Abstract
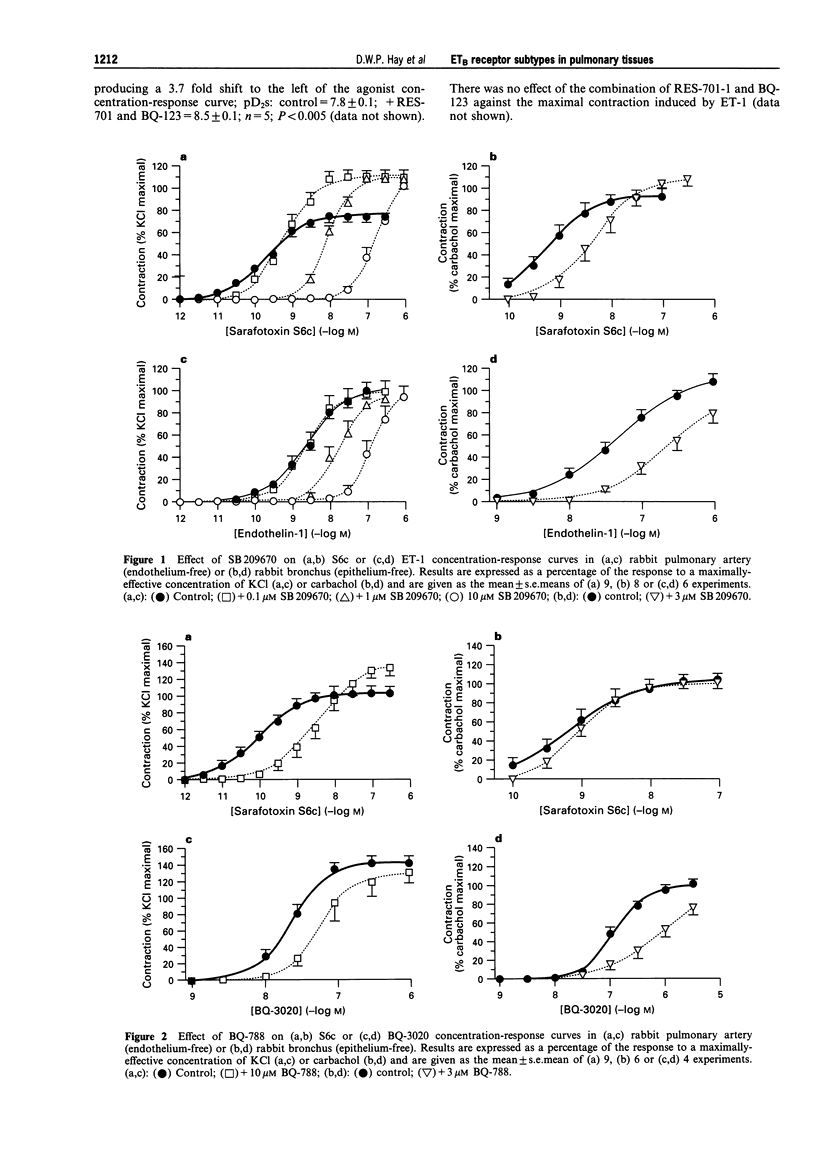
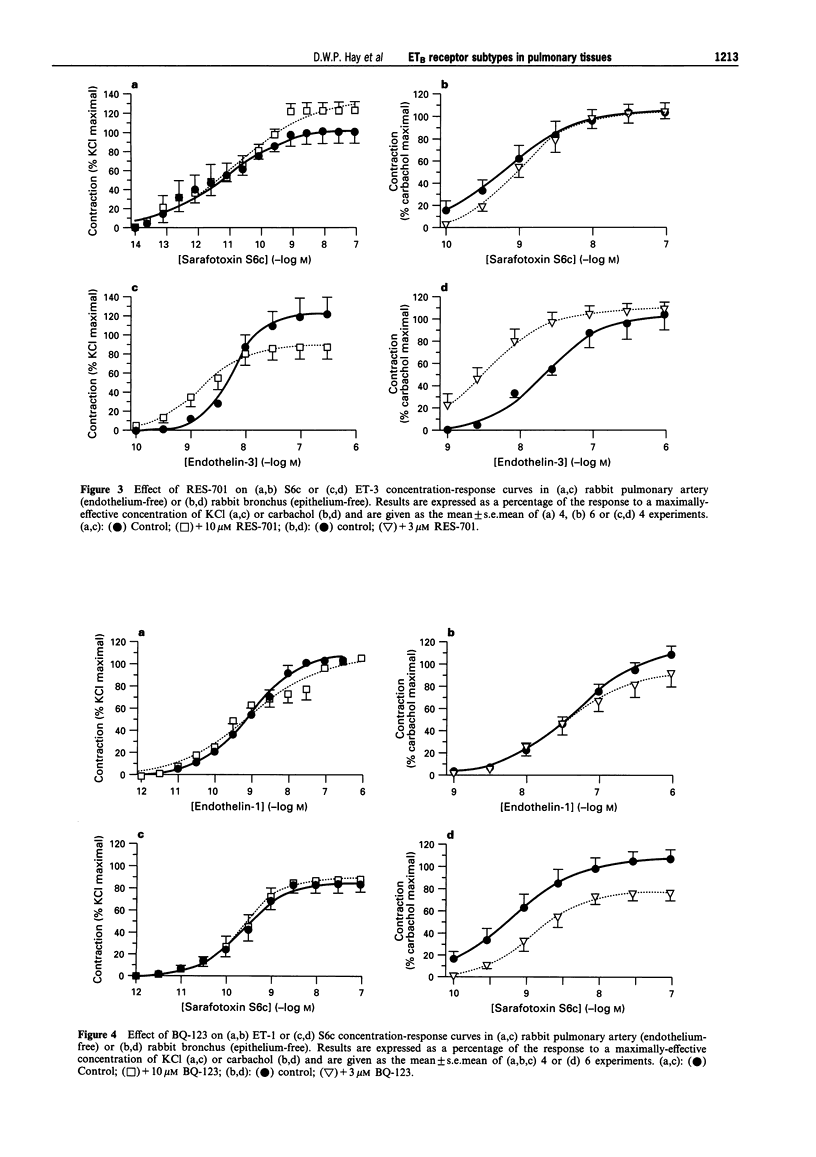
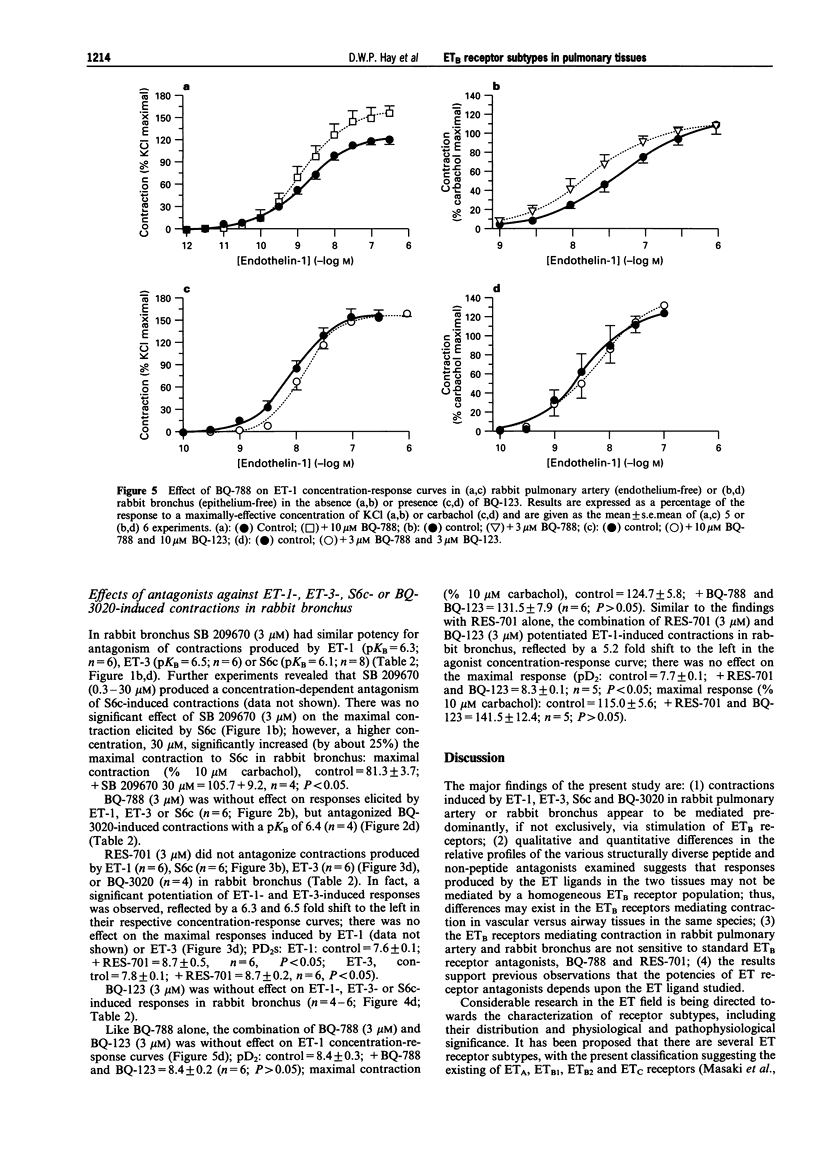
1. To explore potential differences between endothelin (ET) receptors in airway versus vascular smooth muscle from the same species, the ETB receptors mediating contractions produced by ET-1, ET-3 and the selective ETB ligands, sarafotoxin S6c (S6c) and BQ-3020, in rabbit bronchus and pulmonary artery were investigated by use of peptide and non-peptide ET receptor antagonists. 2. In rabbit pulmonary artery SB 209670 (10 microM), a mixed ETA/ETB receptor antagonist, was a more potent antagonist of contractions produced by S6c (pKB = 7.7; n = 9; P < 0.05), than those elicited by ET-1 (pKB = 6.7; n = 6) or ET-3 (pKB = 6.7; n = 5). BQ-788 (10 microM), an ETB receptor antagonist, inhibited responses produced by ET-3 (pKB = 5.1; n = 8), BQ-3020 (pKB = 5.2; n = 4) or S6c (pKB = 6.2; n = 9; P < 0.05 compared to potency versus ET-3- or BQ-3020-induced contractions), but was without inhibitory effect on ET-1-induced contractions (n = 5). RES-701 (10 microM), another selective ETB receptor antagonist, was without effect on contractions produced by S6c (n = 4) or ET-1 (n = 4), and potentiated ET-3- (n = 5) or BQ-3020-induced responses (n = 4). 