., Morris P. J. Isolation of rat pancreatic islets by ductal injection of collagenase. Transplantation. 1986 Dec;42(6):689–691. doi: 10.1097/00007890-198612000-00022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Touboul P., Atallah G., Kirkorian G., de Zuloaga C., Dufour A., Aymard M. F., Lavaud P., Moleur P. Electrophysiologic effects of cibenzoline in humans related to dose and plasma concentration. Am Heart J. 1986 Aug;112(2):333–339. doi: 10.1016/0002-8703(86)90271-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsuji K., Taminato T., Usami M., Ishida H., Kitano N., Fukumoto H., Koh G., Kurose T., Yamada Y., Yano H. Characteristic features of insulin secretion in the streptozotocin-induced NIDDM rat model. Metabolism. 1988 Nov;37(11):1040–1044. doi: 10.1016/0026-0495(88)90064-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsuura Y., Ishida H., Okamoto Y., Tsuji K., Kurose T., Horie M., Imura H., Okada Y., Seino Y. Impaired glucose sensitivity of ATP-sensitive K+ channels in pancreatic beta-cells in streptozotocin-induced NIDDM rats. Diabetes. 1992 Jul;41(7):861–865. doi: 10.2337/diab.41.7.861. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zünkler B. J., Trube G., Panten U. How do sulfonylureas approach their receptor in the B-cell plasma membrane? Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1989 Sep;340(3):328–332. doi: 10.1007/BF00168518. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