3. The combination of BQ-788 (10 microM) and BQ-123 (10 microM), an ETA-selective receptor antagonist, antagonized contractions produced by lower concentrations of ET-1 (1 and 3 nM) in rabbit pulmonary artery, but was without effect on responses elicited by higher concentrations of ET-1 (n = 5). The combination of RES-701 (10 microM) and BQ-123 (10 microM) potentiated responses elicited by ET-1, producing a 3.7 fold shift to the left in the agonist concentration-response curve (n = 5). 4. In rabbit bronchus SB 209670 (3 microM) had similar potency for antagonism of contractions produced by ET-1 (pKB = 6.3; n = 6), ET-3 (pKB = 6.5; n = 6) or S6c (pKB = 6.1; n = 8). BQ-788 (3 microM) was without effect on responses elicited by ET-1, ET-3 or S6c (n = 6) but antagonized BQ-3020-induced contractions (pKB = 6.4; n = 4). RES-701 (3 microM) was without effect on contractions produced by S6c (n = 6) or BQ-3020 (n = 4), and potentiated rather than antagonized ET-1- or ET-3-induced responses (n = 6), reflected by a significant (about 6 fold) shift to the left in ET-1 or ET-3 concentration-response curves. The combination of BQ-788 (3 microM) and BQ-123 (3 microM) was without effect on contractions produced by ET-1 in rabbit bronchus (n = 6). The combination of RES-701 (3 microM) and BQ-123 (3 microM) potentiated responses elicited by ET-1, producing a 5.2 fold shift to the left in the agonist concentration-response curve (n = 5). 5. BQ-123 (3 or 10 microM), an ETA-selective receptor antagonist, was without effect on ET-1, ET-3 or S6c concentration-response curves (n = 3-6) in rabbit pulmonary artery or rabbit bronchus. 6. These data indicate that contractions induced by ET-1, ET-3, S6c and BQ-3020 in rabbit pulmonary artery or rabbit bronchus appear to be mediated predominantly via stimulation of ETB receptors. However, the qualitative and quantitative differences in the relative profiles of the various structurally diverse peptide and non-peptide antagonists examined suggests that responses produced by the ET ligands may not be mediated by a homogeneous ETB receptor population. In addition, the results suggest that differences exist in the ETB receptors mediating contraction in pulmonary vascular versus airway tissues in the same species. These receptors are not very sensitive to the standard ETB receptor antagonists, BQ-788 and RES-701. Furthermore, the results also provide further evidence that the potencies of ET receptor antagonists depend upon the ET agonist.
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ARUNLAKSHANA O., SCHILD H. O. Some quantitative uses of drug antagonists. Br J Pharmacol Chemother. 1959 Mar;14(1):48–58. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1959.tb00928.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arai H., Hori S., Aramori I., Ohkubo H., Nakanishi S. Cloning and expression of a cDNA encoding an endothelin receptor. Nature. 1990 Dec 20;348(6303):730–732. doi: 10.1038/348730a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Battistini B., Warner T. D., Fournier A., Vane J. R. Characterization of ETB receptors mediating contractions induced by endothelin-1 or IRL 1620 in guinea-pig isolated airways: effects of BQ-123, FR139317 or PD 145065. Br J Pharmacol. 1994 Apr;111(4):1009–1016. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1994.tb14844.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bax W. A., Saxena P. R. The current endothelin receptor classification: time for reconsideration? Trends Pharmacol Sci. 1994 Oct;15(10):379–386. doi: 10.1016/0165-6147(94)90159-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Douglas S. A., Beck G. R., Jr, Elliott J. D., Ohlstein E. H. Pharmacological evidence for the presence of three distinct functional endothelin receptor subtypes in the rabbit lateral saphenous vein. Br J Pharmacol. 1995 Apr;114(8):1529–1540. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1995.tb14936.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fukuroda T., Kobayashi M., Ozaki S., Yano M., Miyauchi T., Onizuka M., Sugishita Y., Goto K., Nishikibe M. Endothelin receptor subtypes in human versus rabbit pulmonary arteries. J Appl Physiol (1985) 1994 May;76(5):1976–1982. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1994.76.5.1976. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fukuroda T., Nishikibe M., Ohta Y., Ihara M., Yano M., Ishikawa K., Fukami T., Ikemoto F. Analysis of responses to endothelins in isolated porcine blood vessels by using a novel endothelin antagonist, BQ-153. Life Sci. 1992;50(15):PL107–PL112. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(92)90353-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldie R. G., Grayson P. S., Knott P. G., Self G. J., Henry P. J. Predominance of endothelinA (ETA) receptors in ovine airway smooth muscle and their mediation of ET-1-induced contraction. Br J Pharmacol. 1994 Jul;112(3):749–756. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1994.tb13142.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hay D. W., Henry P. J., Goldie R. G. Endothelin and the respiratory system. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 1993 Jan;14(1):29–32. doi: 10.1016/0165-6147(93)90111-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hay D. W., Luttmann M. A., Hubbard W. C., Undem B. J. Endothelin receptor subtypes in human and guinea-pig pulmonary tissues. Br J Pharmacol. 1993 Nov;110(3):1175–1183. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1993.tb13938.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henry P. J. Endothelin-1 (ET-1)-induced contraction in rat isolated trachea: involvement of ETA and ETB receptors and multiple signal transduction systems. Br J Pharmacol. 1993 Sep;110(1):435–441. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1993.tb13829.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ihara M., Noguchi K., Saeki T., Fukuroda T., Tsuchida S., Kimura S., Fukami T., Ishikawa K., Nishikibe M., Yano M. Biological profiles of highly potent novel endothelin antagonists selective for the ETA receptor. Life Sci. 1992;50(4):247–255. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(92)90331-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inoue A., Yanagisawa M., Kimura S., Kasuya Y., Miyauchi T., Goto K., Masaki T. The human endothelin family: three structurally and pharmacologically distinct isopeptides predicted by three separate genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Apr;86(8):2863–2867. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.8.2863. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishikawa K., Ihara M., Noguchi K., Mase T., Mino N., Saeki T., Fukuroda T., Fukami T., Ozaki S., Nagase T. Biochemical and pharmacological profile of a potent and selective endothelin B-receptor antagonist, BQ-788. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 May 24;91(11):4892–4896. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.11.4892. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karaki H., Sudjarwo S. A., Hori M. Novel antagonist of endothelin ETB1 and ETB2 receptors, BQ-788: effects on blood vessel and small intestine. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1994 Nov 30;205(1):168–173. doi: 10.1006/bbrc.1994.2645. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karaki H., Sudjarwo S. A., Hori M., Tanaka T., Matsuda Y. Endothelin ETB receptor antagonist, RES-701-1: effects on isolated blood vessels and small intestine. Eur J Pharmacol. 1994 Sep 12;262(3):255–259. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(94)90739-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kizawa Y., Nakajima Y., Nakano J., Uno H., Sano M., Murakami H. Pharmacological profiles of contractile endothelin receptors in guinea pig hilar bronchus. Receptor. 1994 Winter;4(4):269–276. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LaDouceur D. M., Flynn M. A., Keiser J. A., Reynolds E., Haleen S. J. ETA and ETB receptors coexist on rabbit pulmonary artery vascular smooth muscle mediating contraction. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1993 Oct 15;196(1):209–215. doi: 10.1006/bbrc.1993.2236. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marsault R., Vigne P., Breittmayer J. P., Frelin C. Kinetics of vasoconstrictor action of endothelins. Am J Physiol. 1991 Dec;261(6 Pt 1):C987–C993. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1991.261.6.C986. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin E. R., Brenner B. M., Ballermann B. J. Heterogeneity of cell surface endothelin receptors. J Biol Chem. 1990 Aug 15;265(23):14044–14049. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Masaki T., Yanagisawa M., Goto K. Physiology and pharmacology of endothelins. Med Res Rev. 1992 Jul;12(4):391–421. doi: 10.1002/med.2610120405. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakamichi K., Ihara M., Kobayashi M., Saeki T., Ishikawa K., Yano M. Different distribution of endothelin receptor subtypes in pulmonary tissues revealed by the novel selective ligands BQ-123 and [Ala1,3,11,15]ET-1. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1992 Jan 15;182(1):144–150. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(05)80123-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohlstein E. H., Beck G. R., Jr, Douglas S. A., Nambi P., Lago M. A., Gleason J. G., Ruffolo R. R., Jr, Feuerstein G., Elliott J. D. Nonpeptide endothelin receptor antagonists. II. Pharmacological characterization of SB 209670. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1994 Nov;271(2):762–768. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohlstein E. H., Nambi P., Douglas S. A., Edwards R. M., Gellai M., Lago A., Leber J. D., Cousins R. D., Gao A., Frazee J. S. SB 209670, a rationally designed potent nonpeptide endothelin receptor antagonist. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Aug 16;91(17):8052–8056. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.17.8052. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Panek R. L., Major T. C., Hingorani G. P., Doherty A. M., Taylor D. G., Rapundalo S. T. Endothelin and structurally related analogs distinguish between endothelin receptor subtypes. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1992 Mar 16;183(2):566–571. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(92)90519-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robertson M. J., Dougall I. G., Harper D., McKechnie K. C., Leff P. Agonist-antagonist interactions at angiotensin receptors: application of a two-state receptor model. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 1994 Oct;15(10):364–369. doi: 10.1016/0165-6147(94)90156-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sakurai T., Yanagisawa M., Masaki T. Molecular characterization of endothelin receptors. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 1992 Mar;13(3):103–108. doi: 10.1016/0165-6147(92)90038-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sakurai T., Yanagisawa M., Takuwa Y., Miyazaki H., Kimura S., Goto K., Masaki T. Cloning of a cDNA encoding a non-isopeptide-selective subtype of the endothelin receptor. Nature. 1990 Dec 20;348(6303):732–735. doi: 10.1038/348732a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Samson W. K., Skala K. D., Alexander B. D., Huang F. L. Pituitary site of action of endothelin: selective inhibition of prolactin release in vitro. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1990 Jun 15;169(2):737–743. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(90)90393-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sokolovsky M., Ambar I., Galron R. A novel subtype of endothelin receptors. J Biol Chem. 1992 Oct 15;267(29):20551–20554. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Springall D. R., Howarth P. H., Counihan H., Djukanovic R., Holgate S. T., Polak J. M. Endothelin immunoreactivity of airway epithelium in asthmatic patients. Lancet. 1991 Mar 23;337(8743):697–701. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(91)90279-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stewart D. J., Levy R. D., Cernacek P., Langleben D. Increased plasma endothelin-1 in pulmonary hypertension: marker or mediator of disease? Ann Intern Med. 1991 Mar 15;114(6):464–469. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-114-6-464. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sudjarwo S. A., Hori M., Takai M., Urade Y., Okada T., Karaki H. A novel subtype of endothelin B receptor mediating contraction in swine pulmonary vein. Life Sci. 1993;53(5):431–437. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(93)90647-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sudjarwo S. A., Hori M., Tanaka T., Matsuda Y., Okada T., Karaki H. Subtypes of endothelin ETA and ETB receptors mediating venous smooth muscle contraction. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1994 Apr 15;200(1):627–633. doi: 10.1006/bbrc.1994.1494. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanaka T., Ogawa T., Matsuda Y. Species difference in the binding characteristics of RES-701-1: potent endothelin ETB receptor-selective antagonist. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1995 Apr 17;209(2):712–716. doi: 10.1006/bbrc.1995.1557. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanaka T., Tsukuda E., Nozawa M., Nonaka H., Ohno T., Kase H., Yamada K., Matsuda Y. RES-701-1, a novel, potent, endothelin type B receptor-selective antagonist of microbial origin. Mol Pharmacol. 1994 Apr;45(4):724–730. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- VAN ROSSUM J. M. Cumulative dose-response curves. II. Technique for the making of dose-response curves in isolated organs and the evaluation of drug parameters. Arch Int Pharmacodyn Ther. 1963;143:299–330. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waggoner W. G., Genova S. L., Rash V. A. Kinetic analyses demonstrate that the equilibrium assumption does not apply to [125I]endothelin-1 binding data. Life Sci. 1992;51(24):1869–1876. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(92)90038-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Warner T. D., Allcock G. H., Mickley E. J., Corder R., Vane J. R. Comparative studies with the endothelin receptor antagonists BQ-123 and PD 142893 indicate at least three endothelin receptors. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol. 1993;22 (Suppl 8):S117–S120. doi: 10.1097/00005344-199322008-00032. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams D. L., Jr, Jones K. L., Pettibone D. J., Lis E. V., Clineschmidt B. V. Sarafotoxin S6c: an agonist which distinguishes between endothelin receptor subtypes. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1991 Mar 15;175(2):556–561. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(91)91601-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yanagisawa M., Kurihara H., Kimura S., Tomobe Y., Kobayashi M., Mitsui Y., Yazaki Y., Goto K., Masaki T. A novel potent vasoconstrictor peptide produced by vascular endothelial cells. Nature. 1988 Mar 31;332(6163):411–415. doi: 10.1038/332411a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yanagisawa M., Masaki T. Endothelin, a novel endothelium-derived peptide. Pharmacological activities, regulation and possible roles in cardiovascular control. Biochem Pharmacol. 1989 Jun 15;38(12):1877–1883. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(89)90484-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoneyama T., Hori M., Makatani M., Yamamura T., Tanaka T., Matsuda Y., Karaki H. Subtypes of endothelin ETA and ETB receptors mediating tracheal smooth muscle contraction. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1995 Feb 15;207(2):668–674. doi: 10.1006/bbrc.1995.1239. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


